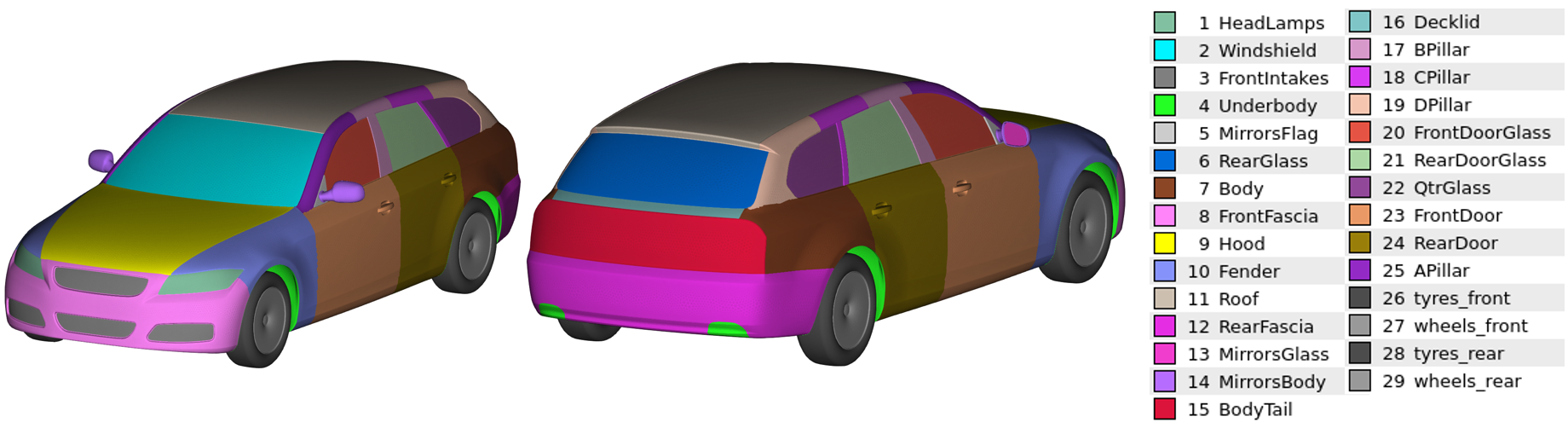
COMPOSITION
DESIGN
-
AI Dresses by MaryAnna
Read more: AI Dresses by MaryAnnahttps://www.linkedin.com/feed/update/urn:li:activity:7015985798567067648
Created by Discord user: @MaryAnna
COLOR
-
Tim Kang – calibrated white light values in sRGB color space
Read more: Tim Kang – calibrated white light values in sRGB color space8bit sRGB encoded
2000K 255 139 22
2700K 255 172 89
3000K 255 184 109
3200K 255 190 122
4000K 255 211 165
4300K 255 219 178
D50 255 235 205
D55 255 243 224
D5600 255 244 227
D6000 255 249 240
D65 255 255 255
D10000 202 221 255
D20000 166 196 2558bit Rec709 Gamma 2.4
2000K 255 145 34
2700K 255 177 97
3000K 255 187 117
3200K 255 193 129
4000K 255 214 170
4300K 255 221 182
D50 255 236 208
D55 255 243 226
D5600 255 245 229
D6000 255 250 241
D65 255 255 255
D10000 204 222 255
D20000 170 199 2558bit Display P3 encoded
2000K 255 154 63
2700K 255 185 109
3000K 255 195 127
3200K 255 201 138
4000K 255 219 176
4300K 255 225 187
D50 255 239 212
D55 255 245 228
D5600 255 246 231
D6000 255 251 242
D65 255 255 255
D10000 208 223 255
D20000 175 199 25510bit Rec2020 PQ (100 nits)
2000K 520 435 273
2700K 520 466 358
3000K 520 475 384
3200K 520 480 399
4000K 520 495 446
4300K 520 500 458
D50 520 510 482
D55 520 514 497
D5600 520 514 500
D6000 520 517 509
D65 520 520 520
D10000 479 489 520
D20000 448 464 520 -
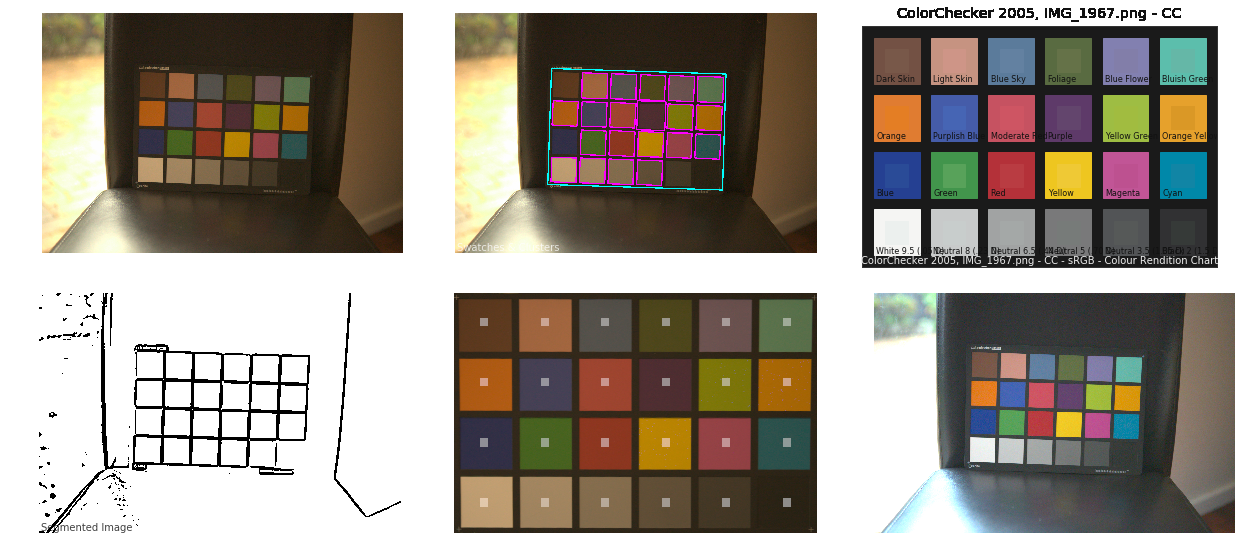
Colour – MacBeth Chart Checker Detection
Read more: Colour – MacBeth Chart Checker Detectiongithub.com/colour-science/colour-checker-detection
A Python package implementing various colour checker detection algorithms and related utilities.
-
Scene Referred vs Display Referred color workflows
Read more: Scene Referred vs Display Referred color workflowsDisplay Referred it is tied to the target hardware, as such it bakes color requirements into every type of media output request.
Scene Referred uses a common unified wide gamut and targeting audience through CDL and DI libraries instead.
So that color information stays untouched and only “transformed” as/when needed.Sources:
– Victor Perez – Color Management Fundamentals & ACES Workflows in Nuke
– https://z-fx.nl/ColorspACES.pdf
– Wicus
-
OpenColorIO standard
Read more: OpenColorIO standardhttps://www.provideocoalition.com/color-management-part-11-introducing-opencolorio/
OpenColorIO (OCIO) is a new open source project from Sony Imageworks.
Based on development started in 2003, OCIO enables color transforms and image display to be handled in a consistent manner across multiple graphics applications. Unlike other color management solutions, OCIO is geared towards motion-picture post production, with an emphasis on visual effects and animation color pipelines.
-
Willem Zwarthoed – Aces gamut in VFX production pdf
Read more: Willem Zwarthoed – Aces gamut in VFX production pdfhttps://www.provideocoalition.com/color-management-part-12-introducing-aces/
Local copy:
https://www.slideshare.net/hpduiker/acescg-a-common-color-encoding-for-visual-effects-applications
LIGHTING
-
Narcis Calin’s Galaxy Engine – A free, open source simulation software
Read more: Narcis Calin’s Galaxy Engine – A free, open source simulation softwareThis 2025 I decided to start learning how to code, so I installed Visual Studio and I started looking into C++. After days of watching tutorials and guides about the basics of C++ and programming, I decided to make something physics-related. I started with a dot that fell to the ground and then I wanted to simulate gravitational attraction, so I made 2 circles attracting each other. I thought it was really cool to see something I made with code actually work, so I kept building on top of that small, basic program. And here we are after roughly 8 months of learning programming. This is Galaxy Engine, and it is a simulation software I have been making ever since I started my learning journey. It currently can simulate gravity, dark matter, galaxies, the Big Bang, temperature, fluid dynamics, breakable solids, planetary interactions, etc. The program can run many tens of thousands of particles in real time on the CPU thanks to the Barnes-Hut algorithm, mixed with Morton curves. It also includes its own PBR 2D path tracer with BVH optimizations. The path tracer can simulate a bunch of stuff like diffuse lighting, specular reflections, refraction, internal reflection, fresnel, emission, dispersion, roughness, IOR, nested IOR and more! I tried to make the path tracer closer to traditional 3D render engines like V-Ray. I honestly never imagined I would go this far with programming, and it has been an amazing learning experience so far. I think that mixing this knowledge with my 3D knowledge can unlock countless new possibilities. In case you are curious about Galaxy Engine, I made it completely free and Open-Source so that anyone can build and compile it locally! You can find the source code in GitHub
https://github.com/NarcisCalin/Galaxy-Engine
-
What’s the Difference Between Ray Casting, Ray Tracing, Path Tracing and Rasterization? Physical light tracing…
Read more: What’s the Difference Between Ray Casting, Ray Tracing, Path Tracing and Rasterization? Physical light tracing…RASTERIZATION
Rasterisation (or rasterization) is the task of taking the information described in a vector graphics format OR the vertices of triangles making 3D shapes and converting them into a raster image (a series of pixels, dots or lines, which, when displayed together, create the image which was represented via shapes), or in other words “rasterizing” vectors or 3D models onto a 2D plane for display on a computer screen.For each triangle of a 3D shape, you project the corners of the triangle on the virtual screen with some math (projective geometry). Then you have the position of the 3 corners of the triangle on the pixel screen. Those 3 points have texture coordinates, so you know where in the texture are the 3 corners. The cost is proportional to the number of triangles, and is only a little bit affected by the screen resolution.
In computer graphics, a raster graphics or bitmap image is a dot matrix data structure that represents a generally rectangular grid of pixels (points of color), viewable via a monitor, paper, or other display medium.
With rasterization, objects on the screen are created from a mesh of virtual triangles, or polygons, that create 3D models of objects. A lot of information is associated with each vertex, including its position in space, as well as information about color, texture and its “normal,” which is used to determine the way the surface of an object is facing.
Computers then convert the triangles of the 3D models into pixels, or dots, on a 2D screen. Each pixel can be assigned an initial color value from the data stored in the triangle vertices.
Further pixel processing or “shading,” including changing pixel color based on how lights in the scene hit the pixel, and applying one or more textures to the pixel, combine to generate the final color applied to a pixel.
The main advantage of rasterization is its speed. However, rasterization is simply the process of computing the mapping from scene geometry to pixels and does not prescribe a particular way to compute the color of those pixels. So it cannot take shading, especially the physical light, into account and it cannot promise to get a photorealistic output. That’s a big limitation of rasterization.
There are also multiple problems:
If you have two triangles one is behind the other, you will draw twice all the pixels. you only keep the pixel from the triangle that is closer to you (Z-buffer), but you still do the work twice.
The borders of your triangles are jagged as it is hard to know if a pixel is in the triangle or out. You can do some smoothing on those, that is anti-aliasing.
You have to handle every triangles (including the ones behind you) and then see that they do not touch the screen at all. (we have techniques to mitigate this where we only look at triangles that are in the field of view)
Transparency is hard to handle (you can’t just do an average of the color of overlapping transparent triangles, you have to do it in the right order)
-
HDRI Resources
Read more: HDRI ResourcesText2Light
- https://www.cgtrader.com/free-3d-models/exterior/other/10-free-hdr-panoramas-created-with-text2light-zero-shot
- https://frozenburning.github.io/projects/text2light/
- https://github.com/FrozenBurning/Text2Light
Royalty free links
- https://locationtextures.com/panoramas/
- http://www.noahwitchell.com/freebies
- https://polyhaven.com/hdris
- https://hdrmaps.com/
- https://www.ihdri.com/
- https://hdrihaven.com/
- https://www.domeble.com/
- http://www.hdrlabs.com/sibl/archive.html
- https://www.hdri-hub.com/hdrishop/hdri
- http://noemotionhdrs.net/hdrevening.html
- https://www.openfootage.net/hdri-panorama/
- https://www.zwischendrin.com/en/browse/hdri
Nvidia GauGAN360
-
Types of Film Lights and their efficiency – CRI, Color Temperature and Luminous Efficacy
Read more: Types of Film Lights and their efficiency – CRI, Color Temperature and Luminous Efficacynofilmschool.com/types-of-film-lights
“Not every light performs the same way. Lights and lighting are tricky to handle. You have to plan for every circumstance. But the good news is, lighting can be adjusted. Let’s look at different factors that affect lighting in every scene you shoot. “
Use CRI, Luminous Efficacy and color temperature controls to match your needs.Color Temperature
Color temperature describes the “color” of white light by a light source radiated by a perfect black body at a given temperature measured in degrees Kelvinhttps://www.pixelsham.com/2019/10/18/color-temperature/
CRI
“The Color Rendering Index is a measurement of how faithfully a light source reveals the colors of whatever it illuminates, it describes the ability of a light source to reveal the color of an object, as compared to the color a natural light source would provide. The highest possible CRI is 100. A CRI of 100 generally refers to a perfect black body, like a tungsten light source or the sun. “https://www.studiobinder.com/blog/what-is-color-rendering-index
(more…)
COLLECTIONS
| Featured AI
| Design And Composition
| Explore posts
POPULAR SEARCHES
unreal | pipeline | virtual production | free | learn | photoshop | 360 | macro | google | nvidia | resolution | open source | hdri | real-time | photography basics | nuke
FEATURED POSTS
-
Photography basics: Solid Angle measures
-
AI and the Law – Netflix : Using Generative AI in Content Production
-
Photography basics: Color Temperature and White Balance
-
Game Development tips
-
FFmpeg – examples and convenience lines
-
Sensitivity of human eye
-
WhatDreamsCost Spline-Path-Control – Create motion controls for ComfyUI
-
RawTherapee – a free, open source, cross-platform raw image and HDRi processing program
Social Links
DISCLAIMER – Links and images on this website may be protected by the respective owners’ copyright. All data submitted by users through this site shall be treated as freely available to share.