COMPOSITION
-
Photography basics: Depth of Field and composition
Read more: Photography basics: Depth of Field and compositionDepth of field is the range within which focusing is resolved in a photo.
Aperture has a huge affect on to the depth of field.Changing the f-stops (f/#) of a lens will change aperture and as such the DOF.
f-stops are a just certain number which is telling you the size of the aperture. That’s how f-stop is related to aperture (and DOF).
If you increase f-stops, it will increase DOF, the area in focus (and decrease the aperture). On the other hand, decreasing the f-stop it will decrease DOF (and increase the aperture).
The red cone in the figure is an angular representation of the resolution of the system. Versus the dotted lines, which indicate the aperture coverage. Where the lines of the two cones intersect defines the total range of the depth of field.
This image explains why the longer the depth of field, the greater the range of clarity.
-
Cinematographers Blueprint 300dpi poster
Read more: Cinematographers Blueprint 300dpi posterThe 300dpi digital poster is now available to all PixelSham.com subscribers.
If you have already subscribed and wish a copy, please send me a note through the contact page.
DESIGN
COLOR
-
Scene Referred vs Display Referred color workflows
Read more: Scene Referred vs Display Referred color workflowsDisplay Referred it is tied to the target hardware, as such it bakes color requirements into every type of media output request.
Scene Referred uses a common unified wide gamut and targeting audience through CDL and DI libraries instead.
So that color information stays untouched and only “transformed” as/when needed.Sources:
– Victor Perez – Color Management Fundamentals & ACES Workflows in Nuke
– https://z-fx.nl/ColorspACES.pdf
– Wicus
-
About green screens
Read more: About green screenshackaday.com/2015/02/07/how-green-screen-worked-before-computers/
www.newtek.com/blog/tips/best-green-screen-materials/
www.chromawall.com/blog//chroma-key-green
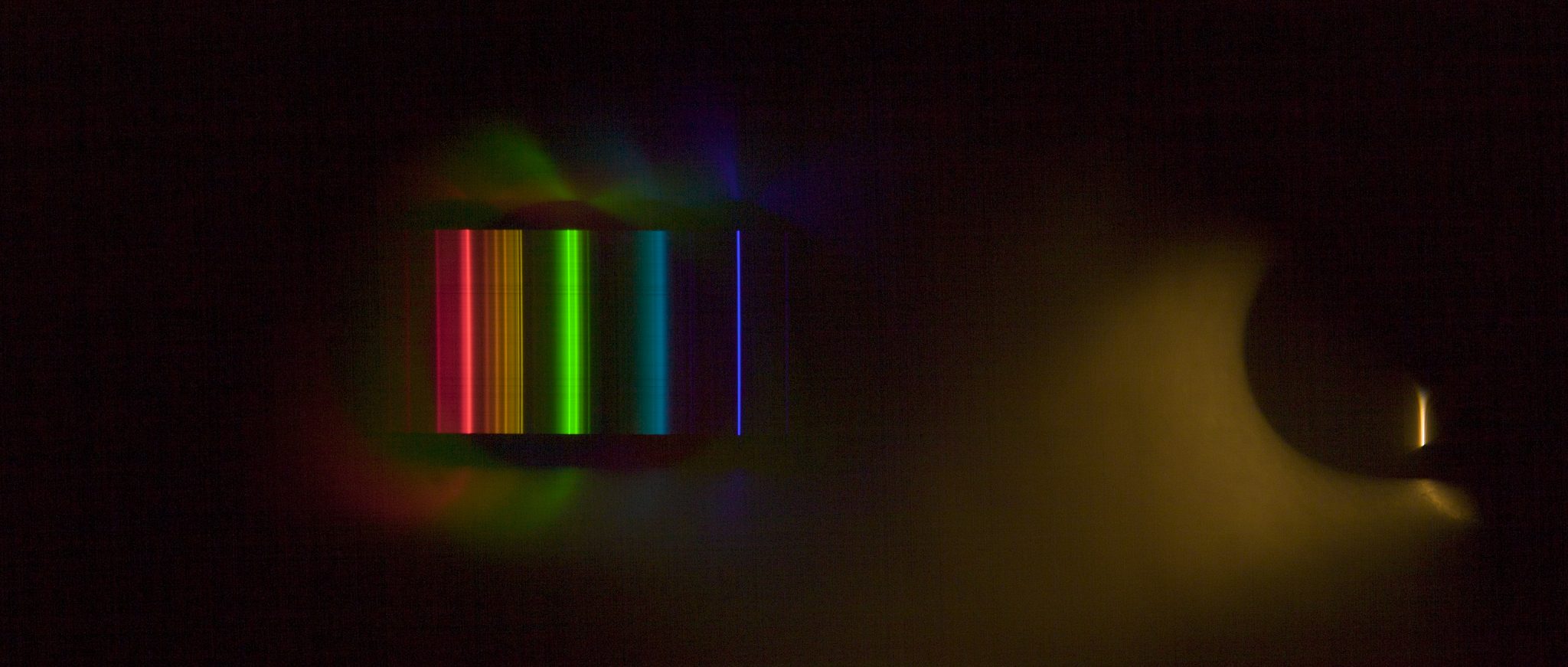
Chroma Key Green, the color of green screens is also known as Chroma Green and is valued at approximately 354C in the Pantone color matching system (PMS).
Chroma Green can be broken down in many different ways. Here is green screen green as other values useful for both physical and digital production:
Green Screen as RGB Color Value: 0, 177, 64
Green Screen as CMYK Color Value: 81, 0, 92, 0
Green Screen as Hex Color Value: #00b140
Green Screen as Websafe Color Value: #009933Chroma Key Green is reasonably close to an 18% gray reflectance.
Illuminate your green screen with an uniform source with less than 2/3 EV variation.
The level of brightness at any given f-stop should be equivalent to a 90% white card under the same lighting. -
mmColorTarget – Nuke Gizmo for color matching a MacBeth chart
Read more: mmColorTarget – Nuke Gizmo for color matching a MacBeth charthttps://www.marcomeyer-vfx.de/posts/2014-04-11-mmcolortarget-nuke-gizmo/
https://www.marcomeyer-vfx.de/posts/mmcolortarget-nuke-gizmo/
https://vimeo.com/9.1652466e+07
https://www.nukepedia.com/gizmos/colour/mmcolortarget
LIGHTING
-
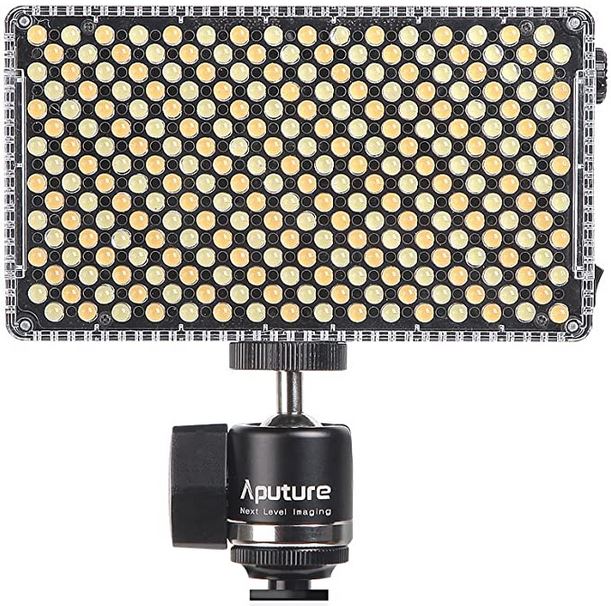
Aputure AL-F7 – dimmable Led Video Light, CRI95+, 3200-9500K
Read more: Aputure AL-F7 – dimmable Led Video Light, CRI95+, 3200-9500KHigh CRI of ≥95
256 LEDs with 45° beam angle
3200 to 9500K variable color temperature
1 to 100% Stepless Dimming, 1500 Lux Brightness at 3.3′
LCD Info Screen. Powered by an L-series battery, D-Tap, or USB-C
Because the light has a variable color range of 3200 to 9500K, when the light is set to 5500K (daylight balanced) both sets of LEDs are on at full, providing the maximum brightness from this fixture when compared to using the light at 3200 or 9500K.
The LCD screen provides information on the fixture’s output as well as the charge state of the battery. The screen also indicates whether the adjustment knob is controlling brightness or color temperature. To switch from brightness to CCT or CCT to brightness, just apply a short press to the adjustment knob.
The included cold shoe ball joint adapter enables mounting the light to your camera’s accessory shoe via the 1/4″-20 threaded hole on the fixture. In addition, the bottom of the cold shoe foot features a 3/8″-16 threaded hole, and includes a 3/8″-16 to 1/4″-20 reducing bushing.

-
Is a MacBeth Colour Rendition Chart the Safest Way to Calibrate a Camera?
Read more: Is a MacBeth Colour Rendition Chart the Safest Way to Calibrate a Camera?www.colour-science.org/posts/the-colorchecker-considered-mostly-harmless/
“Unless you have all the relevant spectral measurements, a colour rendition chart should not be used to perform colour-correction of camera imagery but only for white balancing and relative exposure adjustments.”
“Using a colour rendition chart for colour-correction might dramatically increase error if the scene light source spectrum is different from the illuminant used to compute the colour rendition chart’s reference values.”
“other factors make using a colour rendition chart unsuitable for camera calibration:
– Uncontrolled geometry of the colour rendition chart with the incident illumination and the camera.
– Unknown sample reflectances and ageing as the colour of the samples vary with time.
– Low samples count.
– Camera noise and flare.
– Etc…“Those issues are well understood in the VFX industry, and when receiving plates, we almost exclusively use colour rendition charts to white balance and perform relative exposure adjustments, i.e. plate neutralisation.”
-
NVidia DiffusionRenderer – Neural Inverse and Forward Rendering with Video Diffusion Models. How NVIDIA reimagined relighting
Read more: NVidia DiffusionRenderer – Neural Inverse and Forward Rendering with Video Diffusion Models. How NVIDIA reimagined relightinghttps://www.fxguide.com/quicktakes/diffusing-reality-how-nvidia-reimagined-relighting/
https://research.nvidia.com/labs/toronto-ai/DiffusionRenderer/
-
Free HDRI libraries
Read more: Free HDRI librariesnoahwitchell.com
http://www.noahwitchell.com/freebieslocationtextures.com
https://locationtextures.com/panoramas/maxroz.com
https://www.maxroz.com/hdri/listHDRI Haven
https://hdrihaven.com/Poly Haven
https://polyhaven.com/hdrisDomeble
https://www.domeble.com/IHDRI
https://www.ihdri.com/HDRMaps
https://hdrmaps.com/NoEmotionHdrs.net
http://noemotionhdrs.net/hdrday.htmlOpenFootage.net
https://www.openfootage.net/hdri-panorama/HDRI-hub
https://www.hdri-hub.com/hdrishop/hdri.zwischendrin
https://www.zwischendrin.com/en/browse/hdriLonger list here:
https://cgtricks.com/list-sites-free-hdri/
-
What light is best to illuminate gems for resale
Read more: What light is best to illuminate gems for resalewww.palagems.com/gem-lighting2
Artificial light sources, not unlike the diverse phases of natural light, vary considerably in their properties. As a result, some lamps render an object’s color better than others do.
The most important criterion for assessing the color-rendering ability of any lamp is its spectral power distribution curve.
Natural daylight varies too much in strength and spectral composition to be taken seriously as a lighting standard for grading and dealing colored stones. For anything to be a standard, it must be constant in its properties, which natural light is not.
For dealers in particular to make the transition from natural light to an artificial light source, that source must offer:
1- A degree of illuminance at least as strong as the common phases of natural daylight.
2- Spectral properties identical or comparable to a phase of natural daylight.A source combining these two things makes gems appear much the same as when viewed under a given phase of natural light. From the viewpoint of many dealers, this corresponds to a naturalappearance.
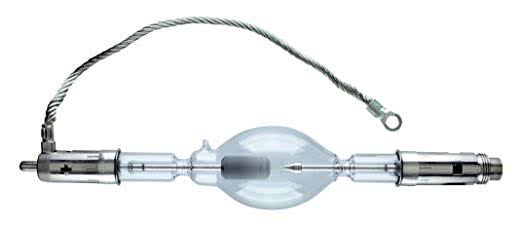
The 6000° Kelvin xenon short-arc lamp appears closest to meeting the criteria for a standard light source. Besides the strong illuminance this lamp affords, its spectrum is very similar to CIE standard illuminants of similar color temperature.

COLLECTIONS
| Featured AI
| Design And Composition
| Explore posts
POPULAR SEARCHES
unreal | pipeline | virtual production | free | learn | photoshop | 360 | macro | google | nvidia | resolution | open source | hdri | real-time | photography basics | nuke
FEATURED POSTS
-
ComfyDock – The Easiest (Free) Way to Safely Run ComfyUI Sessions in a Boxed Container
-
Photography basics: Color Temperature and White Balance
-
Glossary of Lighting Terms – cheat sheet
-
Top 3D Printing Website Resources
-
ComfyUI FLOAT – A container for FLOAT Generative Motion Latent Flow Matching for Audio-driven Talking Portrait – lip sync
-
Steven Stahlberg – Perception and Composition
-
NVidia – High-Fidelity 3D Mesh Generation at Scale with Meshtron
-
3D Gaussian Splatting step by step beginner course
Social Links
DISCLAIMER – Links and images on this website may be protected by the respective owners’ copyright. All data submitted by users through this site shall be treated as freely available to share.