COMPOSITION
-
Mastering Camera Shots and Angles: A Guide for Filmmakers
Read more: Mastering Camera Shots and Angles: A Guide for Filmmakershttps://website.ltx.studio/blog/mastering-camera-shots-and-angles
1. Extreme Wide Shot
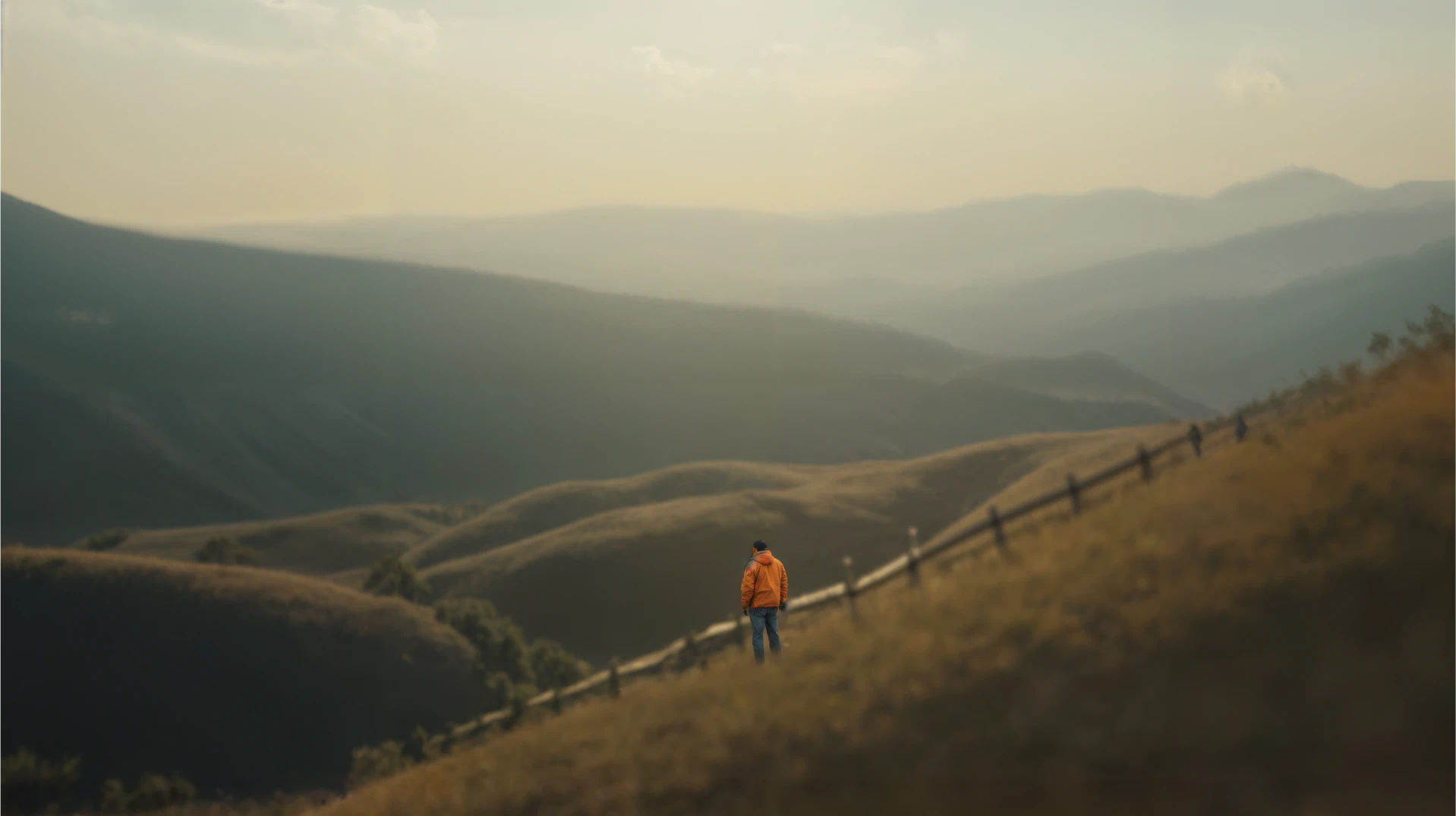

2. Wide Shot
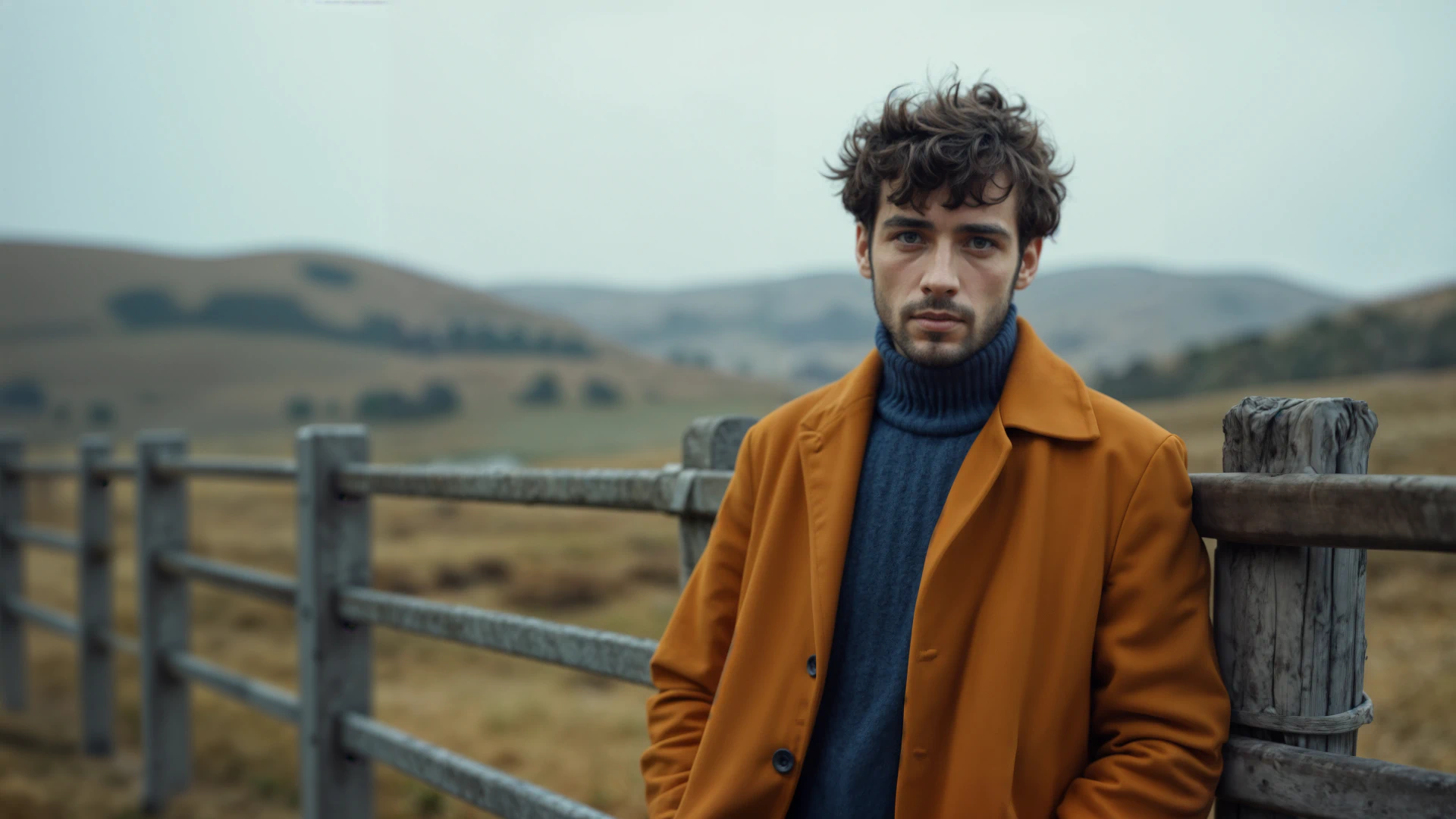

3. Medium Shot
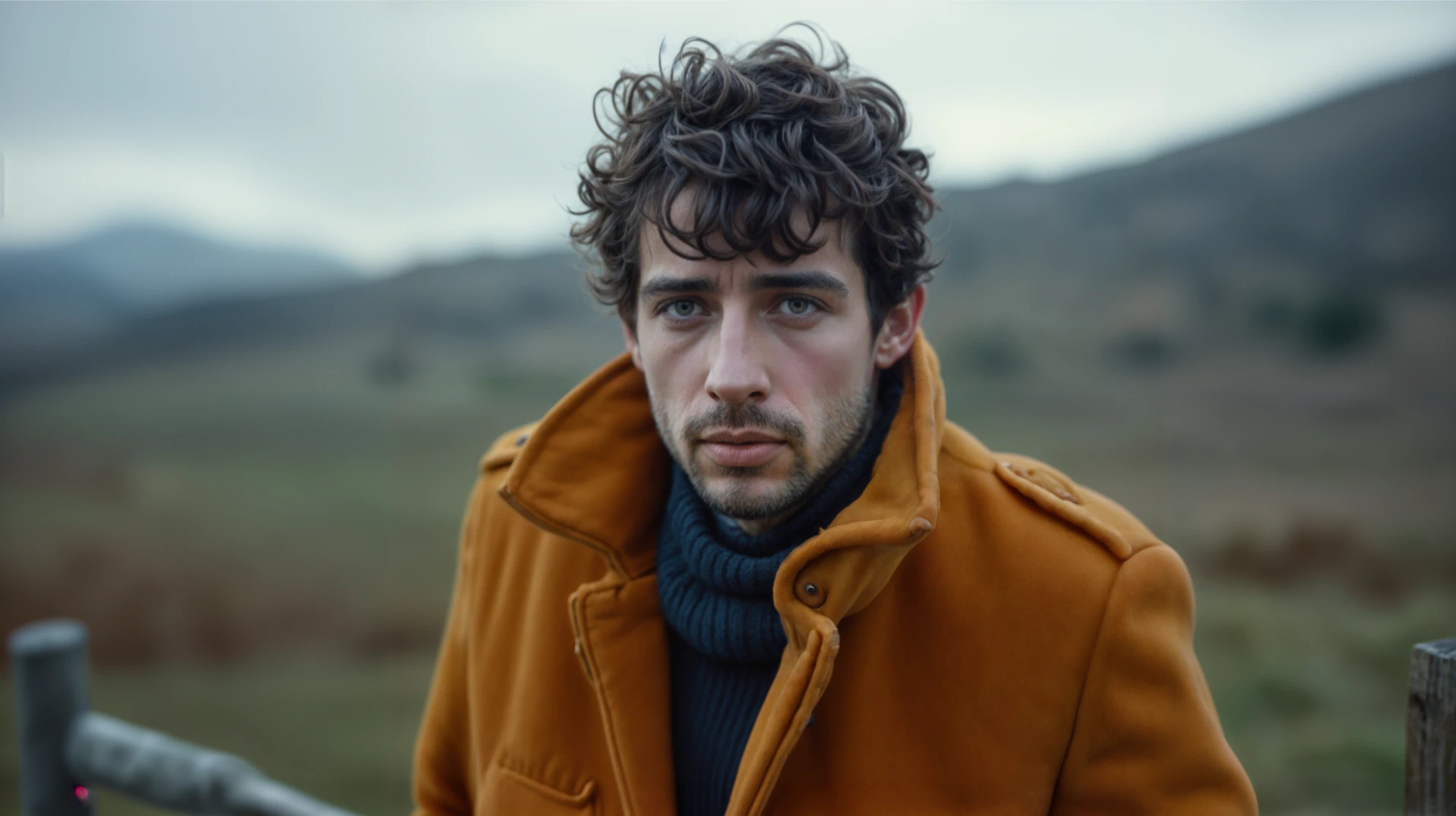

4. Close Up
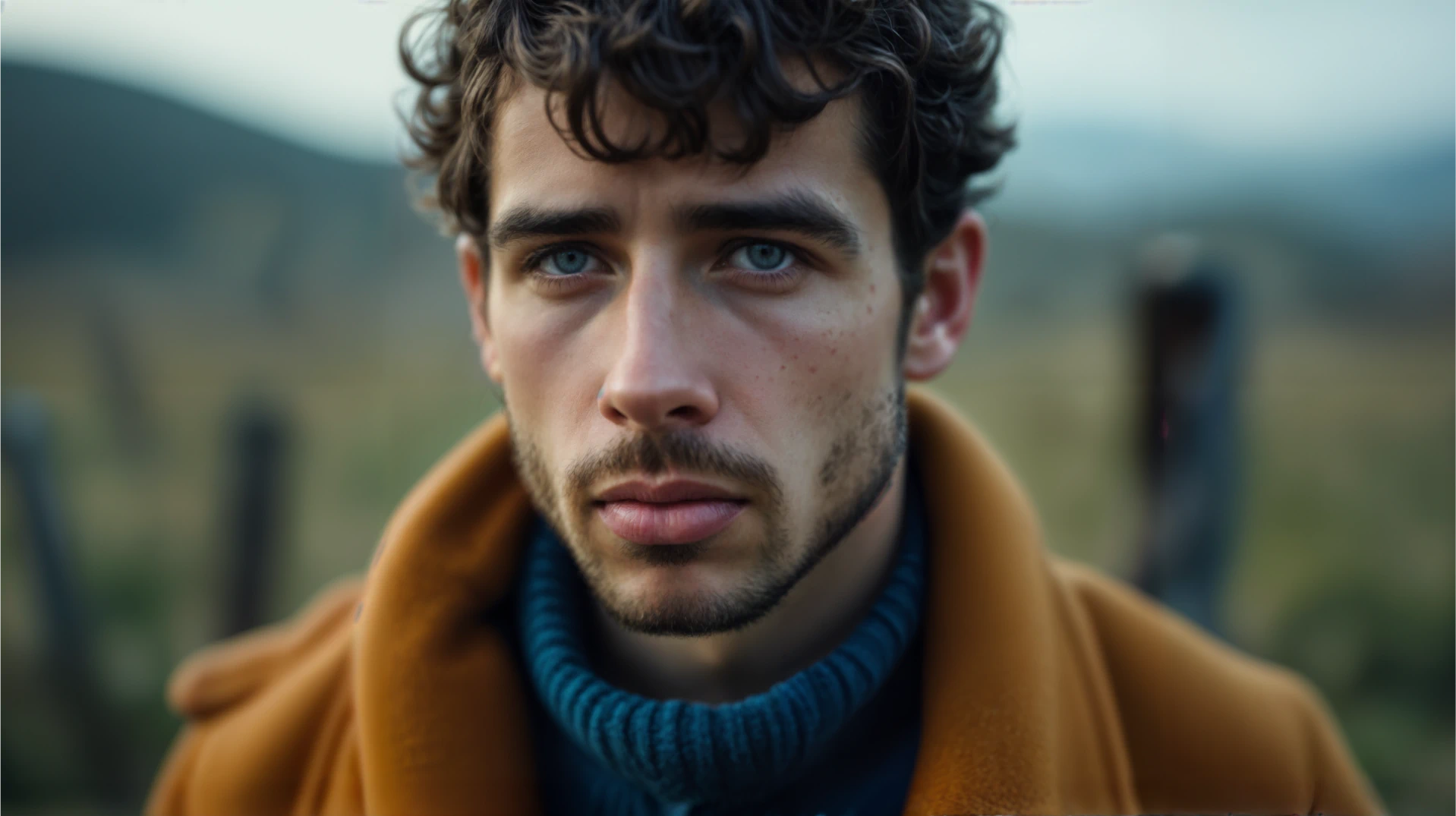

5. Extreme Close Up

-
7 Commandments of Film Editing and composition
Read more: 7 Commandments of Film Editing and composition1. Watch every frame of raw footage twice. On the second time, take notes. If you don’t do this and try to start developing a scene premature, then it’s a big disservice to yourself and to the director, actors and production crew.
2. Nurture the relationships with the director. You are the secondary person in the relationship. Be calm and continually offer solutions. Get the main intention of the film as soon as possible from the director.
3. Organize your media so that you can find any shot instantly.
4. Factor in extra time for renders, exports, errors and crashes.
5. Attempt edits and ideas that shouldn’t work. It just might work. Until you do it and watch it, you won’t know. Don’t rule out ideas just because they don’t make sense in your mind.
6. Spend more time on your audio. It’s the glue of your edit. AUDIO SAVES EVERYTHING. Create fluid and seamless audio under your video.
7. Make cuts for the scene, but always in context for the whole film. Have a macro and a micro view at all times.
DESIGN
-
Create striked-out text
Read more: Create striked-out texthttp://fsymbols.com/generators/strikethrough/
s̶t̶r̶i̶k̶e̶ ̶i̶t̶ ̶l̶i̶k̶̶e̶ ̶i̶t̶s̶ ̶h̶o̶t
COLOR
-
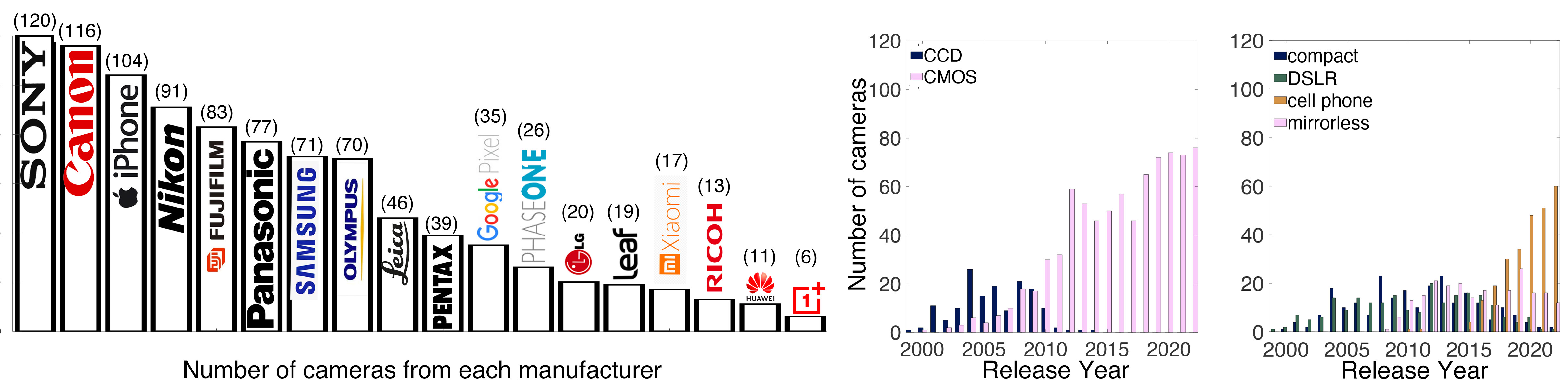
Photography Basics : Spectral Sensitivity Estimation Without a Camera
Read more: Photography Basics : Spectral Sensitivity Estimation Without a Camerahttps://color-lab-eilat.github.io/Spectral-sensitivity-estimation-web/
A number of problems in computer vision and related fields would be mitigated if camera spectral sensitivities were known. As consumer cameras are not designed for high-precision visual tasks, manufacturers do not disclose spectral sensitivities. Their estimation requires a costly optical setup, which triggered researchers to come up with numerous indirect methods that aim to lower cost and complexity by using color targets. However, the use of color targets gives rise to new complications that make the estimation more difficult, and consequently, there currently exists no simple, low-cost, robust go-to method for spectral sensitivity estimation that non-specialized research labs can adopt. Furthermore, even if not limited by hardware or cost, researchers frequently work with imagery from multiple cameras that they do not have in their possession.
To provide a practical solution to this problem, we propose a framework for spectral sensitivity estimation that not only does not require any hardware (including a color target), but also does not require physical access to the camera itself. Similar to other work, we formulate an optimization problem that minimizes a two-term objective function: a camera-specific term from a system of equations, and a universal term that bounds the solution space.
Different than other work, we utilize publicly available high-quality calibration data to construct both terms. We use the colorimetric mapping matrices provided by the Adobe DNG Converter to formulate the camera-specific system of equations, and constrain the solutions using an autoencoder trained on a database of ground-truth curves. On average, we achieve reconstruction errors as low as those that can arise due to manufacturing imperfections between two copies of the same camera. We provide predicted sensitivities for more than 1,000 cameras that the Adobe DNG Converter currently supports, and discuss which tasks can become trivial when camera responses are available.
-
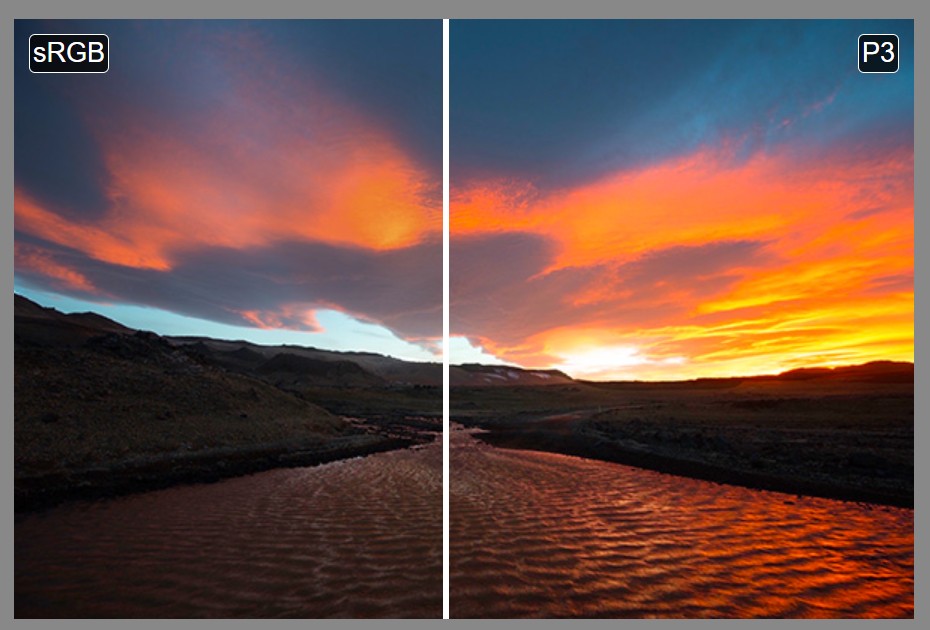
Colormaxxing – What if I told you that rgb(255, 0, 0) is not actually the reddest red you can have in your browser?
Read more: Colormaxxing – What if I told you that rgb(255, 0, 0) is not actually the reddest red you can have in your browser?https://karuna.dev/colormaxxing
https://webkit.org/blog-files/color-gamut/comparison.html
https://oklch.com/#70,0.1,197,100

-
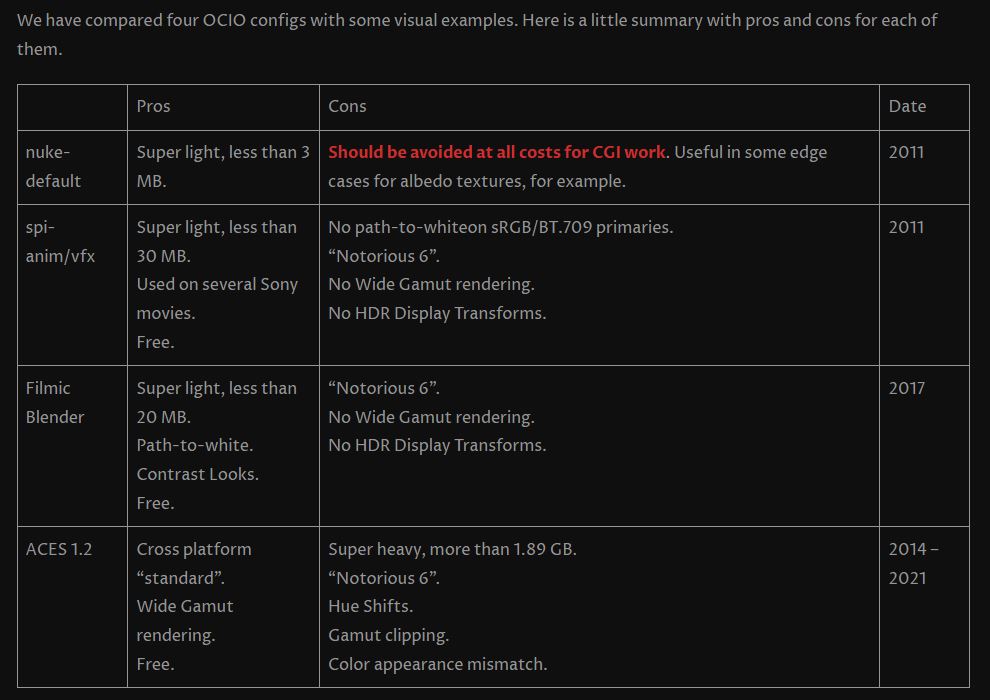
sRGB vs REC709 – An introduction and FFmpeg implementations
Read more: sRGB vs REC709 – An introduction and FFmpeg implementations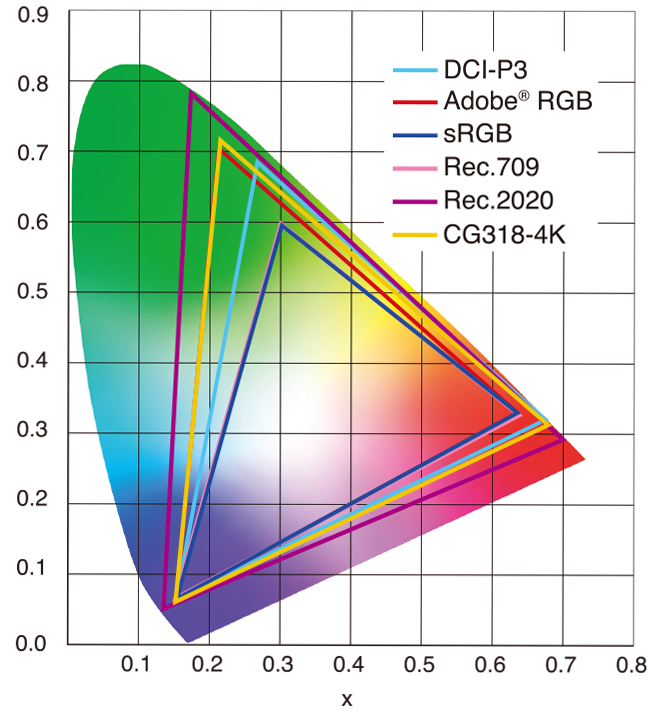
1. Basic Comparison
- What they are
- sRGB: A standard “web”/computer-display RGB color space defined by IEC 61966-2-1. It’s used for most monitors, cameras, printers, and the vast majority of images on the Internet.
- Rec. 709: An HD-video color space defined by ITU-R BT.709. It’s the go-to standard for HDTV broadcasts, Blu-ray discs, and professional video pipelines.
- Why they exist
- sRGB: Ensures consistent colors across different consumer devices (PCs, phones, webcams).
- Rec. 709: Ensures consistent colors across video production and playback chains (cameras → editing → broadcast → TV).
- What you’ll see
- On your desktop or phone, images tagged sRGB will look “right” without extra tweaking.
- On an HDTV or video-editing timeline, footage tagged Rec. 709 will display accurate contrast and hue on broadcast-grade monitors.
2. Digging Deeper
Feature sRGB Rec. 709 White point D65 (6504 K), same for both D65 (6504 K) Primaries (x,y) R: (0.640, 0.330) G: (0.300, 0.600) B: (0.150, 0.060) R: (0.640, 0.330) G: (0.300, 0.600) B: (0.150, 0.060) Gamut size Identical triangle on CIE 1931 chart Identical to sRGB Gamma / transfer Piecewise curve: approximate 2.2 with linear toe Pure power-law γ≈2.4 (often approximated as 2.2 in practice) Matrix coefficients N/A (pure RGB usage) Y = 0.2126 R + 0.7152 G + 0.0722 B (Rec. 709 matrix) Typical bit-depth 8-bit/channel (with 16-bit variants) 8-bit/channel (10-bit for professional video) Usage metadata Tagged as “sRGB” in image files (PNG, JPEG, etc.) Tagged as “bt709” in video containers (MP4, MOV) Color range Full-range RGB (0–255) Studio-range Y′CbCr (Y′ [16–235], Cb/Cr [16–240])
Why the Small Differences Matter
(more…) - What they are
-
Björn Ottosson – How software gets color wrong
Read more: Björn Ottosson – How software gets color wronghttps://bottosson.github.io/posts/colorwrong/
Most software around us today are decent at accurately displaying colors. Processing of colors is another story unfortunately, and is often done badly.
To understand what the problem is, let’s start with an example of three ways of blending green and magenta:
- Perceptual blend – A smooth transition using a model designed to mimic human perception of color. The blending is done so that the perceived brightness and color varies smoothly and evenly.
- Linear blend – A model for blending color based on how light behaves physically. This type of blending can occur in many ways naturally, for example when colors are blended together by focus blur in a camera or when viewing a pattern of two colors at a distance.
- sRGB blend – This is how colors would normally be blended in computer software, using sRGB to represent the colors.
Let’s look at some more examples of blending of colors, to see how these problems surface more practically. The examples use strong colors since then the differences are more pronounced. This is using the same three ways of blending colors as the first example.
Instead of making it as easy as possible to work with color, most software make it unnecessarily hard, by doing image processing with representations not designed for it. Approximating the physical behavior of light with linear RGB models is one easy thing to do, but more work is needed to create image representations tailored for image processing and human perception.
Also see:
-
3D Lighting Tutorial by Amaan Kram
Read more: 3D Lighting Tutorial by Amaan Kramhttp://www.amaanakram.com/lightingT/part1.htm
The goals of lighting in 3D computer graphics are more or less the same as those of real world lighting.
Lighting serves a basic function of bringing out, or pushing back the shapes of objects visible from the camera’s view.
It gives a two-dimensional image on the monitor an illusion of the third dimension-depth.But it does not just stop there. It gives an image its personality, its character. A scene lit in different ways can give a feeling of happiness, of sorrow, of fear etc., and it can do so in dramatic or subtle ways. Along with personality and character, lighting fills a scene with emotion that is directly transmitted to the viewer.
Trying to simulate a real environment in an artificial one can be a daunting task. But even if you make your 3D rendering look absolutely photo-realistic, it doesn’t guarantee that the image carries enough emotion to elicit a “wow” from the people viewing it.
Making 3D renderings photo-realistic can be hard. Putting deep emotions in them can be even harder. However, if you plan out your lighting strategy for the mood and emotion that you want your rendering to express, you make the process easier for yourself.
Each light source can be broken down in to 4 distinct components and analyzed accordingly.
· Intensity
· Direction
· Color
· SizeThe overall thrust of this writing is to produce photo-realistic images by applying good lighting techniques.
LIGHTING
-
Photography basics: Lumens vs Candelas (candle) vs Lux vs FootCandle vs Watts vs Irradiance vs Illuminance
Read more: Photography basics: Lumens vs Candelas (candle) vs Lux vs FootCandle vs Watts vs Irradiance vs Illuminancehttps://www.translatorscafe.com/unit-converter/en-US/illumination/1-11/
The power output of a light source is measured using the unit of watts W. This is a direct measure to calculate how much power the light is going to drain from your socket and it is not relatable to the light brightness itself.
The amount of energy emitted from it per second. That energy comes out in a form of photons which we can crudely represent with rays of light coming out of the source. The higher the power the more rays emitted from the source in a unit of time.
Not all energy emitted is visible to the human eye, so we often rely on photometric measurements, which takes in account the sensitivity of human eye to different wavelenghts
Details in the post
(more…) -
Convert between light exposure and intensity
Read more: Convert between light exposure and intensityimport math,sys def Exposure2Intensity(exposure): exp = float(exposure) result = math.pow(2,exp) print(result) Exposure2Intensity(0) def Intensity2Exposure(intensity): inarg = float(intensity) if inarg == 0: print("Exposure of zero intensity is undefined.") return if inarg < 1e-323: inarg = max(inarg, 1e-323) print("Exposure of negative intensities is undefined. Clamping to a very small value instead (1e-323)") result = math.log(inarg, 2) print(result) Intensity2Exposure(0.1)Why Exposure?
Exposure is a stop value that multiplies the intensity by 2 to the power of the stop. Increasing exposure by 1 results in double the amount of light.
Artists think in “stops.” Doubling or halving brightness is easy math and common in grading and look-dev.
Exposure counts doublings in whole stops:- +1 stop = ×2 brightness
- −1 stop = ×0.5 brightness
This gives perceptually even controls across both bright and dark values.
Why Intensity?
Intensity is linear.
It’s what render engines and compositors expect when:- Summing values
- Averaging pixels
- Multiplying or filtering pixel data
Use intensity when you need the actual math on pixel/light data.
Formulas (from your Python)
- Intensity from exposure: intensity = 2**exposure
- Exposure from intensity: exposure = log₂(intensity)
Guardrails:
- Intensity must be > 0 to compute exposure.
- If intensity = 0 → exposure is undefined.
- Clamp tiny values (e.g.
1e−323) before using log₂.
Use Exposure (stops) when…
- You want artist-friendly sliders (−5…+5 stops)
- Adjusting look-dev or grading in even stops
- Matching plates with quick ±1 stop tweaks
- Tweening brightness changes smoothly across ranges
Use Intensity (linear) when…
- Storing raw pixel/light values
- Multiplying textures or lights by a gain
- Performing sums, averages, and filters
- Feeding values to render engines expecting linear data
Examples
- +2 stops → 2**2 = 4.0 (×4)
- +1 stop → 2**1 = 2.0 (×2)
- 0 stop → 2**0 = 1.0 (×1)
- −1 stop → 2**(−1) = 0.5 (×0.5)
- −2 stops → 2**(−2) = 0.25 (×0.25)
- Intensity 0.1 → exposure = log₂(0.1) ≈ −3.32
Rule of thumb
Think in stops (exposure) for controls and matching.
Compute in linear (intensity) for rendering and math. -
HDRI Resources
Read more: HDRI ResourcesText2Light
- https://www.cgtrader.com/free-3d-models/exterior/other/10-free-hdr-panoramas-created-with-text2light-zero-shot
- https://frozenburning.github.io/projects/text2light/
- https://github.com/FrozenBurning/Text2Light
Royalty free links
- https://locationtextures.com/panoramas/
- http://www.noahwitchell.com/freebies
- https://polyhaven.com/hdris
- https://hdrmaps.com/
- https://www.ihdri.com/
- https://hdrihaven.com/
- https://www.domeble.com/
- http://www.hdrlabs.com/sibl/archive.html
- https://www.hdri-hub.com/hdrishop/hdri
- http://noemotionhdrs.net/hdrevening.html
- https://www.openfootage.net/hdri-panorama/
- https://www.zwischendrin.com/en/browse/hdri
Nvidia GauGAN360
-
NVidia DiffusionRenderer – Neural Inverse and Forward Rendering with Video Diffusion Models. How NVIDIA reimagined relighting
Read more: NVidia DiffusionRenderer – Neural Inverse and Forward Rendering with Video Diffusion Models. How NVIDIA reimagined relightinghttps://www.fxguide.com/quicktakes/diffusing-reality-how-nvidia-reimagined-relighting/
https://research.nvidia.com/labs/toronto-ai/DiffusionRenderer/
-
DiffusionLight: HDRI Light Probes for Free by Painting a Chrome Ball
Read more: DiffusionLight: HDRI Light Probes for Free by Painting a Chrome Ballhttps://diffusionlight.github.io/
https://github.com/DiffusionLight/DiffusionLight
https://github.com/DiffusionLight/DiffusionLight?tab=MIT-1-ov-file#readme
https://colab.research.google.com/drive/15pC4qb9mEtRYsW3utXkk-jnaeVxUy-0S
“a simple yet effective technique to estimate lighting in a single input image. Current techniques rely heavily on HDR panorama datasets to train neural networks to regress an input with limited field-of-view to a full environment map. However, these approaches often struggle with real-world, uncontrolled settings due to the limited diversity and size of their datasets. To address this problem, we leverage diffusion models trained on billions of standard images to render a chrome ball into the input image. Despite its simplicity, this task remains challenging: the diffusion models often insert incorrect or inconsistent objects and cannot readily generate images in HDR format. Our research uncovers a surprising relationship between the appearance of chrome balls and the initial diffusion noise map, which we utilize to consistently generate high-quality chrome balls. We further fine-tune an LDR difusion model (Stable Diffusion XL) with LoRA, enabling it to perform exposure bracketing for HDR light estimation. Our method produces convincing light estimates across diverse settings and demonstrates superior generalization to in-the-wild scenarios.”

-
Is a MacBeth Colour Rendition Chart the Safest Way to Calibrate a Camera?
Read more: Is a MacBeth Colour Rendition Chart the Safest Way to Calibrate a Camera?www.colour-science.org/posts/the-colorchecker-considered-mostly-harmless/
“Unless you have all the relevant spectral measurements, a colour rendition chart should not be used to perform colour-correction of camera imagery but only for white balancing and relative exposure adjustments.”
“Using a colour rendition chart for colour-correction might dramatically increase error if the scene light source spectrum is different from the illuminant used to compute the colour rendition chart’s reference values.”
“other factors make using a colour rendition chart unsuitable for camera calibration:
– Uncontrolled geometry of the colour rendition chart with the incident illumination and the camera.
– Unknown sample reflectances and ageing as the colour of the samples vary with time.
– Low samples count.
– Camera noise and flare.
– Etc…“Those issues are well understood in the VFX industry, and when receiving plates, we almost exclusively use colour rendition charts to white balance and perform relative exposure adjustments, i.e. plate neutralisation.”
COLLECTIONS
| Featured AI
| Design And Composition
| Explore posts
POPULAR SEARCHES
unreal | pipeline | virtual production | free | learn | photoshop | 360 | macro | google | nvidia | resolution | open source | hdri | real-time | photography basics | nuke
FEATURED POSTS
-
Glossary of Lighting Terms – cheat sheet
-
Canva bought Affinity – Now Affinity Photo and Affinity Designer are… GONE?!
-
GretagMacbeth Color Checker Numeric Values and Middle Gray
-
Sensitivity of human eye
-
Most common ways to smooth 3D prints
-
N8N.io – From Zero to Your First AI Agent in 25 Minutes
-
copypastecharacter.com – alphabets, special characters, alt codes and symbols library
-
Cinematographers Blueprint 300dpi poster
Social Links
DISCLAIMER – Links and images on this website may be protected by the respective owners’ copyright. All data submitted by users through this site shall be treated as freely available to share.