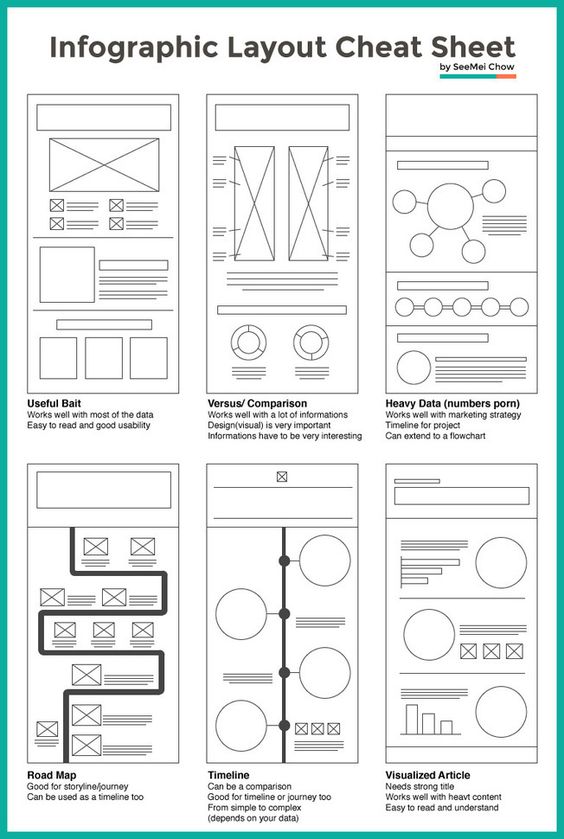
COMPOSITION
DESIGN
-
Principles of Interior Design – Balance
Read more: Principles of Interior Design – Balancehttps://www.yankodesign.com/2024/09/18/principles-of-interior-design-balance
The three types of balance include:
- Symmetrical Balance
- Asymmetrical Balance
- Radial Balance
COLOR
-
Light and Matter : The 2018 theory of Physically-Based Rendering and Shading by Allegorithmic
Read more: Light and Matter : The 2018 theory of Physically-Based Rendering and Shading by Allegorithmicacademy.substance3d.com/courses/the-pbr-guide-part-1
academy.substance3d.com/courses/the-pbr-guide-part-2
Local copy:
-
Gamma correction
Read more: Gamma correction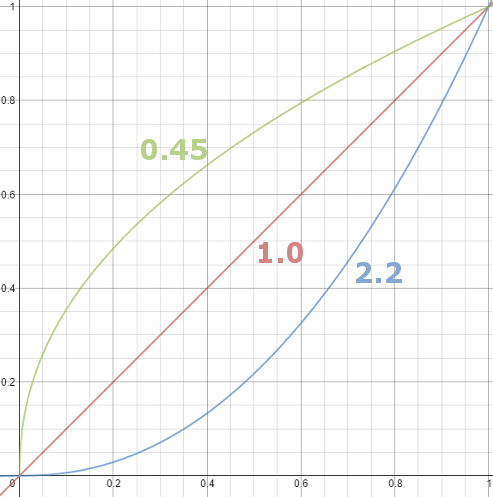
http://www.normankoren.com/makingfineprints1A.html#Gammabox
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gamma_correction
http://www.photoscientia.co.uk/Gamma.htm
https://www.w3.org/Graphics/Color/sRGB.html
http://www.eizoglobal.com/library/basics/lcd_display_gamma/index.html
https://forum.reallusion.com/PrintTopic308094.aspx
Basically, gamma is the relationship between the brightness of a pixel as it appears on the screen, and the numerical value of that pixel. Generally Gamma is just about defining relationships.
Three main types:
– Image Gamma encoded in images
– Display Gammas encoded in hardware and/or viewing time
– System or Viewing Gamma which is the net effect of all gammas when you look back at a final image. In theory this should flatten back to 1.0 gamma.
(more…) -
HDR and Color
Read more: HDR and Colorhttps://www.soundandvision.com/content/nits-and-bits-hdr-and-color
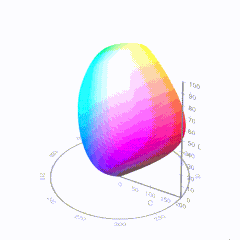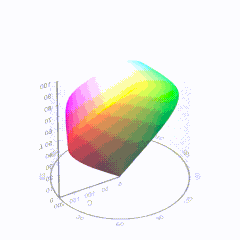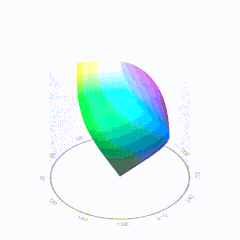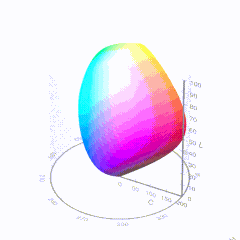
In HD we often refer to the range of available colors as a color gamut. Such a color gamut is typically plotted on a two-dimensional diagram, called a CIE chart, as shown in at the top of this blog. Each color is characterized by its x/y coordinates.
Good enough for government work, perhaps. But for HDR, with its higher luminance levels and wider color, the gamut becomes three-dimensional.
For HDR the color gamut therefore becomes a characteristic we now call the color volume. It isn’t easy to show color volume on a two-dimensional medium like the printed page or a computer screen, but one method is shown below. As the luminance becomes higher, the picture eventually turns to white. As it becomes darker, it fades to black. The traditional color gamut shown on the CIE chart is simply a slice through this color volume at a selected luminance level, such as 50%.
Three different color volumes—we still refer to them as color gamuts though their third dimension is important—are currently the most significant. The first is BT.709 (sometimes referred to as Rec.709), the color gamut used for pre-UHD/HDR formats, including standard HD.
The largest is known as BT.2020; it encompasses (roughly) the range of colors visible to the human eye (though ET might find it insufficient!).
Between these two is the color gamut used in digital cinema, known as DCI-P3.
sRGB
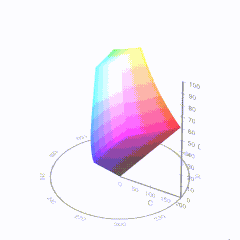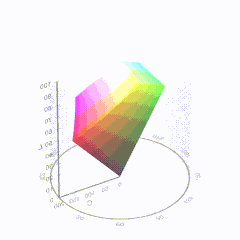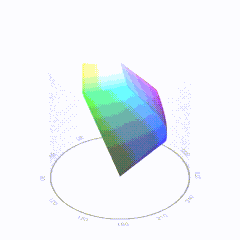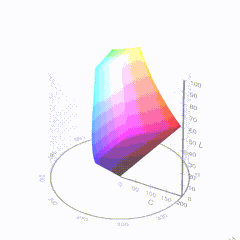
D65
-
3D Lighting Tutorial by Amaan Kram
Read more: 3D Lighting Tutorial by Amaan Kramhttp://www.amaanakram.com/lightingT/part1.htm
The goals of lighting in 3D computer graphics are more or less the same as those of real world lighting.
Lighting serves a basic function of bringing out, or pushing back the shapes of objects visible from the camera’s view.
It gives a two-dimensional image on the monitor an illusion of the third dimension-depth.But it does not just stop there. It gives an image its personality, its character. A scene lit in different ways can give a feeling of happiness, of sorrow, of fear etc., and it can do so in dramatic or subtle ways. Along with personality and character, lighting fills a scene with emotion that is directly transmitted to the viewer.
Trying to simulate a real environment in an artificial one can be a daunting task. But even if you make your 3D rendering look absolutely photo-realistic, it doesn’t guarantee that the image carries enough emotion to elicit a “wow” from the people viewing it.
Making 3D renderings photo-realistic can be hard. Putting deep emotions in them can be even harder. However, if you plan out your lighting strategy for the mood and emotion that you want your rendering to express, you make the process easier for yourself.
Each light source can be broken down in to 4 distinct components and analyzed accordingly.
· Intensity
· Direction
· Color
· SizeThe overall thrust of this writing is to produce photo-realistic images by applying good lighting techniques.
-
Mysterious animation wins best illusion of 2011 – Motion silencing illusion
Read more: Mysterious animation wins best illusion of 2011 – Motion silencing illusionThe 2011 Best Illusion of the Year uses motion to render color changes invisible, and so reveals a quirk in our visual systems that is new to scientists.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Motion_silencing_illusion
“It is a really beautiful effect, revealing something about how our visual system works that we didn’t know before,” said Daniel Simons, a professor at the University of Illinois, Champaign-Urbana. Simons studies visual cognition, and did not work on this illusion. Before its creation, scientists didn’t know that motion had this effect on perception, Simons said.
A viewer stares at a speck at the center of a ring of colored dots, which continuously change color. When the ring begins to rotate around the speck, the color changes appear to stop. But this is an illusion. For some reason, the motion causes our visual system to ignore the color changes. (You can, however, see the color changes if you follow the rotating circles with your eyes.)
-
Paul Debevec, Chloe LeGendre, Lukas Lepicovsky – Jointly Optimizing Color Rendition and In-Camera Backgrounds in an RGB Virtual Production Stage
Read more: Paul Debevec, Chloe LeGendre, Lukas Lepicovsky – Jointly Optimizing Color Rendition and In-Camera Backgrounds in an RGB Virtual Production Stagehttps://arxiv.org/pdf/2205.12403.pdf
RGB LEDs vs RGBWP (RGB + lime + phospor converted amber) LEDs
Local copy:
LIGHTING
-
Light properties
Read more: Light propertiesHow It Works – Issue 114
https://www.howitworksdaily.com/ -
IES Light Profiles and editing software
Read more: IES Light Profiles and editing softwarehttp://www.derekjenson.com/3d-blog/ies-light-profiles
https://ieslibrary.com/en/browse#ies
https://leomoon.com/store/shaders/ies-lights-pack
https://docs.arnoldrenderer.com/display/a5afmug/ai+photometric+light
IES profiles are useful for creating life-like lighting, as they can represent the physical distribution of light from any light source.
The IES format was created by the Illumination Engineering Society, and most lighting manufacturers provide IES profile for the lights they manufacture.
COLLECTIONS
| Featured AI
| Design And Composition
| Explore posts
POPULAR SEARCHES
unreal | pipeline | virtual production | free | learn | photoshop | 360 | macro | google | nvidia | resolution | open source | hdri | real-time | photography basics | nuke
FEATURED POSTS
-
AI Data Laundering: How Academic and Nonprofit Researchers Shield Tech Companies from Accountability
-
Top 3D Printing Website Resources
-
Guide to Prompt Engineering
-
How to paint a boardgame miniatures
-
Canva bought Affinity – Now Affinity Photo and Affinity Designer are… GONE?!
-
MiniTunes V1 – Free MP3 library app
-
Glossary of Lighting Terms – cheat sheet
-
HDRI Median Cut plugin
Social Links
DISCLAIMER – Links and images on this website may be protected by the respective owners’ copyright. All data submitted by users through this site shall be treated as freely available to share.