COMPOSITION
DESIGN
COLOR
-
PTGui 13 beta adds control through a Patch Editor
Read more: PTGui 13 beta adds control through a Patch EditorAdditions:
- Patch Editor (PTGui Pro)
- DNG output
- Improved RAW / DNG handling
- JPEG 2000 support
- Performance improvements
-
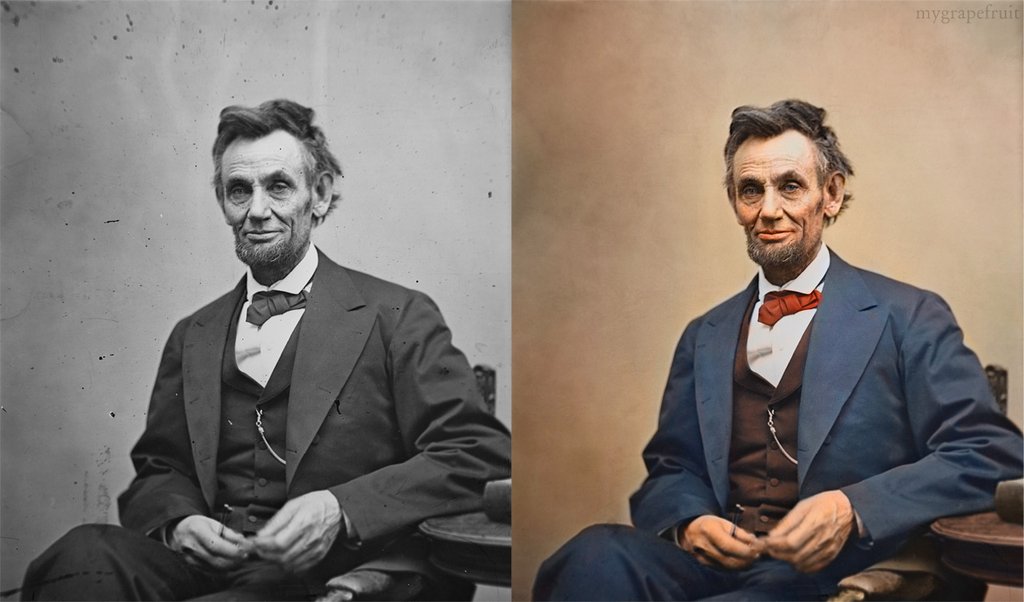
The Color of Infinite Temperature
Read more: The Color of Infinite TemperatureThis is the color of something infinitely hot.

Of course you’d instantly be fried by gamma rays of arbitrarily high frequency, but this would be its spectrum in the visible range.
johncarlosbaez.wordpress.com/2022/01/16/the-color-of-infinite-temperature/
This is also the color of a typical neutron star. They’re so hot they look the same.
It’s also the color of the early Universe!This was worked out by David Madore.
The color he got is sRGB(148,177,255).
www.htmlcsscolor.com/hex/94B1FFAnd according to the experts who sip latte all day and make up names for colors, this color is called ‘Perano’.
-
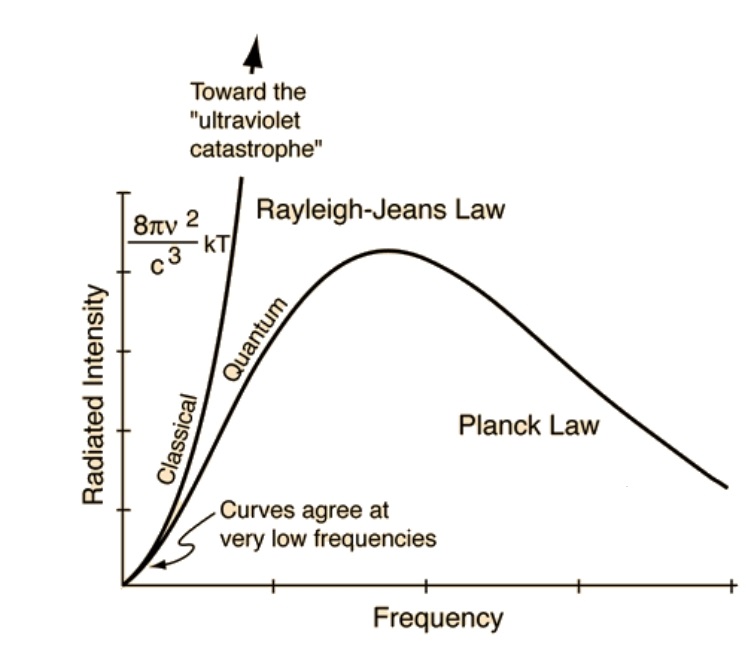
Black Body color aka the Planckian Locus curve for white point eye perception
Read more: Black Body color aka the Planckian Locus curve for white point eye perceptionhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Black-body_radiation
Black-body radiation is the type of electromagnetic radiation within or surrounding a body in thermodynamic equilibrium with its environment, or emitted by a black body (an opaque and non-reflective body) held at constant, uniform temperature. The radiation has a specific spectrum and intensity that depends only on the temperature of the body.
A black-body at room temperature appears black, as most of the energy it radiates is infra-red and cannot be perceived by the human eye. At higher temperatures, black bodies glow with increasing intensity and colors that range from dull red to blindingly brilliant blue-white as the temperature increases.
The Black Body Ultraviolet Catastrophe Experiment
In photography, color temperature describes the spectrum of light which is radiated from a “blackbody” with that surface temperature. A blackbody is an object which absorbs all incident light — neither reflecting it nor allowing it to pass through.
The Sun closely approximates a black-body radiator. Another rough analogue of blackbody radiation in our day to day experience might be in heating a metal or stone: these are said to become “red hot” when they attain one temperature, and then “white hot” for even higher temperatures. Similarly, black bodies at different temperatures also have varying color temperatures of “white light.”
Despite its name, light which may appear white does not necessarily contain an even distribution of colors across the visible spectrum.
Although planets and stars are neither in thermal equilibrium with their surroundings nor perfect black bodies, black-body radiation is used as a first approximation for the energy they emit. Black holes are near-perfect black bodies, and it is believed that they emit black-body radiation (called Hawking radiation), with a temperature that depends on the mass of the hole.
LIGHTING
-
Composition – 5 tips for creating perfect cinematic lighting and making your work look stunning
Read more: Composition – 5 tips for creating perfect cinematic lighting and making your work look stunninghttp://www.diyphotography.net/5-tips-creating-perfect-cinematic-lighting-making-work-look-stunning/
1. Learn the rules of lighting
2. Learn when to break the rules
3. Make your key light larger
4. Reverse keying
5. Always be backlighting
-
Lighting Every Darkness with 3DGS: Fast Training and Real-Time Rendering and Denoising for HDR View Synthesis
Read more: Lighting Every Darkness with 3DGS: Fast Training and Real-Time Rendering and Denoising for HDR View Synthesishttps://srameo.github.io/projects/le3d/
LE3D is a method for real-time HDR view synthesis from RAW images. It is particularly effective for nighttime scenes.
https://github.com/Srameo/LE3D
-
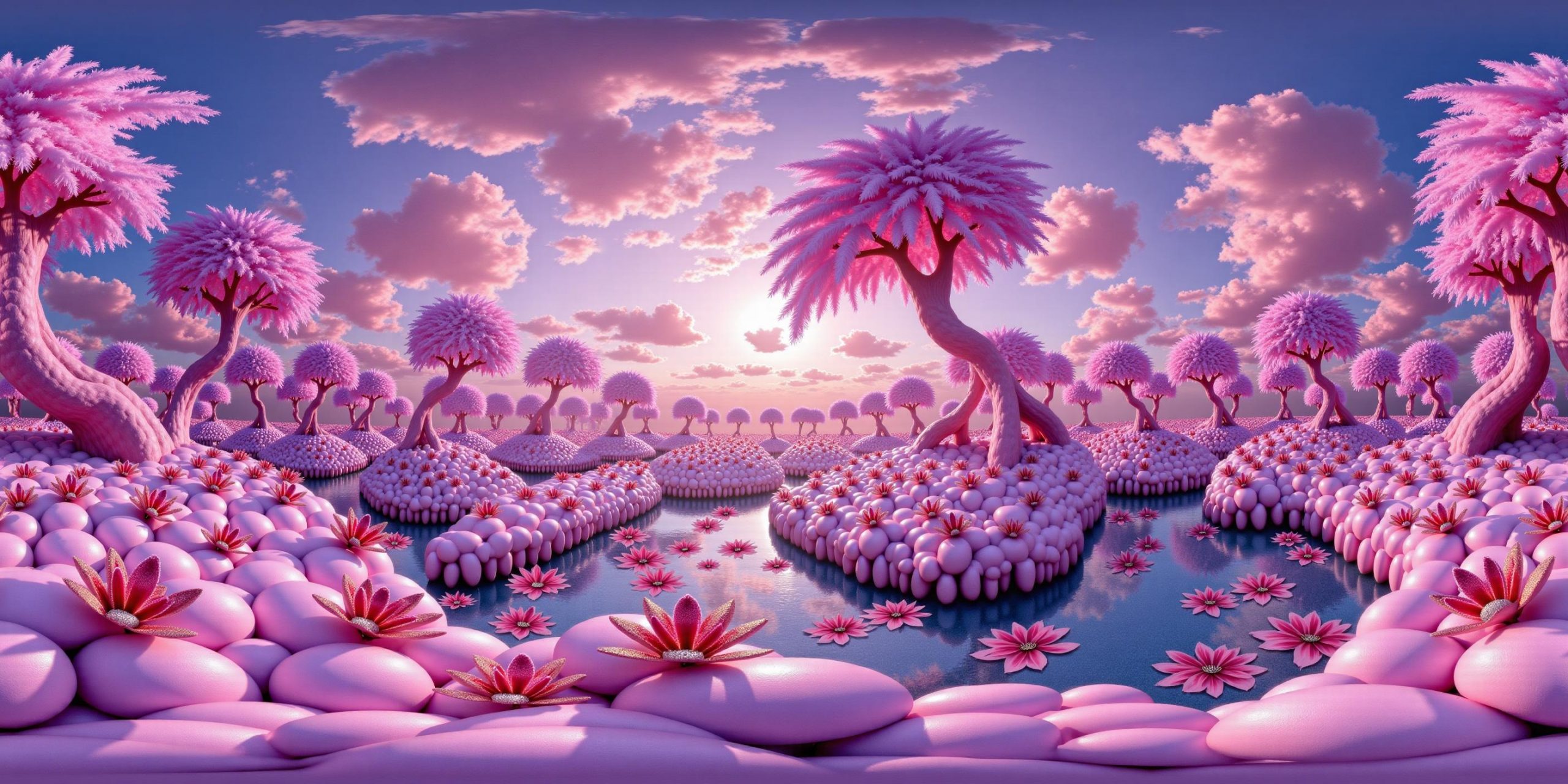
Arto T. – A workflow for creating photorealistic, equirectangular 360° panoramas in ComfyUI using Flux
Read more: Arto T. – A workflow for creating photorealistic, equirectangular 360° panoramas in ComfyUI using Fluxhttps://civitai.com/models/735980/flux-equirectangular-360-panorama
https://civitai.com/models/745010?modelVersionId=833115
The trigger phrase is “equirectangular 360 degree panorama”. I would avoid saying “spherical projection” since that tends to result in non-equirectangular spherical images.
Image resolution should always be a 2:1 aspect ratio. 1024 x 512 or 1408 x 704 work quite well and were used in the training data. 2048 x 1024 also works.
I suggest using a weight of 0.5 – 1.5. If you are having issues with the image generating too flat instead of having the necessary spherical distortion, try increasing the weight above 1, though this could negatively impact small details of the image. For Flux guidance, I recommend a value of about 2.5 for realistic scenes.
8-bit output at the moment

-
Simulon – a Hollywood production studio app in the hands of an independent creator with access to consumer hardware, LDRi to HDRi through ML
Read more: Simulon – a Hollywood production studio app in the hands of an independent creator with access to consumer hardware, LDRi to HDRi through MLDivesh Naidoo: The video below was made with a live in-camera preview and auto-exposure matching, no camera solve, no HDRI capture and no manual compositing setup. Using the new Simulon phone app.
LDR to HDR through ML
https://simulon.typeform.com/betatest
(more…)Process example
-
7 Easy Portrait Lighting Setups
Read more: 7 Easy Portrait Lighting SetupsButterfly
Loop
Rembrandt
Split
Rim
Broad
Short
COLLECTIONS
| Featured AI
| Design And Composition
| Explore posts
POPULAR SEARCHES
unreal | pipeline | virtual production | free | learn | photoshop | 360 | macro | google | nvidia | resolution | open source | hdri | real-time | photography basics | nuke
FEATURED POSTS
Social Links
DISCLAIMER – Links and images on this website may be protected by the respective owners’ copyright. All data submitted by users through this site shall be treated as freely available to share.





