COMPOSITION
-
SlowMoVideo – How to make a slow motion shot with the open source program
Read more: SlowMoVideo – How to make a slow motion shot with the open source programhttp://slowmovideo.granjow.net/
slowmoVideo is an OpenSource program that creates slow-motion videos from your footage.
Slow motion cinematography is the result of playing back frames for a longer duration than they were exposed. For example, if you expose 240 frames of film in one second, then play them back at 24 fps, the resulting movie is 10 times longer (slower) than the original filmed event….
Film cameras are relatively simple mechanical devices that allow you to crank up the speed to whatever rate the shutter and pull-down mechanism allow. Some film cameras can operate at 2,500 fps or higher (although film shot in these cameras often needs some readjustment in postproduction). Video, on the other hand, is always captured, recorded, and played back at a fixed rate, with a current limit around 60fps. This makes extreme slow motion effects harder to achieve (and less elegant) on video, because slowing down the video results in each frame held still on the screen for a long time, whereas with high-frame-rate film there are plenty of frames to fill the longer durations of time. On video, the slow motion effect is more like a slide show than smooth, continuous motion.
One obvious solution is to shoot film at high speed, then transfer it to video (a case where film still has a clear advantage, sorry George). Another possibility is to cross dissolve or blur from one frame to the next. This adds a smooth transition from one still frame to the next. The blur reduces the sharpness of the image, and compared to slowing down images shot at a high frame rate, this is somewhat of a cheat. However, there isn’t much you can do about it until video can be recorded at much higher rates. Of course, many film cameras can’t shoot at high frame rates either, so the whole super-slow-motion endeavor is somewhat specialized no matter what medium you are using. (There are some high speed digital cameras available now that allow you to capture lots of digital frames directly to your computer, so technology is starting to catch up with film. However, this feature isn’t going to appear in consumer camcorders any time soon.)
-
Types of Film Lights and their efficiency – CRI, Color Temperature and Luminous Efficacy
Read more: Types of Film Lights and their efficiency – CRI, Color Temperature and Luminous Efficacynofilmschool.com/types-of-film-lights
“Not every light performs the same way. Lights and lighting are tricky to handle. You have to plan for every circumstance. But the good news is, lighting can be adjusted. Let’s look at different factors that affect lighting in every scene you shoot. “
Use CRI, Luminous Efficacy and color temperature controls to match your needs.Color Temperature
Color temperature describes the “color” of white light by a light source radiated by a perfect black body at a given temperature measured in degrees Kelvinhttps://www.pixelsham.com/2019/10/18/color-temperature/
CRI
“The Color Rendering Index is a measurement of how faithfully a light source reveals the colors of whatever it illuminates, it describes the ability of a light source to reveal the color of an object, as compared to the color a natural light source would provide. The highest possible CRI is 100. A CRI of 100 generally refers to a perfect black body, like a tungsten light source or the sun. “https://www.studiobinder.com/blog/what-is-color-rendering-index
(more…)
DESIGN
COLOR
-
StudioBinder.com – CRI color rendering index
Read more: StudioBinder.com – CRI color rendering indexwww.studiobinder.com/blog/what-is-color-rendering-index
“The Color Rendering Index is a measurement of how faithfully a light source reveals the colors of whatever it illuminates, it describes the ability of a light source to reveal the color of an object, as compared to the color a natural light source would provide. The highest possible CRI is 100. A CRI of 100 generally refers to a perfect black body, like a tungsten light source or the sun. ”
www.pixelsham.com/2021/04/28/types-of-film-lights-and-their-efficiency
-
OLED vs QLED – What TV is better?
Read more: OLED vs QLED – What TV is better?Supported by LG, Philips, Panasonic and Sony sell the OLED system TVs.
OLED stands for “organic light emitting diode.”
It is a fundamentally different technology from LCD, the major type of TV today.
OLED is “emissive,” meaning the pixels emit their own light.Samsung is branding its best TVs with a new acronym: “QLED”
QLED (according to Samsung) stands for “quantum dot LED TV.”
It is a variation of the common LED LCD, adding a quantum dot film to the LCD “sandwich.”
QLED, like LCD, is, in its current form, “transmissive” and relies on an LED backlight.OLED is the only technology capable of absolute blacks and extremely bright whites on a per-pixel basis. LCD definitely can’t do that, and even the vaunted, beloved, dearly departed plasma couldn’t do absolute blacks.
QLED, as an improvement over OLED, significantly improves the picture quality. QLED can produce an even wider range of colors than OLED, which says something about this new tech. QLED is also known to produce up to 40% higher luminance efficiency than OLED technology. Further, many tests conclude that QLED is far more efficient in terms of power consumption than its predecessor, OLED.
(more…) -
A Brief History of Color in Art
Read more: A Brief History of Color in Artwww.artsy.net/article/the-art-genome-project-a-brief-history-of-color-in-art
Of all the pigments that have been banned over the centuries, the color most missed by painters is likely Lead White.
This hue could capture and reflect a gleam of light like no other, though its production was anything but glamorous. The 17th-century Dutch method for manufacturing the pigment involved layering cow and horse manure over lead and vinegar. After three months in a sealed room, these materials would combine to create flakes of pure white. While scientists in the late 19th century identified lead as poisonous, it wasn’t until 1978 that the United States banned the production of lead white paint.
More reading:
www.canva.com/learn/color-meanings/https://www.infogrades.com/history-events-infographics/bizarre-history-of-colors/
-
Photography basics: Color Temperature and White Balance
Read more: Photography basics: Color Temperature and White BalanceColor Temperature of a light source describes the spectrum of light which is radiated from a theoretical “blackbody” (an ideal physical body that absorbs all radiation and incident light – neither reflecting it nor allowing it to pass through) with a given surface temperature.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Color_temperature
Or. Most simply it is a method of describing the color characteristics of light through a numerical value that corresponds to the color emitted by a light source, measured in degrees of Kelvin (K) on a scale from 1,000 to 10,000.
More accurately. The color temperature of a light source is the temperature of an ideal backbody that radiates light of comparable hue to that of the light source.
(more…)
LIGHTING
-
Photography basics: Why Use a (MacBeth) Color Chart?
Read more: Photography basics: Why Use a (MacBeth) Color Chart?Start here: https://www.pixelsham.com/2013/05/09/gretagmacbeth-color-checker-numeric-values/
https://www.studiobinder.com/blog/what-is-a-color-checker-tool/
In LightRoom
in Final Cut
in Nuke
Note: In Foundry’s Nuke, the software will map 18% gray to whatever your center f/stop is set to in the viewer settings (f/8 by default… change that to EV by following the instructions below).
You can experiment with this by attaching an Exposure node to a Constant set to 0.18, setting your viewer read-out to Spotmeter, and adjusting the stops in the node up and down. You will see that a full stop up or down will give you the respective next value on the aperture scale (f8, f11, f16 etc.).One stop doubles or halves the amount or light that hits the filmback/ccd, so everything works in powers of 2.
So starting with 0.18 in your constant, you will see that raising it by a stop will give you .36 as a floating point number (in linear space), while your f/stop will be f/11 and so on.If you set your center stop to 0 (see below) you will get a relative readout in EVs, where EV 0 again equals 18% constant gray.
In other words. Setting the center f-stop to 0 means that in a neutral plate, the middle gray in the macbeth chart will equal to exposure value 0. EV 0 corresponds to an exposure time of 1 sec and an aperture of f/1.0.
This will set the sun usually around EV12-17 and the sky EV1-4 , depending on cloud coverage.
To switch Foundry’s Nuke’s SpotMeter to return the EV of an image, click on the main viewport, and then press s, this opens the viewer’s properties. Now set the center f-stop to 0 in there. And the SpotMeter in the viewport will change from aperture and fstops to EV.
-
How are Energy and Matter the Same?
Read more: How are Energy and Matter the Same?www.turnerpublishing.com/blog/detail/everything-is-energy-everything-is-one-everything-is-possible/
www.universetoday.com/116615/how-are-energy-and-matter-the-same/
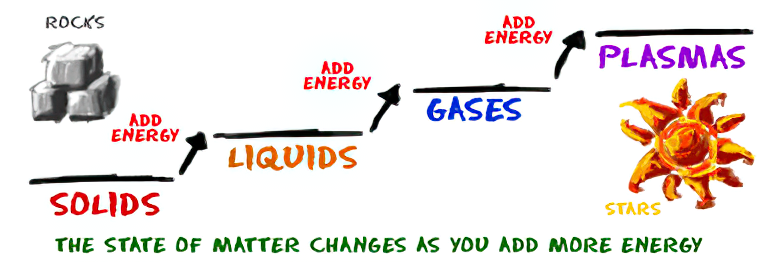
As Einstein showed us, light and matter and just aspects of the same thing. Matter is just frozen light. And light is matter on the move. Albert Einstein’s most famous equation says that energy and matter are two sides of the same coin. How does one become the other?
Relativity requires that the faster an object moves, the more mass it appears to have. This means that somehow part of the energy of the car’s motion appears to transform into mass. Hence the origin of Einstein’s equation. How does that happen? We don’t really know. We only know that it does.
Matter is 99.999999999999 percent empty space. Not only do the atom and solid matter consist mainly of empty space, it is the same in outer space
The quantum theory researchers discovered the answer: Not only do particles consist of energy, but so does the space between. This is the so-called zero-point energy. Therefore it is true: Everything consists of energy.
Energy is the basis of material reality. Every type of particle is conceived of as a quantum vibration in a field: Electrons are vibrations in electron fields, protons vibrate in a proton field, and so on. Everything is energy, and everything is connected to everything else through fields.
-
Light properties
Read more: Light propertiesHow It Works – Issue 114
https://www.howitworksdaily.com/
COLLECTIONS
| Featured AI
| Design And Composition
| Explore posts
POPULAR SEARCHES
unreal | pipeline | virtual production | free | learn | photoshop | 360 | macro | google | nvidia | resolution | open source | hdri | real-time | photography basics | nuke
FEATURED POSTS
-
FFmpeg – examples and convenience lines
-
4dv.ai – Remote Interactive 3D Holographic Presentation Technology and System running on the PlayCanvas engine
-
AI Search – Find The Best AI Tools & Apps
-
Decart AI Mirage – The first ever World Transformation Model – turning any video, game, or camera feed into a new digital world, in real time
-
Scene Referred vs Display Referred color workflows
-
How to paint a boardgame miniatures
-
VFX pipeline – Render Wall Farm management topics
-
sRGB vs REC709 – An introduction and FFmpeg implementations
Social Links
DISCLAIMER – Links and images on this website may be protected by the respective owners’ copyright. All data submitted by users through this site shall be treated as freely available to share.