COMPOSITION
-
Photography basics: Camera Aspect Ratio, Sensor Size and Depth of Field – resolutions
Read more: Photography basics: Camera Aspect Ratio, Sensor Size and Depth of Field – resolutionshttp://www.shutterangle.com/2012/cinematic-look-aspect-ratio-sensor-size-depth-of-field/
http://www.shutterangle.com/2012/film-video-aspect-ratio-artistic-choice/
-
Christopher Butler – Understanding the Eye-Mind Connection – Vision is a mental process
Read more: Christopher Butler – Understanding the Eye-Mind Connection – Vision is a mental processhttps://www.chrbutler.com/understanding-the-eye-mind-connection
The intricate relationship between the eyes and the brain, often termed the eye-mind connection, reveals that vision is predominantly a cognitive process. This understanding has profound implications for fields such as design, where capturing and maintaining attention is paramount. This essay delves into the nuances of visual perception, the brain’s role in interpreting visual data, and how this knowledge can be applied to effective design strategies.
This cognitive aspect of vision is evident in phenomena such as optical illusions, where the brain interprets visual information in a way that contradicts physical reality. These illusions underscore that what we “see” is not merely a direct recording of the external world but a constructed experience shaped by cognitive processes.
Understanding the cognitive nature of vision is crucial for effective design. Designers must consider how the brain processes visual information to create compelling and engaging visuals. This involves several key principles:
- Attention and Engagement
- Visual Hierarchy
- Cognitive Load Management
- Context and Meaning
DESIGN
COLOR
-
THOMAS MANSENCAL – The Apparent Simplicity of RGB Rendering
Read more: THOMAS MANSENCAL – The Apparent Simplicity of RGB Renderinghttps://thomasmansencal.substack.com/p/the-apparent-simplicity-of-rgb-rendering
The primary goal of physically-based rendering (PBR) is to create a simulation that accurately reproduces the imaging process of electro-magnetic spectrum radiation incident to an observer. This simulation should be indistinguishable from reality for a similar observer.
Because a camera is not sensitive to incident light the same way than a human observer, the images it captures are transformed to be colorimetric. A project might require infrared imaging simulation, a portion of the electro-magnetic spectrum that is invisible to us. Radically different observers might image the same scene but the act of observing does not change the intrinsic properties of the objects being imaged. Consequently, the physical modelling of the virtual scene should be independent of the observer.
-
About color: What is a LUT
Read more: About color: What is a LUThttp://www.lightillusion.com/luts.html
https://www.shutterstock.com/blog/how-use-luts-color-grading
A LUT (Lookup Table) is essentially the modifier between two images, the original image and the displayed image, based on a mathematical formula. Basically conversion matrices of different complexities. There are different types of LUTS – viewing, transform, calibration, 1D and 3D.
-
Tim Kang – calibrated white light values in sRGB color space
Read more: Tim Kang – calibrated white light values in sRGB color space8bit sRGB encoded
2000K 255 139 22
2700K 255 172 89
3000K 255 184 109
3200K 255 190 122
4000K 255 211 165
4300K 255 219 178
D50 255 235 205
D55 255 243 224
D5600 255 244 227
D6000 255 249 240
D65 255 255 255
D10000 202 221 255
D20000 166 196 2558bit Rec709 Gamma 2.4
2000K 255 145 34
2700K 255 177 97
3000K 255 187 117
3200K 255 193 129
4000K 255 214 170
4300K 255 221 182
D50 255 236 208
D55 255 243 226
D5600 255 245 229
D6000 255 250 241
D65 255 255 255
D10000 204 222 255
D20000 170 199 2558bit Display P3 encoded
2000K 255 154 63
2700K 255 185 109
3000K 255 195 127
3200K 255 201 138
4000K 255 219 176
4300K 255 225 187
D50 255 239 212
D55 255 245 228
D5600 255 246 231
D6000 255 251 242
D65 255 255 255
D10000 208 223 255
D20000 175 199 25510bit Rec2020 PQ (100 nits)
2000K 520 435 273
2700K 520 466 358
3000K 520 475 384
3200K 520 480 399
4000K 520 495 446
4300K 520 500 458
D50 520 510 482
D55 520 514 497
D5600 520 514 500
D6000 520 517 509
D65 520 520 520
D10000 479 489 520
D20000 448 464 520 -
No one could see the colour blue until modern times
Read more: No one could see the colour blue until modern timeshttps://www.businessinsider.com/what-is-blue-and-how-do-we-see-color-2015-2

The way humans see the world… until we have a way to describe something, even something so fundamental as a colour, we may not even notice that something it’s there.
Ancient languages didn’t have a word for blue — not Greek, not Chinese, not Japanese, not Hebrew, not Icelandic cultures. And without a word for the colour, there’s evidence that they may not have seen it at all.
https://www.wnycstudios.org/story/211119-colorsEvery language first had a word for black and for white, or dark and light. The next word for a colour to come into existence — in every language studied around the world — was red, the colour of blood and wine.
After red, historically, yellow appears, and later, green (though in a couple of languages, yellow and green switch places). The last of these colours to appear in every language is blue.The only ancient culture to develop a word for blue was the Egyptians — and as it happens, they were also the only culture that had a way to produce a blue dye.
https://mymodernmet.com/shades-of-blue-color-history/True blue hues are rare in the natural world because synthesizing pigments that absorb longer-wavelength light (reds and yellows) while reflecting shorter-wavelength blue light requires exceptionally elaborate molecular structures—biochemical feats that most plants and animals simply don’t undertake.
When you gaze at a blueberry’s deep blue surface, you’re actually seeing structural coloration rather than a true blue pigment. A fine, waxy bloom on the berry’s skin contains nanostructures that preferentially scatter blue and violet light, giving the fruit its signature blue sheen even though its inherent pigment is reddish.
Similarly, many of nature’s most striking blues—like those of blue jays and morpho butterflies—arise not from blue pigments but from microscopic architectures in feathers or wing scales. These tiny ridges and air pockets manipulate incoming light so that blue wavelengths emerge most prominently, creating vivid, angle-dependent colors through scattering rather than pigment alone.
(more…) -
Weta Digital – Manuka Raytracer and Gazebo GPU renderers – pipeline
Read more: Weta Digital – Manuka Raytracer and Gazebo GPU renderers – pipelinehttps://jo.dreggn.org/home/2018_manuka.pdf
http://www.fxguide.com/featured/manuka-weta-digitals-new-renderer/
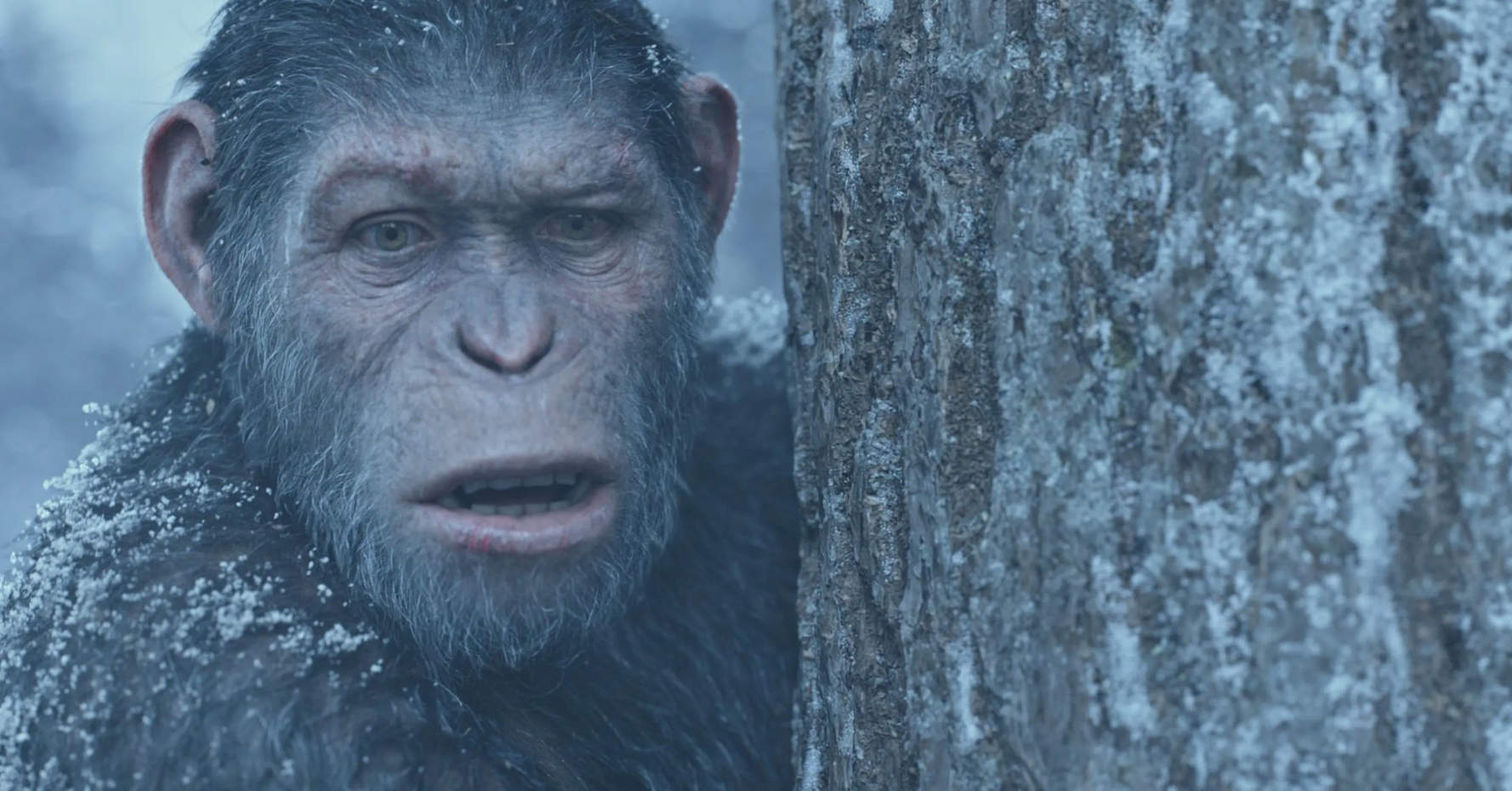

The Manuka rendering architecture has been designed in the spirit of the classic reyes rendering architecture. In its core, reyes is based on stochastic rasterisation of micropolygons, facilitating depth of field, motion blur, high geometric complexity,and programmable shading.
This is commonly achieved with Monte Carlo path tracing, using a paradigm often called shade-on-hit, in which the renderer alternates tracing rays with running shaders on the various ray hits. The shaders take the role of generating the inputs of the local material structure which is then used bypath sampling logic to evaluate contributions and to inform what further rays to cast through the scene.
Over the years, however, the expectations have risen substantially when it comes to image quality. Computing pictures which are indistinguishable from real footage requires accurate simulation of light transport, which is most often performed using some variant of Monte Carlo path tracing. Unfortunately this paradigm requires random memory accesses to the whole scene and does not lend itself well to a rasterisation approach at all.
Manuka is both a uni-directional and bidirectional path tracer and encompasses multiple importance sampling (MIS). Interestingly, and importantly for production character skin work, it is the first major production renderer to incorporate spectral MIS in the form of a new ‘Hero Spectral Sampling’ technique, which was recently published at Eurographics Symposium on Rendering 2014.
Manuka propose a shade-before-hit paradigm in-stead and minimise I/O strain (and some memory costs) on the system, leveraging locality of reference by running pattern generation shaders before we execute light transport simulation by path sampling, “compressing” any bvh structure as needed, and as such also limiting duplication of source data.
The difference with reyes is that instead of baking colors into the geometry like in Reyes, manuka bakes surface closures. This means that light transport is still calculated with path tracing, but all texture lookups etc. are done up-front and baked into the geometry.The main drawback with this method is that geometry has to be tessellated to its highest, stable topology before shading can be evaluated properly. As such, the high cost to first pixel. Even a basic 4 vertices square becomes a much more complex model with this approach.
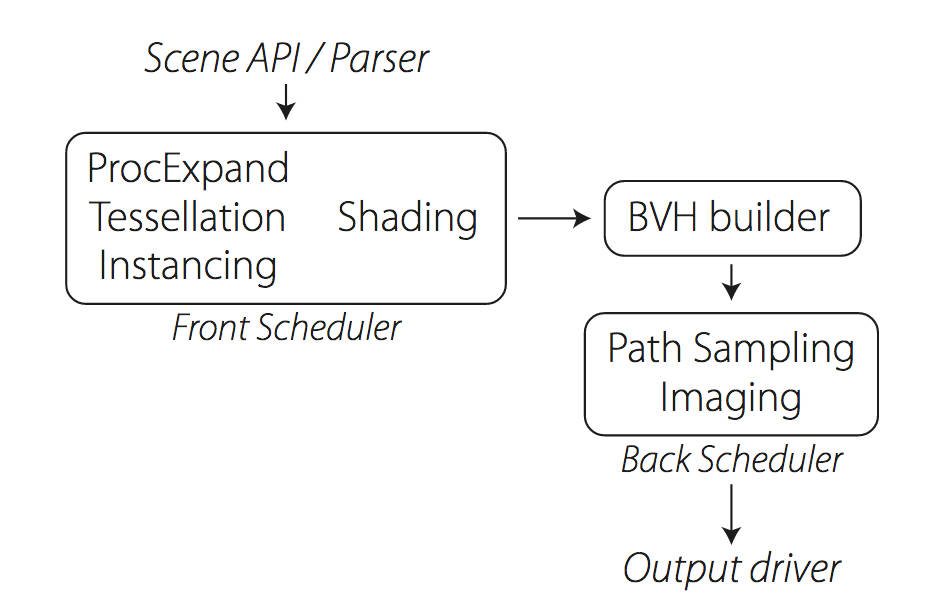
Manuka use the RenderMan Shading Language (rsl) for programmable shading [Pixar Animation Studios 2015], but we do not invoke rsl shaders when intersecting a ray with a surface (often called shade-on-hit). Instead, we pre-tessellate and pre-shade all the input geometry in the front end of the renderer.
This way, we can efficiently order shading computations to sup-port near-optimal texture locality, vectorisation, and parallelism. This system avoids repeated evaluation of shaders at the same surface point, and presents a minimal amount of memory to be accessed during light transport time. An added benefit is that the acceleration structure for ray tracing (abounding volume hierarchy, bvh) is built once on the final tessellated geometry, which allows us to ray trace more efficiently than multi-level bvhs and avoids costly caching of on-demand tessellated micropolygons and the associated scheduling issues.For the shading reasons above, in terms of AOVs, the studio approach is to succeed at combining complex shading with ray paths in the render rather than pass a multi-pass render to compositing.
For the Spectral Rendering component. The light transport stage is fully spectral, using a continuously sampled wavelength which is traced with each path and used to apply the spectral camera sensitivity of the sensor. This allows for faithfully support any degree of observer metamerism as the camera footage they are intended to match as well as complex materials which require wavelength dependent phenomena such as diffraction, dispersion, interference, iridescence, or chromatic extinction and Rayleigh scattering in participating media.
As opposed to the original reyes paper, we use bilinear interpolation of these bsdf inputs later when evaluating bsdfs per pathv ertex during light transport4. This improves temporal stability of geometry which moves very slowly with respect to the pixel raster
In terms of the pipeline, everything rendered at Weta was already completely interwoven with their deep data pipeline. Manuka very much was written with deep data in mind. Here, Manuka not so much extends the deep capabilities, rather it fully matches the already extremely complex and powerful setup Weta Digital already enjoy with RenderMan. For example, an ape in a scene can be selected, its ID is available and a NUKE artist can then paint in 3D say a hand and part of the way up the neutral posed ape.
We called our system Manuka, as a respectful nod to reyes: we had heard a story froma former ILM employee about how reyes got its name from how fond the early Pixar people were of their lunches at Point Reyes, and decided to name our system after our surrounding natural environment, too. Manuka is a kind of tea tree very common in New Zealand which has very many very small leaves, in analogy to micropolygons ina tree structure for ray tracing. It also happens to be the case that Weta Digital’s main site is on Manuka Street.

-
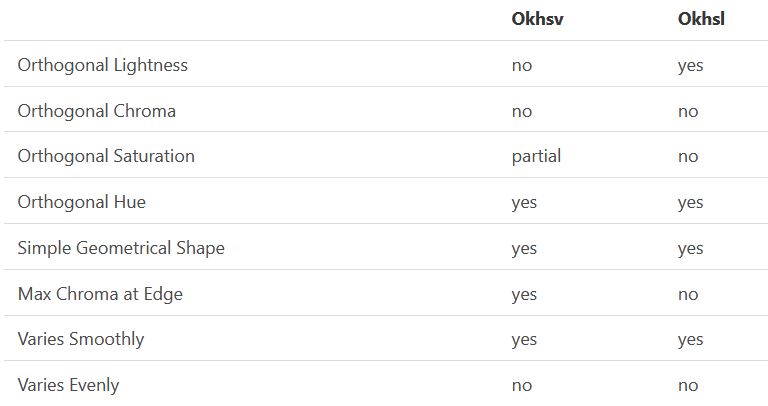
Björn Ottosson – OKHSV and OKHSL – Two new color spaces for color picking
Read more: Björn Ottosson – OKHSV and OKHSL – Two new color spaces for color pickinghttps://bottosson.github.io/misc/colorpicker
https://bottosson.github.io/posts/colorpicker/
https://www.smashingmagazine.com/2024/10/interview-bjorn-ottosson-creator-oklab-color-space/
One problem with sRGB is that in a gradient between blue and white, it becomes a bit purple in the middle of the transition. That’s because sRGB really isn’t created to mimic how the eye sees colors; rather, it is based on how CRT monitors work. That means it works with certain frequencies of red, green, and blue, and also the non-linear coding called gamma. It’s a miracle it works as well as it does, but it’s not connected to color perception. When using those tools, you sometimes get surprising results, like purple in the gradient.
There were also attempts to create simple models matching human perception based on XYZ, but as it turned out, it’s not possible to model all color vision that way. Perception of color is incredibly complex and depends, among other things, on whether it is dark or light in the room and the background color it is against. When you look at a photograph, it also depends on what you think the color of the light source is. The dress is a typical example of color vision being very context-dependent. It is almost impossible to model this perfectly.
I based Oklab on two other color spaces, CIECAM16 and IPT. I used the lightness and saturation prediction from CIECAM16, which is a color appearance model, as a target. I actually wanted to use the datasets used to create CIECAM16, but I couldn’t find them.
IPT was designed to have better hue uniformity. In experiments, they asked people to match light and dark colors, saturated and unsaturated colors, which resulted in a dataset for which colors, subjectively, have the same hue. IPT has a few other issues but is the basis for hue in Oklab.
In the Munsell color system, colors are described with three parameters, designed to match the perceived appearance of colors: Hue, Chroma and Value. The parameters are designed to be independent and each have a uniform scale. This results in a color solid with an irregular shape. The parameters are designed to be independent and each have a uniform scale. This results in a color solid with an irregular shape. Modern color spaces and models, such as CIELAB, Cam16 and Björn Ottosson own Oklab, are very similar in their construction.
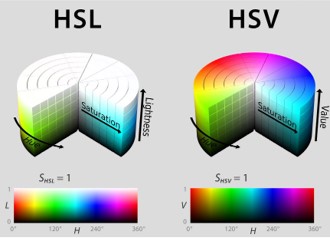
By far the most used color spaces today for color picking are HSL and HSV, two representations introduced in the classic 1978 paper “Color Spaces for Computer Graphics”. HSL and HSV designed to roughly correlate with perceptual color properties while being very simple and cheap to compute.
Today HSL and HSV are most commonly used together with the sRGB color space.

One of the main advantages of HSL and HSV over the different Lab color spaces is that they map the sRGB gamut to a cylinder. This makes them easy to use since all parameters can be changed independently, without the risk of creating colors outside of the target gamut.
The main drawback on the other hand is that their properties don’t match human perception particularly well.
Reconciling these conflicting goals perfectly isn’t possible, but given that HSV and HSL don’t use anything derived from experiments relating to human perception, creating something that makes a better tradeoff does not seem unreasonable.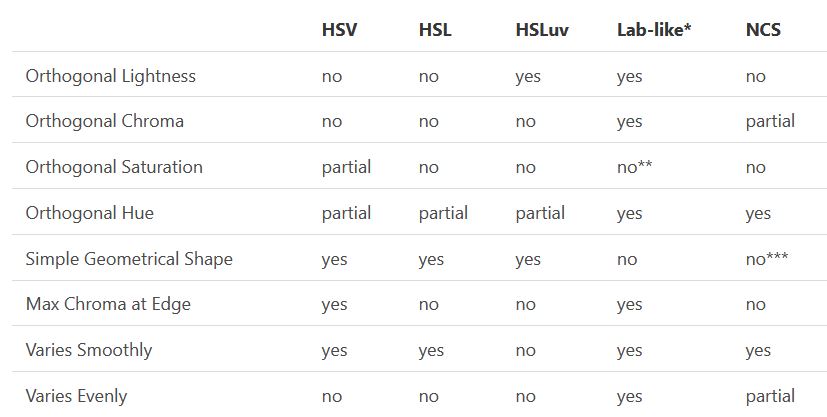
With this new lightness estimate, we are ready to look into the construction of Okhsv and Okhsl.
-
3D Lighting Tutorial by Amaan Kram
Read more: 3D Lighting Tutorial by Amaan Kramhttp://www.amaanakram.com/lightingT/part1.htm
The goals of lighting in 3D computer graphics are more or less the same as those of real world lighting.
Lighting serves a basic function of bringing out, or pushing back the shapes of objects visible from the camera’s view.
It gives a two-dimensional image on the monitor an illusion of the third dimension-depth.But it does not just stop there. It gives an image its personality, its character. A scene lit in different ways can give a feeling of happiness, of sorrow, of fear etc., and it can do so in dramatic or subtle ways. Along with personality and character, lighting fills a scene with emotion that is directly transmitted to the viewer.
Trying to simulate a real environment in an artificial one can be a daunting task. But even if you make your 3D rendering look absolutely photo-realistic, it doesn’t guarantee that the image carries enough emotion to elicit a “wow” from the people viewing it.
Making 3D renderings photo-realistic can be hard. Putting deep emotions in them can be even harder. However, if you plan out your lighting strategy for the mood and emotion that you want your rendering to express, you make the process easier for yourself.
Each light source can be broken down in to 4 distinct components and analyzed accordingly.
· Intensity
· Direction
· Color
· SizeThe overall thrust of this writing is to produce photo-realistic images by applying good lighting techniques.
-
Capturing textures albedo
Read more: Capturing textures albedoBuilding a Portable PBR Texture Scanner by Stephane Lb
http://rtgfx.com/pbr-texture-scanner/How To Split Specular And Diffuse In Real Images, by John Hable
http://filmicworlds.com/blog/how-to-split-specular-and-diffuse-in-real-images/Capturing albedo using a Spectralon
https://www.activision.com/cdn/research/Real_World_Measurements_for_Call_of_Duty_Advanced_Warfare.pdfReal_World_Measurements_for_Call_of_Duty_Advanced_Warfare.pdf
Spectralon is a teflon-based pressed powderthat comes closest to being a pure Lambertian diffuse material that reflects 100% of all light. If we take an HDR photograph of the Spectralon alongside the material to be measured, we can derive thediffuse albedo of that material.
The process to capture diffuse reflectance is very similar to the one outlined by Hable.
1. We put a linear polarizing filter in front of the camera lens and a second linear polarizing filterin front of a modeling light or a flash such that the two filters are oriented perpendicular to eachother, i.e. cross polarized.
2. We place Spectralon close to and parallel with the material we are capturing and take brack-eted shots of the setup7. Typically, we’ll take nine photographs, from -4EV to +4EV in 1EVincrements.
3. We convert the bracketed shots to a linear HDR image. We found that many HDR packagesdo not produce an HDR image in which the pixel values are linear. PTGui is an example of apackage which does generate a linear HDR image. At this point, because of the cross polarization,the image is one of surface diffuse response.
4. We open the file in Photoshop and normalize the image by color picking the Spectralon, filling anew layer with that color and setting that layer to “Divide”. This sets the Spectralon to 1 in theimage. All other color values are relative to this so we can consider them as diffuse albedo.
-
Scene Referred vs Display Referred color workflows
Read more: Scene Referred vs Display Referred color workflowsDisplay Referred it is tied to the target hardware, as such it bakes color requirements into every type of media output request.
Scene Referred uses a common unified wide gamut and targeting audience through CDL and DI libraries instead.
So that color information stays untouched and only “transformed” as/when needed.Sources:
– Victor Perez – Color Management Fundamentals & ACES Workflows in Nuke
– https://z-fx.nl/ColorspACES.pdf
– Wicus
LIGHTING
-
Outpost VFX lighting tips
Read more: Outpost VFX lighting tipswww.outpost-vfx.com/en/news/18-pro-tips-and-tricks-for-lighting
Get as much information regarding your plate lighting as possible
- Always use a reference
- Replicate what is happening in real life
- Invest into a solid HDRI
- Start Simple
- Observe real world lighting, photography and cinematography
- Don’t neglect the theory
- Learn the difference between realism and photo-realism.
- Keep your scenes organised

-
Romain Chauliac – LightIt a lighting script for Maya and Arnold
Read more: Romain Chauliac – LightIt a lighting script for Maya and ArnoldLightIt is a script for Maya and Arnold that will help you and improve your lighting workflow.
Thanks to preset studio lighting components (lights, backdrop…), high quality studio scenes and HDRI library manager.https://www.artstation.com/artwork/393emJ
COLLECTIONS
| Featured AI
| Design And Composition
| Explore posts
POPULAR SEARCHES
unreal | pipeline | virtual production | free | learn | photoshop | 360 | macro | google | nvidia | resolution | open source | hdri | real-time | photography basics | nuke
FEATURED POSTS
-
Glossary of Lighting Terms – cheat sheet
-
Animation/VFX/Game Industry JOB POSTINGS by Chris Mayne
-
Matt Hallett – WAN 2.1 VACE Total Video Control in ComfyUI
-
Daniele Tosti Interview for the magazine InCG, Taiwan, Issue 28, 201609
-
GretagMacbeth Color Checker Numeric Values and Middle Gray
-
Want to build a start up company that lasts? Think three-layer cake
-
Free fonts
-
VFX pipeline – Render Wall management topics
Social Links
DISCLAIMER – Links and images on this website may be protected by the respective owners’ copyright. All data submitted by users through this site shall be treated as freely available to share.






