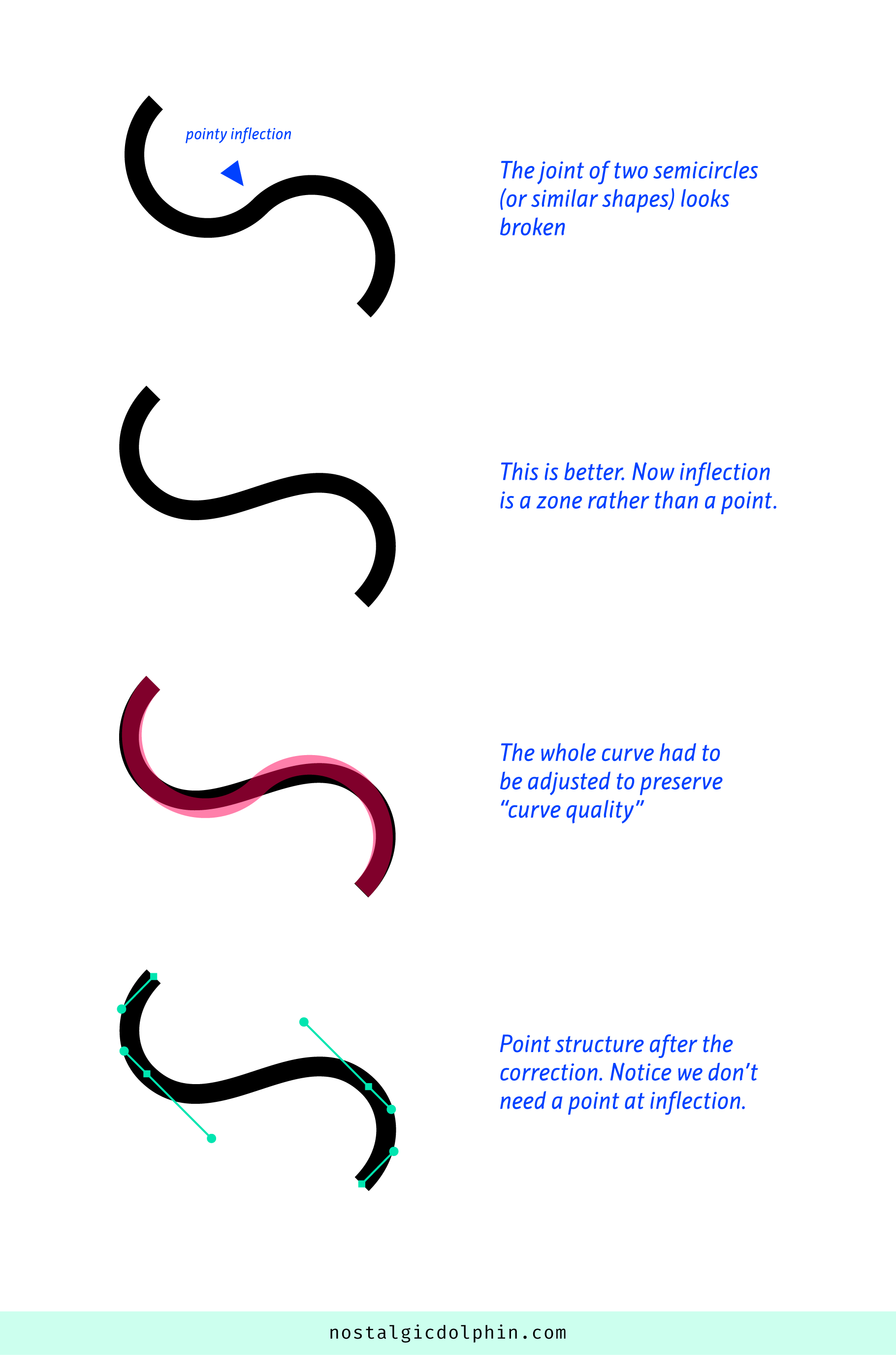COMPOSITION
-
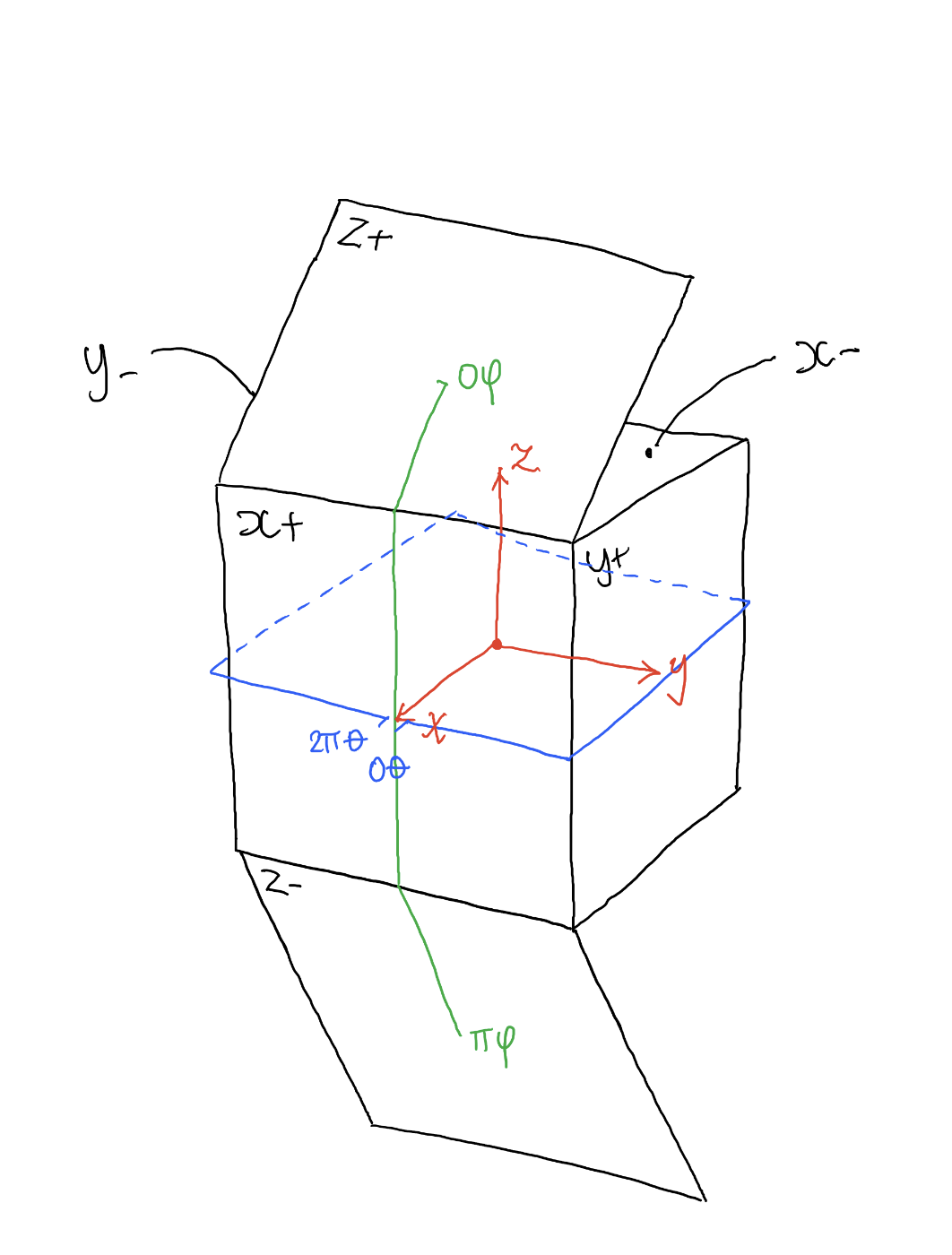
Mastering Camera Shots and Angles: A Guide for Filmmakers
Read more: Mastering Camera Shots and Angles: A Guide for Filmmakershttps://website.ltx.studio/blog/mastering-camera-shots-and-angles
1. Extreme Wide Shot
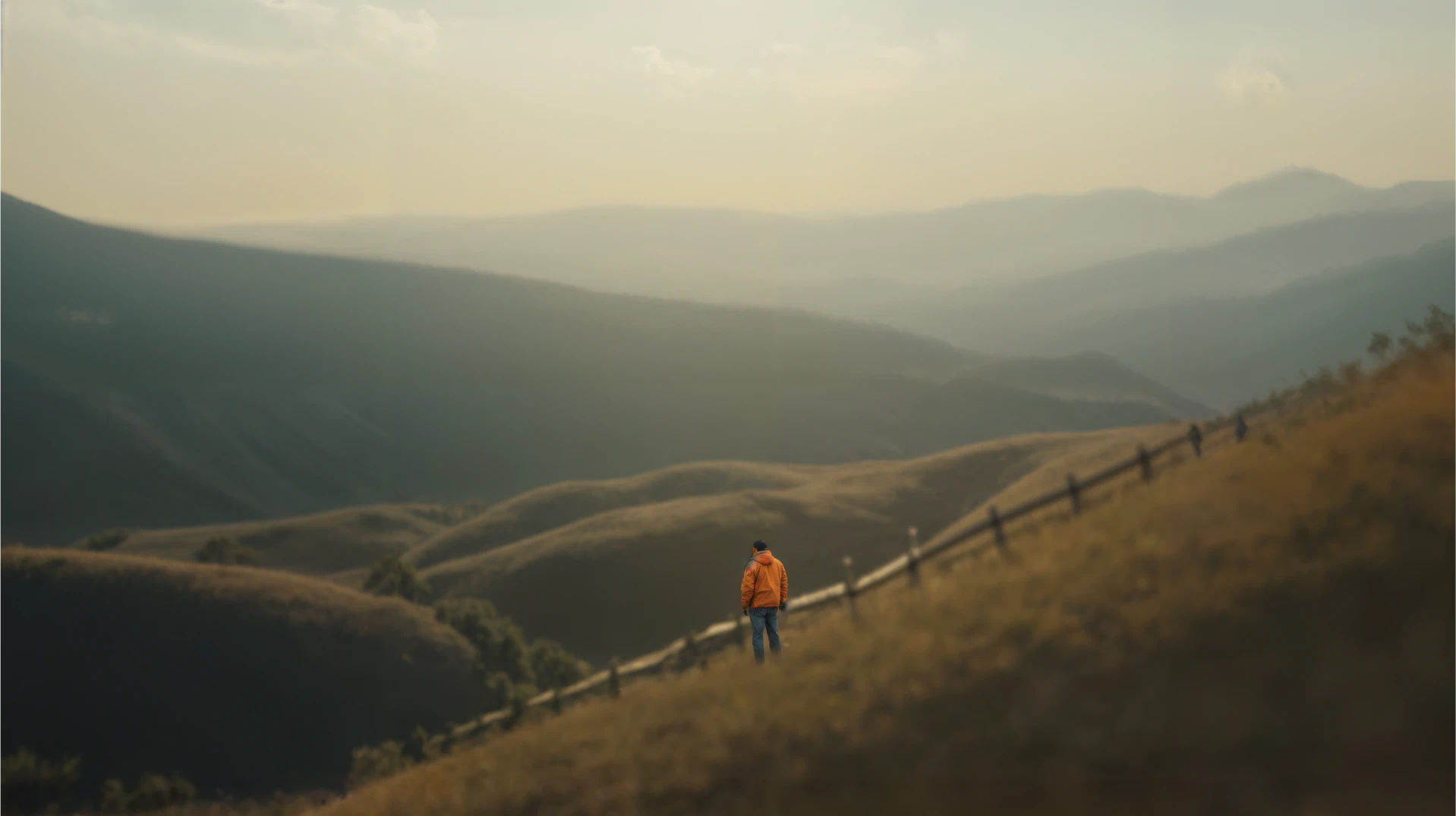

2. Wide Shot
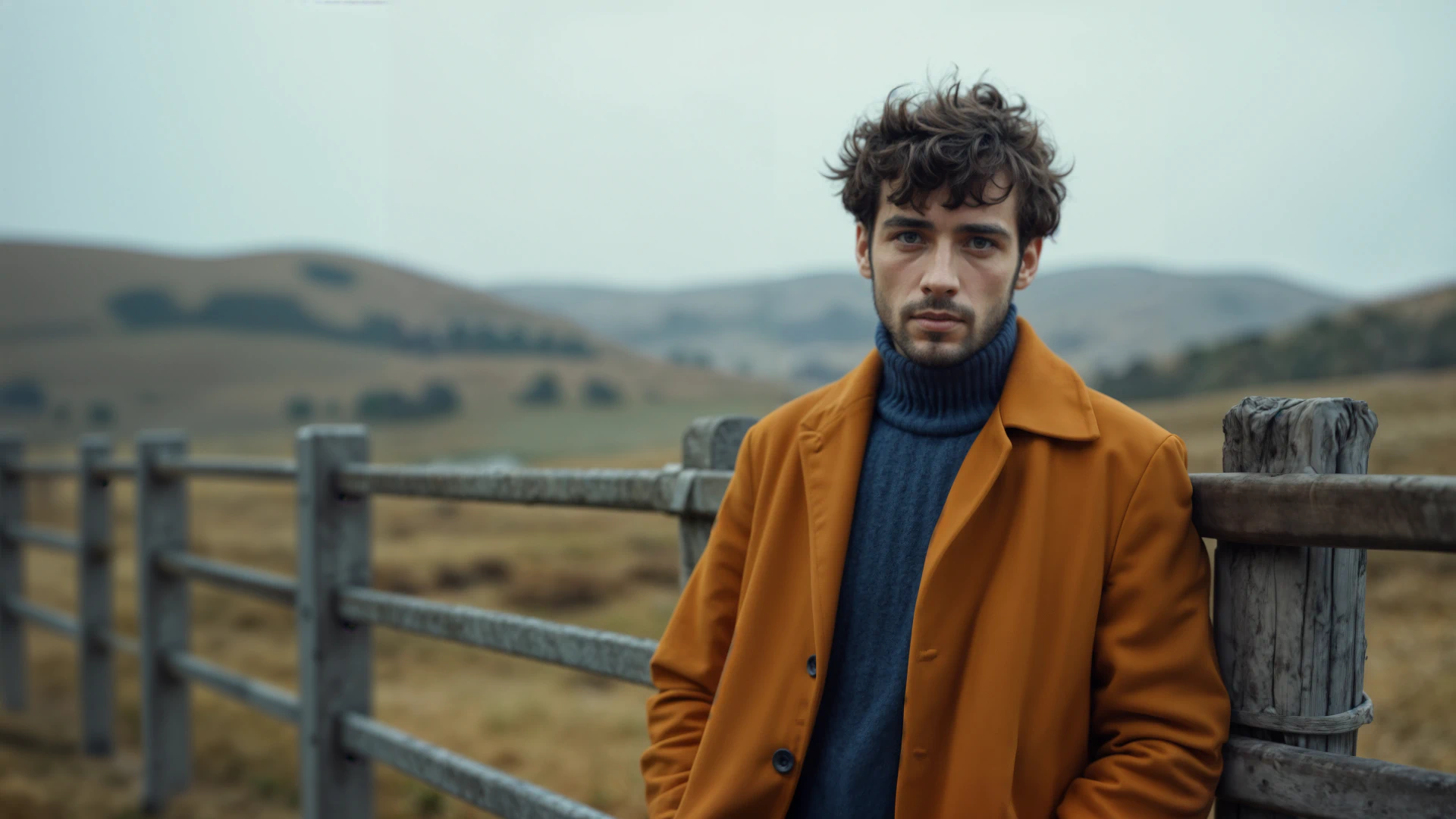

3. Medium Shot
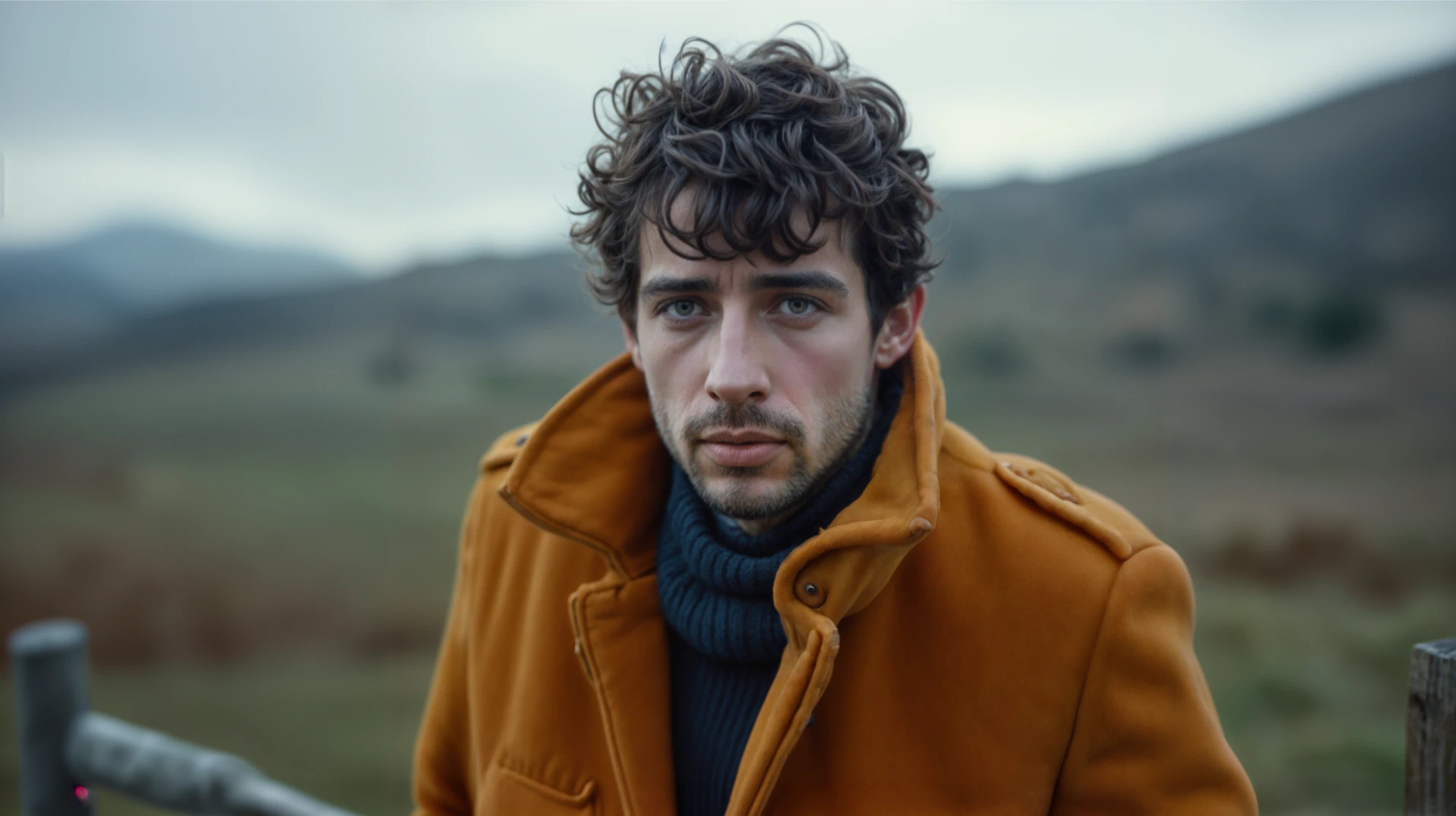

4. Close Up

5. Extreme Close Up

DESIGN
-
-
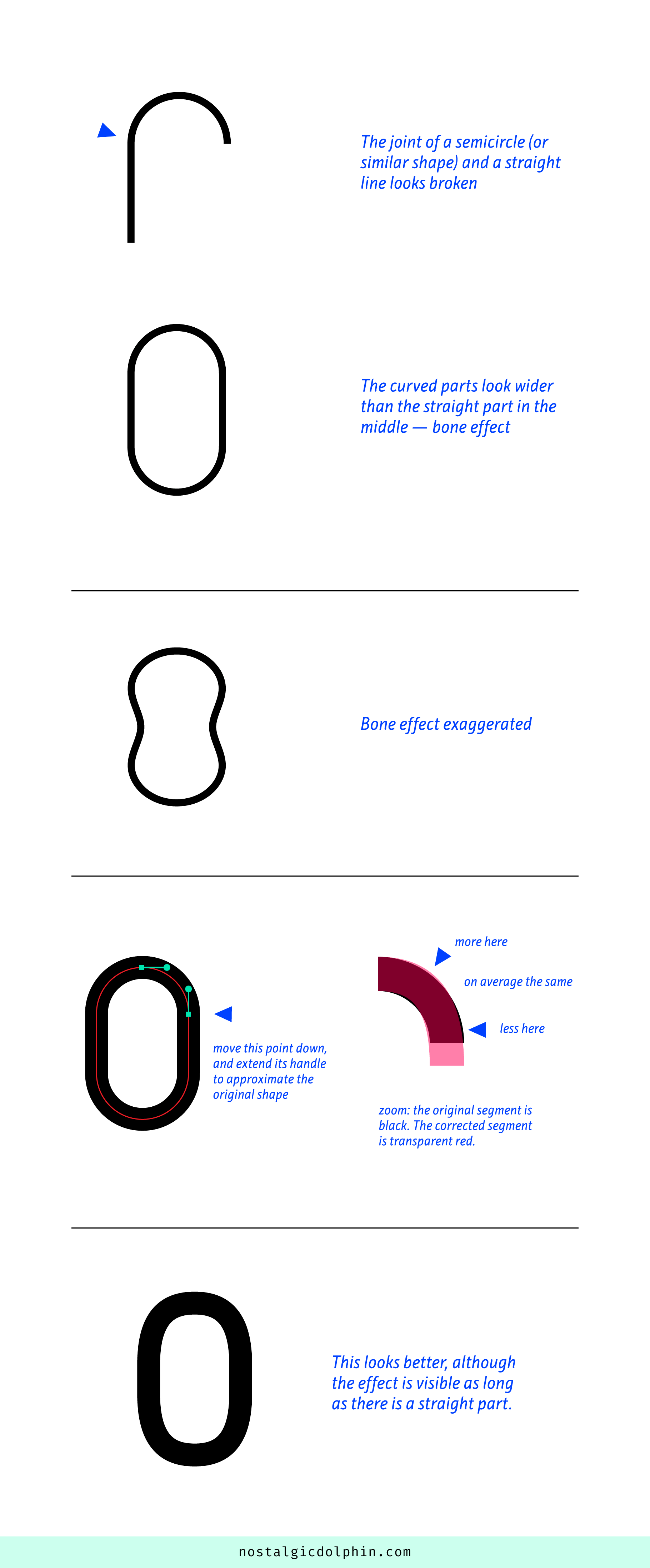
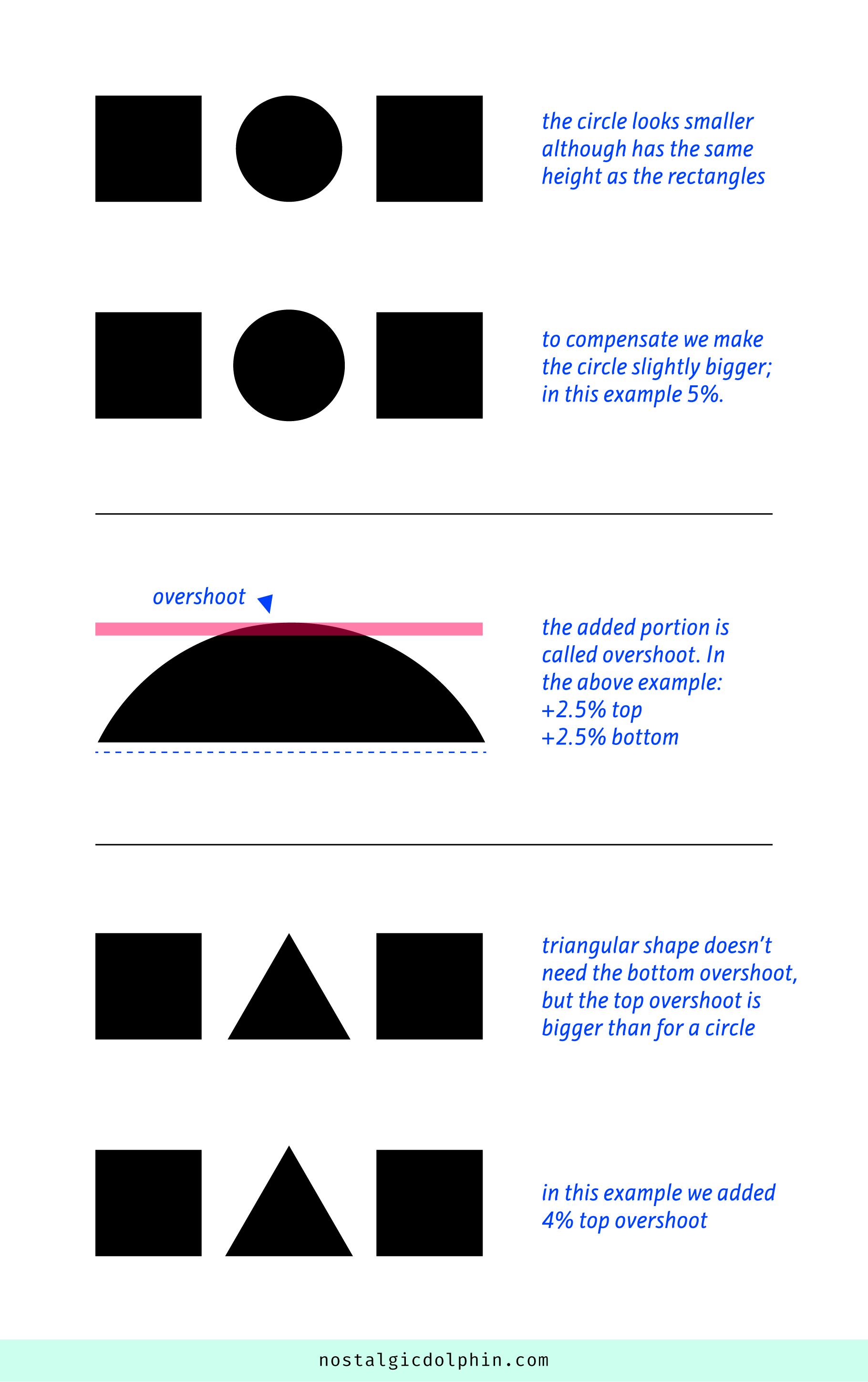
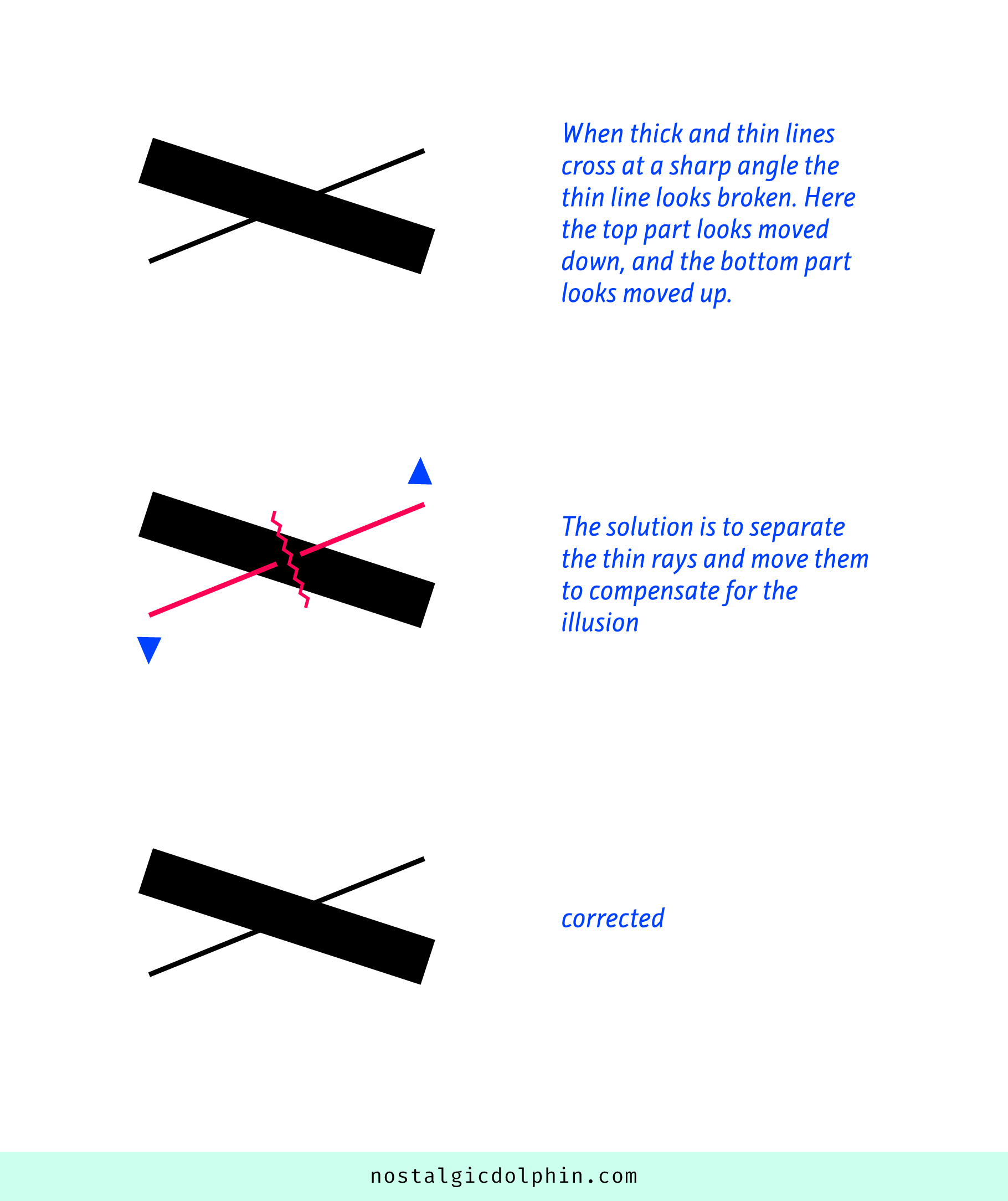
Ranko Prozo – Modelling design tips
Read more: Ranko Prozo – Modelling design tipsEvery Project I work on I always create a stylization Cheat sheet. Every project is unique but some principles carry over no matter what. This is a sheet I use a lot when I work on isometric stylized projects to help keep my assets consistent and interesting. None of these concepts are my own, just lots of tips I learned over the years. I have also added this to a page on my website, will continue to update with more tips and tricks, just need time to compile it all :)

COLOR
-
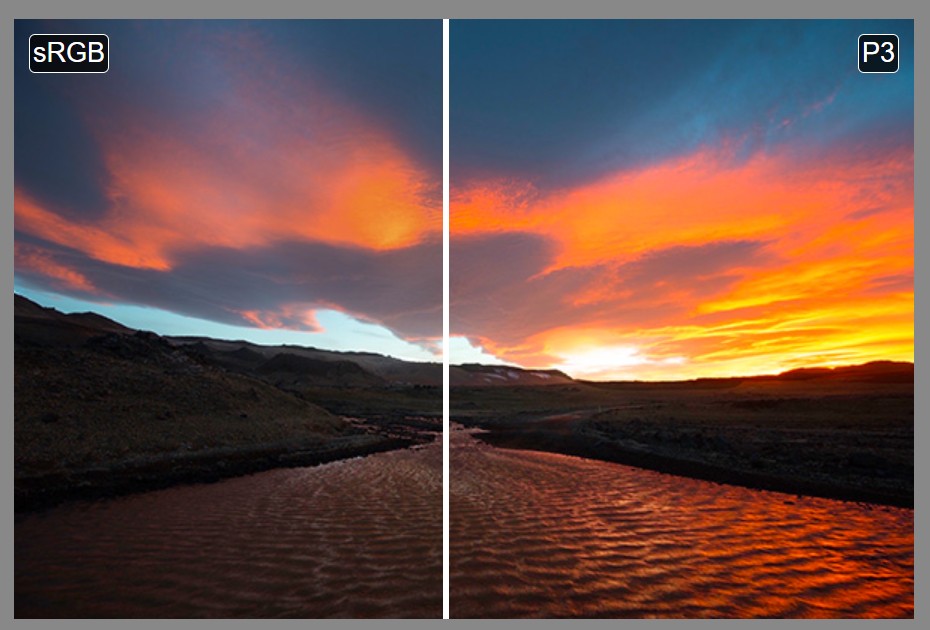
Colormaxxing – What if I told you that rgb(255, 0, 0) is not actually the reddest red you can have in your browser?
Read more: Colormaxxing – What if I told you that rgb(255, 0, 0) is not actually the reddest red you can have in your browser?https://karuna.dev/colormaxxing
https://webkit.org/blog-files/color-gamut/comparison.html
https://oklch.com/#70,0.1,197,100

-
sRGB vs REC709 – An introduction and FFmpeg implementations
Read more: sRGB vs REC709 – An introduction and FFmpeg implementations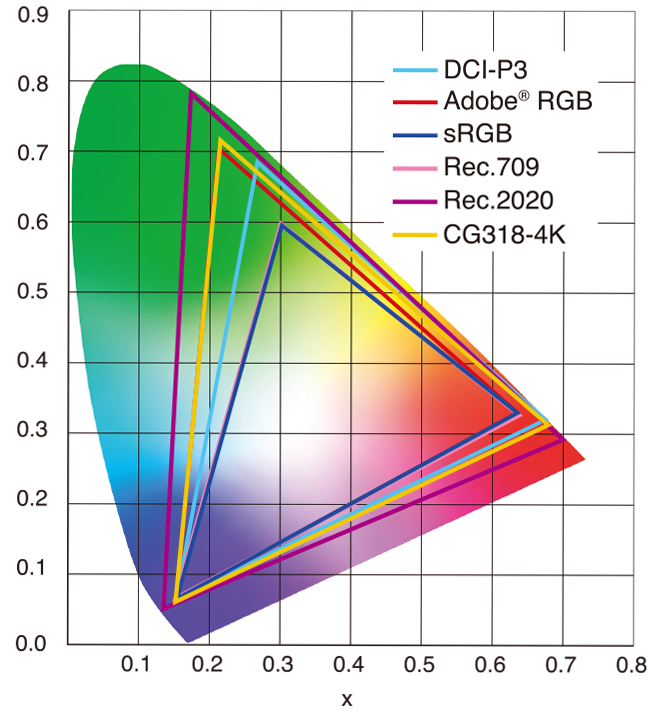
1. Basic Comparison
- What they are
- sRGB: A standard “web”/computer-display RGB color space defined by IEC 61966-2-1. It’s used for most monitors, cameras, printers, and the vast majority of images on the Internet.
- Rec. 709: An HD-video color space defined by ITU-R BT.709. It’s the go-to standard for HDTV broadcasts, Blu-ray discs, and professional video pipelines.
- Why they exist
- sRGB: Ensures consistent colors across different consumer devices (PCs, phones, webcams).
- Rec. 709: Ensures consistent colors across video production and playback chains (cameras → editing → broadcast → TV).
- What you’ll see
- On your desktop or phone, images tagged sRGB will look “right” without extra tweaking.
- On an HDTV or video-editing timeline, footage tagged Rec. 709 will display accurate contrast and hue on broadcast-grade monitors.
2. Digging Deeper
Feature sRGB Rec. 709 White point D65 (6504 K), same for both D65 (6504 K) Primaries (x,y) R: (0.640, 0.330) G: (0.300, 0.600) B: (0.150, 0.060) R: (0.640, 0.330) G: (0.300, 0.600) B: (0.150, 0.060) Gamut size Identical triangle on CIE 1931 chart Identical to sRGB Gamma / transfer Piecewise curve: approximate 2.2 with linear toe Pure power-law γ≈2.4 (often approximated as 2.2 in practice) Matrix coefficients N/A (pure RGB usage) Y = 0.2126 R + 0.7152 G + 0.0722 B (Rec. 709 matrix) Typical bit-depth 8-bit/channel (with 16-bit variants) 8-bit/channel (10-bit for professional video) Usage metadata Tagged as “sRGB” in image files (PNG, JPEG, etc.) Tagged as “bt709” in video containers (MP4, MOV) Color range Full-range RGB (0–255) Studio-range Y′CbCr (Y′ [16–235], Cb/Cr [16–240])
Why the Small Differences Matter
(more…) - What they are
-
Björn Ottosson – How software gets color wrong
Read more: Björn Ottosson – How software gets color wronghttps://bottosson.github.io/posts/colorwrong/
Most software around us today are decent at accurately displaying colors. Processing of colors is another story unfortunately, and is often done badly.
To understand what the problem is, let’s start with an example of three ways of blending green and magenta:
- Perceptual blend – A smooth transition using a model designed to mimic human perception of color. The blending is done so that the perceived brightness and color varies smoothly and evenly.
- Linear blend – A model for blending color based on how light behaves physically. This type of blending can occur in many ways naturally, for example when colors are blended together by focus blur in a camera or when viewing a pattern of two colors at a distance.
- sRGB blend – This is how colors would normally be blended in computer software, using sRGB to represent the colors.
Let’s look at some more examples of blending of colors, to see how these problems surface more practically. The examples use strong colors since then the differences are more pronounced. This is using the same three ways of blending colors as the first example.
Instead of making it as easy as possible to work with color, most software make it unnecessarily hard, by doing image processing with representations not designed for it. Approximating the physical behavior of light with linear RGB models is one easy thing to do, but more work is needed to create image representations tailored for image processing and human perception.
Also see:
-
The Forbidden colors – Red-Green & Blue-Yellow: The Stunning Colors You Can’t See
Read more: The Forbidden colors – Red-Green & Blue-Yellow: The Stunning Colors You Can’t Seewww.livescience.com/17948-red-green-blue-yellow-stunning-colors.html
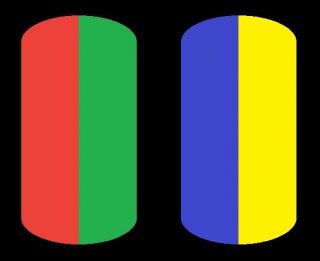
While the human eye has red, green, and blue-sensing cones, those cones are cross-wired in the retina to produce a luminance channel plus a red-green and a blue-yellow channel, and it’s data in that color space (known technically as “LAB”) that goes to the brain. That’s why we can’t perceive a reddish-green or a yellowish-blue, whereas such colors can be represented in the RGB color space used by digital cameras.
https://en.rockcontent.com/blog/the-use-of-yellow-in-data-design
The back of the retina is covered in light-sensitive neurons known as cone cells and rod cells. There are three types of cone cells, each sensitive to different ranges of light. These ranges overlap, but for convenience the cones are referred to as blue (short-wavelength), green (medium-wavelength), and red (long-wavelength). The rod cells are primarily used in low-light situations, so we’ll ignore those for now.
When light enters the eye and hits the cone cells, the cones get excited and send signals to the brain through the visual cortex. Different wavelengths of light excite different combinations of cones to varying levels, which generates our perception of color. You can see that the red cones are most sensitive to light, and the blue cones are least sensitive. The sensitivity of green and red cones overlaps for most of the visible spectrum.
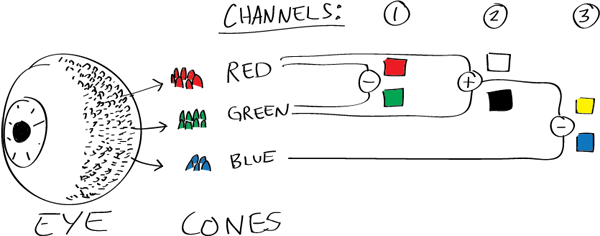
Here’s how your brain takes the signals of light intensity from the cones and turns it into color information. To see red or green, your brain finds the difference between the levels of excitement in your red and green cones. This is the red-green channel.
To get “brightness,” your brain combines the excitement of your red and green cones. This creates the luminance, or black-white, channel. To see yellow or blue, your brain then finds the difference between this luminance signal and the excitement of your blue cones. This is the yellow-blue channel.
From the calculations made in the brain along those three channels, we get four basic colors: blue, green, yellow, and red. Seeing blue is what you experience when low-wavelength light excites the blue cones more than the green and red.
Seeing green happens when light excites the green cones more than the red cones. Seeing red happens when only the red cones are excited by high-wavelength light.
Here’s where it gets interesting. Seeing yellow is what happens when BOTH the green AND red cones are highly excited near their peak sensitivity. This is the biggest collective excitement that your cones ever have, aside from seeing pure white.
Notice that yellow occurs at peak intensity in the graph to the right. Further, the lens and cornea of the eye happen to block shorter wavelengths, reducing sensitivity to blue and violet light.
-
Rec-2020 – TVs new color gamut standard used by Dolby Vision?
Read more: Rec-2020 – TVs new color gamut standard used by Dolby Vision?https://www.hdrsoft.com/resources/dri.html#bit-depth
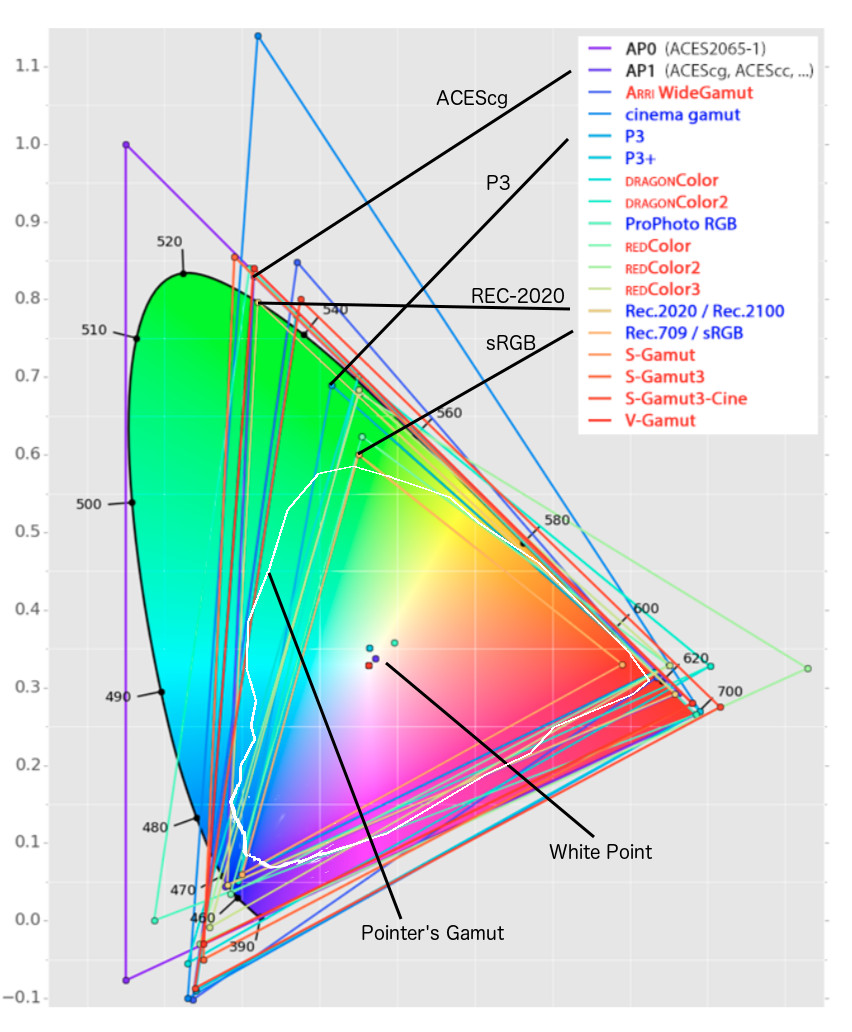
The dynamic range is a ratio between the maximum and minimum values of a physical measurement. Its definition depends on what the dynamic range refers to.
For a scene: Dynamic range is the ratio between the brightest and darkest parts of the scene.
For a camera: Dynamic range is the ratio of saturation to noise. More specifically, the ratio of the intensity that just saturates the camera to the intensity that just lifts the camera response one standard deviation above camera noise.
For a display: Dynamic range is the ratio between the maximum and minimum intensities emitted from the screen.
The Dynamic Range of real-world scenes can be quite high — ratios of 100,000:1 are common in the natural world. An HDR (High Dynamic Range) image stores pixel values that span the whole tonal range of real-world scenes. Therefore, an HDR image is encoded in a format that allows the largest range of values, e.g. floating-point values stored with 32 bits per color channel. Another characteristics of an HDR image is that it stores linear values. This means that the value of a pixel from an HDR image is proportional to the amount of light measured by the camera.
For TVs HDR is great, but it’s not the only new TV feature worth discussing.
(more…)
LIGHTING
-
Fast, optimized ‘for’ pixel loops with OpenCV and Python to create tone mapped HDR images
Read more: Fast, optimized ‘for’ pixel loops with OpenCV and Python to create tone mapped HDR imageshttps://pyimagesearch.com/2017/08/28/fast-optimized-for-pixel-loops-with-opencv-and-python/
https://learnopencv.com/exposure-fusion-using-opencv-cpp-python/
Exposure Fusion is a method for combining images taken with different exposure settings into one image that looks like a tone mapped High Dynamic Range (HDR) image.
-
Photography basics: Color Temperature and White Balance
Read more: Photography basics: Color Temperature and White BalanceColor Temperature of a light source describes the spectrum of light which is radiated from a theoretical “blackbody” (an ideal physical body that absorbs all radiation and incident light – neither reflecting it nor allowing it to pass through) with a given surface temperature.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Color_temperature
Or. Most simply it is a method of describing the color characteristics of light through a numerical value that corresponds to the color emitted by a light source, measured in degrees of Kelvin (K) on a scale from 1,000 to 10,000.
More accurately. The color temperature of a light source is the temperature of an ideal backbody that radiates light of comparable hue to that of the light source.
(more…) -
Light properties
Read more: Light propertiesHow It Works – Issue 114
https://www.howitworksdaily.com/ -
Gamma correction
Read more: Gamma correction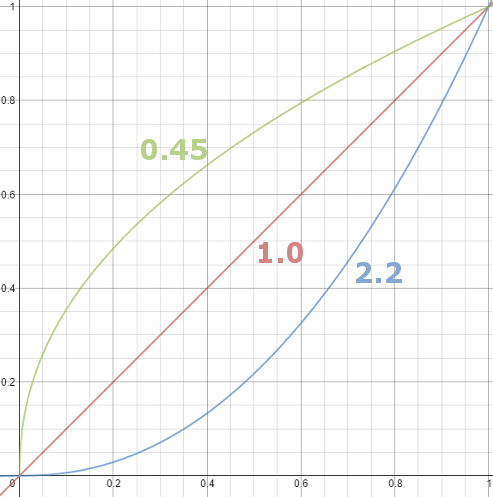
http://www.normankoren.com/makingfineprints1A.html#Gammabox
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gamma_correction
http://www.photoscientia.co.uk/Gamma.htm
https://www.w3.org/Graphics/Color/sRGB.html
http://www.eizoglobal.com/library/basics/lcd_display_gamma/index.html
https://forum.reallusion.com/PrintTopic308094.aspx
Basically, gamma is the relationship between the brightness of a pixel as it appears on the screen, and the numerical value of that pixel. Generally Gamma is just about defining relationships.
Three main types:
– Image Gamma encoded in images
– Display Gammas encoded in hardware and/or viewing time
– System or Viewing Gamma which is the net effect of all gammas when you look back at a final image. In theory this should flatten back to 1.0 gamma.
(more…) -
HDRI Median Cut plugin
Read more: HDRI Median Cut pluginwww.hdrlabs.com/picturenaut/plugins.html
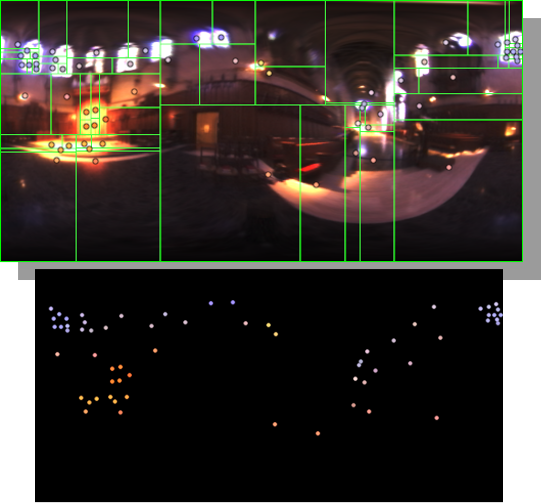
Note. The Median Cut algorithm is typically used for color quantization, which involves reducing the number of colors in an image while preserving its visual quality. It doesn’t directly provide a way to identify the brightest areas in an image. However, if you’re interested in identifying the brightest areas, you might want to look into other methods like thresholding, histogram analysis, or edge detection, through openCV for example.
Here is an openCV example:
(more…)
COLLECTIONS
| Featured AI
| Design And Composition
| Explore posts
POPULAR SEARCHES
unreal | pipeline | virtual production | free | learn | photoshop | 360 | macro | google | nvidia | resolution | open source | hdri | real-time | photography basics | nuke
FEATURED POSTS
-
Photography basics: Lumens vs Candelas (candle) vs Lux vs FootCandle vs Watts vs Irradiance vs Illuminance
-
Godot Cheat Sheets
-
White Balance is Broken!
-
Survivorship Bias: The error resulting from systematically focusing on successes and ignoring failures. How a young statistician saved his planes during WW2.
-
Kling 1.6 and competitors – advanced tests and comparisons
-
Cinematographers Blueprint 300dpi poster
-
Sensitivity of human eye
-
Mastering The Art Of Photography – PixelSham.com Photography Basics
Social Links
DISCLAIMER – Links and images on this website may be protected by the respective owners’ copyright. All data submitted by users through this site shall be treated as freely available to share.