COMPOSITION
-
Composition and The Expressive Nature Of Light
Read more: Composition and The Expressive Nature Of Lighthttp://www.huffingtonpost.com/bill-danskin/post_12457_b_10777222.html
George Sand once said “ The artist vocation is to send light into the human heart.”
-
7 Commandments of Film Editing and composition
Read more: 7 Commandments of Film Editing and composition1. Watch every frame of raw footage twice. On the second time, take notes. If you don’t do this and try to start developing a scene premature, then it’s a big disservice to yourself and to the director, actors and production crew.
2. Nurture the relationships with the director. You are the secondary person in the relationship. Be calm and continually offer solutions. Get the main intention of the film as soon as possible from the director.
3. Organize your media so that you can find any shot instantly.
4. Factor in extra time for renders, exports, errors and crashes.
5. Attempt edits and ideas that shouldn’t work. It just might work. Until you do it and watch it, you won’t know. Don’t rule out ideas just because they don’t make sense in your mind.
6. Spend more time on your audio. It’s the glue of your edit. AUDIO SAVES EVERYTHING. Create fluid and seamless audio under your video.
7. Make cuts for the scene, but always in context for the whole film. Have a macro and a micro view at all times.
-
Composition – cinematography Cheat Sheet
Read more: Composition – cinematography Cheat Sheet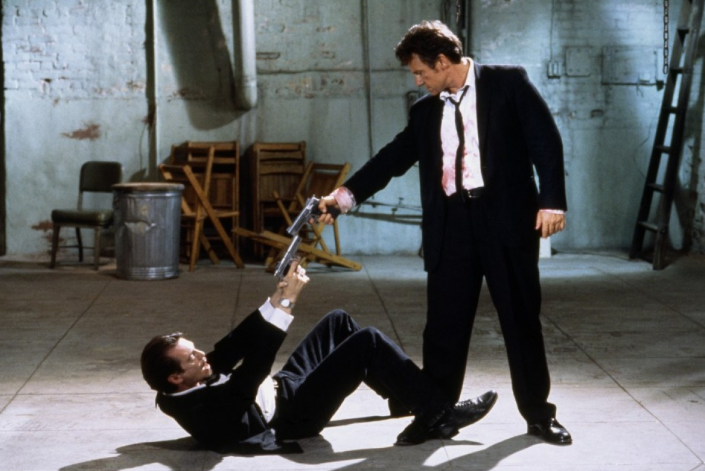
Where is our eye attracted first? Why?
Size. Focus. Lighting. Color.
Size. Mr. White (Harvey Keitel) on the right.
Focus. He’s one of the two objects in focus.
Lighting. Mr. White is large and in focus and Mr. Pink (Steve Buscemi) is highlighted by
a shaft of light.
Color. Both are black and white but the read on Mr. White’s shirt now really stands out.
(more…)
What type of lighting? -
Mastering Camera Shots and Angles: A Guide for Filmmakers
Read more: Mastering Camera Shots and Angles: A Guide for Filmmakershttps://website.ltx.studio/blog/mastering-camera-shots-and-angles
1. Extreme Wide Shot

2. Wide Shot

3. Medium Shot

4. Close Up
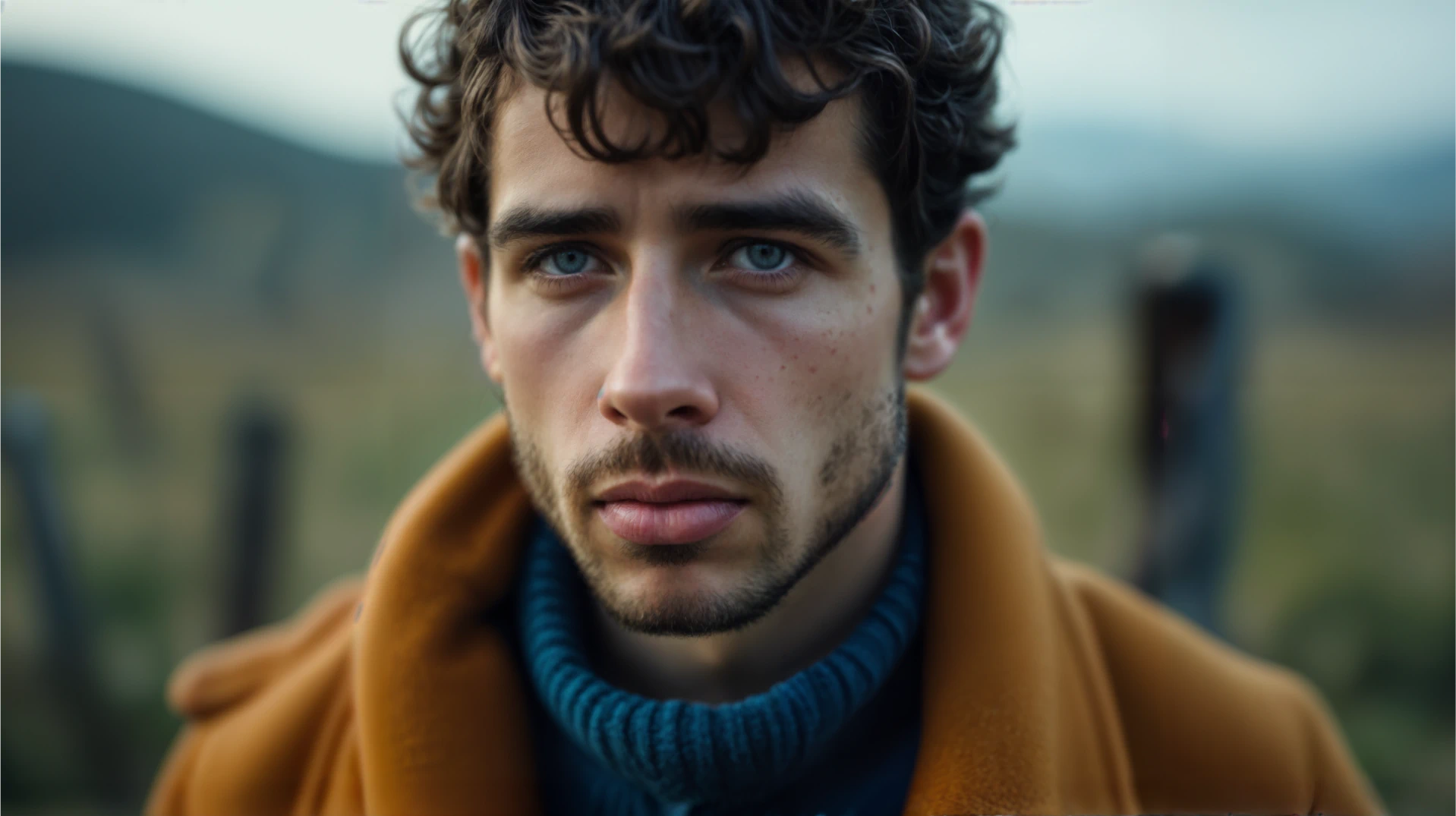

5. Extreme Close Up
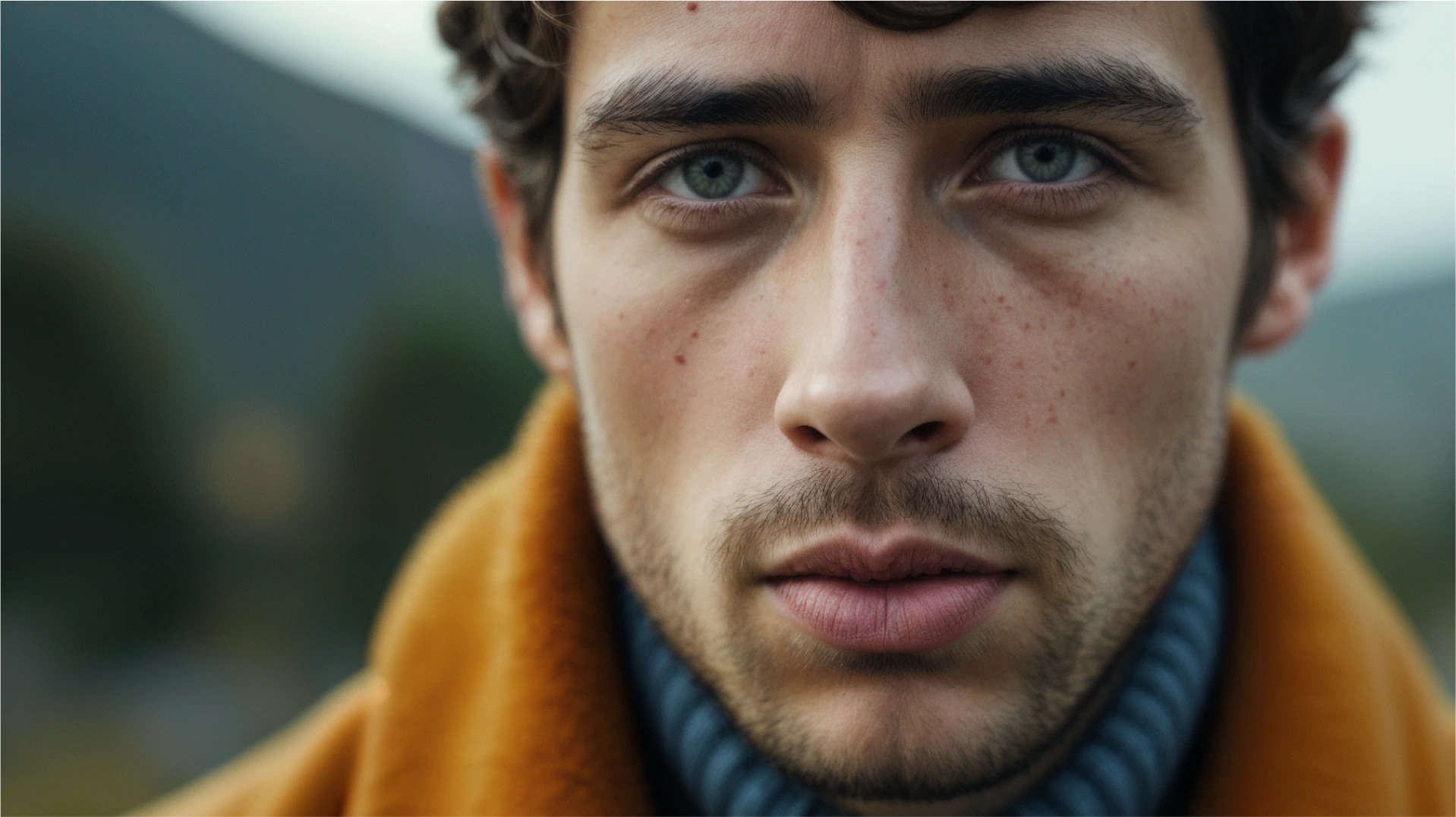

DESIGN
-
Arminas Valunas – “Coca-Cola: Wherever you are.”
Read more: Arminas Valunas – “Coca-Cola: Wherever you are.”Arminas created this using Juggernaut Xl model and QR Code Monster SDXL ControlNet.
His pipeline:
Static Images – Forge UI.
Upscaled with Leonardo AI universal upscaler.
Animated with Runway ML and Minimax.
Video upscale – Topaz Video AI.
Composited in Adobe Premiere.
Juggernaut Xl download here:
https://civitai.com/models/133005/juggernaut-xl
QR Code Monster SDXL:
https://civitai.com/models/197247?modelVersionId=221829 -
Hand made Settlers of Catan board
Read more: Hand made Settlers of Catan boardtrytrytry.de/2016/07/mega-diy-siedler-von-catan-in-3d/
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Lqww2yZkeh0
COLOR
-
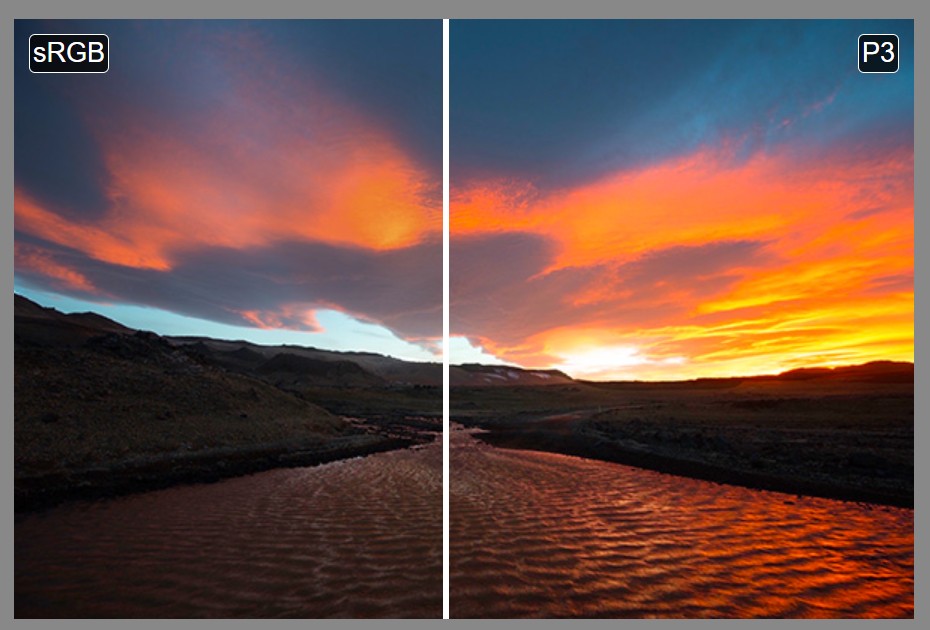
Colormaxxing – What if I told you that rgb(255, 0, 0) is not actually the reddest red you can have in your browser?
Read more: Colormaxxing – What if I told you that rgb(255, 0, 0) is not actually the reddest red you can have in your browser?https://karuna.dev/colormaxxing
https://webkit.org/blog-files/color-gamut/comparison.html
https://oklch.com/#70,0.1,197,100

-
About green screens
Read more: About green screenshackaday.com/2015/02/07/how-green-screen-worked-before-computers/
www.newtek.com/blog/tips/best-green-screen-materials/
www.chromawall.com/blog//chroma-key-green
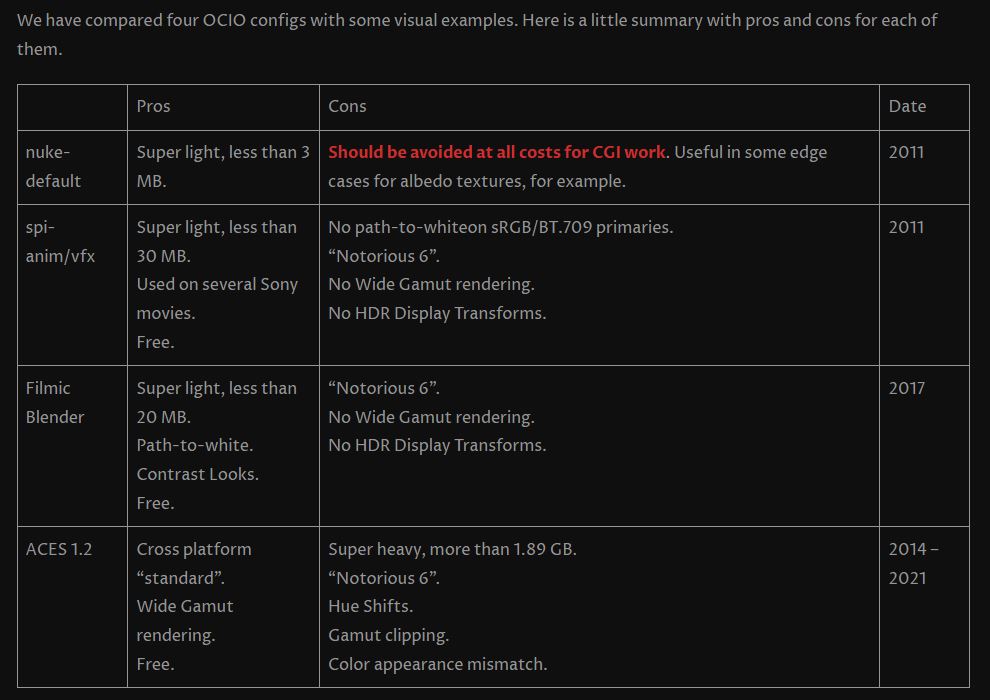
Chroma Key Green, the color of green screens is also known as Chroma Green and is valued at approximately 354C in the Pantone color matching system (PMS).
Chroma Green can be broken down in many different ways. Here is green screen green as other values useful for both physical and digital production:
Green Screen as RGB Color Value: 0, 177, 64
Green Screen as CMYK Color Value: 81, 0, 92, 0
Green Screen as Hex Color Value: #00b140
Green Screen as Websafe Color Value: #009933Chroma Key Green is reasonably close to an 18% gray reflectance.
Illuminate your green screen with an uniform source with less than 2/3 EV variation.
The level of brightness at any given f-stop should be equivalent to a 90% white card under the same lighting. -
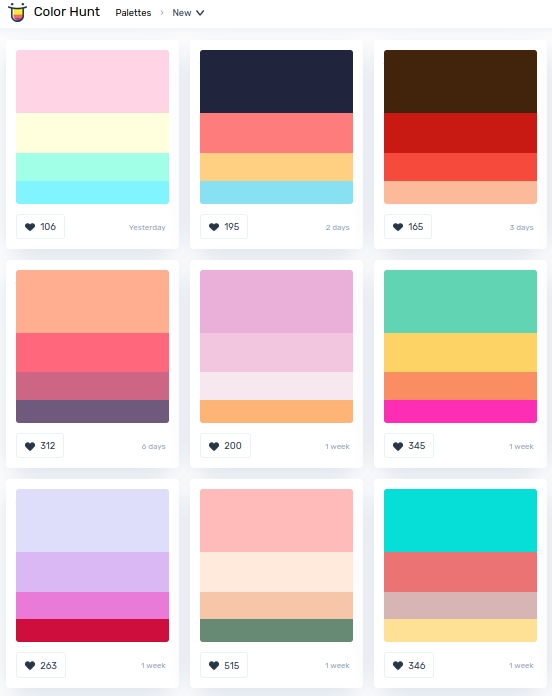
colorhunt.co
Read more: colorhunt.coColor Hunt is a free and open platform for color inspiration with thousands of trendy hand-picked color palettes.
-
mmColorTarget – Nuke Gizmo for color matching a MacBeth chart
Read more: mmColorTarget – Nuke Gizmo for color matching a MacBeth charthttps://www.marcomeyer-vfx.de/posts/2014-04-11-mmcolortarget-nuke-gizmo/
https://www.marcomeyer-vfx.de/posts/mmcolortarget-nuke-gizmo/
https://vimeo.com/9.1652466e+07
https://www.nukepedia.com/gizmos/colour/mmcolortarget
-
Tim Kang – calibrated white light values in sRGB color space
Read more: Tim Kang – calibrated white light values in sRGB color space8bit sRGB encoded
2000K 255 139 22
2700K 255 172 89
3000K 255 184 109
3200K 255 190 122
4000K 255 211 165
4300K 255 219 178
D50 255 235 205
D55 255 243 224
D5600 255 244 227
D6000 255 249 240
D65 255 255 255
D10000 202 221 255
D20000 166 196 2558bit Rec709 Gamma 2.4
2000K 255 145 34
2700K 255 177 97
3000K 255 187 117
3200K 255 193 129
4000K 255 214 170
4300K 255 221 182
D50 255 236 208
D55 255 243 226
D5600 255 245 229
D6000 255 250 241
D65 255 255 255
D10000 204 222 255
D20000 170 199 2558bit Display P3 encoded
2000K 255 154 63
2700K 255 185 109
3000K 255 195 127
3200K 255 201 138
4000K 255 219 176
4300K 255 225 187
D50 255 239 212
D55 255 245 228
D5600 255 246 231
D6000 255 251 242
D65 255 255 255
D10000 208 223 255
D20000 175 199 25510bit Rec2020 PQ (100 nits)
2000K 520 435 273
2700K 520 466 358
3000K 520 475 384
3200K 520 480 399
4000K 520 495 446
4300K 520 500 458
D50 520 510 482
D55 520 514 497
D5600 520 514 500
D6000 520 517 509
D65 520 520 520
D10000 479 489 520
D20000 448 464 520 -
A Brief History of Color in Art
Read more: A Brief History of Color in Artwww.artsy.net/article/the-art-genome-project-a-brief-history-of-color-in-art
Of all the pigments that have been banned over the centuries, the color most missed by painters is likely Lead White.
This hue could capture and reflect a gleam of light like no other, though its production was anything but glamorous. The 17th-century Dutch method for manufacturing the pigment involved layering cow and horse manure over lead and vinegar. After three months in a sealed room, these materials would combine to create flakes of pure white. While scientists in the late 19th century identified lead as poisonous, it wasn’t until 1978 that the United States banned the production of lead white paint.
More reading:
www.canva.com/learn/color-meanings/https://www.infogrades.com/history-events-infographics/bizarre-history-of-colors/
LIGHTING
-
NVidia DiffusionRenderer – Neural Inverse and Forward Rendering with Video Diffusion Models. How NVIDIA reimagined relighting
Read more: NVidia DiffusionRenderer – Neural Inverse and Forward Rendering with Video Diffusion Models. How NVIDIA reimagined relightinghttps://www.fxguide.com/quicktakes/diffusing-reality-how-nvidia-reimagined-relighting/
https://research.nvidia.com/labs/toronto-ai/DiffusionRenderer/
-
What’s the Difference Between Ray Casting, Ray Tracing, Path Tracing and Rasterization? Physical light tracing…
Read more: What’s the Difference Between Ray Casting, Ray Tracing, Path Tracing and Rasterization? Physical light tracing…RASTERIZATION
Rasterisation (or rasterization) is the task of taking the information described in a vector graphics format OR the vertices of triangles making 3D shapes and converting them into a raster image (a series of pixels, dots or lines, which, when displayed together, create the image which was represented via shapes), or in other words “rasterizing” vectors or 3D models onto a 2D plane for display on a computer screen.For each triangle of a 3D shape, you project the corners of the triangle on the virtual screen with some math (projective geometry). Then you have the position of the 3 corners of the triangle on the pixel screen. Those 3 points have texture coordinates, so you know where in the texture are the 3 corners. The cost is proportional to the number of triangles, and is only a little bit affected by the screen resolution.
In computer graphics, a raster graphics or bitmap image is a dot matrix data structure that represents a generally rectangular grid of pixels (points of color), viewable via a monitor, paper, or other display medium.
With rasterization, objects on the screen are created from a mesh of virtual triangles, or polygons, that create 3D models of objects. A lot of information is associated with each vertex, including its position in space, as well as information about color, texture and its “normal,” which is used to determine the way the surface of an object is facing.
Computers then convert the triangles of the 3D models into pixels, or dots, on a 2D screen. Each pixel can be assigned an initial color value from the data stored in the triangle vertices.
Further pixel processing or “shading,” including changing pixel color based on how lights in the scene hit the pixel, and applying one or more textures to the pixel, combine to generate the final color applied to a pixel.
The main advantage of rasterization is its speed. However, rasterization is simply the process of computing the mapping from scene geometry to pixels and does not prescribe a particular way to compute the color of those pixels. So it cannot take shading, especially the physical light, into account and it cannot promise to get a photorealistic output. That’s a big limitation of rasterization.
There are also multiple problems:
If you have two triangles one is behind the other, you will draw twice all the pixels. you only keep the pixel from the triangle that is closer to you (Z-buffer), but you still do the work twice.
The borders of your triangles are jagged as it is hard to know if a pixel is in the triangle or out. You can do some smoothing on those, that is anti-aliasing.
You have to handle every triangles (including the ones behind you) and then see that they do not touch the screen at all. (we have techniques to mitigate this where we only look at triangles that are in the field of view)
Transparency is hard to handle (you can’t just do an average of the color of overlapping transparent triangles, you have to do it in the right order)
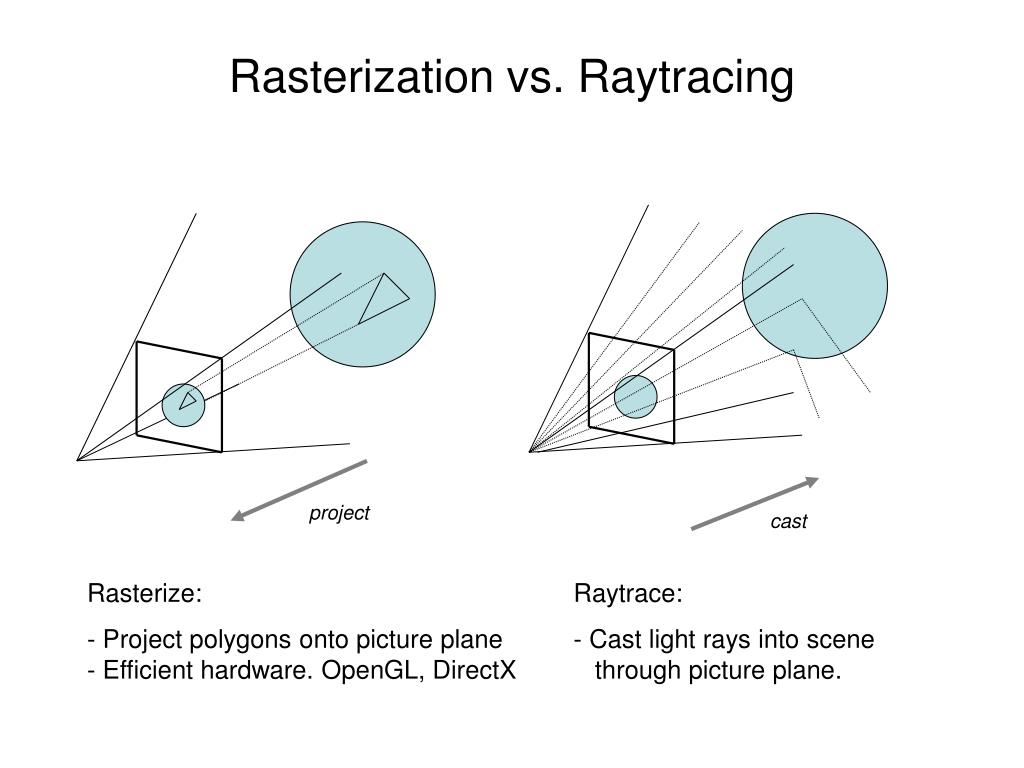
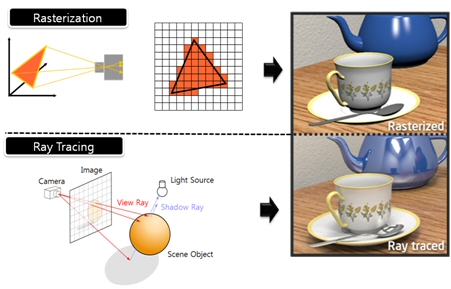
RAY CASTING
It is almost the exact reverse of rasterization: you start from the virtual screen instead of the vector or 3D shapes, and you project a ray, starting from each pixel of the screen, until it intersect with a triangle.The cost is directly correlated to the number of pixels in the screen and you need a really cheap way of finding the first triangle that intersect a ray. In the end, it is more expensive than rasterization but it will, by design, ignore the triangles that are out of the field of view.
You can use it to continue after the first triangle it hit, to take a little bit of the color of the next one, etc… This is useful to handle the border of the triangle cleanly (less jagged) and to handle transparency correctly.
RAYTRACING
Same idea as ray casting except once you hit a triangle you reflect on it and go into a different direction. The number of reflection you allow is the “depth” of your ray tracing. The color of the pixel can be calculated, based off the light source and all the polygons it had to reflect off of to get to that screen pixel.The easiest way to think of ray tracing is to look around you, right now. The objects you’re seeing are illuminated by beams of light. Now turn that around and follow the path of those beams backwards from your eye to the objects that light interacts with. That’s ray tracing.
Ray tracing is eye-oriented process that needs walking through each pixel looking for what object should be shown there, which is also can be described as a technique that follows a beam of light (in pixels) from a set point and simulates how it reacts when it encounters objects.
Compared with rasterization, ray tracing is hard to be implemented in real time, since even one ray can be traced and processed without much trouble, but after one ray bounces off an object, it can turn into 10 rays, and those 10 can turn into 100, 1000…The increase is exponential, and the the calculation for all these rays will be time consuming.
Historically, computer hardware hasn’t been fast enough to use these techniques in real time, such as in video games. Moviemakers can take as long as they like to render a single frame, so they do it offline in render farms. Video games have only a fraction of a second. As a result, most real-time graphics rely on the another technique called rasterization.
PATH TRACING
Path tracing can be used to solve more complex lighting situations.
Path tracing is a type of ray tracing. When using path tracing for rendering, the rays only produce a single ray per bounce. The rays do not follow a defined line per bounce (to a light, for example), but rather shoot off in a random direction. The path tracing algorithm then takes a random sampling of all of the rays to create the final image. This results in sampling a variety of different types of lighting.When a ray hits a surface it doesn’t trace a path to every light source, instead it bounces the ray off the surface and keeps bouncing it until it hits a light source or exhausts some bounce limit.
It then calculates the amount of light transferred all the way to the pixel, including any color information gathered from surfaces along the way.
It then averages out the values calculated from all the paths that were traced into the scene to get the final pixel color value.It requires a ton of computing power and if you don’t send out enough rays per pixel or don’t trace the paths far enough into the scene then you end up with a very spotty image as many pixels fail to find any light sources from their rays. So when you increase the the samples per pixel, you can see the image quality becomes better and better.
Ray tracing tends to be more efficient than path tracing. Basically, the render time of a ray tracer depends on the number of polygons in the scene. The more polygons you have, the longer it will take.
Meanwhile, the rendering time of a path tracer can be indifferent to the number of polygons, but it is related to light situation: If you add a light, transparency, translucence, or other shader effects, the path tracer will slow down considerably.blogs.nvidia.com/blog/2018/03/19/whats-difference-between-ray-tracing-rasterization/
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Rasterisation
https://www.quora.com/Whats-the-difference-between-ray-tracing-and-path-tracing
-
Debayer – A free command line tool to convert camera raw images into scene-linear exr
Read more: Debayer – A free command line tool to convert camera raw images into scene-linear exr
https://github.com/jedypod/debayer
The only required dependency is oiiotool. However other “debayer engines” are also supported.
- OpenImageIO – oiiotool is used for converting debayered tif images to exr.
- Debayer Engines
- RawTherapee – Powerful raw development software used to decode raw images. High quality, good selection of debayer algorithms, and more advanced raw processing like chromatic aberration removal.
- LibRaw – dcraw_emu commandline utility included with LibRaw. Optional alternative for debayer. Simple, fast and effective.
- Darktable – Uses darktable-cli plus an xmp config to process.
- vkdt – uses vkdt-cli to debayer. Pretty experimental still. Uses Vulkan for image processing. Stupidly fast. Pretty limited.
-
3D Lighting Tutorial by Amaan Kram
Read more: 3D Lighting Tutorial by Amaan Kramhttp://www.amaanakram.com/lightingT/part1.htm
The goals of lighting in 3D computer graphics are more or less the same as those of real world lighting.
Lighting serves a basic function of bringing out, or pushing back the shapes of objects visible from the camera’s view.
It gives a two-dimensional image on the monitor an illusion of the third dimension-depth.But it does not just stop there. It gives an image its personality, its character. A scene lit in different ways can give a feeling of happiness, of sorrow, of fear etc., and it can do so in dramatic or subtle ways. Along with personality and character, lighting fills a scene with emotion that is directly transmitted to the viewer.
Trying to simulate a real environment in an artificial one can be a daunting task. But even if you make your 3D rendering look absolutely photo-realistic, it doesn’t guarantee that the image carries enough emotion to elicit a “wow” from the people viewing it.
Making 3D renderings photo-realistic can be hard. Putting deep emotions in them can be even harder. However, if you plan out your lighting strategy for the mood and emotion that you want your rendering to express, you make the process easier for yourself.
Each light source can be broken down in to 4 distinct components and analyzed accordingly.
· Intensity
· Direction
· Color
· SizeThe overall thrust of this writing is to produce photo-realistic images by applying good lighting techniques.
COLLECTIONS
| Featured AI
| Design And Composition
| Explore posts
POPULAR SEARCHES
unreal | pipeline | virtual production | free | learn | photoshop | 360 | macro | google | nvidia | resolution | open source | hdri | real-time | photography basics | nuke
FEATURED POSTS
-
Daniele Tosti Interview for the magazine InCG, Taiwan, Issue 28, 201609
-
QR code logos
-
Convert 2D Images or Text to 3D Models
-
Jesse Zumstein – Jobs in games
-
AnimationXpress.com interviews Daniele Tosti for TheCgCareer.com channel
-
SourceTree vs Github Desktop – Which one to use
-
Principles of Animation with Alan Becker, Dermot OConnor and Shaun Keenan
-
Ross Pettit on The Agile Manager – How tech firms went for prioritizing cash flow instead of talent (and artists)
Social Links
DISCLAIMER – Links and images on this website may be protected by the respective owners’ copyright. All data submitted by users through this site shall be treated as freely available to share.