COMPOSITION
-
Photography basics: Depth of Field and composition
Read more: Photography basics: Depth of Field and compositionDepth of field is the range within which focusing is resolved in a photo.
Aperture has a huge affect on to the depth of field.Changing the f-stops (f/#) of a lens will change aperture and as such the DOF.
f-stops are a just certain number which is telling you the size of the aperture. That’s how f-stop is related to aperture (and DOF).
If you increase f-stops, it will increase DOF, the area in focus (and decrease the aperture). On the other hand, decreasing the f-stop it will decrease DOF (and increase the aperture).
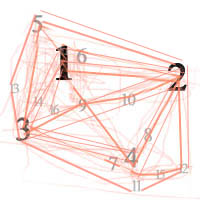
The red cone in the figure is an angular representation of the resolution of the system. Versus the dotted lines, which indicate the aperture coverage. Where the lines of the two cones intersect defines the total range of the depth of field.
This image explains why the longer the depth of field, the greater the range of clarity.
-
StudioBinder – Roger Deakins on How to Choose a Camera Lens — Cinematography Composition Techniques
Read more: StudioBinder – Roger Deakins on How to Choose a Camera Lens — Cinematography Composition Techniqueshttps://www.studiobinder.com/blog/camera-lens-buying-guide/
https://www.studiobinder.com/blog/e-books/camera-lenses-explained-volume-1-ebook
DESIGN
COLOR
-
About color: What is a LUT
Read more: About color: What is a LUThttp://www.lightillusion.com/luts.html
https://www.shutterstock.com/blog/how-use-luts-color-grading
A LUT (Lookup Table) is essentially the modifier between two images, the original image and the displayed image, based on a mathematical formula. Basically conversion matrices of different complexities. There are different types of LUTS – viewing, transform, calibration, 1D and 3D.
-
Light and Matter : The 2018 theory of Physically-Based Rendering and Shading by Allegorithmic
Read more: Light and Matter : The 2018 theory of Physically-Based Rendering and Shading by Allegorithmicacademy.substance3d.com/courses/the-pbr-guide-part-1
academy.substance3d.com/courses/the-pbr-guide-part-2
Local copy:
-
OLED vs QLED – What TV is better?
Read more: OLED vs QLED – What TV is better?Supported by LG, Philips, Panasonic and Sony sell the OLED system TVs.
OLED stands for “organic light emitting diode.”
It is a fundamentally different technology from LCD, the major type of TV today.
OLED is “emissive,” meaning the pixels emit their own light.Samsung is branding its best TVs with a new acronym: “QLED”
QLED (according to Samsung) stands for “quantum dot LED TV.”
It is a variation of the common LED LCD, adding a quantum dot film to the LCD “sandwich.”
QLED, like LCD, is, in its current form, “transmissive” and relies on an LED backlight.OLED is the only technology capable of absolute blacks and extremely bright whites on a per-pixel basis. LCD definitely can’t do that, and even the vaunted, beloved, dearly departed plasma couldn’t do absolute blacks.
QLED, as an improvement over OLED, significantly improves the picture quality. QLED can produce an even wider range of colors than OLED, which says something about this new tech. QLED is also known to produce up to 40% higher luminance efficiency than OLED technology. Further, many tests conclude that QLED is far more efficient in terms of power consumption than its predecessor, OLED.
(more…) -
Anders Langlands – Render Color Spaces
Read more: Anders Langlands – Render Color Spaceshttps://www.colour-science.org/anders-langlands/
This page compares images rendered in Arnold using spectral rendering and different sets of colourspace primaries: Rec.709, Rec.2020, ACES and DCI-P3. The SPD data for the GretagMacbeth Color Checker are the measurements of Noburu Ohta, taken from Mansencal, Mauderer and Parsons (2014) colour-science.org.
-
VES Cinematic Color – Motion-Picture Color Management
Read more: VES Cinematic Color – Motion-Picture Color ManagementThis paper presents an introduction to the color pipelines behind modern feature-film visual-effects and animation.
Authored by Jeremy Selan, and reviewed by the members of the VES Technology Committee including Rob Bredow, Dan Candela, Nick Cannon, Paul Debevec, Ray Feeney, Andy Hendrickson, Gautham Krishnamurti, Sam Richards, Jordan Soles, and Sebastian Sylwan.
-
What light is best to illuminate gems for resale
Read more: What light is best to illuminate gems for resalewww.palagems.com/gem-lighting2
Artificial light sources, not unlike the diverse phases of natural light, vary considerably in their properties. As a result, some lamps render an object’s color better than others do.
The most important criterion for assessing the color-rendering ability of any lamp is its spectral power distribution curve.
Natural daylight varies too much in strength and spectral composition to be taken seriously as a lighting standard for grading and dealing colored stones. For anything to be a standard, it must be constant in its properties, which natural light is not.
For dealers in particular to make the transition from natural light to an artificial light source, that source must offer:
1- A degree of illuminance at least as strong as the common phases of natural daylight.
2- Spectral properties identical or comparable to a phase of natural daylight.A source combining these two things makes gems appear much the same as when viewed under a given phase of natural light. From the viewpoint of many dealers, this corresponds to a naturalappearance.
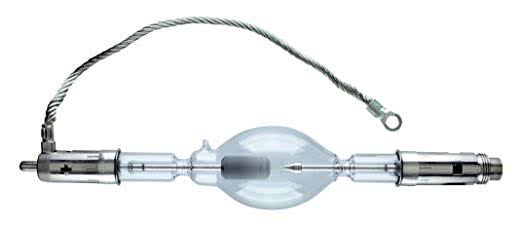
The 6000° Kelvin xenon short-arc lamp appears closest to meeting the criteria for a standard light source. Besides the strong illuminance this lamp affords, its spectrum is very similar to CIE standard illuminants of similar color temperature.

LIGHTING
-
Photography basics: Exposure Value vs Photographic Exposure vs Il/Luminance vs Pixel luminance measurements
Read more: Photography basics: Exposure Value vs Photographic Exposure vs Il/Luminance vs Pixel luminance measurementsAlso see: https://www.pixelsham.com/2015/05/16/how-aperture-shutter-speed-and-iso-affect-your-photos/
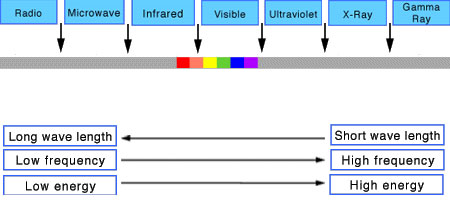
In photography, exposure value (EV) is a number that represents a combination of a camera’s shutter speed and f-number, such that all combinations that yield the same exposure have the same EV (for any fixed scene luminance).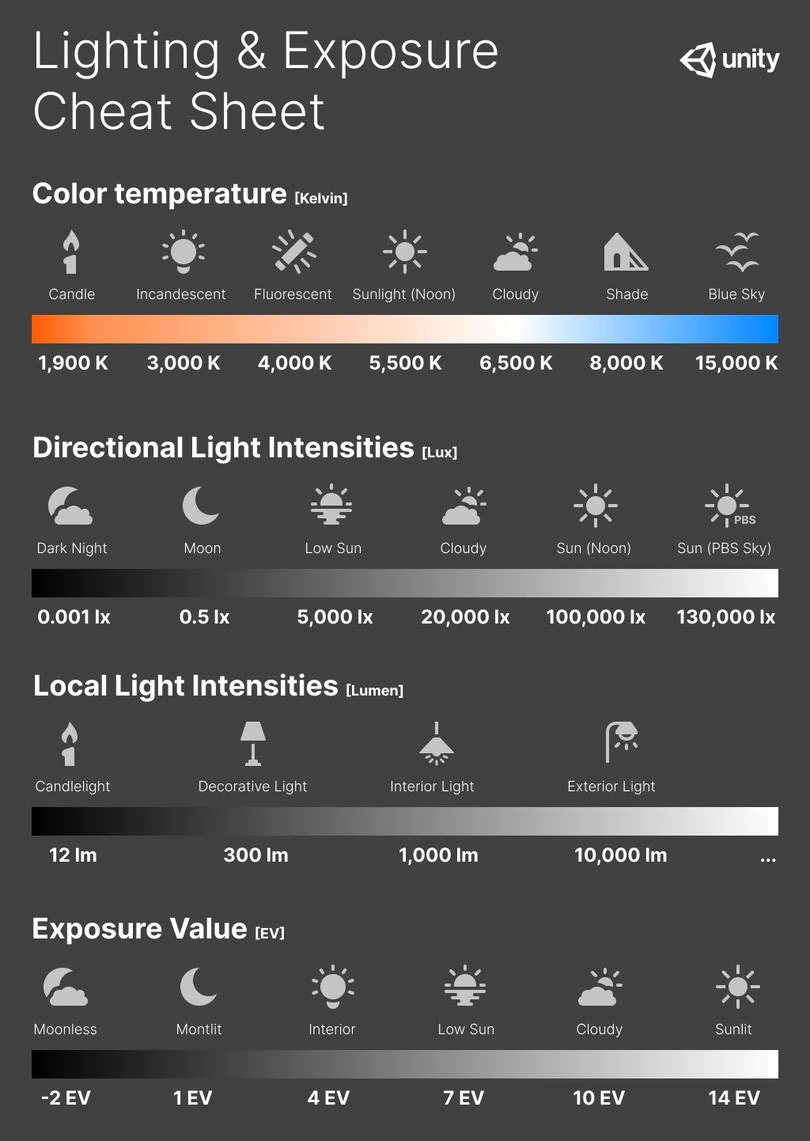
The EV concept was developed in an attempt to simplify choosing among combinations of equivalent camera settings. Although all camera settings with the same EV nominally give the same exposure, they do not necessarily give the same picture. EV is also used to indicate an interval on the photographic exposure scale. 1 EV corresponding to a standard power-of-2 exposure step, commonly referred to as a stop
EV 0 corresponds to an exposure time of 1 sec and a relative aperture of f/1.0. If the EV is known, it can be used to select combinations of exposure time and f-number.Note EV does not equal to photographic exposure. Photographic Exposure is defined as how much light hits the camera’s sensor. It depends on the camera settings mainly aperture and shutter speed. Exposure value (known as EV) is a number that represents the exposure setting of the camera.
Thus, strictly, EV is not a measure of luminance (indirect or reflected exposure) or illuminance (incidentl exposure); rather, an EV corresponds to a luminance (or illuminance) for which a camera with a given ISO speed would use the indicated EV to obtain the nominally correct exposure. Nonetheless, it is common practice among photographic equipment manufacturers to express luminance in EV for ISO 100 speed, as when specifying metering range or autofocus sensitivity.
The exposure depends on two things: how much light gets through the lenses to the camera’s sensor and for how long the sensor is exposed. The former is a function of the aperture value while the latter is a function of the shutter speed. Exposure value is a number that represents this potential amount of light that could hit the sensor. It is important to understand that exposure value is a measure of how exposed the sensor is to light and not a measure of how much light actually hits the sensor. The exposure value is independent of how lit the scene is. For example a pair of aperture value and shutter speed represents the same exposure value both if the camera is used during a very bright day or during a dark night.
Each exposure value number represents all the possible shutter and aperture settings that result in the same exposure. Although the exposure value is the same for different combinations of aperture values and shutter speeds the resulting photo can be very different (the aperture controls the depth of field while shutter speed controls how much motion is captured).
EV 0.0 is defined as the exposure when setting the aperture to f-number 1.0 and the shutter speed to 1 second. All other exposure values are relative to that number. Exposure values are on a base two logarithmic scale. This means that every single step of EV – plus or minus 1 – represents the exposure (actual light that hits the sensor) being halved or doubled.Formulas
(more…) -
Magnific.ai Relight – change the entire lighting of a scene
Read more: Magnific.ai Relight – change the entire lighting of a sceneIt’s a new Magnific spell that allows you to change the entire lighting of a scene and, optionally, the background with just:
1/ A prompt OR
2/ A reference image OR
3/ A light map (drawing your own lights)https://x.com/javilopen/status/1805274155065176489
-
Christopher Butler – Understanding the Eye-Mind Connection – Vision is a mental process
Read more: Christopher Butler – Understanding the Eye-Mind Connection – Vision is a mental processhttps://www.chrbutler.com/understanding-the-eye-mind-connection
The intricate relationship between the eyes and the brain, often termed the eye-mind connection, reveals that vision is predominantly a cognitive process. This understanding has profound implications for fields such as design, where capturing and maintaining attention is paramount. This essay delves into the nuances of visual perception, the brain’s role in interpreting visual data, and how this knowledge can be applied to effective design strategies.
This cognitive aspect of vision is evident in phenomena such as optical illusions, where the brain interprets visual information in a way that contradicts physical reality. These illusions underscore that what we “see” is not merely a direct recording of the external world but a constructed experience shaped by cognitive processes.
Understanding the cognitive nature of vision is crucial for effective design. Designers must consider how the brain processes visual information to create compelling and engaging visuals. This involves several key principles:
- Attention and Engagement
- Visual Hierarchy
- Cognitive Load Management
- Context and Meaning
COLLECTIONS
| Featured AI
| Design And Composition
| Explore posts
POPULAR SEARCHES
unreal | pipeline | virtual production | free | learn | photoshop | 360 | macro | google | nvidia | resolution | open source | hdri | real-time | photography basics | nuke
FEATURED POSTS
-
Gamma correction
-
UV maps
-
Principles of Animation with Alan Becker, Dermot OConnor and Shaun Keenan
-
Jesse Zumstein – Jobs in games
-
Generative AI Glossary / AI Dictionary / AI Terminology
-
Black Body color aka the Planckian Locus curve for white point eye perception
-
MiniMax-Remover – Taming Bad Noise Helps Video Object Removal Rotoscoping
-
Image rendering bit depth
Social Links
DISCLAIMER – Links and images on this website may be protected by the respective owners’ copyright. All data submitted by users through this site shall be treated as freely available to share.