COMPOSITION
-
Photography basics: Depth of Field and composition
Read more: Photography basics: Depth of Field and compositionDepth of field is the range within which focusing is resolved in a photo.
Aperture has a huge affect on to the depth of field.Changing the f-stops (f/#) of a lens will change aperture and as such the DOF.
f-stops are a just certain number which is telling you the size of the aperture. That’s how f-stop is related to aperture (and DOF).
If you increase f-stops, it will increase DOF, the area in focus (and decrease the aperture). On the other hand, decreasing the f-stop it will decrease DOF (and increase the aperture).
The red cone in the figure is an angular representation of the resolution of the system. Versus the dotted lines, which indicate the aperture coverage. Where the lines of the two cones intersect defines the total range of the depth of field.
This image explains why the longer the depth of field, the greater the range of clarity.
DESIGN
COLOR
-
PTGui 13 beta adds control through a Patch Editor
Read more: PTGui 13 beta adds control through a Patch EditorAdditions:
- Patch Editor (PTGui Pro)
- DNG output
- Improved RAW / DNG handling
- JPEG 2000 support
- Performance improvements
-
sRGB vs REC709 – An introduction and FFmpeg implementations
Read more: sRGB vs REC709 – An introduction and FFmpeg implementations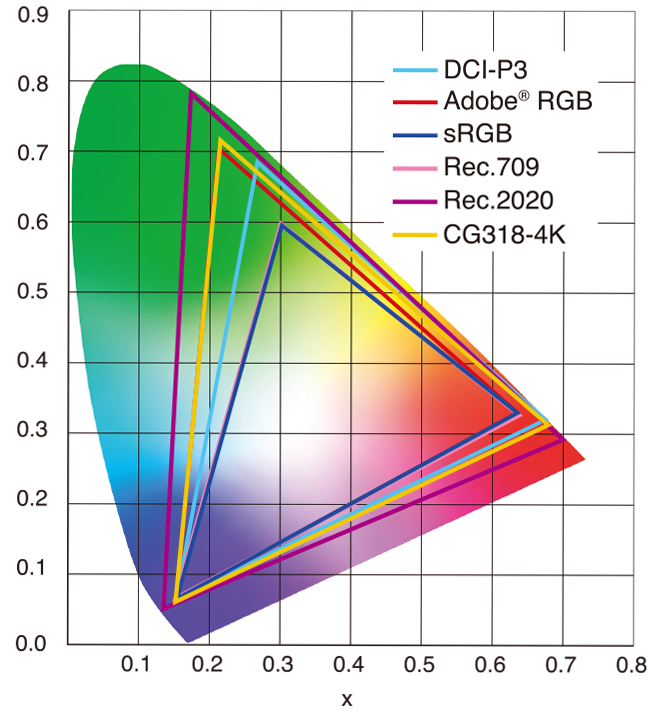
1. Basic Comparison
- What they are
- sRGB: A standard “web”/computer-display RGB color space defined by IEC 61966-2-1. It’s used for most monitors, cameras, printers, and the vast majority of images on the Internet.
- Rec. 709: An HD-video color space defined by ITU-R BT.709. It’s the go-to standard for HDTV broadcasts, Blu-ray discs, and professional video pipelines.
- Why they exist
- sRGB: Ensures consistent colors across different consumer devices (PCs, phones, webcams).
- Rec. 709: Ensures consistent colors across video production and playback chains (cameras → editing → broadcast → TV).
- What you’ll see
- On your desktop or phone, images tagged sRGB will look “right” without extra tweaking.
- On an HDTV or video-editing timeline, footage tagged Rec. 709 will display accurate contrast and hue on broadcast-grade monitors.
2. Digging Deeper
Feature sRGB Rec. 709 White point D65 (6504 K), same for both D65 (6504 K) Primaries (x,y) R: (0.640, 0.330) G: (0.300, 0.600) B: (0.150, 0.060) R: (0.640, 0.330) G: (0.300, 0.600) B: (0.150, 0.060) Gamut size Identical triangle on CIE 1931 chart Identical to sRGB Gamma / transfer Piecewise curve: approximate 2.2 with linear toe Pure power-law γ≈2.4 (often approximated as 2.2 in practice) Matrix coefficients N/A (pure RGB usage) Y = 0.2126 R + 0.7152 G + 0.0722 B (Rec. 709 matrix) Typical bit-depth 8-bit/channel (with 16-bit variants) 8-bit/channel (10-bit for professional video) Usage metadata Tagged as “sRGB” in image files (PNG, JPEG, etc.) Tagged as “bt709” in video containers (MP4, MOV) Color range Full-range RGB (0–255) Studio-range Y′CbCr (Y′ [16–235], Cb/Cr [16–240])
Why the Small Differences Matter
(more…) - What they are
-
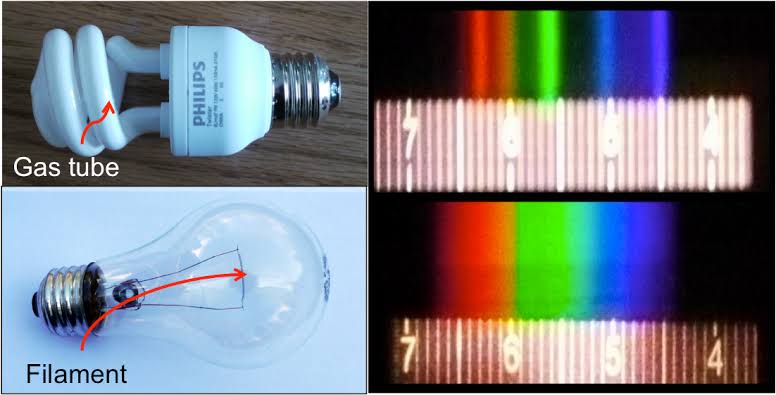
Space bodies’ components and light spectroscopy
Read more: Space bodies’ components and light spectroscopywww.plutorules.com/page-111-space-rocks.html
This help’s us understand the composition of components in/on solar system bodies.
Dips in the observed light spectrum, also known as, lines of absorption occur as gasses absorb energy from light at specific points along the light spectrum.
These dips or darkened zones (lines of absorption) leave a finger print which identify elements and compounds.
In this image the dark absorption bands appear as lines of emission which occur as the result of emitted not reflected (absorbed) light.
Lines of absorption
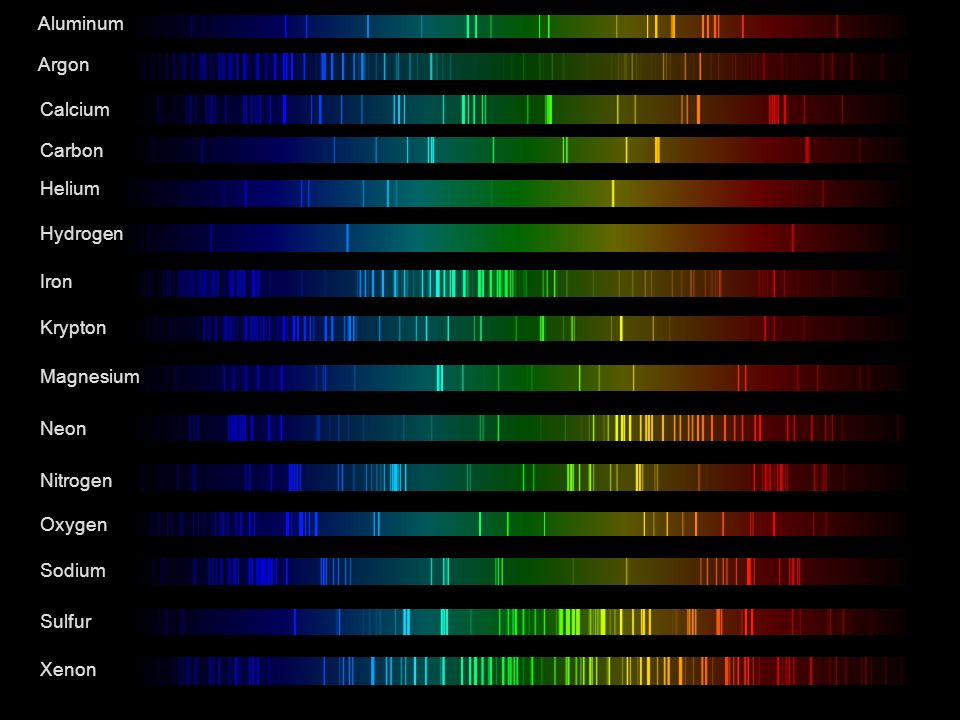 Lines of emission
Lines of emission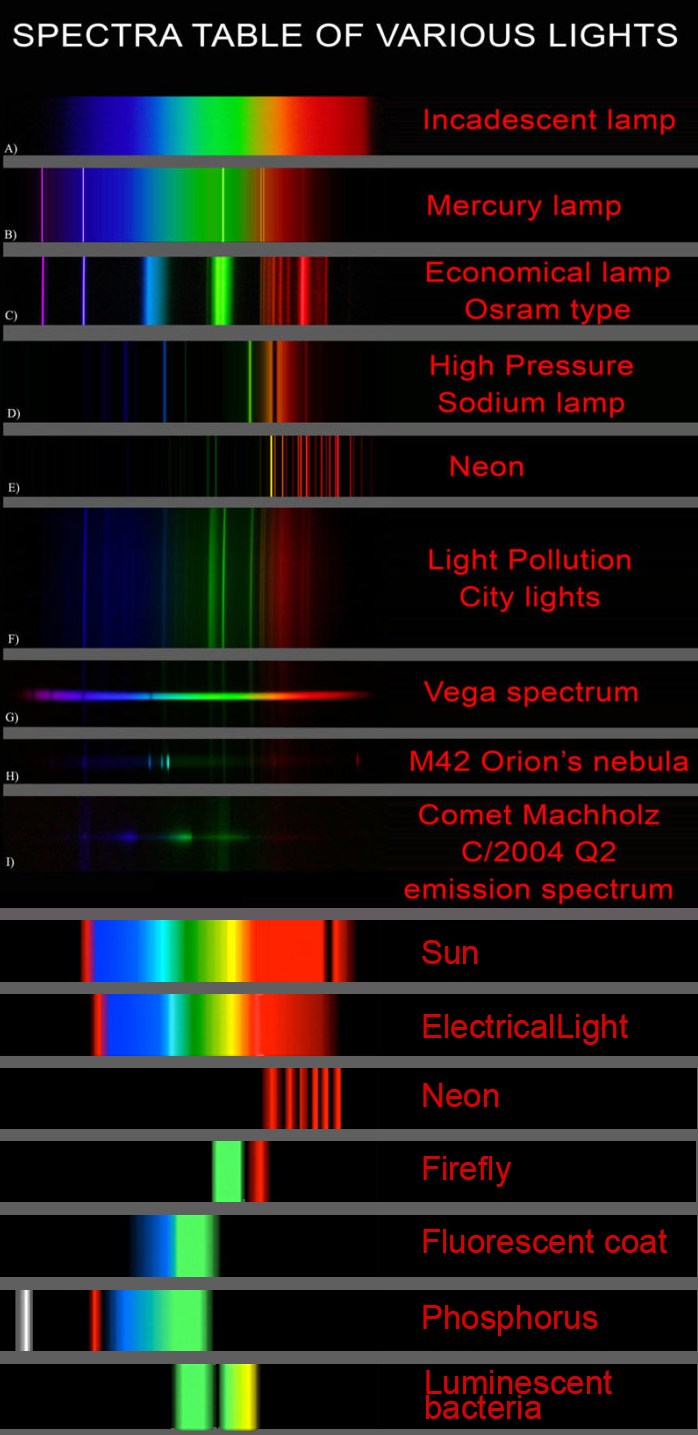
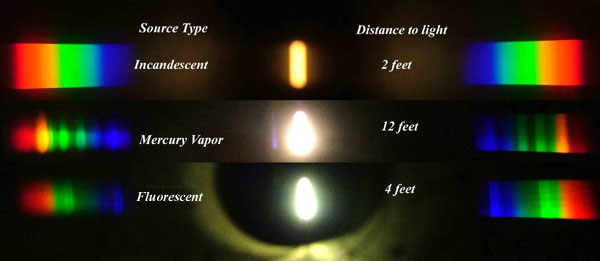

-
The 7 key elements of brand identity design + 10 corporate identity examples
Read more: The 7 key elements of brand identity design + 10 corporate identity exampleswww.lucidpress.com/blog/the-7-key-elements-of-brand-identity-design
1. Clear brand purpose and positioning
2. Thorough market research
3. Likable brand personality
4. Memorable logo
5. Attractive color palette
6. Professional typography
7. On-brand supporting graphics
-
Christopher Butler – Understanding the Eye-Mind Connection – Vision is a mental process
Read more: Christopher Butler – Understanding the Eye-Mind Connection – Vision is a mental processhttps://www.chrbutler.com/understanding-the-eye-mind-connection
The intricate relationship between the eyes and the brain, often termed the eye-mind connection, reveals that vision is predominantly a cognitive process. This understanding has profound implications for fields such as design, where capturing and maintaining attention is paramount. This essay delves into the nuances of visual perception, the brain’s role in interpreting visual data, and how this knowledge can be applied to effective design strategies.
This cognitive aspect of vision is evident in phenomena such as optical illusions, where the brain interprets visual information in a way that contradicts physical reality. These illusions underscore that what we “see” is not merely a direct recording of the external world but a constructed experience shaped by cognitive processes.
Understanding the cognitive nature of vision is crucial for effective design. Designers must consider how the brain processes visual information to create compelling and engaging visuals. This involves several key principles:
- Attention and Engagement
- Visual Hierarchy
- Cognitive Load Management
- Context and Meaning
LIGHTING
-
Photography basics: Solid Angle measures
Read more: Photography basics: Solid Angle measureshttp://www.calculator.org/property.aspx?name=solid+angle
A measure of how large the object appears to an observer looking from that point. Thus. A measure for objects in the sky. Useful to retuen the size of the sun and moon… and in perspective, how much of their contribution to lighting. Solid angle can be represented in ‘angular diameter’ as well.
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Solid_angle
http://www.mathsisfun.com/geometry/steradian.html
A solid angle is expressed in a dimensionless unit called a steradian (symbol: sr). By default in terms of the total celestial sphere and before atmospheric’s scattering, the Sun and the Moon subtend fractional areas of 0.000546% (Sun) and 0.000531% (Moon).
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Solid_angle#Sun_and_Moon
On earth the sun is likely closer to 0.00011 solid angle after athmospheric scattering. The sun as perceived from earth has a diameter of 0.53 degrees. This is about 0.000064 solid angle.
http://www.numericana.com/answer/angles.htm
The mean angular diameter of the full moon is 2q = 0.52° (it varies with time around that average, by about 0.009°). This translates into a solid angle of 0.0000647 sr, which means that the whole night sky covers a solid angle roughly one hundred thousand times greater than the full moon.
More info
http://lcogt.net/spacebook/using-angles-describe-positions-and-apparent-sizes-objects
http://amazing-space.stsci.edu/glossary/def.php.s=topic_astronomy
Angular Size
The apparent size of an object as seen by an observer; expressed in units of degrees (of arc), arc minutes, or arc seconds. The moon, as viewed from the Earth, has an angular diameter of one-half a degree.
The angle covered by the diameter of the full moon is about 31 arcmin or 1/2°, so astronomers would say the Moon’s angular diameter is 31 arcmin, or the Moon subtends an angle of 31 arcmin.
-
Photography basics: Lumens vs Candelas (candle) vs Lux vs FootCandle vs Watts vs Irradiance vs Illuminance
Read more: Photography basics: Lumens vs Candelas (candle) vs Lux vs FootCandle vs Watts vs Irradiance vs Illuminancehttps://www.translatorscafe.com/unit-converter/en-US/illumination/1-11/
The power output of a light source is measured using the unit of watts W. This is a direct measure to calculate how much power the light is going to drain from your socket and it is not relatable to the light brightness itself.
The amount of energy emitted from it per second. That energy comes out in a form of photons which we can crudely represent with rays of light coming out of the source. The higher the power the more rays emitted from the source in a unit of time.
Not all energy emitted is visible to the human eye, so we often rely on photometric measurements, which takes in account the sensitivity of human eye to different wavelenghts
Details in the post
(more…) -
Neural Microfacet Fields for Inverse Rendering
Read more: Neural Microfacet Fields for Inverse Renderinghttps://half-potato.gitlab.io/posts/nmf/
COLLECTIONS
| Featured AI
| Design And Composition
| Explore posts
POPULAR SEARCHES
unreal | pipeline | virtual production | free | learn | photoshop | 360 | macro | google | nvidia | resolution | open source | hdri | real-time | photography basics | nuke
FEATURED POSTS
-
3D Gaussian Splatting step by step beginner course
-
White Balance is Broken!
-
What the Boeing 737 MAX’s crashes can teach us about production business – the effects of commoditisation
-
Zibra.AI – Real-Time Volumetric Effects in Virtual Production. Now free for Indies!
-
SourceTree vs Github Desktop – Which one to use
-
Kling 1.6 and competitors – advanced tests and comparisons
-
Embedding frame ranges into Quicktime movies with FFmpeg
-
AI and the Law – Netflix : Using Generative AI in Content Production
Social Links
DISCLAIMER – Links and images on this website may be protected by the respective owners’ copyright. All data submitted by users through this site shall be treated as freely available to share.











