COMPOSITION
-
HuggingFace ai-comic-factory – a FREE AI Comic Book Creator
Read more: HuggingFace ai-comic-factory – a FREE AI Comic Book Creatorhttps://huggingface.co/spaces/jbilcke-hf/ai-comic-factory
this is the epic story of a group of talented digital artists trying to overcame daily technical challenges to achieve incredibly photorealistic projects of monsters and aliens
DESIGN
-
Creative duo Joseph Lattimer and Caitlin Derer Creates Absolutely Amazing The Beatles Collectable Toys
Read more: Creative duo Joseph Lattimer and Caitlin Derer Creates Absolutely Amazing The Beatles Collectable Toyshttps://designyoutrust.com/2024/11/artist-duo-creates-absolutely-amazing-the-beatles-collectable-toys
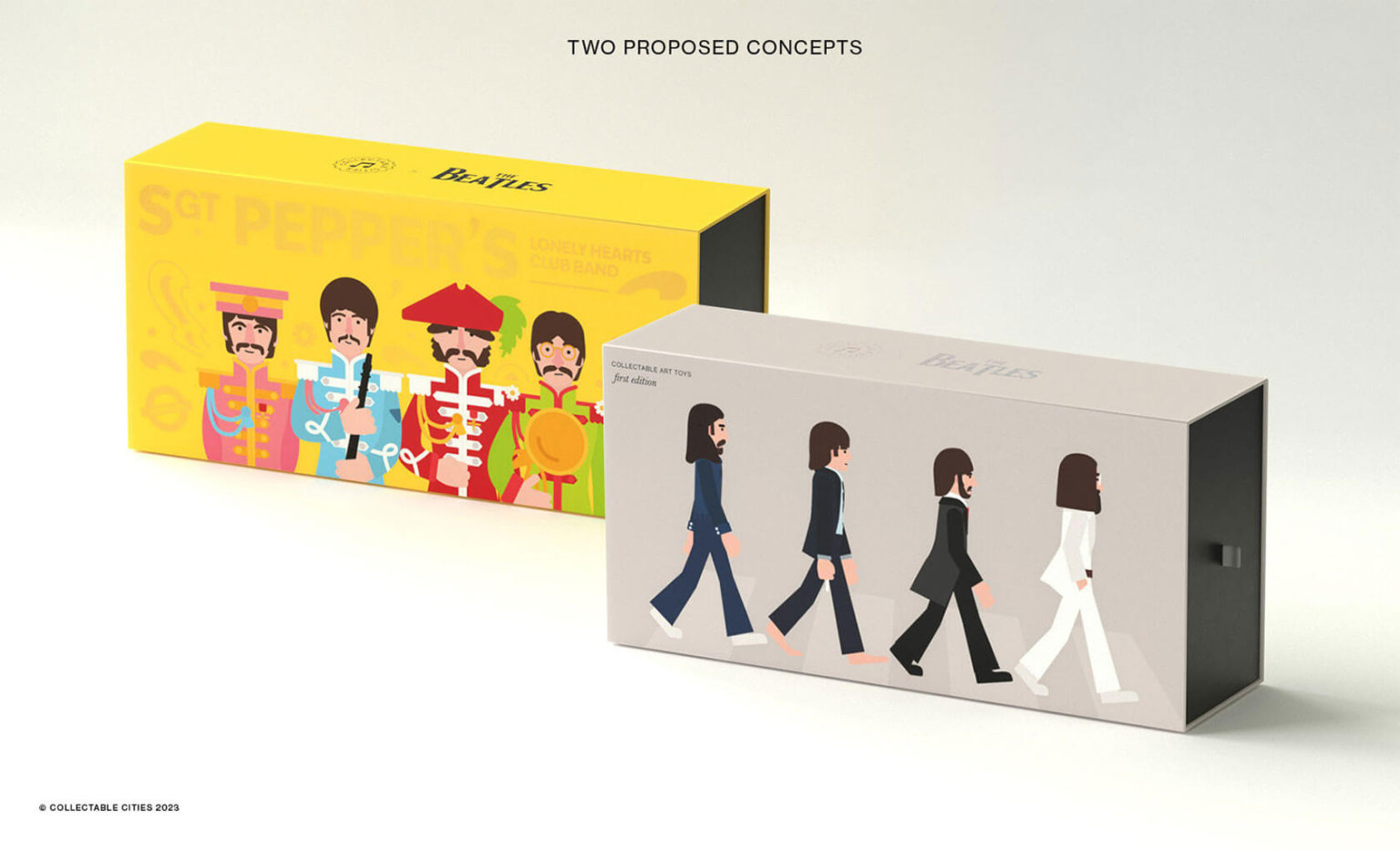
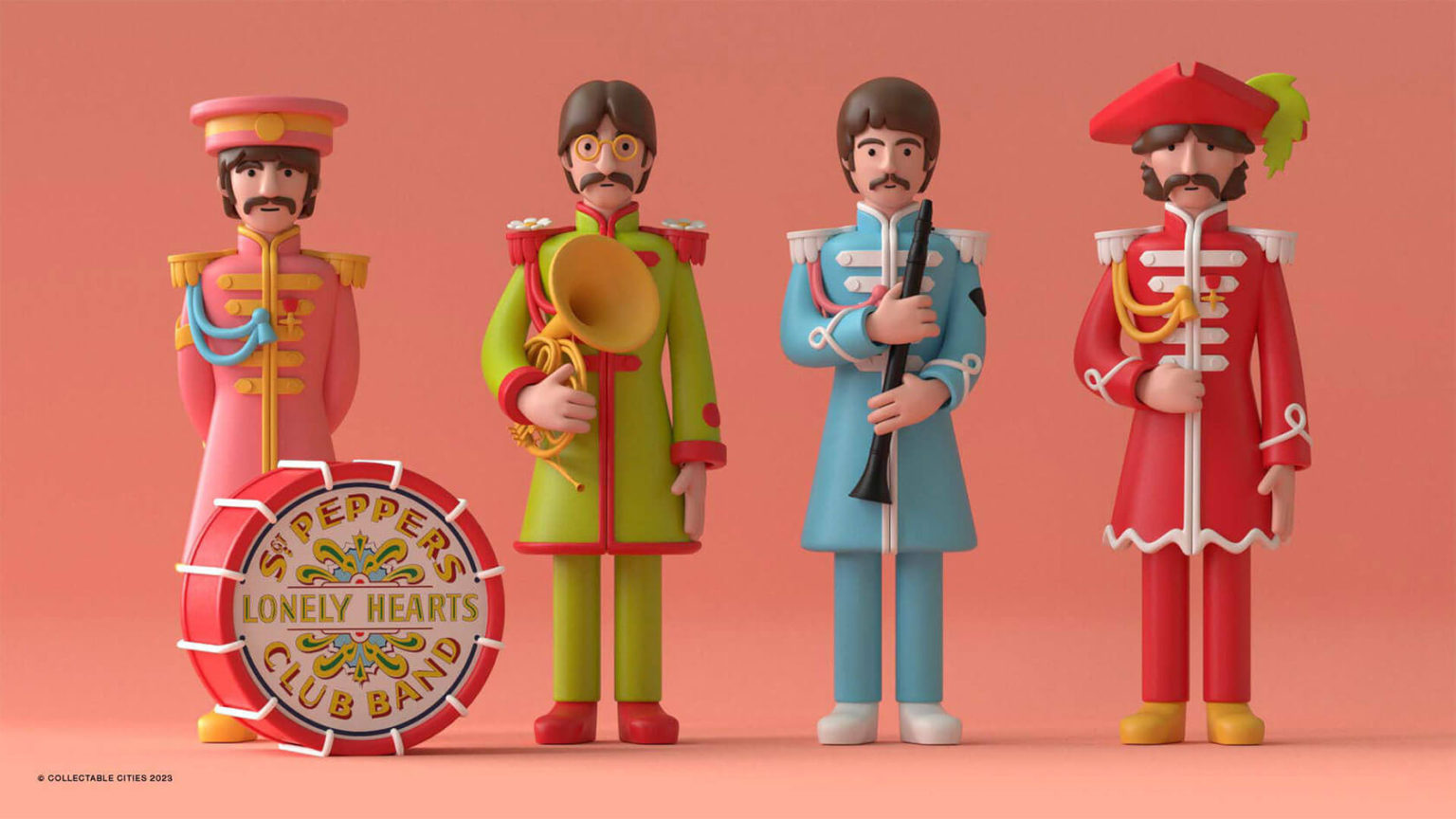
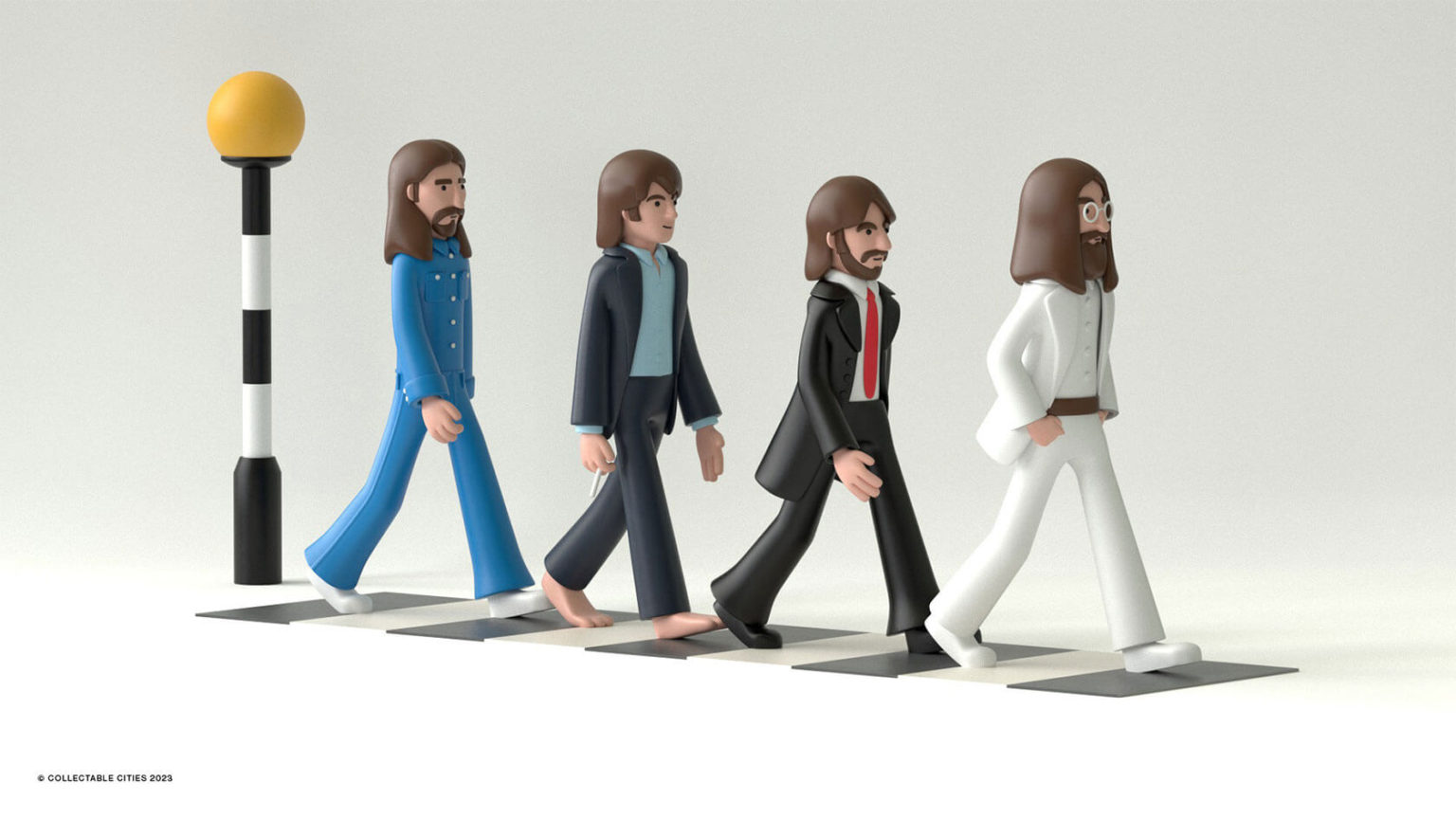



COLOR
LIGHTING
-
domeble – Hi-Resolution CGI Backplates and 360° HDRI
Read more: domeble – Hi-Resolution CGI Backplates and 360° HDRIWhen collecting hdri make sure the data supports basic metadata, such as:
- Iso
- Aperture
- Exposure time or shutter time
- Color temperature
- Color space Exposure value (what the sensor receives of the sun intensity in lux)
- 7+ brackets (with 5 or 6 being the perceived balanced exposure)
In image processing, computer graphics, and photography, high dynamic range imaging (HDRI or just HDR) is a set of techniques that allow a greater dynamic range of luminances (a Photometry measure of the luminous intensity per unit area of light travelling in a given direction. It describes the amount of light that passes through or is emitted from a particular area, and falls within a given solid angle) between the lightest and darkest areas of an image than standard digital imaging techniques or photographic methods. This wider dynamic range allows HDR images to represent more accurately the wide range of intensity levels found in real scenes ranging from direct sunlight to faint starlight and to the deepest shadows.
The two main sources of HDR imagery are computer renderings and merging of multiple photographs, which in turn are known as low dynamic range (LDR) or standard dynamic range (SDR) images. Tone Mapping (Look-up) techniques, which reduce overall contrast to facilitate display of HDR images on devices with lower dynamic range, can be applied to produce images with preserved or exaggerated local contrast for artistic effect. Photography
In photography, dynamic range is measured in Exposure Values (in photography, exposure value denotes all combinations of camera shutter speed and relative aperture that give the same exposure. The concept was developed in Germany in the 1950s) differences or stops, between the brightest and darkest parts of the image that show detail. An increase of one EV or one stop is a doubling of the amount of light.
The human response to brightness is well approximated by a Steven’s power law, which over a reasonable range is close to logarithmic, as described by the Weber�Fechner law, which is one reason that logarithmic measures of light intensity are often used as well.
HDR is short for High Dynamic Range. It’s a term used to describe an image which contains a greater exposure range than the “black” to “white” that 8 or 16-bit integer formats (JPEG, TIFF, PNG) can describe. Whereas these Low Dynamic Range images (LDR) can hold perhaps 8 to 10 f-stops of image information, HDR images can describe beyond 30 stops and stored in 32 bit images.

-
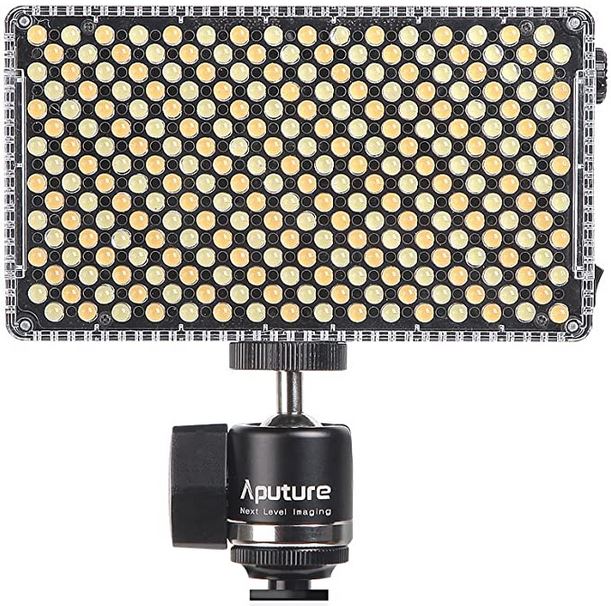
Aputure AL-F7 – dimmable Led Video Light, CRI95+, 3200-9500K
Read more: Aputure AL-F7 – dimmable Led Video Light, CRI95+, 3200-9500KHigh CRI of ≥95
256 LEDs with 45° beam angle
3200 to 9500K variable color temperature
1 to 100% Stepless Dimming, 1500 Lux Brightness at 3.3′
LCD Info Screen. Powered by an L-series battery, D-Tap, or USB-C
Because the light has a variable color range of 3200 to 9500K, when the light is set to 5500K (daylight balanced) both sets of LEDs are on at full, providing the maximum brightness from this fixture when compared to using the light at 3200 or 9500K.
The LCD screen provides information on the fixture’s output as well as the charge state of the battery. The screen also indicates whether the adjustment knob is controlling brightness or color temperature. To switch from brightness to CCT or CCT to brightness, just apply a short press to the adjustment knob.
The included cold shoe ball joint adapter enables mounting the light to your camera’s accessory shoe via the 1/4″-20 threaded hole on the fixture. In addition, the bottom of the cold shoe foot features a 3/8″-16 threaded hole, and includes a 3/8″-16 to 1/4″-20 reducing bushing.

-
Magnific.ai Relight – change the entire lighting of a scene
Read more: Magnific.ai Relight – change the entire lighting of a sceneIt’s a new Magnific spell that allows you to change the entire lighting of a scene and, optionally, the background with just:
1/ A prompt OR
2/ A reference image OR
3/ A light map (drawing your own lights)https://x.com/javilopen/status/1805274155065176489
-
Composition – These are the basic lighting techniques you need to know for photography and film
Read more: Composition – These are the basic lighting techniques you need to know for photography and filmhttp://www.diyphotography.net/basic-lighting-techniques-need-know-photography-film/
Amongst the basic techniques, there’s…
1- Side lighting – Literally how it sounds, lighting a subject from the side when they’re faced toward you
2- Rembrandt lighting – Here the light is at around 45 degrees over from the front of the subject, raised and pointing down at 45 degrees
3- Back lighting – Again, how it sounds, lighting a subject from behind. This can help to add drama with silouettes
4- Rim lighting – This produces a light glowing outline around your subject
5- Key light – The main light source, and it’s not necessarily always the brightest light source
6- Fill light – This is used to fill in the shadows and provide detail that would otherwise be blackness
7- Cross lighting – Using two lights placed opposite from each other to light two subjects
-
What light is best to illuminate gems for resale
Read more: What light is best to illuminate gems for resalewww.palagems.com/gem-lighting2
Artificial light sources, not unlike the diverse phases of natural light, vary considerably in their properties. As a result, some lamps render an object’s color better than others do.
The most important criterion for assessing the color-rendering ability of any lamp is its spectral power distribution curve.
Natural daylight varies too much in strength and spectral composition to be taken seriously as a lighting standard for grading and dealing colored stones. For anything to be a standard, it must be constant in its properties, which natural light is not.
For dealers in particular to make the transition from natural light to an artificial light source, that source must offer:
1- A degree of illuminance at least as strong as the common phases of natural daylight.
2- Spectral properties identical or comparable to a phase of natural daylight.A source combining these two things makes gems appear much the same as when viewed under a given phase of natural light. From the viewpoint of many dealers, this corresponds to a naturalappearance.
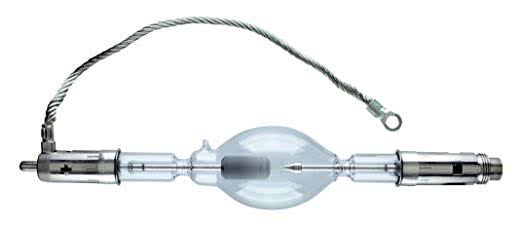
The 6000° Kelvin xenon short-arc lamp appears closest to meeting the criteria for a standard light source. Besides the strong illuminance this lamp affords, its spectrum is very similar to CIE standard illuminants of similar color temperature.

COLLECTIONS
| Featured AI
| Design And Composition
| Explore posts
POPULAR SEARCHES
unreal | pipeline | virtual production | free | learn | photoshop | 360 | macro | google | nvidia | resolution | open source | hdri | real-time | photography basics | nuke
FEATURED POSTS
-
Eddie Yoon – There’s a big misconception about AI creative
-
Web vs Printing or digital RGB vs CMYK
-
Godot Cheat Sheets
-
ComfyDock – The Easiest (Free) Way to Safely Run ComfyUI Sessions in a Boxed Container
-
Python and TCL: Tips and Tricks for Foundry Nuke
-
Ross Pettit on The Agile Manager – How tech firms went for prioritizing cash flow instead of talent (and artists)
-
Tencent Hunyuan3D 2.1 goes Open Source and adds MV (Multi-view) and MV Mini
-
59 AI Filmmaking Tools For Your Workflow
Social Links
DISCLAIMER – Links and images on this website may be protected by the respective owners’ copyright. All data submitted by users through this site shall be treated as freely available to share.










![sRGB gamma correction test [gamma correction test]](http://www.madore.org/~david/misc/color/gammatest.png)
