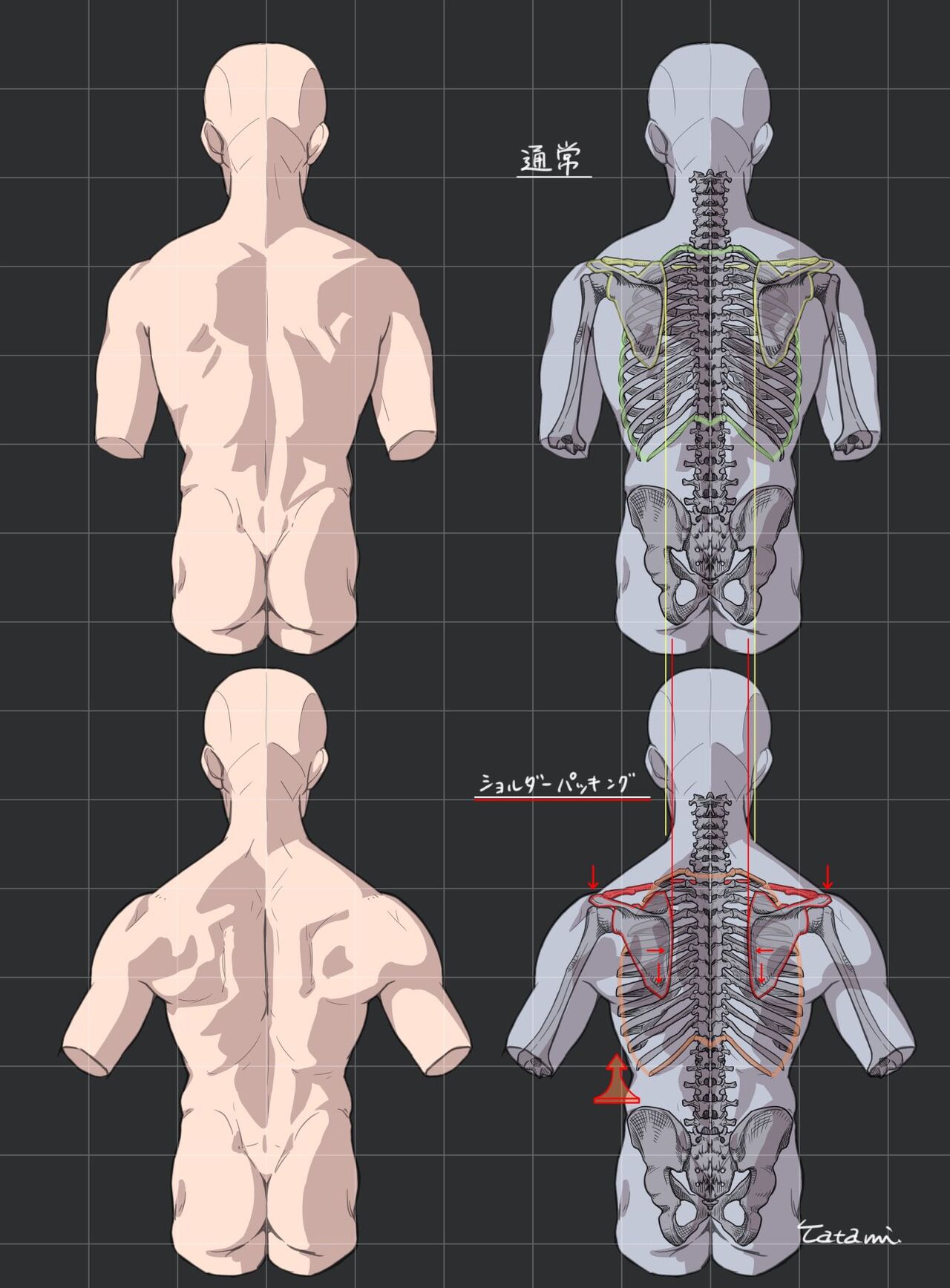
COMPOSITION
DESIGN
-
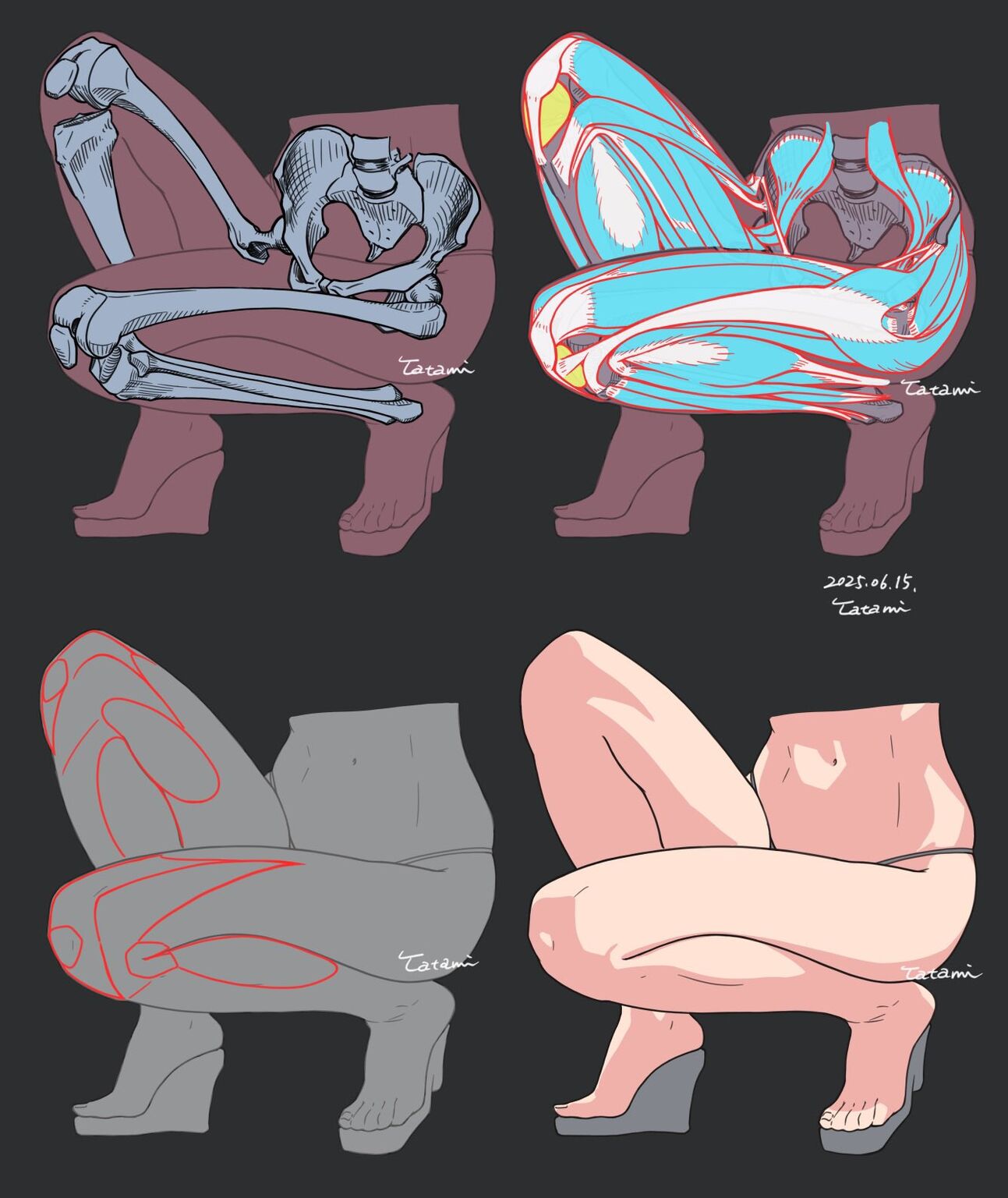
Glenn Marshall – The Crow
Read more: Glenn Marshall – The CrowCreated with AI ‘Style Transfer’ processes to transform video footage into AI video art.
COLOR
-
A Brief History of Color in Art
Read more: A Brief History of Color in Artwww.artsy.net/article/the-art-genome-project-a-brief-history-of-color-in-art
Of all the pigments that have been banned over the centuries, the color most missed by painters is likely Lead White.
This hue could capture and reflect a gleam of light like no other, though its production was anything but glamorous. The 17th-century Dutch method for manufacturing the pigment involved layering cow and horse manure over lead and vinegar. After three months in a sealed room, these materials would combine to create flakes of pure white. While scientists in the late 19th century identified lead as poisonous, it wasn’t until 1978 that the United States banned the production of lead white paint.
More reading:
www.canva.com/learn/color-meanings/https://www.infogrades.com/history-events-infographics/bizarre-history-of-colors/
-
Polarised vs unpolarized filtering
Read more: Polarised vs unpolarized filteringA light wave that is vibrating in more than one plane is referred to as unpolarized light. …
Polarized light waves are light waves in which the vibrations occur in a single plane. The process of transforming unpolarized light into polarized light is known as polarization.
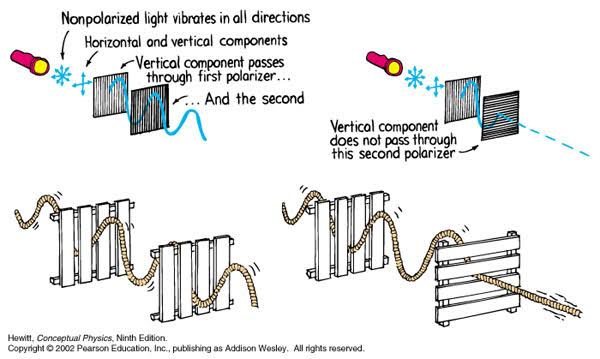
en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Polarizing_filter_(photography)
The most common use of polarized technology is to reduce lighting complexity on the subject.
(more…)
Details such as glare and hard edges are not removed, but greatly reduced. -
Light and Matter : The 2018 theory of Physically-Based Rendering and Shading by Allegorithmic
Read more: Light and Matter : The 2018 theory of Physically-Based Rendering and Shading by Allegorithmicacademy.substance3d.com/courses/the-pbr-guide-part-1
academy.substance3d.com/courses/the-pbr-guide-part-2
Local copy:
-
Types of Film Lights and their efficiency – CRI, Color Temperature and Luminous Efficacy
Read more: Types of Film Lights and their efficiency – CRI, Color Temperature and Luminous Efficacynofilmschool.com/types-of-film-lights
“Not every light performs the same way. Lights and lighting are tricky to handle. You have to plan for every circumstance. But the good news is, lighting can be adjusted. Let’s look at different factors that affect lighting in every scene you shoot. “
Use CRI, Luminous Efficacy and color temperature controls to match your needs.Color Temperature
Color temperature describes the “color” of white light by a light source radiated by a perfect black body at a given temperature measured in degrees Kelvinhttps://www.pixelsham.com/2019/10/18/color-temperature/
CRI
“The Color Rendering Index is a measurement of how faithfully a light source reveals the colors of whatever it illuminates, it describes the ability of a light source to reveal the color of an object, as compared to the color a natural light source would provide. The highest possible CRI is 100. A CRI of 100 generally refers to a perfect black body, like a tungsten light source or the sun. “https://www.studiobinder.com/blog/what-is-color-rendering-index
(more…) -
Weta Digital – Manuka Raytracer and Gazebo GPU renderers – pipeline
Read more: Weta Digital – Manuka Raytracer and Gazebo GPU renderers – pipelinehttps://jo.dreggn.org/home/2018_manuka.pdf
http://www.fxguide.com/featured/manuka-weta-digitals-new-renderer/

The Manuka rendering architecture has been designed in the spirit of the classic reyes rendering architecture. In its core, reyes is based on stochastic rasterisation of micropolygons, facilitating depth of field, motion blur, high geometric complexity,and programmable shading.
This is commonly achieved with Monte Carlo path tracing, using a paradigm often called shade-on-hit, in which the renderer alternates tracing rays with running shaders on the various ray hits. The shaders take the role of generating the inputs of the local material structure which is then used bypath sampling logic to evaluate contributions and to inform what further rays to cast through the scene.
Over the years, however, the expectations have risen substantially when it comes to image quality. Computing pictures which are indistinguishable from real footage requires accurate simulation of light transport, which is most often performed using some variant of Monte Carlo path tracing. Unfortunately this paradigm requires random memory accesses to the whole scene and does not lend itself well to a rasterisation approach at all.
Manuka is both a uni-directional and bidirectional path tracer and encompasses multiple importance sampling (MIS). Interestingly, and importantly for production character skin work, it is the first major production renderer to incorporate spectral MIS in the form of a new ‘Hero Spectral Sampling’ technique, which was recently published at Eurographics Symposium on Rendering 2014.
Manuka propose a shade-before-hit paradigm in-stead and minimise I/O strain (and some memory costs) on the system, leveraging locality of reference by running pattern generation shaders before we execute light transport simulation by path sampling, “compressing” any bvh structure as needed, and as such also limiting duplication of source data.
The difference with reyes is that instead of baking colors into the geometry like in Reyes, manuka bakes surface closures. This means that light transport is still calculated with path tracing, but all texture lookups etc. are done up-front and baked into the geometry.The main drawback with this method is that geometry has to be tessellated to its highest, stable topology before shading can be evaluated properly. As such, the high cost to first pixel. Even a basic 4 vertices square becomes a much more complex model with this approach.
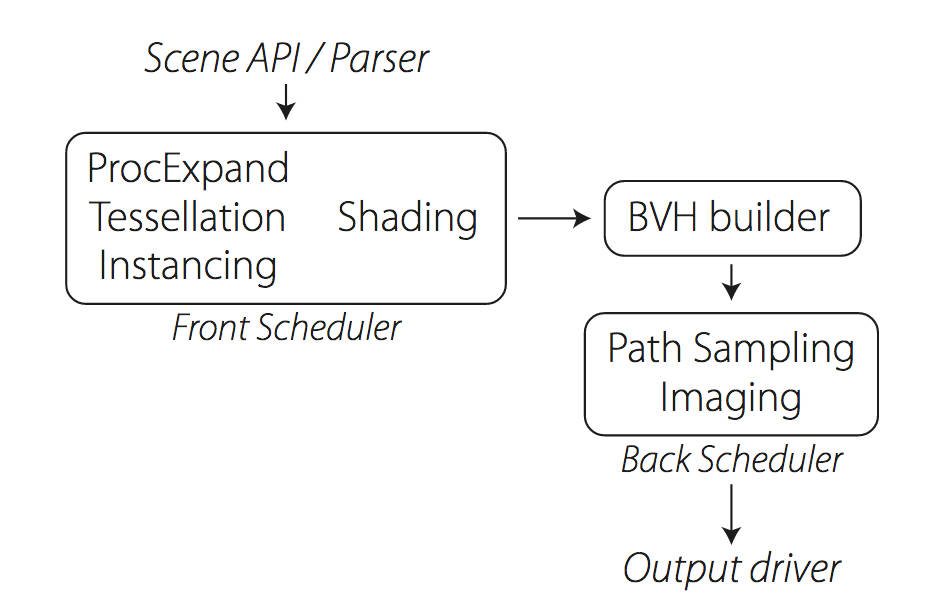
Manuka use the RenderMan Shading Language (rsl) for programmable shading [Pixar Animation Studios 2015], but we do not invoke rsl shaders when intersecting a ray with a surface (often called shade-on-hit). Instead, we pre-tessellate and pre-shade all the input geometry in the front end of the renderer.
This way, we can efficiently order shading computations to sup-port near-optimal texture locality, vectorisation, and parallelism. This system avoids repeated evaluation of shaders at the same surface point, and presents a minimal amount of memory to be accessed during light transport time. An added benefit is that the acceleration structure for ray tracing (abounding volume hierarchy, bvh) is built once on the final tessellated geometry, which allows us to ray trace more efficiently than multi-level bvhs and avoids costly caching of on-demand tessellated micropolygons and the associated scheduling issues.For the shading reasons above, in terms of AOVs, the studio approach is to succeed at combining complex shading with ray paths in the render rather than pass a multi-pass render to compositing.
For the Spectral Rendering component. The light transport stage is fully spectral, using a continuously sampled wavelength which is traced with each path and used to apply the spectral camera sensitivity of the sensor. This allows for faithfully support any degree of observer metamerism as the camera footage they are intended to match as well as complex materials which require wavelength dependent phenomena such as diffraction, dispersion, interference, iridescence, or chromatic extinction and Rayleigh scattering in participating media.
As opposed to the original reyes paper, we use bilinear interpolation of these bsdf inputs later when evaluating bsdfs per pathv ertex during light transport4. This improves temporal stability of geometry which moves very slowly with respect to the pixel raster
In terms of the pipeline, everything rendered at Weta was already completely interwoven with their deep data pipeline. Manuka very much was written with deep data in mind. Here, Manuka not so much extends the deep capabilities, rather it fully matches the already extremely complex and powerful setup Weta Digital already enjoy with RenderMan. For example, an ape in a scene can be selected, its ID is available and a NUKE artist can then paint in 3D say a hand and part of the way up the neutral posed ape.
We called our system Manuka, as a respectful nod to reyes: we had heard a story froma former ILM employee about how reyes got its name from how fond the early Pixar people were of their lunches at Point Reyes, and decided to name our system after our surrounding natural environment, too. Manuka is a kind of tea tree very common in New Zealand which has very many very small leaves, in analogy to micropolygons ina tree structure for ray tracing. It also happens to be the case that Weta Digital’s main site is on Manuka Street.

-
Composition – cinematography Cheat Sheet
Read more: Composition – cinematography Cheat Sheet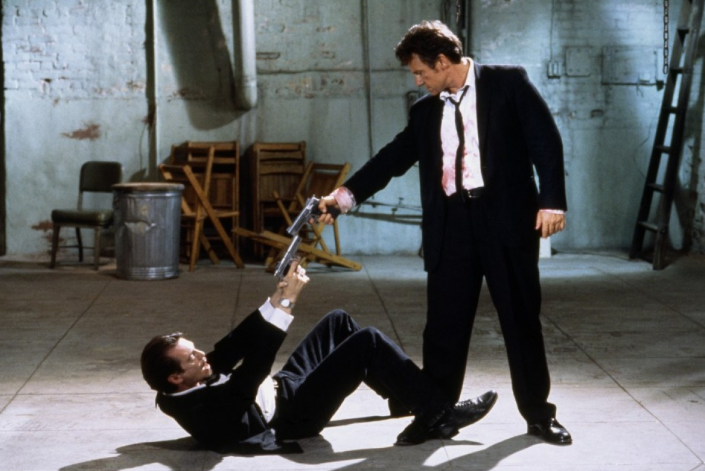
Where is our eye attracted first? Why?
Size. Focus. Lighting. Color.
Size. Mr. White (Harvey Keitel) on the right.
Focus. He’s one of the two objects in focus.
Lighting. Mr. White is large and in focus and Mr. Pink (Steve Buscemi) is highlighted by
a shaft of light.
Color. Both are black and white but the read on Mr. White’s shirt now really stands out.
(more…)
What type of lighting?
LIGHTING
-
3D Lighting Tutorial by Amaan Kram
Read more: 3D Lighting Tutorial by Amaan Kramhttp://www.amaanakram.com/lightingT/part1.htm
The goals of lighting in 3D computer graphics are more or less the same as those of real world lighting.
Lighting serves a basic function of bringing out, or pushing back the shapes of objects visible from the camera’s view.
It gives a two-dimensional image on the monitor an illusion of the third dimension-depth.But it does not just stop there. It gives an image its personality, its character. A scene lit in different ways can give a feeling of happiness, of sorrow, of fear etc., and it can do so in dramatic or subtle ways. Along with personality and character, lighting fills a scene with emotion that is directly transmitted to the viewer.
Trying to simulate a real environment in an artificial one can be a daunting task. But even if you make your 3D rendering look absolutely photo-realistic, it doesn’t guarantee that the image carries enough emotion to elicit a “wow” from the people viewing it.
Making 3D renderings photo-realistic can be hard. Putting deep emotions in them can be even harder. However, if you plan out your lighting strategy for the mood and emotion that you want your rendering to express, you make the process easier for yourself.
Each light source can be broken down in to 4 distinct components and analyzed accordingly.
· Intensity
· Direction
· Color
· SizeThe overall thrust of this writing is to produce photo-realistic images by applying good lighting techniques.
-
7 Easy Portrait Lighting Setups
Read more: 7 Easy Portrait Lighting SetupsButterfly
Loop
Rembrandt
Split
Rim
Broad
Short
-
Practical Aspects of Spectral Data and LEDs in Digital Content Production and Virtual Production – SIGGRAPH 2022
Read more: Practical Aspects of Spectral Data and LEDs in Digital Content Production and Virtual Production – SIGGRAPH 2022Comparison to the commercial side

https://www.ecolorled.com/blog/detail/what-is-rgb-rgbw-rgbic-strip-lights
RGBW (RGB + White) LED strip uses a 4-in-1 LED chip made up of red, green, blue, and white.
RGBWW (RGB + White + Warm White) LED strip uses either a 5-in-1 LED chip with red, green, blue, white, and warm white for color mixing. The only difference between RGBW and RGBWW is the intensity of the white color. The term RGBCCT consists of RGB and CCT. CCT (Correlated Color Temperature) means that the color temperature of the led strip light can be adjusted to change between warm white and white. Thus, RGBWW strip light is another name of RGBCCT strip.
RGBCW is the acronym for Red, Green, Blue, Cold, and Warm. These 5-in-1 chips are used in supper bright smart LED lighting products
-
Polarised vs unpolarized filtering
Read more: Polarised vs unpolarized filteringA light wave that is vibrating in more than one plane is referred to as unpolarized light. …
Polarized light waves are light waves in which the vibrations occur in a single plane. The process of transforming unpolarized light into polarized light is known as polarization.

en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Polarizing_filter_(photography)
The most common use of polarized technology is to reduce lighting complexity on the subject.
(more…)
Details such as glare and hard edges are not removed, but greatly reduced. -
Convert between light exposure and intensity
Read more: Convert between light exposure and intensityimport math,sys def Exposure2Intensity(exposure): exp = float(exposure) result = math.pow(2,exp) print(result) Exposure2Intensity(0) def Intensity2Exposure(intensity): inarg = float(intensity) if inarg == 0: print("Exposure of zero intensity is undefined.") return if inarg < 1e-323: inarg = max(inarg, 1e-323) print("Exposure of negative intensities is undefined. Clamping to a very small value instead (1e-323)") result = math.log(inarg, 2) print(result) Intensity2Exposure(0.1)Why Exposure?
Exposure is a stop value that multiplies the intensity by 2 to the power of the stop. Increasing exposure by 1 results in double the amount of light.
Artists think in “stops.” Doubling or halving brightness is easy math and common in grading and look-dev.
Exposure counts doublings in whole stops:- +1 stop = ×2 brightness
- −1 stop = ×0.5 brightness
This gives perceptually even controls across both bright and dark values.
Why Intensity?
Intensity is linear.
It’s what render engines and compositors expect when:- Summing values
- Averaging pixels
- Multiplying or filtering pixel data
Use intensity when you need the actual math on pixel/light data.
Formulas (from your Python)
- Intensity from exposure: intensity = 2**exposure
- Exposure from intensity: exposure = log₂(intensity)
Guardrails:
- Intensity must be > 0 to compute exposure.
- If intensity = 0 → exposure is undefined.
- Clamp tiny values (e.g.
1e−323) before using log₂.
Use Exposure (stops) when…
- You want artist-friendly sliders (−5…+5 stops)
- Adjusting look-dev or grading in even stops
- Matching plates with quick ±1 stop tweaks
- Tweening brightness changes smoothly across ranges
Use Intensity (linear) when…
- Storing raw pixel/light values
- Multiplying textures or lights by a gain
- Performing sums, averages, and filters
- Feeding values to render engines expecting linear data
Examples
- +2 stops → 2**2 = 4.0 (×4)
- +1 stop → 2**1 = 2.0 (×2)
- 0 stop → 2**0 = 1.0 (×1)
- −1 stop → 2**(−1) = 0.5 (×0.5)
- −2 stops → 2**(−2) = 0.25 (×0.25)
- Intensity 0.1 → exposure = log₂(0.1) ≈ −3.32
Rule of thumb
Think in stops (exposure) for controls and matching.
Compute in linear (intensity) for rendering and math. -
About green screens
Read more: About green screenshackaday.com/2015/02/07/how-green-screen-worked-before-computers/
www.newtek.com/blog/tips/best-green-screen-materials/
www.chromawall.com/blog//chroma-key-green
Chroma Key Green, the color of green screens is also known as Chroma Green and is valued at approximately 354C in the Pantone color matching system (PMS).
Chroma Green can be broken down in many different ways. Here is green screen green as other values useful for both physical and digital production:
Green Screen as RGB Color Value: 0, 177, 64
Green Screen as CMYK Color Value: 81, 0, 92, 0
Green Screen as Hex Color Value: #00b140
Green Screen as Websafe Color Value: #009933Chroma Key Green is reasonably close to an 18% gray reflectance.
Illuminate your green screen with an uniform source with less than 2/3 EV variation.
The level of brightness at any given f-stop should be equivalent to a 90% white card under the same lighting. -
Custom bokeh in a raytraced DOF render
Read more: Custom bokeh in a raytraced DOF renderTo achieve a custom pinhole camera effect with a custom bokeh in Arnold Raytracer, you can follow these steps:
- Set the render camera with a focal length around 50 (or as needed)
- Set the F-Stop to a high value (e.g., 22).
- Set the focus distance as you require
- Turn on DOF
- Place a plane a few cm in front of the camera.
- Texture the plane with a transparent shape at the center of it. (Transmission with no specular roughness)
COLLECTIONS
| Featured AI
| Design And Composition
| Explore posts
POPULAR SEARCHES
unreal | pipeline | virtual production | free | learn | photoshop | 360 | macro | google | nvidia | resolution | open source | hdri | real-time | photography basics | nuke
FEATURED POSTS
-
Python and TCL: Tips and Tricks for Foundry Nuke
-
N8N.io – From Zero to Your First AI Agent in 25 Minutes
-
Generative AI Glossary / AI Dictionary / AI Terminology
-
MiniMax-Remover – Taming Bad Noise Helps Video Object Removal Rotoscoping
-
How do LLMs like ChatGPT (Generative Pre-Trained Transformer) work? Explained by Deep-Fake Ryan Gosling
-
AnimationXpress.com interviews Daniele Tosti for TheCgCareer.com channel
-
Sensitivity of human eye
-
Jesse Zumstein – Jobs in games
Social Links
DISCLAIMER – Links and images on this website may be protected by the respective owners’ copyright. All data submitted by users through this site shall be treated as freely available to share.