COMPOSITION
-
9 Best Hacks to Make a Cinematic Video with Any Camera
Read more: 9 Best Hacks to Make a Cinematic Video with Any Camerahttps://www.flexclip.com/learn/cinematic-video.html
- Frame Your Shots to Create Depth
- Create Shallow Depth of Field
- Avoid Shaky Footage and Use Flexible Camera Movements
- Properly Use Slow Motion
- Use Cinematic Lighting Techniques
- Apply Color Grading
- Use Cinematic Music and SFX
- Add Cinematic Fonts and Text Effects
- Create the Cinematic Bar at the Top and the Bottom

DESIGN
-
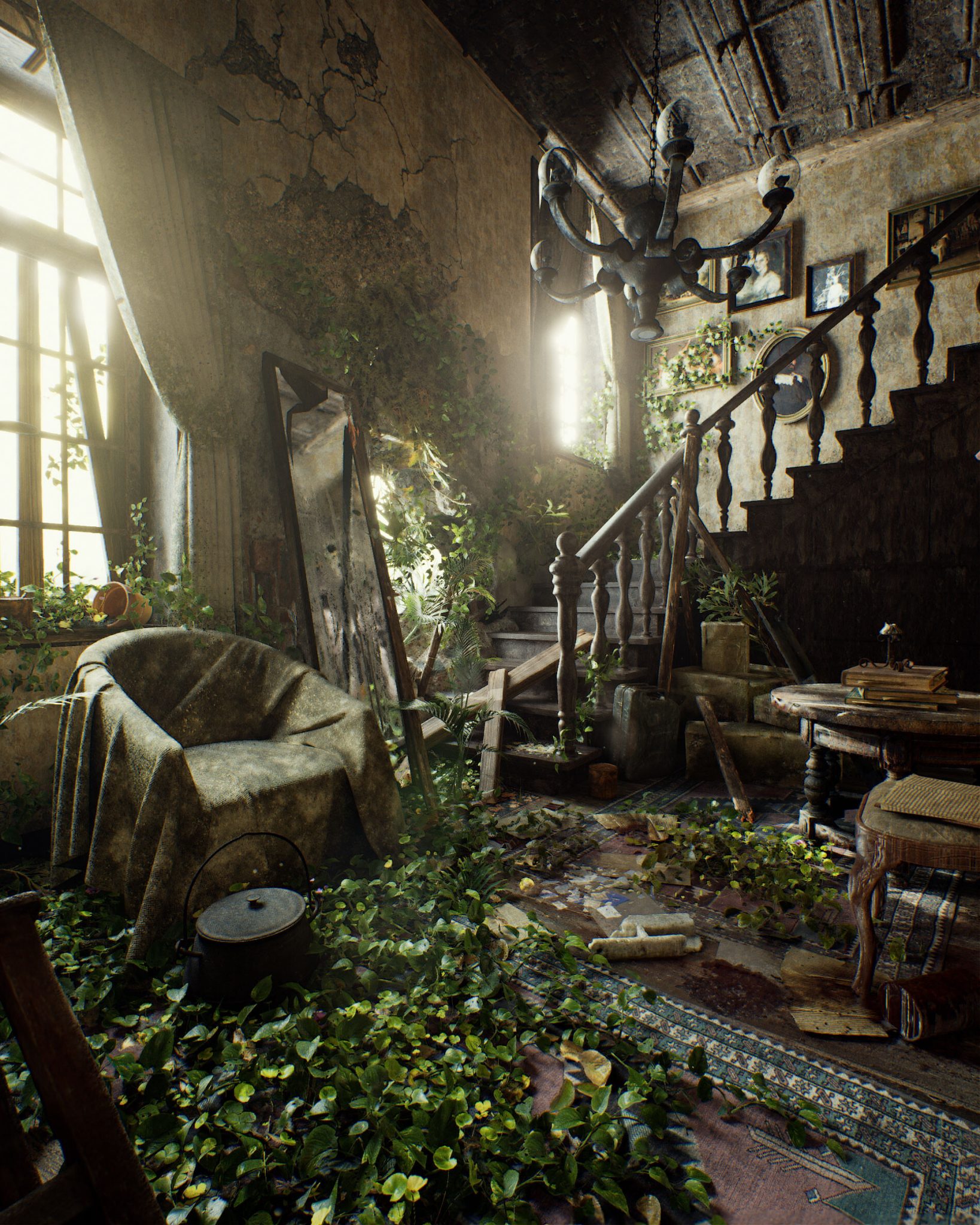
Pasquale Scionti – Production Walkthrough with Virtual Camera and iPad pro 11.5 on Unreal Engine 4.25
Read more: Pasquale Scionti – Production Walkthrough with Virtual Camera and iPad pro 11.5 on Unreal Engine 4.2580.lv/articles/creating-an-old-abandoned-mansion-with-quixel-tools/
www.artstation.com/artwork/Poexyo

COLOR
-
Composition – cinematography Cheat Sheet
Read more: Composition – cinematography Cheat Sheet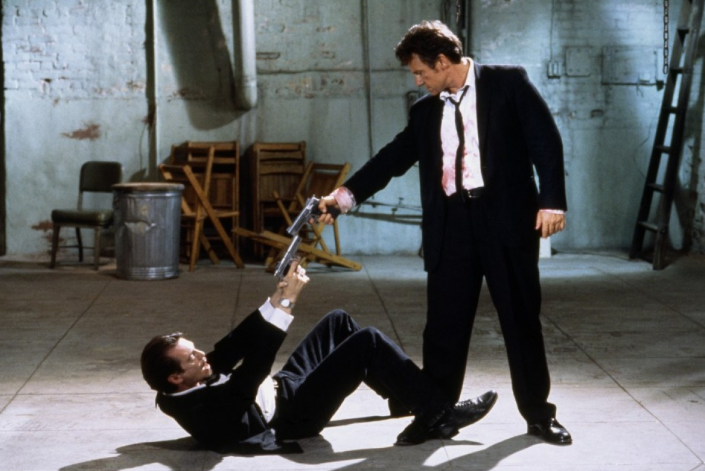
Where is our eye attracted first? Why?
Size. Focus. Lighting. Color.
Size. Mr. White (Harvey Keitel) on the right.
Focus. He’s one of the two objects in focus.
Lighting. Mr. White is large and in focus and Mr. Pink (Steve Buscemi) is highlighted by
a shaft of light.
Color. Both are black and white but the read on Mr. White’s shirt now really stands out.
(more…)
What type of lighting? -
StudioBinder.com – CRI color rendering index
Read more: StudioBinder.com – CRI color rendering indexwww.studiobinder.com/blog/what-is-color-rendering-index
“The Color Rendering Index is a measurement of how faithfully a light source reveals the colors of whatever it illuminates, it describes the ability of a light source to reveal the color of an object, as compared to the color a natural light source would provide. The highest possible CRI is 100. A CRI of 100 generally refers to a perfect black body, like a tungsten light source or the sun. ”
www.pixelsham.com/2021/04/28/types-of-film-lights-and-their-efficiency
-
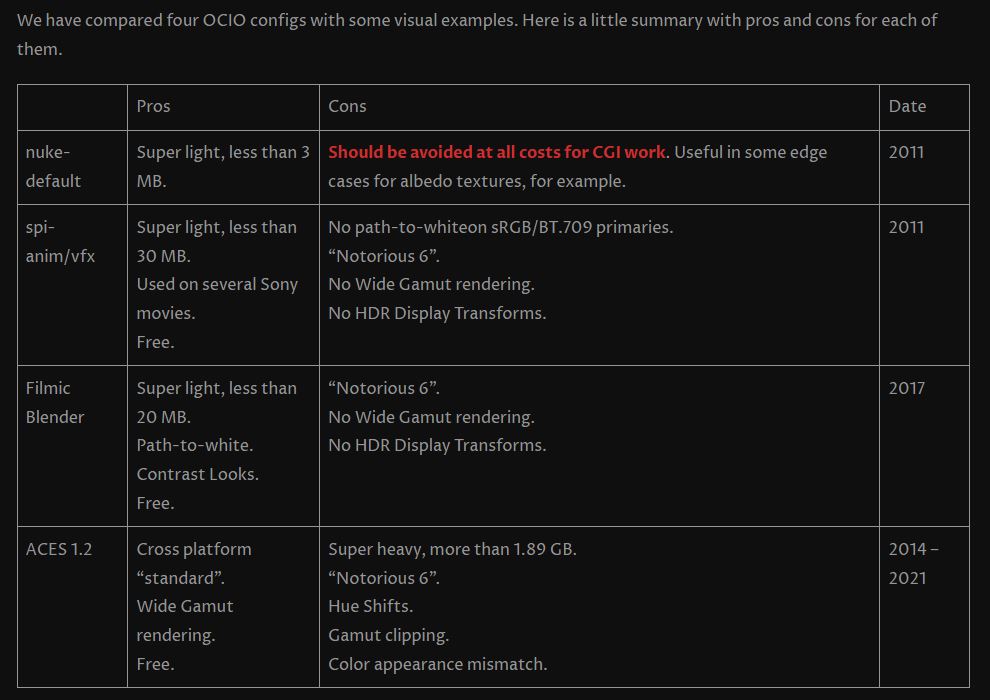
Black Body color aka the Planckian Locus curve for white point eye perception
Read more: Black Body color aka the Planckian Locus curve for white point eye perceptionhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Black-body_radiation
Black-body radiation is the type of electromagnetic radiation within or surrounding a body in thermodynamic equilibrium with its environment, or emitted by a black body (an opaque and non-reflective body) held at constant, uniform temperature. The radiation has a specific spectrum and intensity that depends only on the temperature of the body.
A black-body at room temperature appears black, as most of the energy it radiates is infra-red and cannot be perceived by the human eye. At higher temperatures, black bodies glow with increasing intensity and colors that range from dull red to blindingly brilliant blue-white as the temperature increases.
(more…) -
What light is best to illuminate gems for resale
Read more: What light is best to illuminate gems for resalewww.palagems.com/gem-lighting2
Artificial light sources, not unlike the diverse phases of natural light, vary considerably in their properties. As a result, some lamps render an object’s color better than others do.
The most important criterion for assessing the color-rendering ability of any lamp is its spectral power distribution curve.
Natural daylight varies too much in strength and spectral composition to be taken seriously as a lighting standard for grading and dealing colored stones. For anything to be a standard, it must be constant in its properties, which natural light is not.
For dealers in particular to make the transition from natural light to an artificial light source, that source must offer:
1- A degree of illuminance at least as strong as the common phases of natural daylight.
2- Spectral properties identical or comparable to a phase of natural daylight.A source combining these two things makes gems appear much the same as when viewed under a given phase of natural light. From the viewpoint of many dealers, this corresponds to a naturalappearance.
The 6000° Kelvin xenon short-arc lamp appears closest to meeting the criteria for a standard light source. Besides the strong illuminance this lamp affords, its spectrum is very similar to CIE standard illuminants of similar color temperature.

-
Björn Ottosson – How software gets color wrong
Read more: Björn Ottosson – How software gets color wronghttps://bottosson.github.io/posts/colorwrong/
Most software around us today are decent at accurately displaying colors. Processing of colors is another story unfortunately, and is often done badly.
To understand what the problem is, let’s start with an example of three ways of blending green and magenta:
- Perceptual blend – A smooth transition using a model designed to mimic human perception of color. The blending is done so that the perceived brightness and color varies smoothly and evenly.
- Linear blend – A model for blending color based on how light behaves physically. This type of blending can occur in many ways naturally, for example when colors are blended together by focus blur in a camera or when viewing a pattern of two colors at a distance.
- sRGB blend – This is how colors would normally be blended in computer software, using sRGB to represent the colors.
Let’s look at some more examples of blending of colors, to see how these problems surface more practically. The examples use strong colors since then the differences are more pronounced. This is using the same three ways of blending colors as the first example.
Instead of making it as easy as possible to work with color, most software make it unnecessarily hard, by doing image processing with representations not designed for it. Approximating the physical behavior of light with linear RGB models is one easy thing to do, but more work is needed to create image representations tailored for image processing and human perception.
Also see:
LIGHTING
-
IES Light Profiles and editing software
Read more: IES Light Profiles and editing softwarehttp://www.derekjenson.com/3d-blog/ies-light-profiles
https://ieslibrary.com/en/browse#ies
https://leomoon.com/store/shaders/ies-lights-pack
https://docs.arnoldrenderer.com/display/a5afmug/ai+photometric+light
IES profiles are useful for creating life-like lighting, as they can represent the physical distribution of light from any light source.
The IES format was created by the Illumination Engineering Society, and most lighting manufacturers provide IES profile for the lights they manufacture.
-
Convert between light exposure and intensity
Read more: Convert between light exposure and intensityimport math,sys def Exposure2Intensity(exposure): exp = float(exposure) result = math.pow(2,exp) print(result) Exposure2Intensity(0) def Intensity2Exposure(intensity): inarg = float(intensity) if inarg == 0: print("Exposure of zero intensity is undefined.") return if inarg < 1e-323: inarg = max(inarg, 1e-323) print("Exposure of negative intensities is undefined. Clamping to a very small value instead (1e-323)") result = math.log(inarg, 2) print(result) Intensity2Exposure(0.1)Why Exposure?
Exposure is a stop value that multiplies the intensity by 2 to the power of the stop. Increasing exposure by 1 results in double the amount of light.
Artists think in “stops.” Doubling or halving brightness is easy math and common in grading and look-dev.
Exposure counts doublings in whole stops:- +1 stop = ×2 brightness
- −1 stop = ×0.5 brightness
This gives perceptually even controls across both bright and dark values.
Why Intensity?
Intensity is linear.
It’s what render engines and compositors expect when:- Summing values
- Averaging pixels
- Multiplying or filtering pixel data
Use intensity when you need the actual math on pixel/light data.
Formulas (from your Python)
- Intensity from exposure: intensity = 2**exposure
- Exposure from intensity: exposure = log₂(intensity)
Guardrails:
- Intensity must be > 0 to compute exposure.
- If intensity = 0 → exposure is undefined.
- Clamp tiny values (e.g.
1e−323) before using log₂.
Use Exposure (stops) when…
- You want artist-friendly sliders (−5…+5 stops)
- Adjusting look-dev or grading in even stops
- Matching plates with quick ±1 stop tweaks
- Tweening brightness changes smoothly across ranges
Use Intensity (linear) when…
- Storing raw pixel/light values
- Multiplying textures or lights by a gain
- Performing sums, averages, and filters
- Feeding values to render engines expecting linear data
Examples
- +2 stops → 2**2 = 4.0 (×4)
- +1 stop → 2**1 = 2.0 (×2)
- 0 stop → 2**0 = 1.0 (×1)
- −1 stop → 2**(−1) = 0.5 (×0.5)
- −2 stops → 2**(−2) = 0.25 (×0.25)
- Intensity 0.1 → exposure = log₂(0.1) ≈ −3.32
Rule of thumb
Think in stops (exposure) for controls and matching.
Compute in linear (intensity) for rendering and math.
COLLECTIONS
| Featured AI
| Design And Composition
| Explore posts
POPULAR SEARCHES
unreal | pipeline | virtual production | free | learn | photoshop | 360 | macro | google | nvidia | resolution | open source | hdri | real-time | photography basics | nuke
FEATURED POSTS
-
Yann Lecun: Meta AI, Open Source, Limits of LLMs, AGI & the Future of AI | Lex Fridman Podcast #416
-
Ross Pettit on The Agile Manager – How tech firms went for prioritizing cash flow instead of talent (and artists)
-
Photography basics: Shutter angle and shutter speed and motion blur
-
Alejandro Villabón and Rafał Kaniewski – Recover Highlights With 8-Bit to High Dynamic Range Half Float Copycat – Nuke
-
Godot Cheat Sheets
-
Ethan Roffler interviews CG Supervisor Daniele Tosti
-
FFmpeg – examples and convenience lines
-
Image rendering bit depth
Social Links
DISCLAIMER – Links and images on this website may be protected by the respective owners’ copyright. All data submitted by users through this site shall be treated as freely available to share.
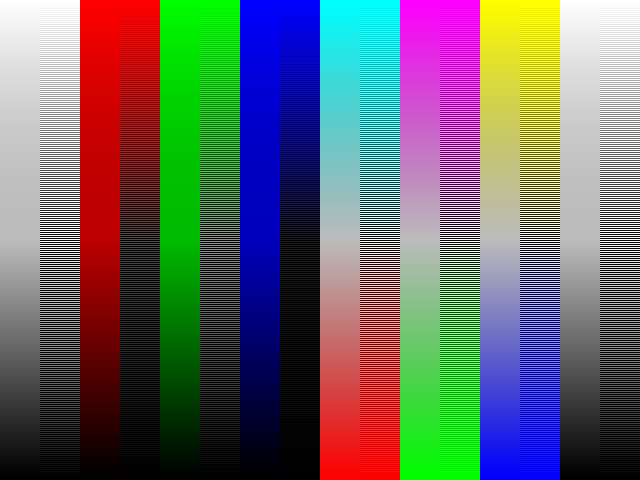
















![sRGB gamma correction test [gamma correction test]](http://www.madore.org/~david/misc/color/gammatest.png)