COMPOSITION
-
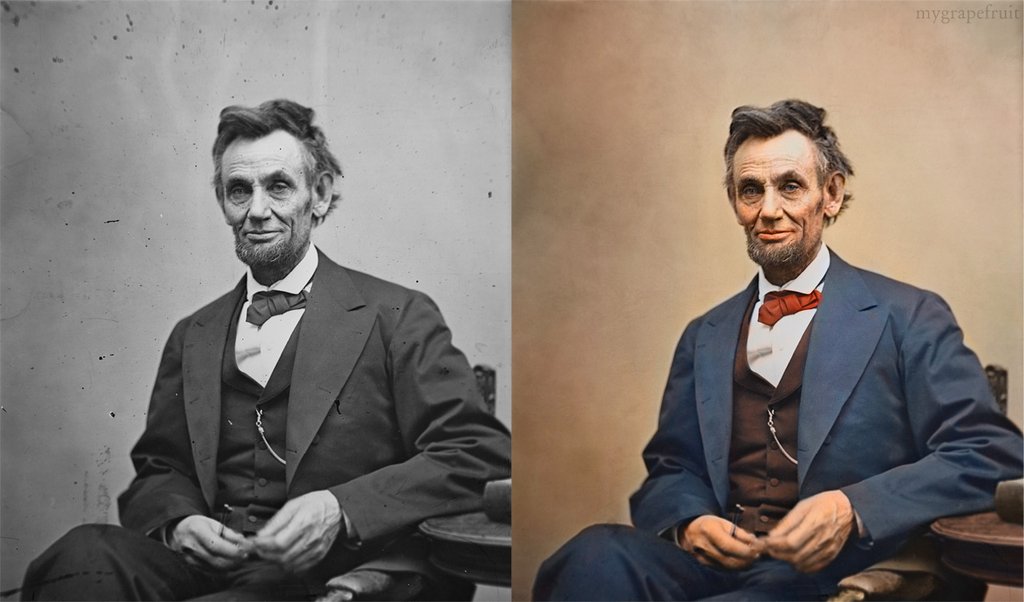
Christopher Butler – Understanding the Eye-Mind Connection – Vision is a mental process
Read more: Christopher Butler – Understanding the Eye-Mind Connection – Vision is a mental processhttps://www.chrbutler.com/understanding-the-eye-mind-connection
The intricate relationship between the eyes and the brain, often termed the eye-mind connection, reveals that vision is predominantly a cognitive process. This understanding has profound implications for fields such as design, where capturing and maintaining attention is paramount. This essay delves into the nuances of visual perception, the brain’s role in interpreting visual data, and how this knowledge can be applied to effective design strategies.
This cognitive aspect of vision is evident in phenomena such as optical illusions, where the brain interprets visual information in a way that contradicts physical reality. These illusions underscore that what we “see” is not merely a direct recording of the external world but a constructed experience shaped by cognitive processes.
Understanding the cognitive nature of vision is crucial for effective design. Designers must consider how the brain processes visual information to create compelling and engaging visuals. This involves several key principles:
- Attention and Engagement
- Visual Hierarchy
- Cognitive Load Management
- Context and Meaning

-
Composition – These are the basic lighting techniques you need to know for photography and film
Read more: Composition – These are the basic lighting techniques you need to know for photography and filmhttp://www.diyphotography.net/basic-lighting-techniques-need-know-photography-film/
Amongst the basic techniques, there’s…
1- Side lighting – Literally how it sounds, lighting a subject from the side when they’re faced toward you
2- Rembrandt lighting – Here the light is at around 45 degrees over from the front of the subject, raised and pointing down at 45 degrees
3- Back lighting – Again, how it sounds, lighting a subject from behind. This can help to add drama with silouettes
4- Rim lighting – This produces a light glowing outline around your subject
5- Key light – The main light source, and it’s not necessarily always the brightest light source
6- Fill light – This is used to fill in the shadows and provide detail that would otherwise be blackness
7- Cross lighting – Using two lights placed opposite from each other to light two subjects
-
Composition – cinematography Cheat Sheet
Read more: Composition – cinematography Cheat Sheet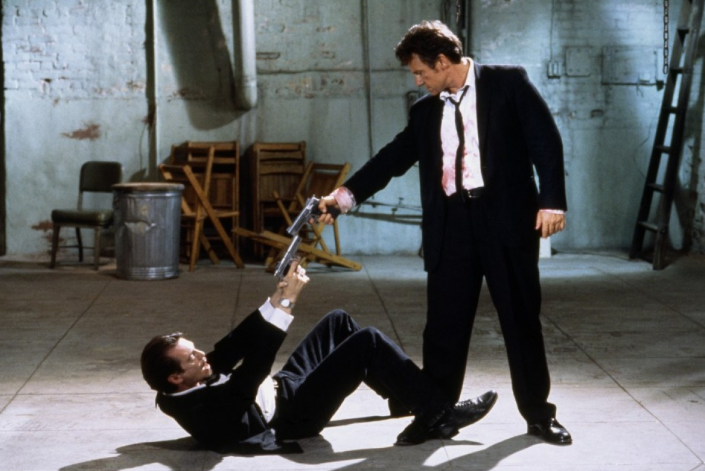
Where is our eye attracted first? Why?
Size. Focus. Lighting. Color.
Size. Mr. White (Harvey Keitel) on the right.
Focus. He’s one of the two objects in focus.
Lighting. Mr. White is large and in focus and Mr. Pink (Steve Buscemi) is highlighted by
a shaft of light.
Color. Both are black and white but the read on Mr. White’s shirt now really stands out.
(more…)
What type of lighting?
DESIGN
-
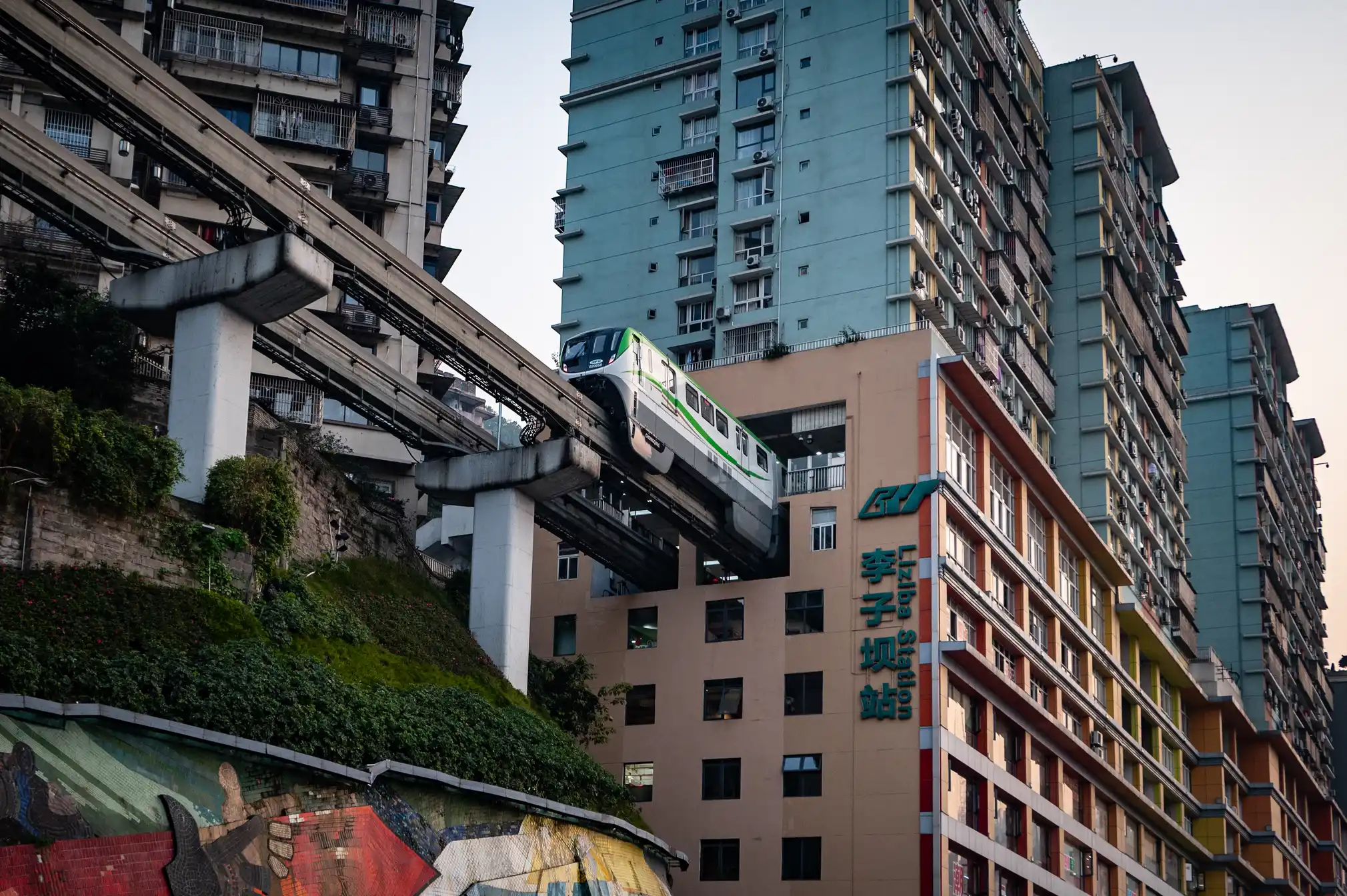
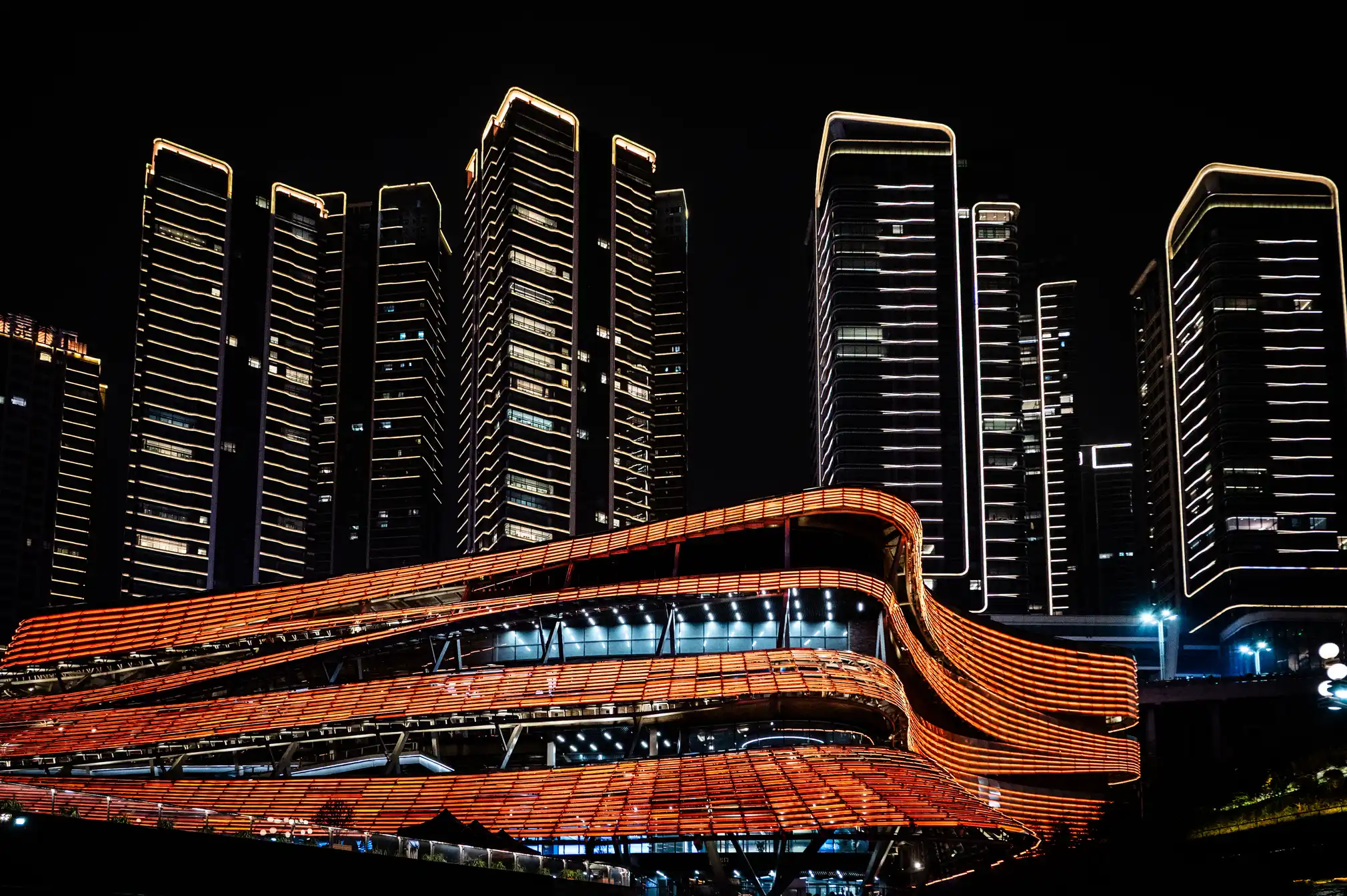
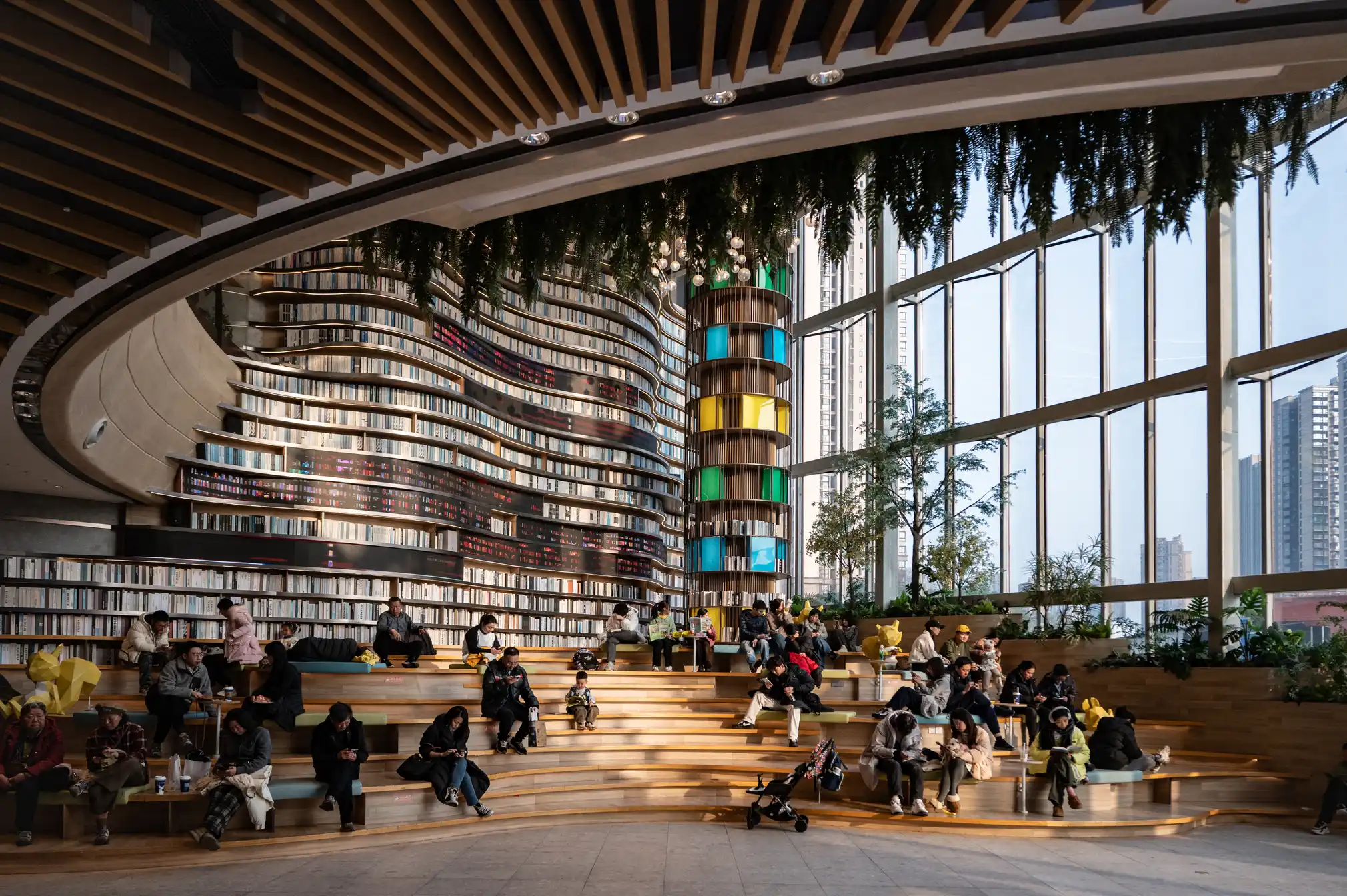
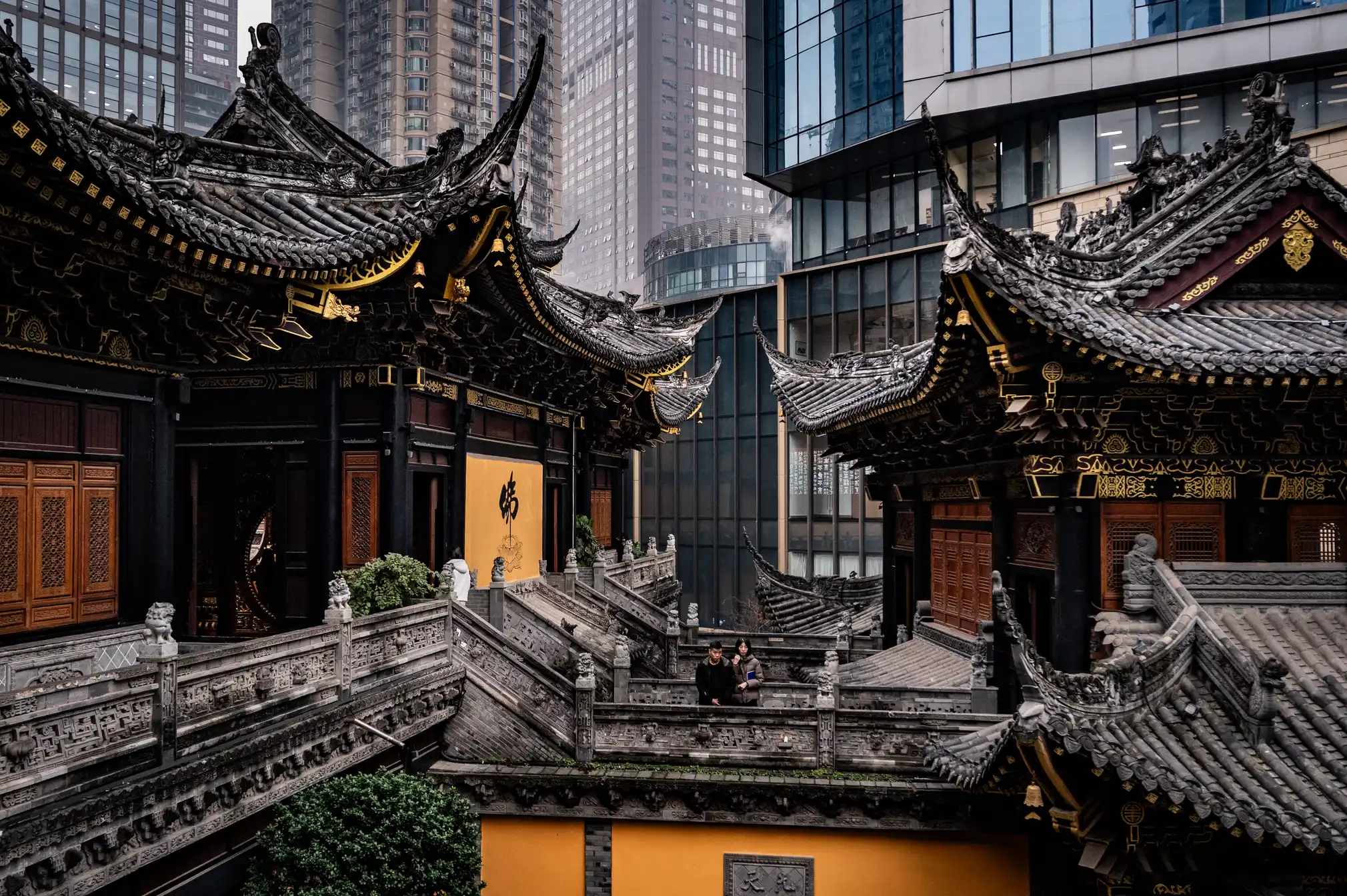
Chongqing the world’s largest city in pictures
Read more: Chongqing the world’s largest city in pictureshttps://www.theguardian.com/world/gallery/2025/apr/27/chongqing-the-worlds-largest-city-in-pictures
The largest city in the world is as big as Austria, but few people have ever heard of it. The megacity of 34 million people in central of China is the emblem of the fastest urban revolution on the planet.




-
Cosmic Motors book by Daniel Simon
Read more: Cosmic Motors book by Daniel Simonhttp://danielsimon.com/cosmic-motors-the-book/
Book Cover Cosmic Motors, Copyright by Cosmic Motors LLC / Daniel Simon www.danielsimon.com -
Realistic Avengers action figures
Read more: Realistic Avengers action figureshttp://kotaku.com/5911846/these-avengers-action-figures-look-so-real-youll-think-theyre-tiny-actors
http://www.sideshowtoy.com/?page_id=37555&ref=Avengers2012
http://www.sideshowtoy.com/?page_id=4489&sku=9017301&ref=ref=avengersLP_9017301#!prettyPhoto/0/
http://animagetoyznews.blogspot.co.nz/
COLOR
-
What is OLED and what can it do for your TV
Read more: What is OLED and what can it do for your TVhttps://www.cnet.com/news/what-is-oled-and-what-can-it-do-for-your-tv/
OLED stands for Organic Light Emitting Diode. Each pixel in an OLED display is made of a material that glows when you jab it with electricity. Kind of like the heating elements in a toaster, but with less heat and better resolution. This effect is called electroluminescence, which is one of those delightful words that is big, but actually makes sense: “electro” for electricity, “lumin” for light and “escence” for, well, basically “essence.”
OLED TV marketing often claims “infinite” contrast ratios, and while that might sound like typical hyperbole, it’s one of the extremely rare instances where such claims are actually true. Since OLED can produce a perfect black, emitting no light whatsoever, its contrast ratio (expressed as the brightest white divided by the darkest black) is technically infinite.
OLED is the only technology capable of absolute blacks and extremely bright whites on a per-pixel basis. LCD definitely can’t do that, and even the vaunted, beloved, dearly departed plasma couldn’t do absolute blacks.
-
Yasuharu YOSHIZAWA – Comparison of sRGB vs ACREScg in Nuke
Read more: Yasuharu YOSHIZAWA – Comparison of sRGB vs ACREScg in NukeAnswering the question that is often asked, “Do I need to use ACEScg to display an sRGB monitor in the end?” (Demonstration shown at an in-house seminar)
Comparison of scanlineRender output with extreme color lights on color charts with sRGB/ACREScg in color – OCIO -working space in NukeDownload the Nuke script:
-
colorhunt.co
Read more: colorhunt.coColor Hunt is a free and open platform for color inspiration with thousands of trendy hand-picked color palettes.
-
Photography basics: Lumens vs Candelas (candle) vs Lux vs FootCandle vs Watts vs Irradiance vs Illuminance
Read more: Photography basics: Lumens vs Candelas (candle) vs Lux vs FootCandle vs Watts vs Irradiance vs Illuminancehttps://www.translatorscafe.com/unit-converter/en-US/illumination/1-11/
The power output of a light source is measured using the unit of watts W. This is a direct measure to calculate how much power the light is going to drain from your socket and it is not relatable to the light brightness itself.
The amount of energy emitted from it per second. That energy comes out in a form of photons which we can crudely represent with rays of light coming out of the source. The higher the power the more rays emitted from the source in a unit of time.
Not all energy emitted is visible to the human eye, so we often rely on photometric measurements, which takes in account the sensitivity of human eye to different wavelenghts
Details in the post
(more…) -
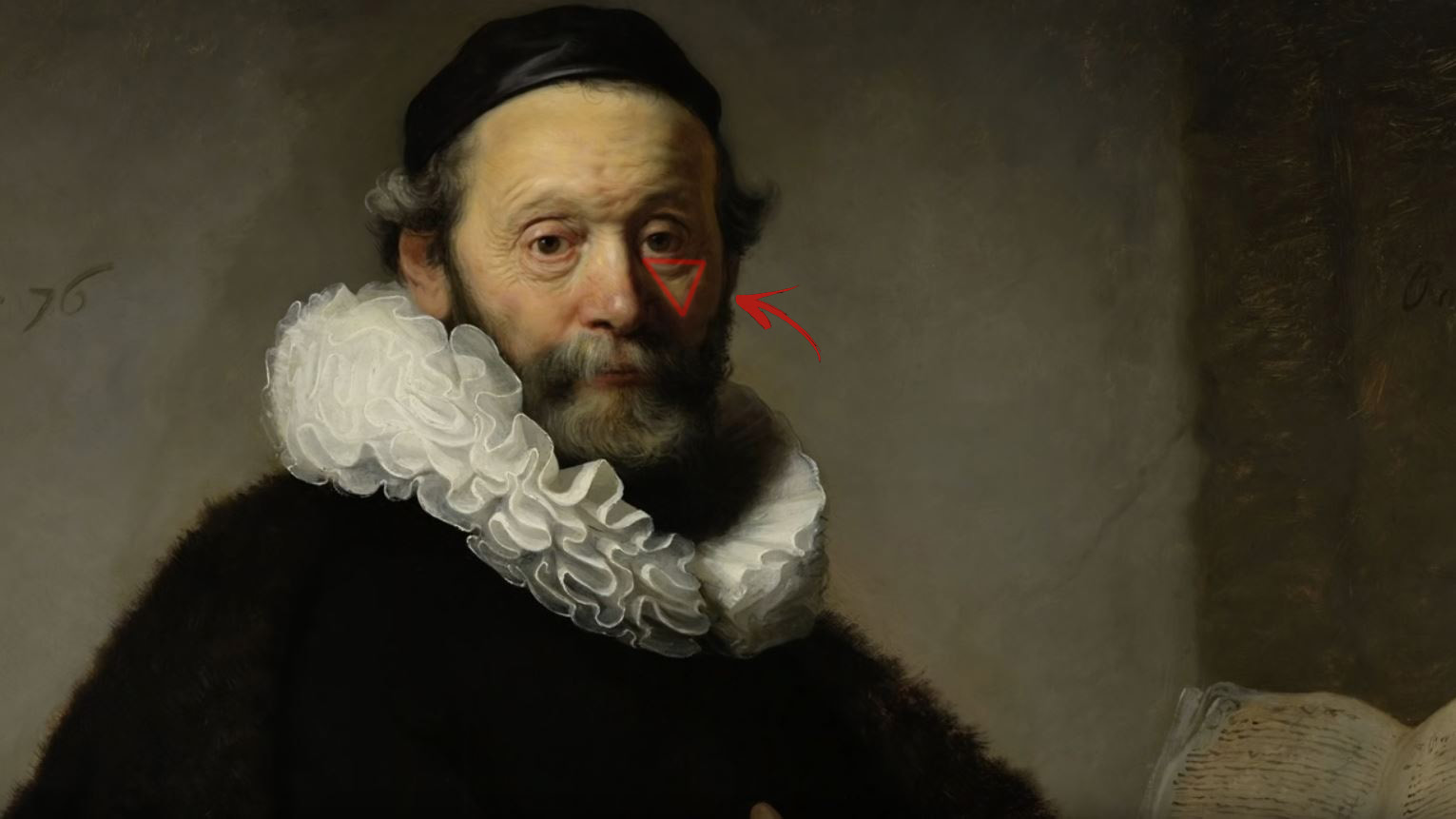
Akiyoshi Kitaoka – Surround biased illumination perception
Read more: Akiyoshi Kitaoka – Surround biased illumination perceptionhttps://x.com/AkiyoshiKitaoka/status/1798705648001327209
The left face appears whitish and the right one blackish, but they are made up of the same luminance.
https://community.wolfram.com/groups/-/m/t/3191015
Illusory staircase Gelb effect
https://www.psy.ritsumei.ac.jp/akitaoka/illgelbe.html
LIGHTING
-
Open Source Nvidia Omniverse
Read more: Open Source Nvidia Omniverseblogs.nvidia.com/blog/2019/03/18/omniverse-collaboration-platform/
developer.nvidia.com/nvidia-omniverse
An open, Interactive 3D Design Collaboration Platform for Multi-Tool Workflows to simplify studio workflows for real-time graphics.
It supports Pixar’s Universal Scene Description technology for exchanging information about modeling, shading, animation, lighting, visual effects and rendering across multiple applications.
It also supports NVIDIA’s Material Definition Language, which allows artists to exchange information about surface materials across multiple tools.
With Omniverse, artists can see live updates made by other artists working in different applications. They can also see changes reflected in multiple tools at the same time.
For example an artist using Maya with a portal to Omniverse can collaborate with another artist using UE4 and both will see live updates of each others’ changes in their application.
-
Narcis Calin’s Galaxy Engine – A free, open source simulation software
Read more: Narcis Calin’s Galaxy Engine – A free, open source simulation softwareThis 2025 I decided to start learning how to code, so I installed Visual Studio and I started looking into C++. After days of watching tutorials and guides about the basics of C++ and programming, I decided to make something physics-related. I started with a dot that fell to the ground and then I wanted to simulate gravitational attraction, so I made 2 circles attracting each other. I thought it was really cool to see something I made with code actually work, so I kept building on top of that small, basic program. And here we are after roughly 8 months of learning programming. This is Galaxy Engine, and it is a simulation software I have been making ever since I started my learning journey. It currently can simulate gravity, dark matter, galaxies, the Big Bang, temperature, fluid dynamics, breakable solids, planetary interactions, etc. The program can run many tens of thousands of particles in real time on the CPU thanks to the Barnes-Hut algorithm, mixed with Morton curves. It also includes its own PBR 2D path tracer with BVH optimizations. The path tracer can simulate a bunch of stuff like diffuse lighting, specular reflections, refraction, internal reflection, fresnel, emission, dispersion, roughness, IOR, nested IOR and more! I tried to make the path tracer closer to traditional 3D render engines like V-Ray. I honestly never imagined I would go this far with programming, and it has been an amazing learning experience so far. I think that mixing this knowledge with my 3D knowledge can unlock countless new possibilities. In case you are curious about Galaxy Engine, I made it completely free and Open-Source so that anyone can build and compile it locally! You can find the source code in GitHub
https://github.com/NarcisCalin/Galaxy-Engine
-
Simulon – a Hollywood production studio app in the hands of an independent creator with access to consumer hardware, LDRi to HDRi through ML
Read more: Simulon – a Hollywood production studio app in the hands of an independent creator with access to consumer hardware, LDRi to HDRi through MLDivesh Naidoo: The video below was made with a live in-camera preview and auto-exposure matching, no camera solve, no HDRI capture and no manual compositing setup. Using the new Simulon phone app.
LDR to HDR through ML
https://simulon.typeform.com/betatest
(more…)Process example
-
Disney’s Moana Island Scene – Free data set
Read more: Disney’s Moana Island Scene – Free data sethttps://www.disneyanimation.com/resources/moana-island-scene/
This data set contains everything necessary to render a version of the Motunui island featured in the 2016 film Moana.
-
Composition – cinematography Cheat Sheet
Read more: Composition – cinematography Cheat Sheet
Where is our eye attracted first? Why?
Size. Focus. Lighting. Color.
Size. Mr. White (Harvey Keitel) on the right.
Focus. He’s one of the two objects in focus.
Lighting. Mr. White is large and in focus and Mr. Pink (Steve Buscemi) is highlighted by
a shaft of light.
Color. Both are black and white but the read on Mr. White’s shirt now really stands out.
(more…)
What type of lighting? -
Sun cone angle (angular diameter) as perceived by earth viewers
Read more: Sun cone angle (angular diameter) as perceived by earth viewersAlso see:
https://www.pixelsham.com/2020/08/01/solid-angle-measures/
The cone angle of the sun refers to the angular diameter of the sun as observed from Earth, which is related to the apparent size of the sun in the sky.
The angular diameter of the sun, or the cone angle of the sunlight as perceived from Earth, is approximately 0.53 degrees on average. This value can vary slightly due to the elliptical nature of Earth’s orbit around the sun, but it generally stays within a narrow range.
Here’s a more precise breakdown:
-
- Average Angular Diameter: About 0.53 degrees (31 arcminutes)
- Minimum Angular Diameter: Approximately 0.52 degrees (when Earth is at aphelion, the farthest point from the sun)
- Maximum Angular Diameter: Approximately 0.54 degrees (when Earth is at perihelion, the closest point to the sun)
This angular diameter remains relatively constant throughout the day because the sun’s distance from Earth does not change significantly over a single day.
To summarize, the cone angle of the sun’s light, or its angular diameter, is typically around 0.53 degrees, regardless of the time of day.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Angular_diameter
-
-
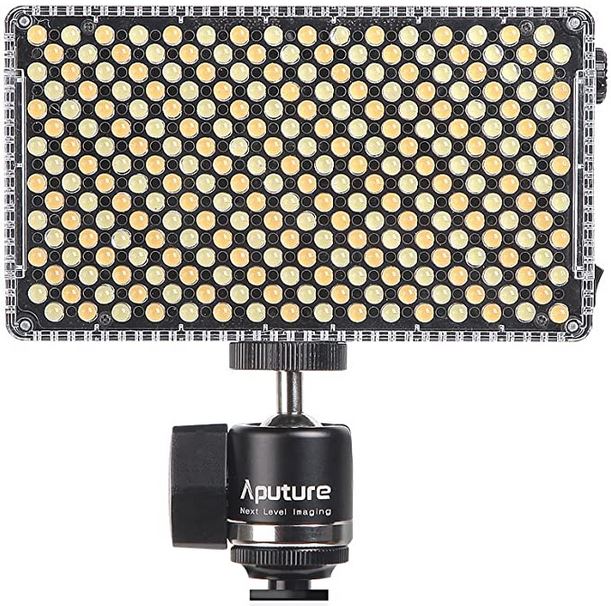
Aputure AL-F7 – dimmable Led Video Light, CRI95+, 3200-9500K
Read more: Aputure AL-F7 – dimmable Led Video Light, CRI95+, 3200-9500KHigh CRI of ≥95
256 LEDs with 45° beam angle
3200 to 9500K variable color temperature
1 to 100% Stepless Dimming, 1500 Lux Brightness at 3.3′
LCD Info Screen. Powered by an L-series battery, D-Tap, or USB-C
Because the light has a variable color range of 3200 to 9500K, when the light is set to 5500K (daylight balanced) both sets of LEDs are on at full, providing the maximum brightness from this fixture when compared to using the light at 3200 or 9500K.
The LCD screen provides information on the fixture’s output as well as the charge state of the battery. The screen also indicates whether the adjustment knob is controlling brightness or color temperature. To switch from brightness to CCT or CCT to brightness, just apply a short press to the adjustment knob.
The included cold shoe ball joint adapter enables mounting the light to your camera’s accessory shoe via the 1/4″-20 threaded hole on the fixture. In addition, the bottom of the cold shoe foot features a 3/8″-16 threaded hole, and includes a 3/8″-16 to 1/4″-20 reducing bushing.

COLLECTIONS
| Featured AI
| Design And Composition
| Explore posts
POPULAR SEARCHES
unreal | pipeline | virtual production | free | learn | photoshop | 360 | macro | google | nvidia | resolution | open source | hdri | real-time | photography basics | nuke
FEATURED POSTS
-
Image rendering bit depth
-
Matt Hallett – WAN 2.1 VACE Total Video Control in ComfyUI
-
Survivorship Bias: The error resulting from systematically focusing on successes and ignoring failures. How a young statistician saved his planes during WW2.
-
ComfyUI FLOAT – A container for FLOAT Generative Motion Latent Flow Matching for Audio-driven Talking Portrait – lip sync
-
STOP FCC – SAVE THE FREE NET
-
Google – Artificial Intelligence free courses
-
Key/Fill ratios and scene composition using false colors and Nuke node
-
Jesse Zumstein – Jobs in games
Social Links
DISCLAIMER – Links and images on this website may be protected by the respective owners’ copyright. All data submitted by users through this site shall be treated as freely available to share.