COMPOSITION
-
SlowMoVideo – How to make a slow motion shot with the open source program
Read more: SlowMoVideo – How to make a slow motion shot with the open source programhttp://slowmovideo.granjow.net/
slowmoVideo is an OpenSource program that creates slow-motion videos from your footage.
Slow motion cinematography is the result of playing back frames for a longer duration than they were exposed. For example, if you expose 240 frames of film in one second, then play them back at 24 fps, the resulting movie is 10 times longer (slower) than the original filmed event….
Film cameras are relatively simple mechanical devices that allow you to crank up the speed to whatever rate the shutter and pull-down mechanism allow. Some film cameras can operate at 2,500 fps or higher (although film shot in these cameras often needs some readjustment in postproduction). Video, on the other hand, is always captured, recorded, and played back at a fixed rate, with a current limit around 60fps. This makes extreme slow motion effects harder to achieve (and less elegant) on video, because slowing down the video results in each frame held still on the screen for a long time, whereas with high-frame-rate film there are plenty of frames to fill the longer durations of time. On video, the slow motion effect is more like a slide show than smooth, continuous motion.
One obvious solution is to shoot film at high speed, then transfer it to video (a case where film still has a clear advantage, sorry George). Another possibility is to cross dissolve or blur from one frame to the next. This adds a smooth transition from one still frame to the next. The blur reduces the sharpness of the image, and compared to slowing down images shot at a high frame rate, this is somewhat of a cheat. However, there isn’t much you can do about it until video can be recorded at much higher rates. Of course, many film cameras can’t shoot at high frame rates either, so the whole super-slow-motion endeavor is somewhat specialized no matter what medium you are using. (There are some high speed digital cameras available now that allow you to capture lots of digital frames directly to your computer, so technology is starting to catch up with film. However, this feature isn’t going to appear in consumer camcorders any time soon.)
DESIGN
-
Principles of Interior Design – Balance
Read more: Principles of Interior Design – Balancehttps://www.yankodesign.com/2024/09/18/principles-of-interior-design-balance
The three types of balance include:
- Symmetrical Balance
- Asymmetrical Balance
- Radial Balance
-
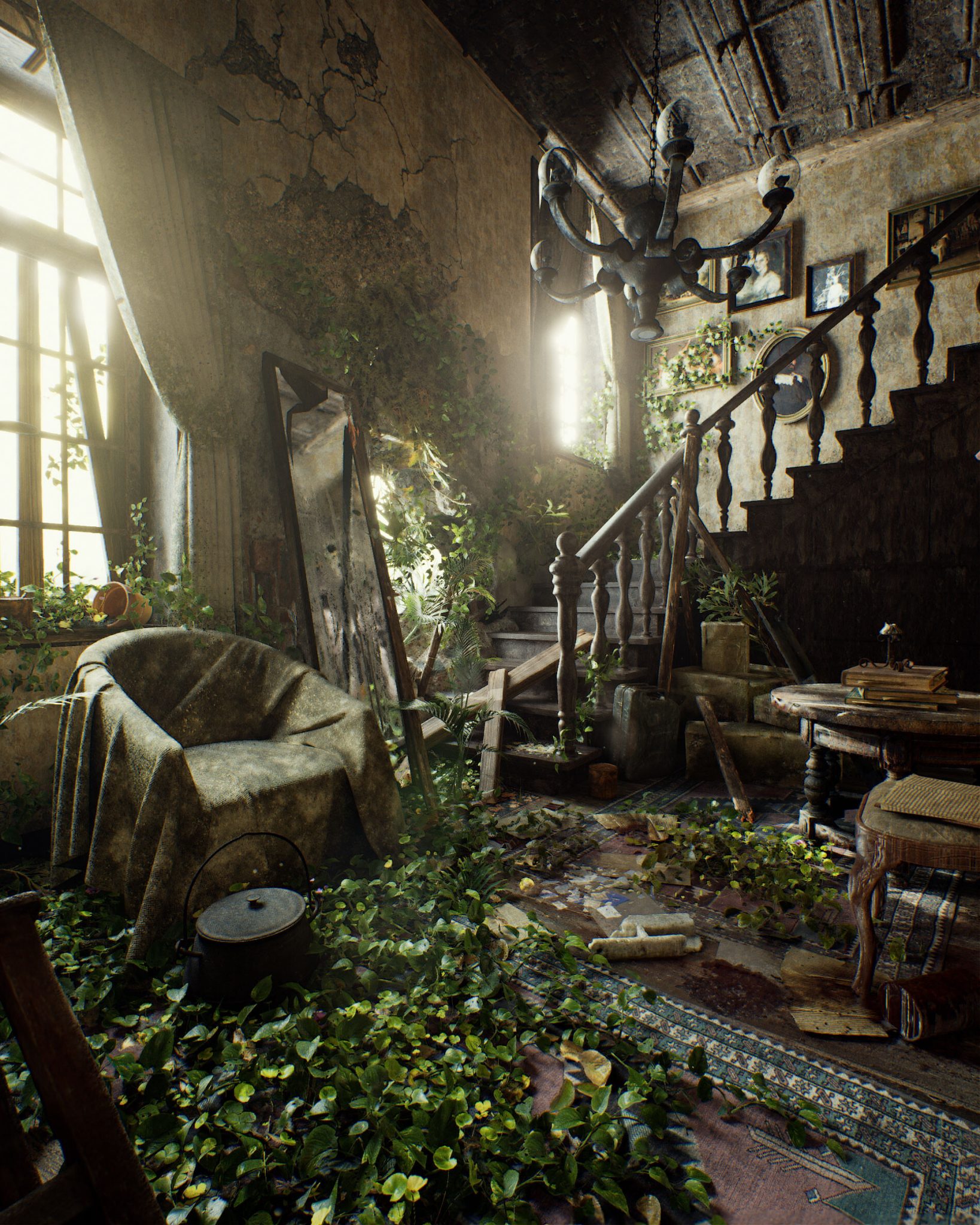
Pasquale Scionti – Production Walkthrough with Virtual Camera and iPad pro 11.5 on Unreal Engine 4.25
Read more: Pasquale Scionti – Production Walkthrough with Virtual Camera and iPad pro 11.5 on Unreal Engine 4.2580.lv/articles/creating-an-old-abandoned-mansion-with-quixel-tools/
www.artstation.com/artwork/Poexyo

COLOR
LIGHTING
-
Magnific.ai Relight – change the entire lighting of a scene
Read more: Magnific.ai Relight – change the entire lighting of a sceneIt’s a new Magnific spell that allows you to change the entire lighting of a scene and, optionally, the background with just:
1/ A prompt OR
2/ A reference image OR
3/ A light map (drawing your own lights)https://x.com/javilopen/status/1805274155065176489
-
Black Body color aka the Planckian Locus curve for white point eye perception
Read more: Black Body color aka the Planckian Locus curve for white point eye perceptionhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Black-body_radiation
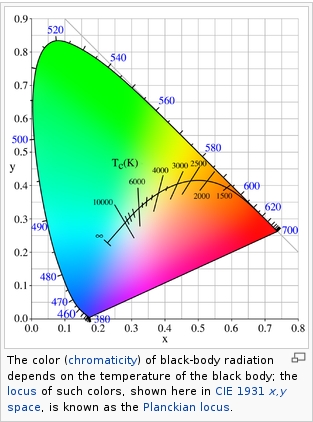
Black-body radiation is the type of electromagnetic radiation within or surrounding a body in thermodynamic equilibrium with its environment, or emitted by a black body (an opaque and non-reflective body) held at constant, uniform temperature. The radiation has a specific spectrum and intensity that depends only on the temperature of the body.
A black-body at room temperature appears black, as most of the energy it radiates is infra-red and cannot be perceived by the human eye. At higher temperatures, black bodies glow with increasing intensity and colors that range from dull red to blindingly brilliant blue-white as the temperature increases.
(more…) -
Willem Zwarthoed – Aces gamut in VFX production pdf
Read more: Willem Zwarthoed – Aces gamut in VFX production pdfhttps://www.provideocoalition.com/color-management-part-12-introducing-aces/
Local copy:
https://www.slideshare.net/hpduiker/acescg-a-common-color-encoding-for-visual-effects-applications
-
What’s the Difference Between Ray Casting, Ray Tracing, Path Tracing and Rasterization? Physical light tracing…
Read more: What’s the Difference Between Ray Casting, Ray Tracing, Path Tracing and Rasterization? Physical light tracing…RASTERIZATION
Rasterisation (or rasterization) is the task of taking the information described in a vector graphics format OR the vertices of triangles making 3D shapes and converting them into a raster image (a series of pixels, dots or lines, which, when displayed together, create the image which was represented via shapes), or in other words “rasterizing” vectors or 3D models onto a 2D plane for display on a computer screen.For each triangle of a 3D shape, you project the corners of the triangle on the virtual screen with some math (projective geometry). Then you have the position of the 3 corners of the triangle on the pixel screen. Those 3 points have texture coordinates, so you know where in the texture are the 3 corners. The cost is proportional to the number of triangles, and is only a little bit affected by the screen resolution.
In computer graphics, a raster graphics or bitmap image is a dot matrix data structure that represents a generally rectangular grid of pixels (points of color), viewable via a monitor, paper, or other display medium.
With rasterization, objects on the screen are created from a mesh of virtual triangles, or polygons, that create 3D models of objects. A lot of information is associated with each vertex, including its position in space, as well as information about color, texture and its “normal,” which is used to determine the way the surface of an object is facing.
Computers then convert the triangles of the 3D models into pixels, or dots, on a 2D screen. Each pixel can be assigned an initial color value from the data stored in the triangle vertices.
Further pixel processing or “shading,” including changing pixel color based on how lights in the scene hit the pixel, and applying one or more textures to the pixel, combine to generate the final color applied to a pixel.
The main advantage of rasterization is its speed. However, rasterization is simply the process of computing the mapping from scene geometry to pixels and does not prescribe a particular way to compute the color of those pixels. So it cannot take shading, especially the physical light, into account and it cannot promise to get a photorealistic output. That’s a big limitation of rasterization.
There are also multiple problems:
If you have two triangles one is behind the other, you will draw twice all the pixels. you only keep the pixel from the triangle that is closer to you (Z-buffer), but you still do the work twice.
The borders of your triangles are jagged as it is hard to know if a pixel is in the triangle or out. You can do some smoothing on those, that is anti-aliasing.
You have to handle every triangles (including the ones behind you) and then see that they do not touch the screen at all. (we have techniques to mitigate this where we only look at triangles that are in the field of view)
Transparency is hard to handle (you can’t just do an average of the color of overlapping transparent triangles, you have to do it in the right order)
-
Custom bokeh in a raytraced DOF render
Read more: Custom bokeh in a raytraced DOF renderTo achieve a custom pinhole camera effect with a custom bokeh in Arnold Raytracer, you can follow these steps:
- Set the render camera with a focal length around 50 (or as needed)
- Set the F-Stop to a high value (e.g., 22).
- Set the focus distance as you require
- Turn on DOF
- Place a plane a few cm in front of the camera.
- Texture the plane with a transparent shape at the center of it. (Transmission with no specular roughness)
-
Outpost VFX lighting tips
Read more: Outpost VFX lighting tipswww.outpost-vfx.com/en/news/18-pro-tips-and-tricks-for-lighting
Get as much information regarding your plate lighting as possible
- Always use a reference
- Replicate what is happening in real life
- Invest into a solid HDRI
- Start Simple
- Observe real world lighting, photography and cinematography
- Don’t neglect the theory
- Learn the difference between realism and photo-realism.
- Keep your scenes organised

COLLECTIONS
| Featured AI
| Design And Composition
| Explore posts
POPULAR SEARCHES
unreal | pipeline | virtual production | free | learn | photoshop | 360 | macro | google | nvidia | resolution | open source | hdri | real-time | photography basics | nuke
FEATURED POSTS
-
What’s the Difference Between Ray Casting, Ray Tracing, Path Tracing and Rasterization? Physical light tracing…
-
Matt Hallett – WAN 2.1 VACE Total Video Control in ComfyUI
-
Photography basics: Exposure Value vs Photographic Exposure vs Il/Luminance vs Pixel luminance measurements
-
Web vs Printing or digital RGB vs CMYK
-
Decart AI Mirage – The first ever World Transformation Model – turning any video, game, or camera feed into a new digital world, in real time
-
Emmanuel Tsekleves – Writing Research Papers
-
AI Data Laundering: How Academic and Nonprofit Researchers Shield Tech Companies from Accountability
-
Yann Lecun: Meta AI, Open Source, Limits of LLMs, AGI & the Future of AI | Lex Fridman Podcast #416
Social Links
DISCLAIMER – Links and images on this website may be protected by the respective owners’ copyright. All data submitted by users through this site shall be treated as freely available to share.












