COMPOSITION
-
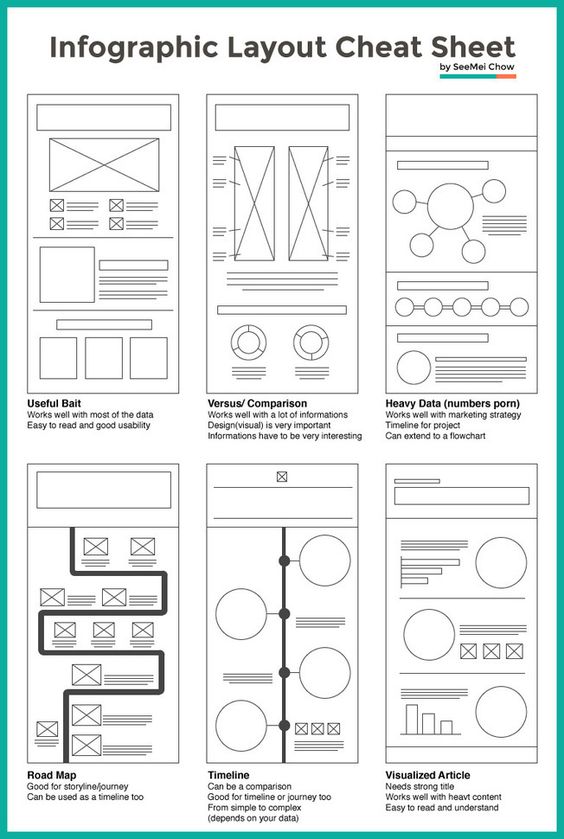
Composition – 5 tips for creating perfect cinematic lighting and making your work look stunning
Read more: Composition – 5 tips for creating perfect cinematic lighting and making your work look stunninghttp://www.diyphotography.net/5-tips-creating-perfect-cinematic-lighting-making-work-look-stunning/
1. Learn the rules of lighting
2. Learn when to break the rules
3. Make your key light larger
4. Reverse keying
5. Always be backlighting
DESIGN
COLOR
-
“Reality” is constructed by your brain. Here’s what that means, and why it matters.
Read more: “Reality” is constructed by your brain. Here’s what that means, and why it matters.“Fix your gaze on the black dot on the left side of this image. But wait! Finish reading this paragraph first. As you gaze at the left dot, try to answer this question: In what direction is the object on the right moving? Is it drifting diagonally, or is it moving up and down?”

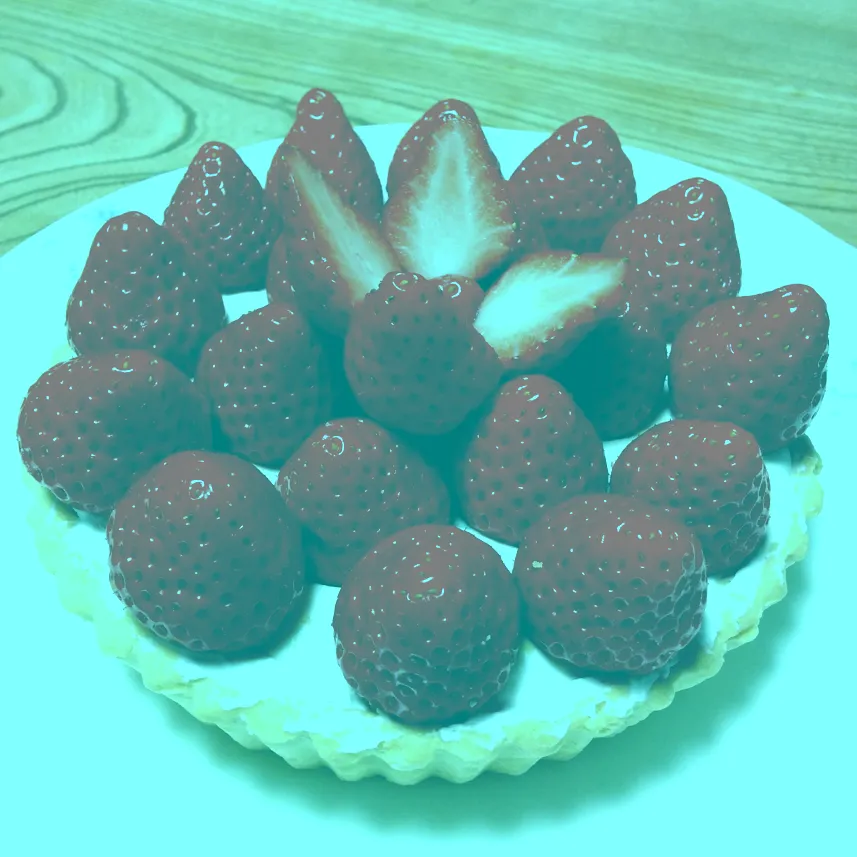
What color are these strawberries?

Are A and B the same gray?

-
Rec-2020 – TVs new color gamut standard used by Dolby Vision?
Read more: Rec-2020 – TVs new color gamut standard used by Dolby Vision?https://www.hdrsoft.com/resources/dri.html#bit-depth
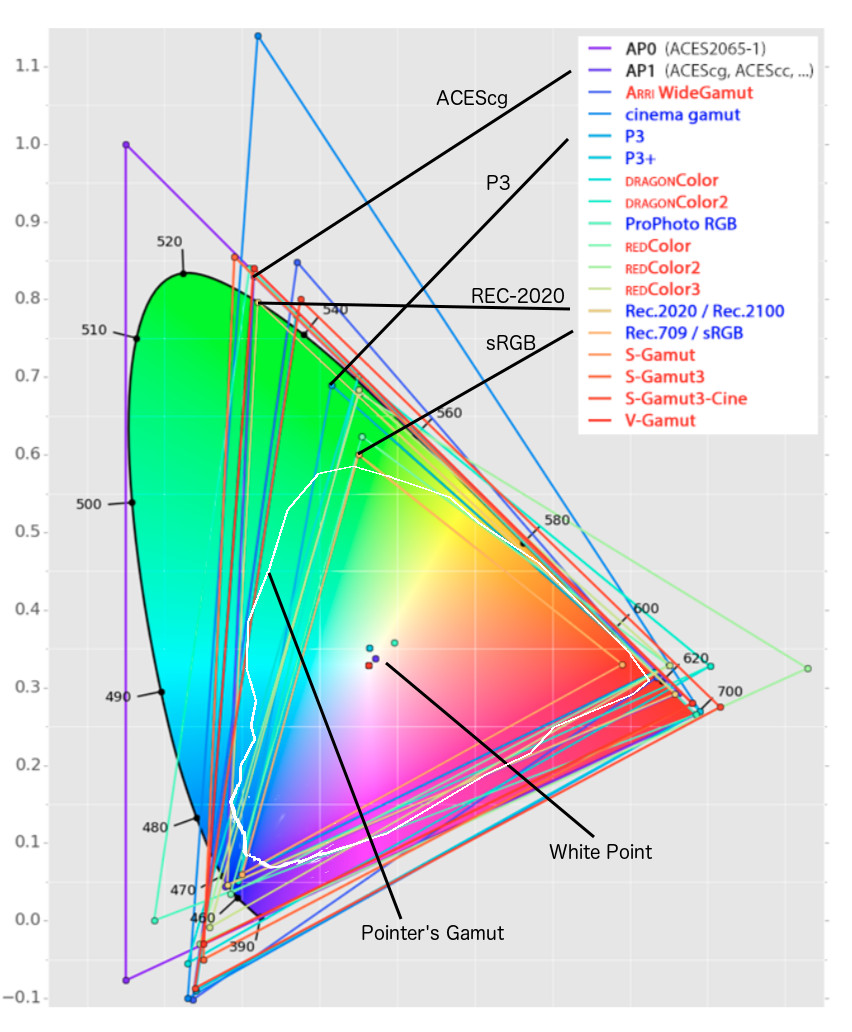
The dynamic range is a ratio between the maximum and minimum values of a physical measurement. Its definition depends on what the dynamic range refers to.
For a scene: Dynamic range is the ratio between the brightest and darkest parts of the scene.
For a camera: Dynamic range is the ratio of saturation to noise. More specifically, the ratio of the intensity that just saturates the camera to the intensity that just lifts the camera response one standard deviation above camera noise.
For a display: Dynamic range is the ratio between the maximum and minimum intensities emitted from the screen.
The Dynamic Range of real-world scenes can be quite high — ratios of 100,000:1 are common in the natural world. An HDR (High Dynamic Range) image stores pixel values that span the whole tonal range of real-world scenes. Therefore, an HDR image is encoded in a format that allows the largest range of values, e.g. floating-point values stored with 32 bits per color channel. Another characteristics of an HDR image is that it stores linear values. This means that the value of a pixel from an HDR image is proportional to the amount of light measured by the camera.
For TVs HDR is great, but it’s not the only new TV feature worth discussing.
(more…) -
Weta Digital – Manuka Raytracer and Gazebo GPU renderers – pipeline
Read more: Weta Digital – Manuka Raytracer and Gazebo GPU renderers – pipelinehttps://jo.dreggn.org/home/2018_manuka.pdf
http://www.fxguide.com/featured/manuka-weta-digitals-new-renderer/

The Manuka rendering architecture has been designed in the spirit of the classic reyes rendering architecture. In its core, reyes is based on stochastic rasterisation of micropolygons, facilitating depth of field, motion blur, high geometric complexity,and programmable shading.
This is commonly achieved with Monte Carlo path tracing, using a paradigm often called shade-on-hit, in which the renderer alternates tracing rays with running shaders on the various ray hits. The shaders take the role of generating the inputs of the local material structure which is then used bypath sampling logic to evaluate contributions and to inform what further rays to cast through the scene.
Over the years, however, the expectations have risen substantially when it comes to image quality. Computing pictures which are indistinguishable from real footage requires accurate simulation of light transport, which is most often performed using some variant of Monte Carlo path tracing. Unfortunately this paradigm requires random memory accesses to the whole scene and does not lend itself well to a rasterisation approach at all.
Manuka is both a uni-directional and bidirectional path tracer and encompasses multiple importance sampling (MIS). Interestingly, and importantly for production character skin work, it is the first major production renderer to incorporate spectral MIS in the form of a new ‘Hero Spectral Sampling’ technique, which was recently published at Eurographics Symposium on Rendering 2014.
Manuka propose a shade-before-hit paradigm in-stead and minimise I/O strain (and some memory costs) on the system, leveraging locality of reference by running pattern generation shaders before we execute light transport simulation by path sampling, “compressing” any bvh structure as needed, and as such also limiting duplication of source data.
The difference with reyes is that instead of baking colors into the geometry like in Reyes, manuka bakes surface closures. This means that light transport is still calculated with path tracing, but all texture lookups etc. are done up-front and baked into the geometry.The main drawback with this method is that geometry has to be tessellated to its highest, stable topology before shading can be evaluated properly. As such, the high cost to first pixel. Even a basic 4 vertices square becomes a much more complex model with this approach.
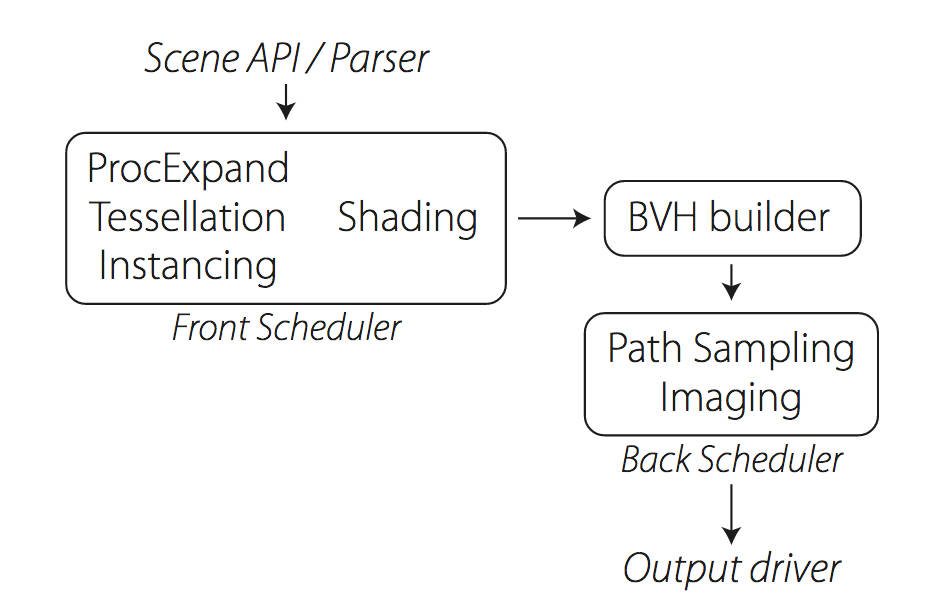
Manuka use the RenderMan Shading Language (rsl) for programmable shading [Pixar Animation Studios 2015], but we do not invoke rsl shaders when intersecting a ray with a surface (often called shade-on-hit). Instead, we pre-tessellate and pre-shade all the input geometry in the front end of the renderer.
This way, we can efficiently order shading computations to sup-port near-optimal texture locality, vectorisation, and parallelism. This system avoids repeated evaluation of shaders at the same surface point, and presents a minimal amount of memory to be accessed during light transport time. An added benefit is that the acceleration structure for ray tracing (abounding volume hierarchy, bvh) is built once on the final tessellated geometry, which allows us to ray trace more efficiently than multi-level bvhs and avoids costly caching of on-demand tessellated micropolygons and the associated scheduling issues.For the shading reasons above, in terms of AOVs, the studio approach is to succeed at combining complex shading with ray paths in the render rather than pass a multi-pass render to compositing.
For the Spectral Rendering component. The light transport stage is fully spectral, using a continuously sampled wavelength which is traced with each path and used to apply the spectral camera sensitivity of the sensor. This allows for faithfully support any degree of observer metamerism as the camera footage they are intended to match as well as complex materials which require wavelength dependent phenomena such as diffraction, dispersion, interference, iridescence, or chromatic extinction and Rayleigh scattering in participating media.
As opposed to the original reyes paper, we use bilinear interpolation of these bsdf inputs later when evaluating bsdfs per pathv ertex during light transport4. This improves temporal stability of geometry which moves very slowly with respect to the pixel raster
In terms of the pipeline, everything rendered at Weta was already completely interwoven with their deep data pipeline. Manuka very much was written with deep data in mind. Here, Manuka not so much extends the deep capabilities, rather it fully matches the already extremely complex and powerful setup Weta Digital already enjoy with RenderMan. For example, an ape in a scene can be selected, its ID is available and a NUKE artist can then paint in 3D say a hand and part of the way up the neutral posed ape.
We called our system Manuka, as a respectful nod to reyes: we had heard a story froma former ILM employee about how reyes got its name from how fond the early Pixar people were of their lunches at Point Reyes, and decided to name our system after our surrounding natural environment, too. Manuka is a kind of tea tree very common in New Zealand which has very many very small leaves, in analogy to micropolygons ina tree structure for ray tracing. It also happens to be the case that Weta Digital’s main site is on Manuka Street.

LIGHTING
-
DiffusionLight: HDRI Light Probes for Free by Painting a Chrome Ball
Read more: DiffusionLight: HDRI Light Probes for Free by Painting a Chrome Ballhttps://diffusionlight.github.io/
https://github.com/DiffusionLight/DiffusionLight
https://github.com/DiffusionLight/DiffusionLight?tab=MIT-1-ov-file#readme
https://colab.research.google.com/drive/15pC4qb9mEtRYsW3utXkk-jnaeVxUy-0S
“a simple yet effective technique to estimate lighting in a single input image. Current techniques rely heavily on HDR panorama datasets to train neural networks to regress an input with limited field-of-view to a full environment map. However, these approaches often struggle with real-world, uncontrolled settings due to the limited diversity and size of their datasets. To address this problem, we leverage diffusion models trained on billions of standard images to render a chrome ball into the input image. Despite its simplicity, this task remains challenging: the diffusion models often insert incorrect or inconsistent objects and cannot readily generate images in HDR format. Our research uncovers a surprising relationship between the appearance of chrome balls and the initial diffusion noise map, which we utilize to consistently generate high-quality chrome balls. We further fine-tune an LDR difusion model (Stable Diffusion XL) with LoRA, enabling it to perform exposure bracketing for HDR light estimation. Our method produces convincing light estimates across diverse settings and demonstrates superior generalization to in-the-wild scenarios.”

-
Vahan Sosoyan MakeHDR – an OpenFX open source plug-in for merging multiple LDR images into a single HDRI
Read more: Vahan Sosoyan MakeHDR – an OpenFX open source plug-in for merging multiple LDR images into a single HDRIhttps://github.com/Sosoyan/make-hdr
Feature notes
- Merge up to 16 inputs with 8, 10 or 12 bit depth processing
- User friendly logarithmic Tone Mapping controls within the tool
- Advanced controls such as Sampling rate and Smoothness
Available at cross platform on Linux, MacOS and Windows Works consistent in compositing applications like Nuke, Fusion, Natron.
NOTE: The goal is to clean the initial individual brackets before or at merging time as much as possible.
This means:- keeping original shooting metadata
- de-fringing
- removing aberration (through camera lens data or automatically)
- at 32 bit
- in ACEScg (or ACES) wherever possible
-
Open Source Nvidia Omniverse
Read more: Open Source Nvidia Omniverseblogs.nvidia.com/blog/2019/03/18/omniverse-collaboration-platform/
developer.nvidia.com/nvidia-omniverse
An open, Interactive 3D Design Collaboration Platform for Multi-Tool Workflows to simplify studio workflows for real-time graphics.
It supports Pixar’s Universal Scene Description technology for exchanging information about modeling, shading, animation, lighting, visual effects and rendering across multiple applications.
It also supports NVIDIA’s Material Definition Language, which allows artists to exchange information about surface materials across multiple tools.
With Omniverse, artists can see live updates made by other artists working in different applications. They can also see changes reflected in multiple tools at the same time.
For example an artist using Maya with a portal to Omniverse can collaborate with another artist using UE4 and both will see live updates of each others’ changes in their application.
-
Rendering – BRDF – Bidirectional reflectance distribution function
Read more: Rendering – BRDF – Bidirectional reflectance distribution functionhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bidirectional_reflectance_distribution_function
The bidirectional reflectance distribution function is a four-dimensional function that defines how light is reflected at an opaque surface
http://www.cs.ucla.edu/~zhu/tutorial/An_Introduction_to_BRDF-Based_Lighting.pdf
In general, when light interacts with matter, a complicated light-matter dynamic occurs. This interaction depends on the physical characteristics of the light as well as the physical composition and characteristics of the matter.
That is, some of the incident light is reflected, some of the light is transmitted, and another portion of the light is absorbed by the medium itself.
A BRDF describes how much light is reflected when light makes contact with a certain material. Similarly, a BTDF (Bi-directional Transmission Distribution Function) describes how much light is transmitted when light makes contact with a certain material
http://www.cs.princeton.edu/~smr/cs348c-97/surveypaper.html
It is difficult to establish exactly how far one should go in elaborating the surface model. A truly complete representation of the reflective behavior of a surface might take into account such phenomena as polarization, scattering, fluorescence, and phosphorescence, all of which might vary with position on the surface. Therefore, the variables in this complete function would be:
incoming and outgoing angle incoming and outgoing wavelength incoming and outgoing polarization (both linear and circular) incoming and outgoing position (which might differ due to subsurface scattering) time delay between the incoming and outgoing light ray
-
Neural Microfacet Fields for Inverse Rendering
Read more: Neural Microfacet Fields for Inverse Renderinghttps://half-potato.gitlab.io/posts/nmf/
COLLECTIONS
| Featured AI
| Design And Composition
| Explore posts
POPULAR SEARCHES
unreal | pipeline | virtual production | free | learn | photoshop | 360 | macro | google | nvidia | resolution | open source | hdri | real-time | photography basics | nuke
FEATURED POSTS
-
Key/Fill ratios and scene composition using false colors and Nuke node
-
QR code logos
-
Decart AI Mirage – The first ever World Transformation Model – turning any video, game, or camera feed into a new digital world, in real time
-
Photography basics: How Exposure Stops (Aperture, Shutter Speed, and ISO) Affect Your Photos – cheat sheet cards
-
Photography basics: Exposure Value vs Photographic Exposure vs Il/Luminance vs Pixel luminance measurements
-
Free fonts
-
Matt Hallett – WAN 2.1 VACE Total Video Control in ComfyUI
-
Jesse Zumstein – Jobs in games
Social Links
DISCLAIMER – Links and images on this website may be protected by the respective owners’ copyright. All data submitted by users through this site shall be treated as freely available to share.