COMPOSITION
DESIGN
COLOR
-
Is a MacBeth Colour Rendition Chart the Safest Way to Calibrate a Camera?
Read more: Is a MacBeth Colour Rendition Chart the Safest Way to Calibrate a Camera?www.colour-science.org/posts/the-colorchecker-considered-mostly-harmless/
“Unless you have all the relevant spectral measurements, a colour rendition chart should not be used to perform colour-correction of camera imagery but only for white balancing and relative exposure adjustments.”
“Using a colour rendition chart for colour-correction might dramatically increase error if the scene light source spectrum is different from the illuminant used to compute the colour rendition chart’s reference values.”
“other factors make using a colour rendition chart unsuitable for camera calibration:
– Uncontrolled geometry of the colour rendition chart with the incident illumination and the camera.
– Unknown sample reflectances and ageing as the colour of the samples vary with time.
– Low samples count.
– Camera noise and flare.
– Etc…“Those issues are well understood in the VFX industry, and when receiving plates, we almost exclusively use colour rendition charts to white balance and perform relative exposure adjustments, i.e. plate neutralisation.”
-
Black Body color aka the Planckian Locus curve for white point eye perception
Read more: Black Body color aka the Planckian Locus curve for white point eye perceptionhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Black-body_radiation
Black-body radiation is the type of electromagnetic radiation within or surrounding a body in thermodynamic equilibrium with its environment, or emitted by a black body (an opaque and non-reflective body) held at constant, uniform temperature. The radiation has a specific spectrum and intensity that depends only on the temperature of the body.
A black-body at room temperature appears black, as most of the energy it radiates is infra-red and cannot be perceived by the human eye. At higher temperatures, black bodies glow with increasing intensity and colors that range from dull red to blindingly brilliant blue-white as the temperature increases.
The Black Body Ultraviolet Catastrophe Experiment
In photography, color temperature describes the spectrum of light which is radiated from a “blackbody” with that surface temperature. A blackbody is an object which absorbs all incident light — neither reflecting it nor allowing it to pass through.
The Sun closely approximates a black-body radiator. Another rough analogue of blackbody radiation in our day to day experience might be in heating a metal or stone: these are said to become “red hot” when they attain one temperature, and then “white hot” for even higher temperatures. Similarly, black bodies at different temperatures also have varying color temperatures of “white light.”
Despite its name, light which may appear white does not necessarily contain an even distribution of colors across the visible spectrum.
Although planets and stars are neither in thermal equilibrium with their surroundings nor perfect black bodies, black-body radiation is used as a first approximation for the energy they emit. Black holes are near-perfect black bodies, and it is believed that they emit black-body radiation (called Hawking radiation), with a temperature that depends on the mass of the hole.
-
HDR and Color
Read more: HDR and Colorhttps://www.soundandvision.com/content/nits-and-bits-hdr-and-color
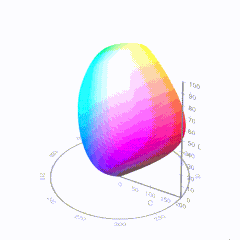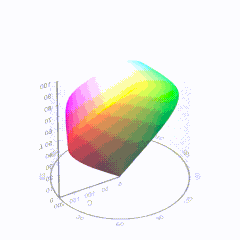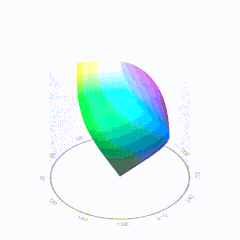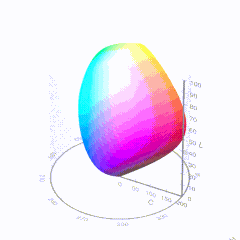
In HD we often refer to the range of available colors as a color gamut. Such a color gamut is typically plotted on a two-dimensional diagram, called a CIE chart, as shown in at the top of this blog. Each color is characterized by its x/y coordinates.
Good enough for government work, perhaps. But for HDR, with its higher luminance levels and wider color, the gamut becomes three-dimensional.
For HDR the color gamut therefore becomes a characteristic we now call the color volume. It isn’t easy to show color volume on a two-dimensional medium like the printed page or a computer screen, but one method is shown below. As the luminance becomes higher, the picture eventually turns to white. As it becomes darker, it fades to black. The traditional color gamut shown on the CIE chart is simply a slice through this color volume at a selected luminance level, such as 50%.
Three different color volumes—we still refer to them as color gamuts though their third dimension is important—are currently the most significant. The first is BT.709 (sometimes referred to as Rec.709), the color gamut used for pre-UHD/HDR formats, including standard HD.
The largest is known as BT.2020; it encompasses (roughly) the range of colors visible to the human eye (though ET might find it insufficient!).
Between these two is the color gamut used in digital cinema, known as DCI-P3.
sRGB
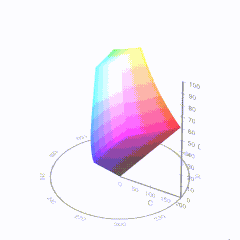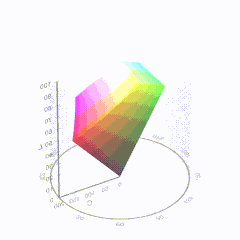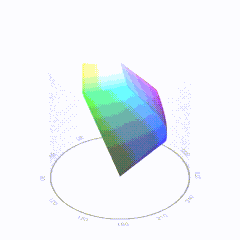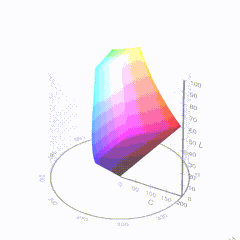
D65
-
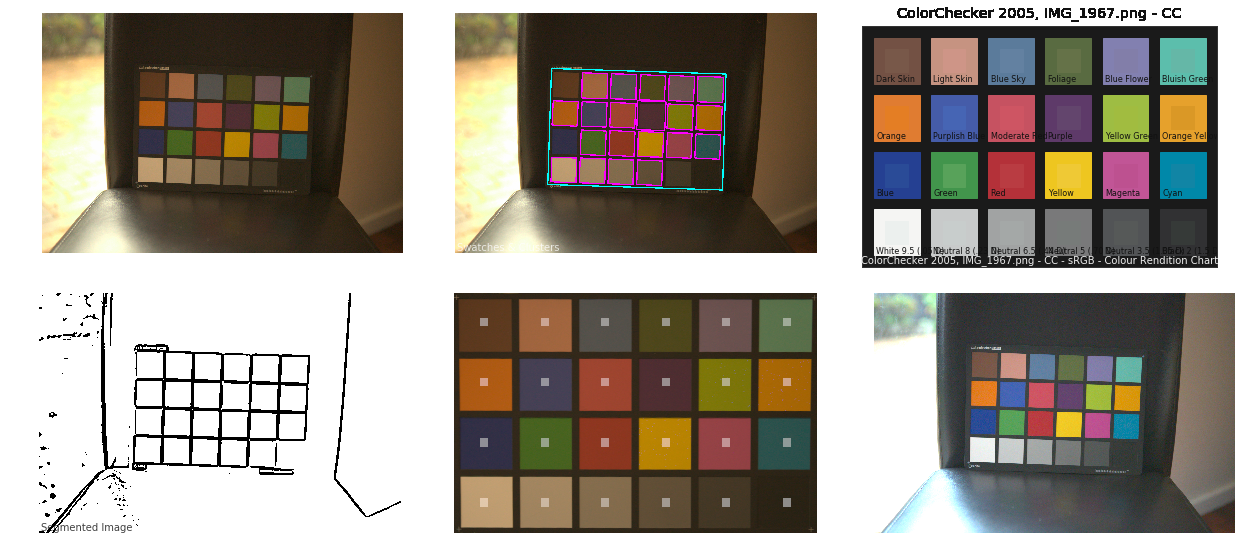
Colour – MacBeth Chart Checker Detection
Read more: Colour – MacBeth Chart Checker Detectiongithub.com/colour-science/colour-checker-detection
A Python package implementing various colour checker detection algorithms and related utilities.
-
A Brief History of Color in Art
Read more: A Brief History of Color in Artwww.artsy.net/article/the-art-genome-project-a-brief-history-of-color-in-art
Of all the pigments that have been banned over the centuries, the color most missed by painters is likely Lead White.
This hue could capture and reflect a gleam of light like no other, though its production was anything but glamorous. The 17th-century Dutch method for manufacturing the pigment involved layering cow and horse manure over lead and vinegar. After three months in a sealed room, these materials would combine to create flakes of pure white. While scientists in the late 19th century identified lead as poisonous, it wasn’t until 1978 that the United States banned the production of lead white paint.
More reading:
www.canva.com/learn/color-meanings/https://www.infogrades.com/history-events-infographics/bizarre-history-of-colors/
LIGHTING
-
LUX vs LUMEN vs NITS vs CANDELA – What is the difference
Read more: LUX vs LUMEN vs NITS vs CANDELA – What is the differenceMore details here: Lumens vs Candelas (candle) vs Lux vs FootCandle vs Watts vs Irradiance vs Illuminance
https://www.inhouseav.com.au/blog/beginners-guide-nits-lumens-brightness/

Candela
Candela is the basic unit of measure of the entire volume of light intensity from any point in a single direction from a light source. Note the detail: it measures the total volume of light within a certain beam angle and direction.
While the luminance of starlight is around 0.001 cd/m2, that of a sunlit scene is around 100,000 cd/m2, which is a hundred millions times higher. The luminance of the sun itself is approximately 1,000,000,000 cd/m2.NIT
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Candela_per_square_metre
The candela per square metre (symbol: cd/m2) is the unit of luminance in the International System of Units (SI). The unit is based on the candela, the SI unit of luminous intensity, and the square metre, the SI unit of area. The nit (symbol: nt) is a non-SI name also used for this unit (1 nt = 1 cd/m2).[1] The term nit is believed to come from the Latin word nitēre, “to shine”. As a measure of light emitted per unit area, this unit is frequently used to specify the brightness of a display device.
NIT and cd/m2 (candela power) represent the same thing and can be used interchangeably. One nit is equivalent to one candela per square meter, where the candela is the amount of light which has been emitted by a common tallow candle, but NIT is not part of the International System of Units (abbreviated SI, from Systeme International, in French).
It’s easiest to think of a TV as emitting light directly, in much the same way as the Sun does. Nits are simply the measurement of the level of light (luminance) in a given area which the emitting source sends to your eyes or a camera sensor.
The Nit can be considered a unit of visible-light intensity which is often used to specify the brightness level of an LCD.
1 Nit is approximately equal to 3.426 Lumens. To work out a comparable number of Nits to Lumens, you need to multiply the number of Nits by 3.426. If you know the number of Lumens, and wish to know the Nits, simply divide the number of Lumens by 3.426.
Most consumer desktop LCDs have Nits of 200 to 300, the average TV most likely has an output capability of between 100 and 200 Nits, and an HDR TV ranges from 400 to 1,500 Nits.
Virtual Production sets currently sport around 6000 NIT ceiling and 1000 NIT wall panels.The ambient brightness of a sunny day with clear blue skies is between 7000-10,000 nits (between 3000-7000 nits for overcast skies and indirect sunlight).
A bright sunny day can have specular highlights that reach over 100,000 nits. Direct sunlight is around 1,600,000,000 nits.
10,000 nits is also the typical brightness of a fluorescent tube – bright, but not painful to look at.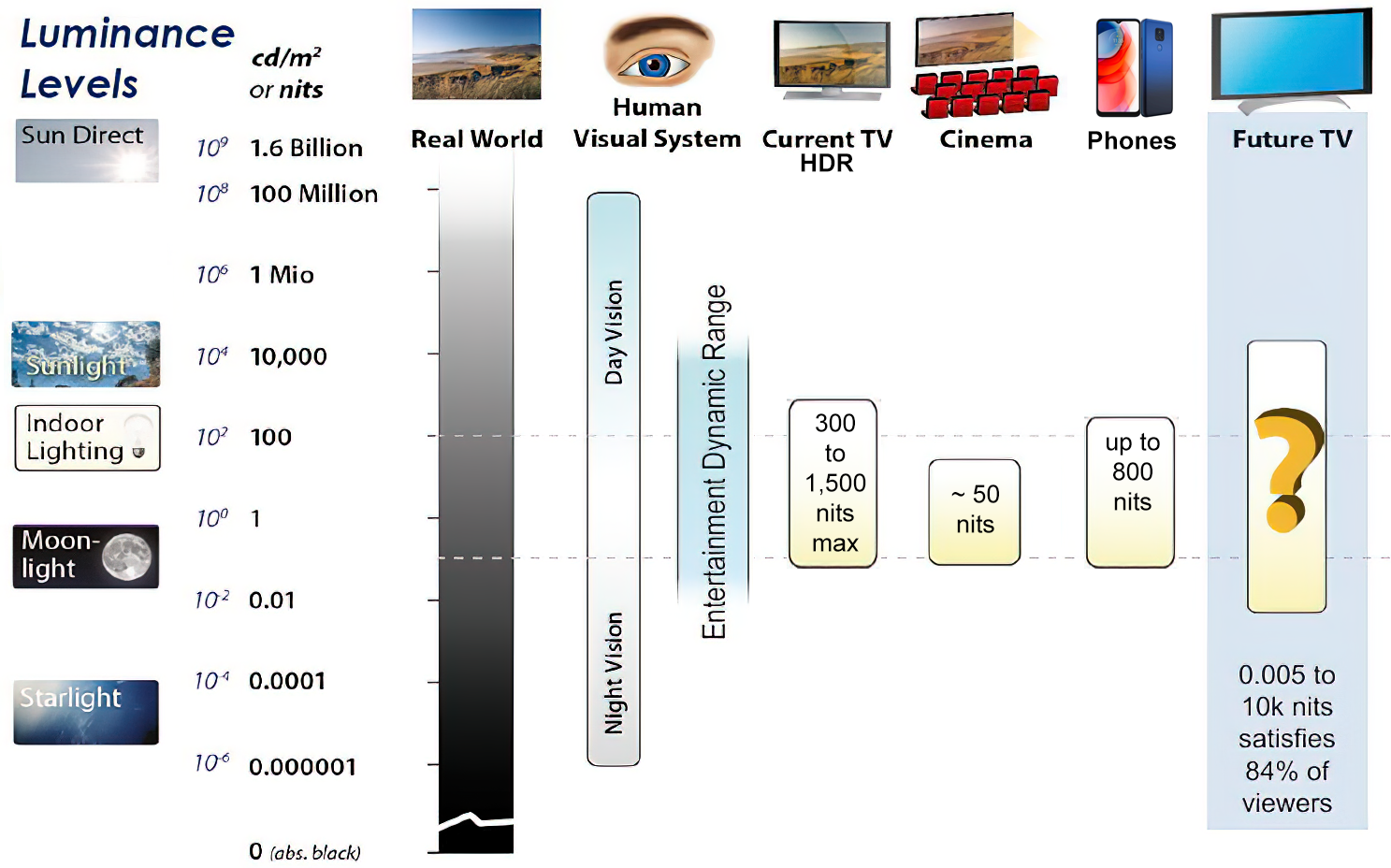
https://www.displaydaily.com/article/display-daily/dolby-vision-vs-hdr10-clarified
Tests showed that a “black level” of 0.005 nits (cd/m²) satisfied the vast majority of viewers. While 0.005 nits is very close to true black, Griffis says Dolby can go down to a black of 0.0001 nits, even though there is no need or ability for displays to get that dark today.
How bright is white? Dolby says the range of 0.005 nits – 10,000 nits satisfied 84% of the viewers in their viewing tests.
The brightest consumer HDR displays today are about 1,500 nits. Professional displays where HDR content is color-graded can achieve up to 4,000 nits peak brightness.High brightness that would be in danger of damaging the eye would be in the neighborhood of 250,000 nits.
Lumens
Lumen is a measure of how much light is emitted (luminance, luminous flux) by an object. It indicates the total potential amount of light from a light source that is visible to the human eye.
Lumen is commonly used in the context of light bulbs or video-projectors as a metric for their brightness power.Lumen is used to describe light output, and about video projectors, it is commonly referred to as ANSI Lumens. Simply put, lumens is how to find out how bright a LED display is. The higher the lumens, the brighter to display!
Technically speaking, a Lumen is the SI unit of luminous flux, which is equal to the amount of light which is emitted per second in a unit solid angle of one steradian from a uniform source of one-candela intensity radiating in all directions.
LUX
Lux (lx) or often Illuminance, is a photometric unit along a given area, which takes in account the sensitivity of human eye to different wavelenghts. It is the measure of light at a specific distance within a specific area at that distance. Often used to measure the incidental sun’s intensity.
-
Ethan Roffler interviews CG Supervisor Daniele Tosti
Read more: Ethan Roffler interviews CG Supervisor Daniele TostiEthan Roffler
I recently had the honor of interviewing this VFX genius and gained great insight into what it takes to work in the entertainment industry. Keep in mind, these questions are coming from an artist’s perspective but can be applied to any creative individual looking for some wisdom from a professional. So grab a drink, sit back, and enjoy this fun and insightful conversation.
Ethan
To start, I just wanted to say thank you so much for taking the time for this interview!Daniele
My pleasure.
When I started my career I struggled to find help. Even people in the industry at the time were not that helpful. Because of that, I decided very early on that I was going to do exactly the opposite. I spend most of my weekends talking or helping students. ;)Ethan
(more…)
That’s awesome! I have also come across the same struggle! Just a heads up, this will probably be the most informal interview you’ll ever have haha! Okay, so let’s start with a small introduction!
COLLECTIONS
| Featured AI
| Design And Composition
| Explore posts
POPULAR SEARCHES
unreal | pipeline | virtual production | free | learn | photoshop | 360 | macro | google | nvidia | resolution | open source | hdri | real-time | photography basics | nuke
FEATURED POSTS
-
STOP FCC – SAVE THE FREE NET
-
Black Forest Labs released FLUX.1 Kontext
-
Zibra.AI – Real-Time Volumetric Effects in Virtual Production. Now free for Indies!
-
Photography basics: Solid Angle measures
-
Embedding frame ranges into Quicktime movies with FFmpeg
-
Scene Referred vs Display Referred color workflows
-
VFX pipeline – Render Wall management topics
-
RawTherapee – a free, open source, cross-platform raw image and HDRi processing program
Social Links
DISCLAIMER – Links and images on this website may be protected by the respective owners’ copyright. All data submitted by users through this site shall be treated as freely available to share.