COMPOSITION
DESIGN
-
Realistic Avengers action figures
Read more: Realistic Avengers action figureshttp://kotaku.com/5911846/these-avengers-action-figures-look-so-real-youll-think-theyre-tiny-actors
http://www.sideshowtoy.com/?page_id=37555&ref=Avengers2012
http://www.sideshowtoy.com/?page_id=4489&sku=9017301&ref=ref=avengersLP_9017301#!prettyPhoto/0/
http://animagetoyznews.blogspot.co.nz/
-
Pantheon of the War – The colossal war painting
Read more: Pantheon of the War – The colossal war paintingFour years in the making with the help of 150 artists, in commemoration of WW1.
edition.cnn.com/style/article/pantheon-de-la-guerre-wwi-painting/index.html
A panoramic canvas measuring 402 feet (122 meters) around and 45 feet (13.7 meters) high. It contained over 5,000 life-size portraits of war heroes, royalty and government officials from the Allies of World War I.
Partial section upload:
COLOR
-
“Reality” is constructed by your brain. Here’s what that means, and why it matters.
Read more: “Reality” is constructed by your brain. Here’s what that means, and why it matters.“Fix your gaze on the black dot on the left side of this image. But wait! Finish reading this paragraph first. As you gaze at the left dot, try to answer this question: In what direction is the object on the right moving? Is it drifting diagonally, or is it moving up and down?”

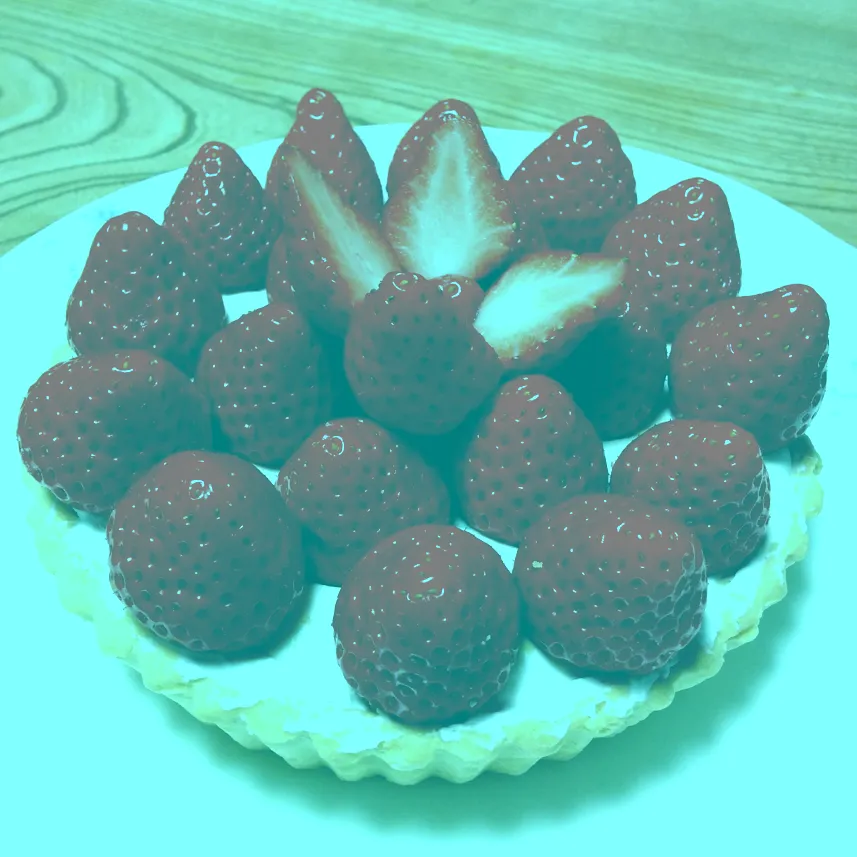
What color are these strawberries?

Are A and B the same gray?

-
Capturing textures albedo
Read more: Capturing textures albedoBuilding a Portable PBR Texture Scanner by Stephane Lb
http://rtgfx.com/pbr-texture-scanner/How To Split Specular And Diffuse In Real Images, by John Hable
http://filmicworlds.com/blog/how-to-split-specular-and-diffuse-in-real-images/Capturing albedo using a Spectralon
https://www.activision.com/cdn/research/Real_World_Measurements_for_Call_of_Duty_Advanced_Warfare.pdfReal_World_Measurements_for_Call_of_Duty_Advanced_Warfare.pdf
Spectralon is a teflon-based pressed powderthat comes closest to being a pure Lambertian diffuse material that reflects 100% of all light. If we take an HDR photograph of the Spectralon alongside the material to be measured, we can derive thediffuse albedo of that material.
The process to capture diffuse reflectance is very similar to the one outlined by Hable.
1. We put a linear polarizing filter in front of the camera lens and a second linear polarizing filterin front of a modeling light or a flash such that the two filters are oriented perpendicular to eachother, i.e. cross polarized.
2. We place Spectralon close to and parallel with the material we are capturing and take brack-eted shots of the setup7. Typically, we’ll take nine photographs, from -4EV to +4EV in 1EVincrements.
3. We convert the bracketed shots to a linear HDR image. We found that many HDR packagesdo not produce an HDR image in which the pixel values are linear. PTGui is an example of apackage which does generate a linear HDR image. At this point, because of the cross polarization,the image is one of surface diffuse response.
4. We open the file in Photoshop and normalize the image by color picking the Spectralon, filling anew layer with that color and setting that layer to “Divide”. This sets the Spectralon to 1 in theimage. All other color values are relative to this so we can consider them as diffuse albedo.
-
GretagMacbeth Color Checker Numeric Values and Middle Gray
Read more: GretagMacbeth Color Checker Numeric Values and Middle GrayThe human eye perceives half scene brightness not as the linear 50% of the present energy (linear nature values) but as 18% of the overall brightness. We are biased to perceive more information in the dark and contrast areas. A Macbeth chart helps with calibrating back into a photographic capture into this “human perspective” of the world.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Middle_gray
In photography, painting, and other visual arts, middle gray or middle grey is a tone that is perceptually about halfway between black and white on a lightness scale in photography and printing, it is typically defined as 18% reflectance in visible light
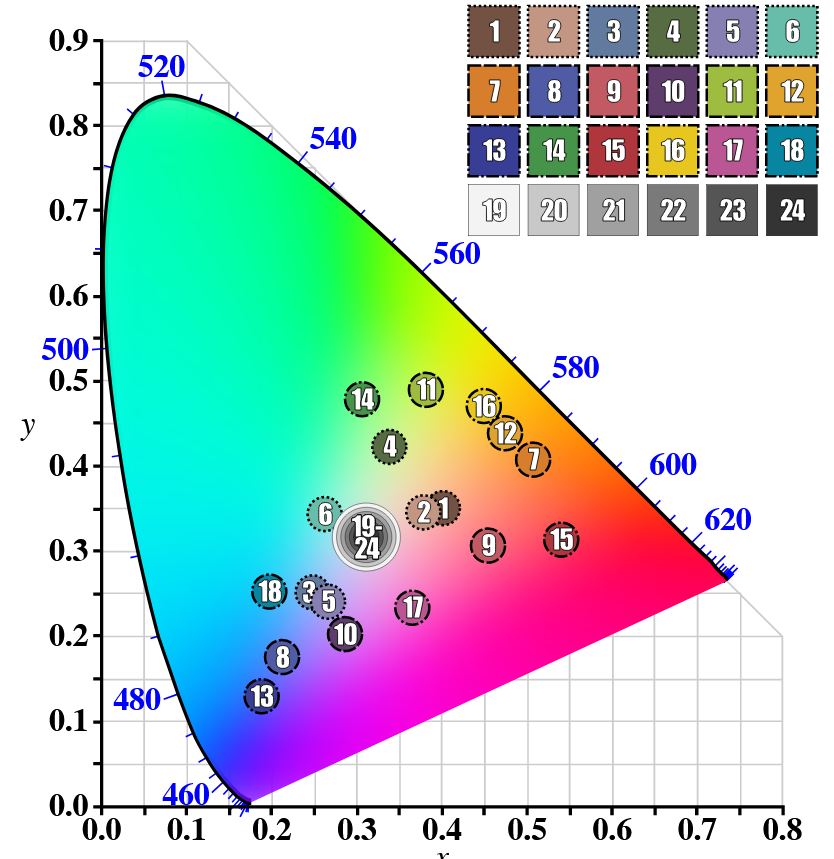
Light meters, cameras, and pictures are often calibrated using an 18% gray card[4][5][6] or a color reference card such as a ColorChecker. On the assumption that 18% is similar to the average reflectance of a scene, a grey card can be used to estimate the required exposure of the film.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ColorChecker
(more…)
LIGHTING
-
studiobinder.com – What is Tenebrism and Hard Lighting — The Art of Light and Shadow and chiaroscuro Explained
Read more: studiobinder.com – What is Tenebrism and Hard Lighting — The Art of Light and Shadow and chiaroscuro Explainedhttps://www.studiobinder.com/blog/what-is-tenebrism-art-definition/
https://www.studiobinder.com/blog/what-is-hard-light-photography/
-
Composition – These are the basic lighting techniques you need to know for photography and film
Read more: Composition – These are the basic lighting techniques you need to know for photography and filmhttp://www.diyphotography.net/basic-lighting-techniques-need-know-photography-film/
Amongst the basic techniques, there’s…
1- Side lighting – Literally how it sounds, lighting a subject from the side when they’re faced toward you
2- Rembrandt lighting – Here the light is at around 45 degrees over from the front of the subject, raised and pointing down at 45 degrees
3- Back lighting – Again, how it sounds, lighting a subject from behind. This can help to add drama with silouettes
4- Rim lighting – This produces a light glowing outline around your subject
5- Key light – The main light source, and it’s not necessarily always the brightest light source
6- Fill light – This is used to fill in the shadows and provide detail that would otherwise be blackness
7- Cross lighting – Using two lights placed opposite from each other to light two subjects
-
3D Lighting Tutorial by Amaan Kram
Read more: 3D Lighting Tutorial by Amaan Kramhttp://www.amaanakram.com/lightingT/part1.htm
The goals of lighting in 3D computer graphics are more or less the same as those of real world lighting.
Lighting serves a basic function of bringing out, or pushing back the shapes of objects visible from the camera’s view.
It gives a two-dimensional image on the monitor an illusion of the third dimension-depth.But it does not just stop there. It gives an image its personality, its character. A scene lit in different ways can give a feeling of happiness, of sorrow, of fear etc., and it can do so in dramatic or subtle ways. Along with personality and character, lighting fills a scene with emotion that is directly transmitted to the viewer.
Trying to simulate a real environment in an artificial one can be a daunting task. But even if you make your 3D rendering look absolutely photo-realistic, it doesn’t guarantee that the image carries enough emotion to elicit a “wow” from the people viewing it.
Making 3D renderings photo-realistic can be hard. Putting deep emotions in them can be even harder. However, if you plan out your lighting strategy for the mood and emotion that you want your rendering to express, you make the process easier for yourself.
Each light source can be broken down in to 4 distinct components and analyzed accordingly.
· Intensity
· Direction
· Color
· SizeThe overall thrust of this writing is to produce photo-realistic images by applying good lighting techniques.
-
Open Source Nvidia Omniverse
Read more: Open Source Nvidia Omniverseblogs.nvidia.com/blog/2019/03/18/omniverse-collaboration-platform/
developer.nvidia.com/nvidia-omniverse
An open, Interactive 3D Design Collaboration Platform for Multi-Tool Workflows to simplify studio workflows for real-time graphics.
It supports Pixar’s Universal Scene Description technology for exchanging information about modeling, shading, animation, lighting, visual effects and rendering across multiple applications.
It also supports NVIDIA’s Material Definition Language, which allows artists to exchange information about surface materials across multiple tools.
With Omniverse, artists can see live updates made by other artists working in different applications. They can also see changes reflected in multiple tools at the same time.
For example an artist using Maya with a portal to Omniverse can collaborate with another artist using UE4 and both will see live updates of each others’ changes in their application.
-
DiffusionLight: HDRI Light Probes for Free by Painting a Chrome Ball
Read more: DiffusionLight: HDRI Light Probes for Free by Painting a Chrome Ballhttps://diffusionlight.github.io/
https://github.com/DiffusionLight/DiffusionLight
https://github.com/DiffusionLight/DiffusionLight?tab=MIT-1-ov-file#readme
https://colab.research.google.com/drive/15pC4qb9mEtRYsW3utXkk-jnaeVxUy-0S
“a simple yet effective technique to estimate lighting in a single input image. Current techniques rely heavily on HDR panorama datasets to train neural networks to regress an input with limited field-of-view to a full environment map. However, these approaches often struggle with real-world, uncontrolled settings due to the limited diversity and size of their datasets. To address this problem, we leverage diffusion models trained on billions of standard images to render a chrome ball into the input image. Despite its simplicity, this task remains challenging: the diffusion models often insert incorrect or inconsistent objects and cannot readily generate images in HDR format. Our research uncovers a surprising relationship between the appearance of chrome balls and the initial diffusion noise map, which we utilize to consistently generate high-quality chrome balls. We further fine-tune an LDR difusion model (Stable Diffusion XL) with LoRA, enabling it to perform exposure bracketing for HDR light estimation. Our method produces convincing light estimates across diverse settings and demonstrates superior generalization to in-the-wild scenarios.”

-
Romain Chauliac – LightIt a lighting script for Maya and Arnold
Read more: Romain Chauliac – LightIt a lighting script for Maya and ArnoldLightIt is a script for Maya and Arnold that will help you and improve your lighting workflow.
Thanks to preset studio lighting components (lights, backdrop…), high quality studio scenes and HDRI library manager.https://www.artstation.com/artwork/393emJ
COLLECTIONS
| Featured AI
| Design And Composition
| Explore posts
POPULAR SEARCHES
unreal | pipeline | virtual production | free | learn | photoshop | 360 | macro | google | nvidia | resolution | open source | hdri | real-time | photography basics | nuke
FEATURED POSTS
Social Links
DISCLAIMER – Links and images on this website may be protected by the respective owners’ copyright. All data submitted by users through this site shall be treated as freely available to share.