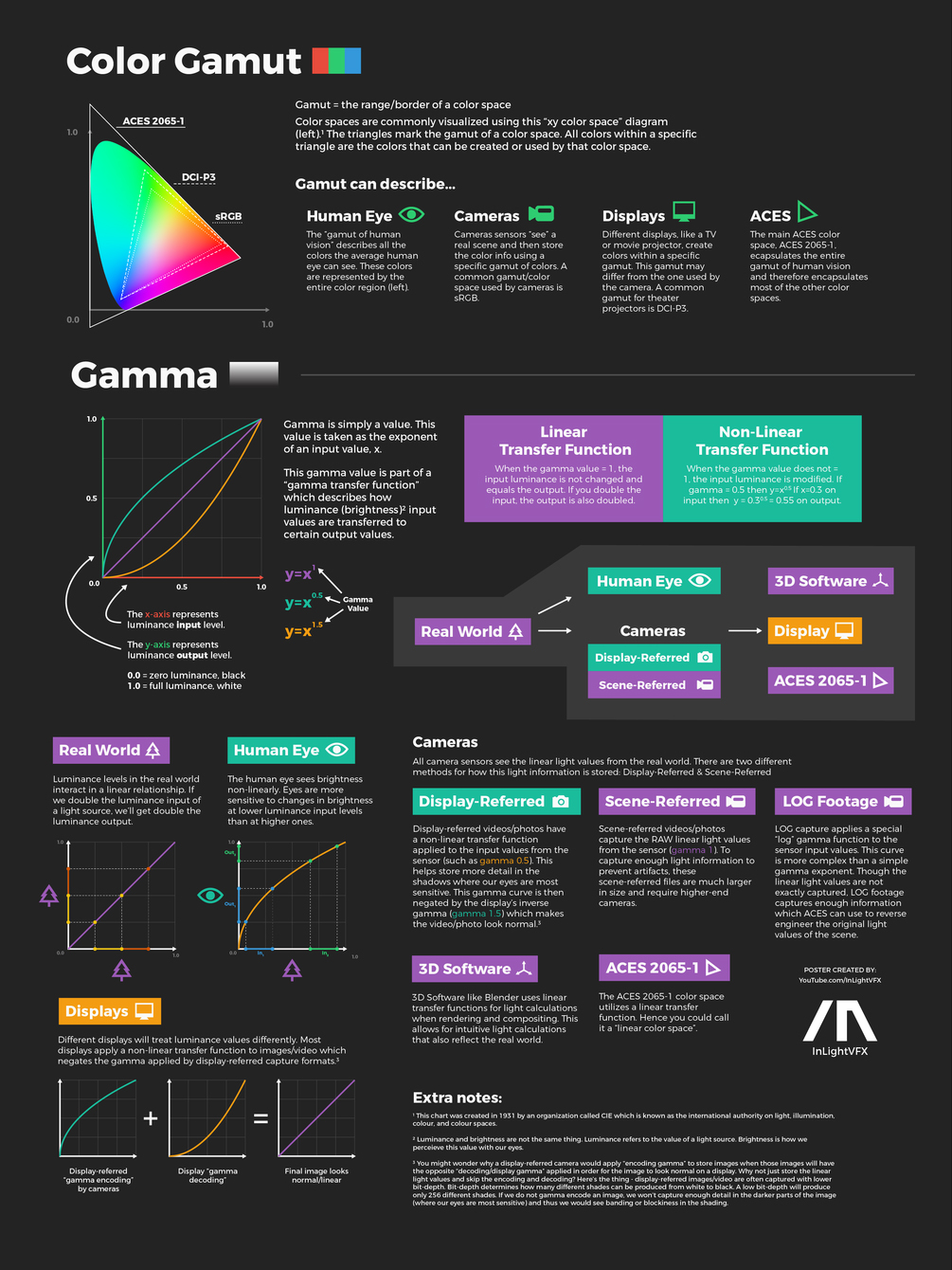
COMPOSITION
-
Mastering Camera Shots and Angles: A Guide for Filmmakers
Read more: Mastering Camera Shots and Angles: A Guide for Filmmakershttps://website.ltx.studio/blog/mastering-camera-shots-and-angles
1. Extreme Wide Shot

2. Wide Shot

3. Medium Shot

4. Close Up
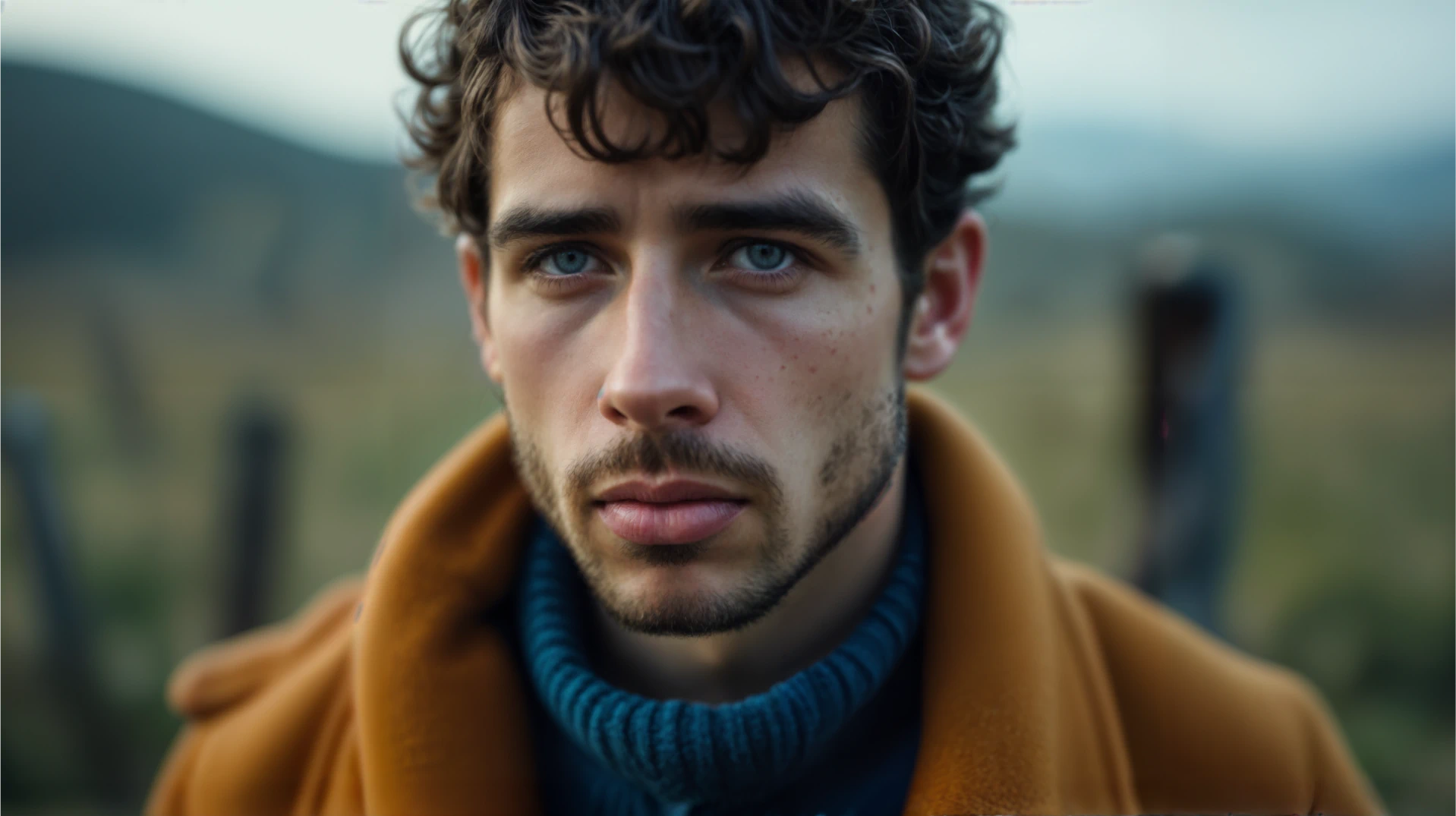

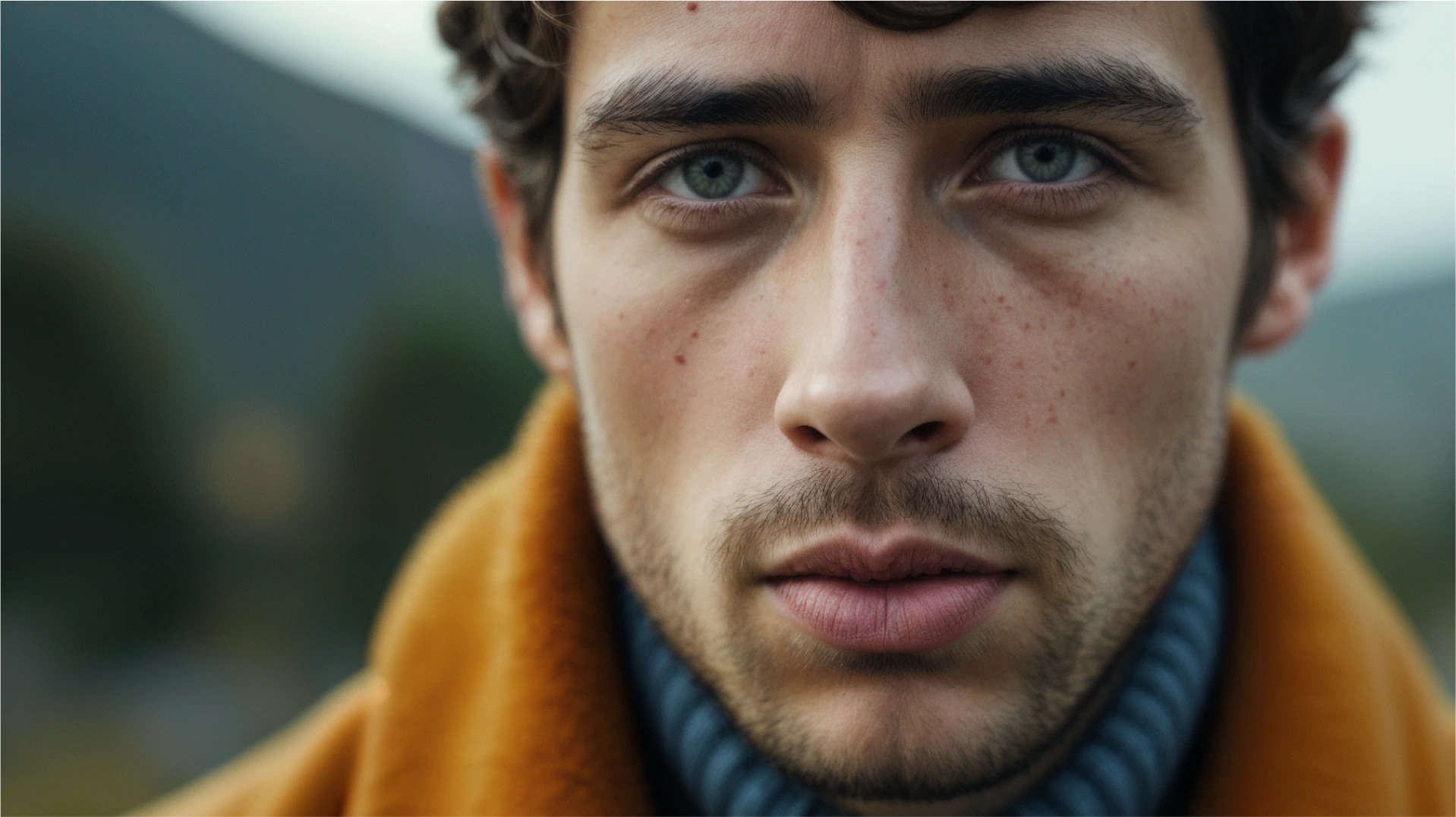
5. Extreme Close Up

-
Photography basics: Depth of Field and composition
Read more: Photography basics: Depth of Field and compositionDepth of field is the range within which focusing is resolved in a photo.
Aperture has a huge affect on to the depth of field.Changing the f-stops (f/#) of a lens will change aperture and as such the DOF.
f-stops are a just certain number which is telling you the size of the aperture. That’s how f-stop is related to aperture (and DOF).
If you increase f-stops, it will increase DOF, the area in focus (and decrease the aperture). On the other hand, decreasing the f-stop it will decrease DOF (and increase the aperture).
The red cone in the figure is an angular representation of the resolution of the system. Versus the dotted lines, which indicate the aperture coverage. Where the lines of the two cones intersect defines the total range of the depth of field.
This image explains why the longer the depth of field, the greater the range of clarity.
-
Composition – cinematography Cheat Sheet
Read more: Composition – cinematography Cheat Sheet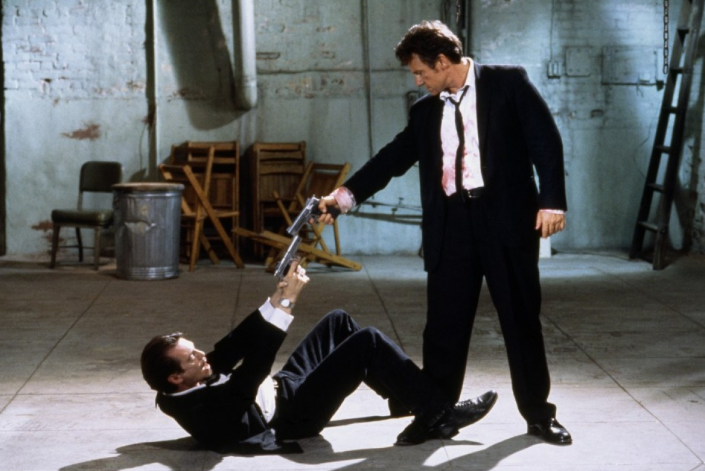
Where is our eye attracted first? Why?
Size. Focus. Lighting. Color.
Size. Mr. White (Harvey Keitel) on the right.
Focus. He’s one of the two objects in focus.
Lighting. Mr. White is large and in focus and Mr. Pink (Steve Buscemi) is highlighted by
a shaft of light.
Color. Both are black and white but the read on Mr. White’s shirt now really stands out.
(more…)
What type of lighting? -
SlowMoVideo – How to make a slow motion shot with the open source program
Read more: SlowMoVideo – How to make a slow motion shot with the open source programhttp://slowmovideo.granjow.net/
slowmoVideo is an OpenSource program that creates slow-motion videos from your footage.
Slow motion cinematography is the result of playing back frames for a longer duration than they were exposed. For example, if you expose 240 frames of film in one second, then play them back at 24 fps, the resulting movie is 10 times longer (slower) than the original filmed event….
Film cameras are relatively simple mechanical devices that allow you to crank up the speed to whatever rate the shutter and pull-down mechanism allow. Some film cameras can operate at 2,500 fps or higher (although film shot in these cameras often needs some readjustment in postproduction). Video, on the other hand, is always captured, recorded, and played back at a fixed rate, with a current limit around 60fps. This makes extreme slow motion effects harder to achieve (and less elegant) on video, because slowing down the video results in each frame held still on the screen for a long time, whereas with high-frame-rate film there are plenty of frames to fill the longer durations of time. On video, the slow motion effect is more like a slide show than smooth, continuous motion.
One obvious solution is to shoot film at high speed, then transfer it to video (a case where film still has a clear advantage, sorry George). Another possibility is to cross dissolve or blur from one frame to the next. This adds a smooth transition from one still frame to the next. The blur reduces the sharpness of the image, and compared to slowing down images shot at a high frame rate, this is somewhat of a cheat. However, there isn’t much you can do about it until video can be recorded at much higher rates. Of course, many film cameras can’t shoot at high frame rates either, so the whole super-slow-motion endeavor is somewhat specialized no matter what medium you are using. (There are some high speed digital cameras available now that allow you to capture lots of digital frames directly to your computer, so technology is starting to catch up with film. However, this feature isn’t going to appear in consumer camcorders any time soon.)
-
Christopher Butler – Understanding the Eye-Mind Connection – Vision is a mental process
Read more: Christopher Butler – Understanding the Eye-Mind Connection – Vision is a mental processhttps://www.chrbutler.com/understanding-the-eye-mind-connection
The intricate relationship between the eyes and the brain, often termed the eye-mind connection, reveals that vision is predominantly a cognitive process. This understanding has profound implications for fields such as design, where capturing and maintaining attention is paramount. This essay delves into the nuances of visual perception, the brain’s role in interpreting visual data, and how this knowledge can be applied to effective design strategies.
This cognitive aspect of vision is evident in phenomena such as optical illusions, where the brain interprets visual information in a way that contradicts physical reality. These illusions underscore that what we “see” is not merely a direct recording of the external world but a constructed experience shaped by cognitive processes.
Understanding the cognitive nature of vision is crucial for effective design. Designers must consider how the brain processes visual information to create compelling and engaging visuals. This involves several key principles:
- Attention and Engagement
- Visual Hierarchy
- Cognitive Load Management
- Context and Meaning

-
9 Best Hacks to Make a Cinematic Video with Any Camera
Read more: 9 Best Hacks to Make a Cinematic Video with Any Camerahttps://www.flexclip.com/learn/cinematic-video.html
- Frame Your Shots to Create Depth
- Create Shallow Depth of Field
- Avoid Shaky Footage and Use Flexible Camera Movements
- Properly Use Slow Motion
- Use Cinematic Lighting Techniques
- Apply Color Grading
- Use Cinematic Music and SFX
- Add Cinematic Fonts and Text Effects
- Create the Cinematic Bar at the Top and the Bottom

DESIGN
-
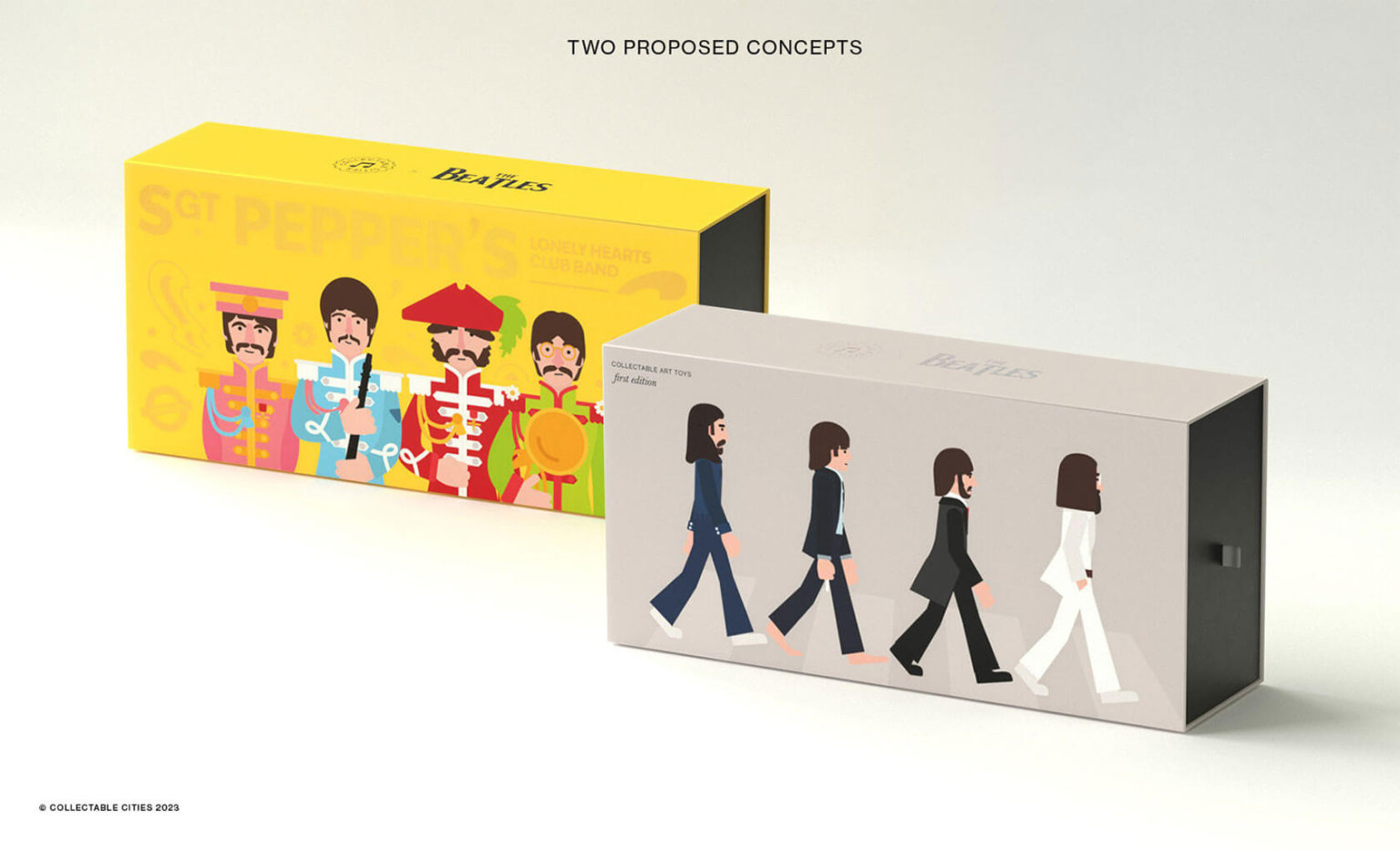
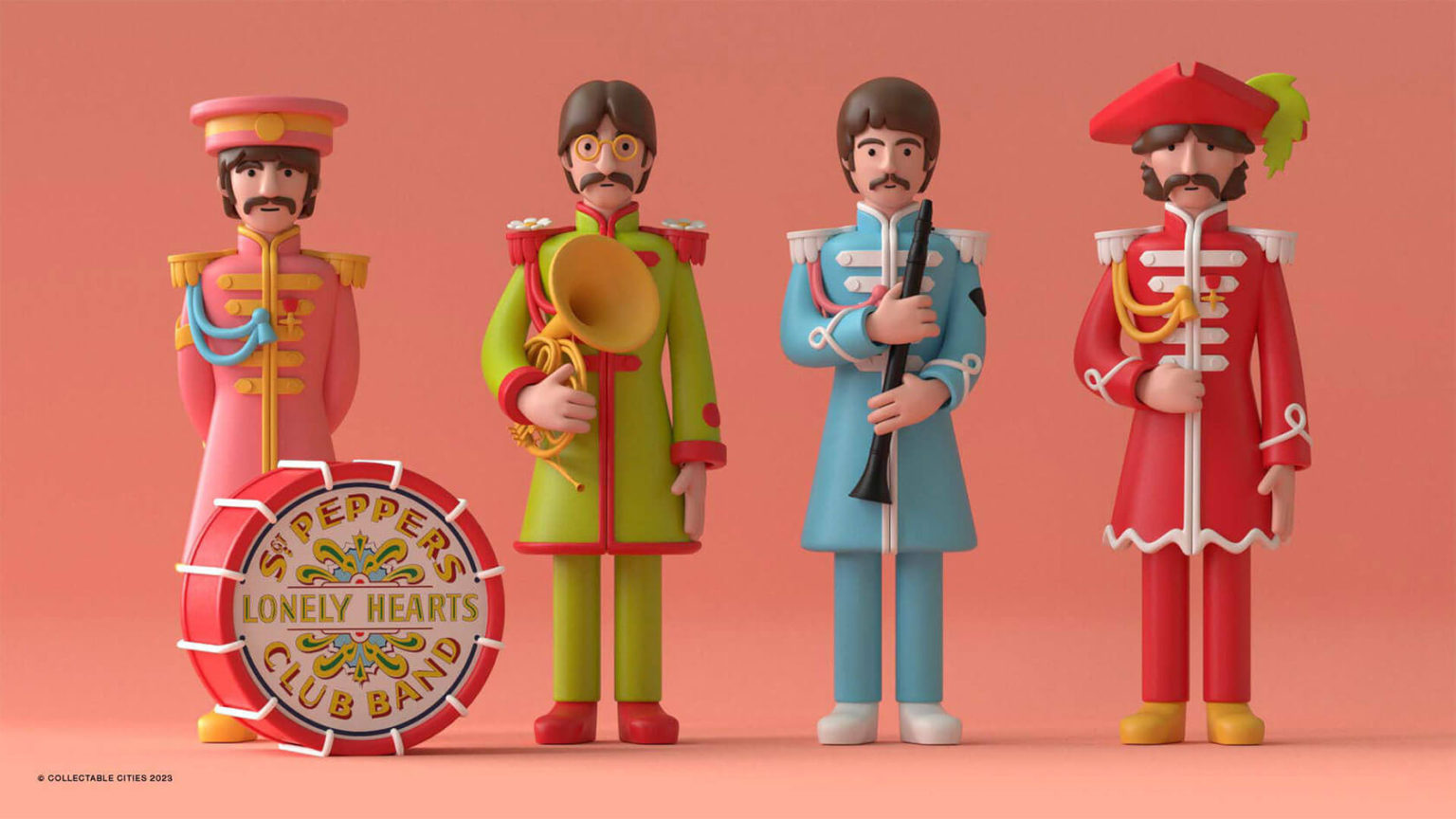
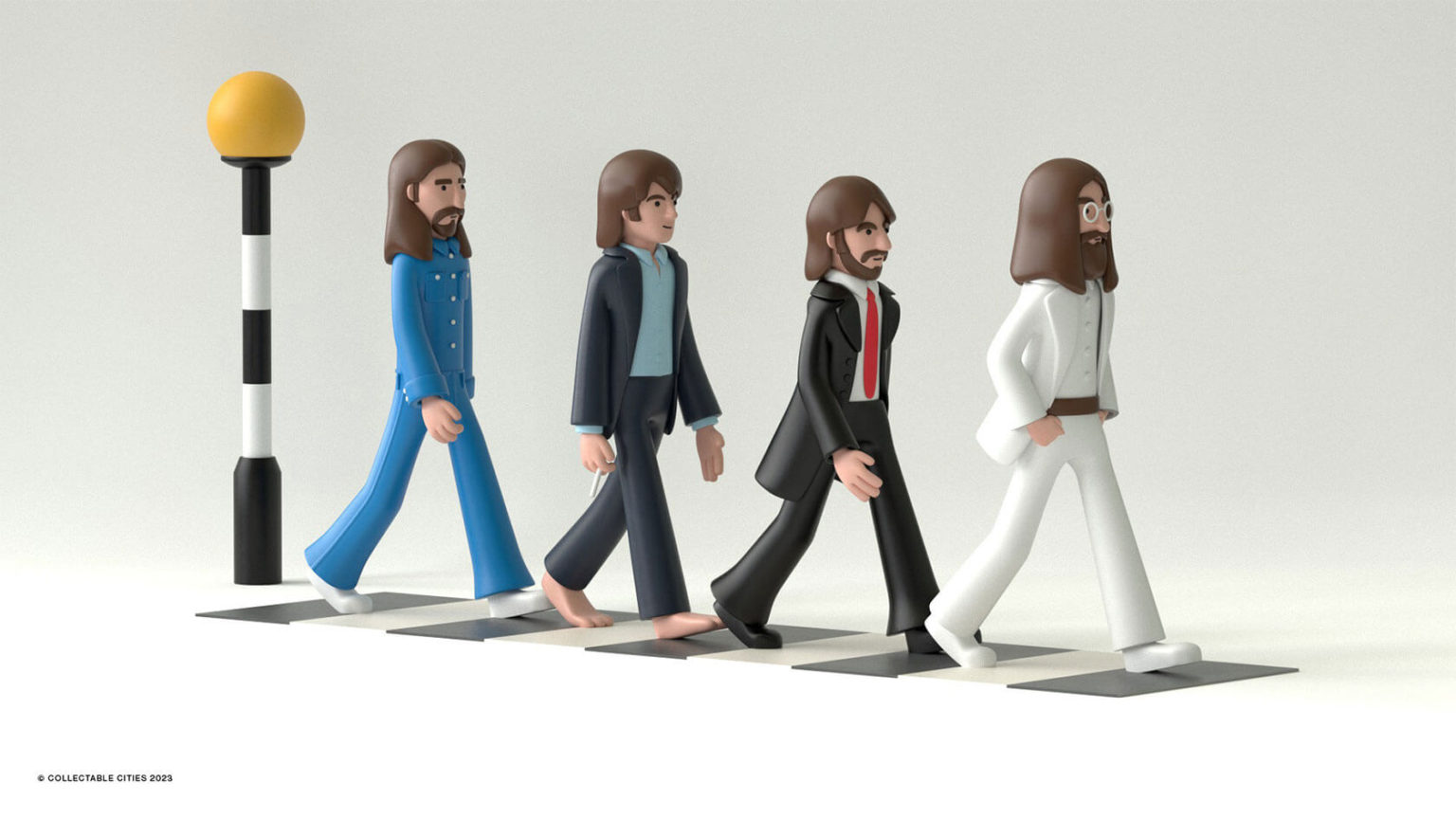
Creative duo Joseph Lattimer and Caitlin Derer Creates Absolutely Amazing The Beatles Collectable Toys
Read more: Creative duo Joseph Lattimer and Caitlin Derer Creates Absolutely Amazing The Beatles Collectable Toyshttps://designyoutrust.com/2024/11/artist-duo-creates-absolutely-amazing-the-beatles-collectable-toys



COLOR
-
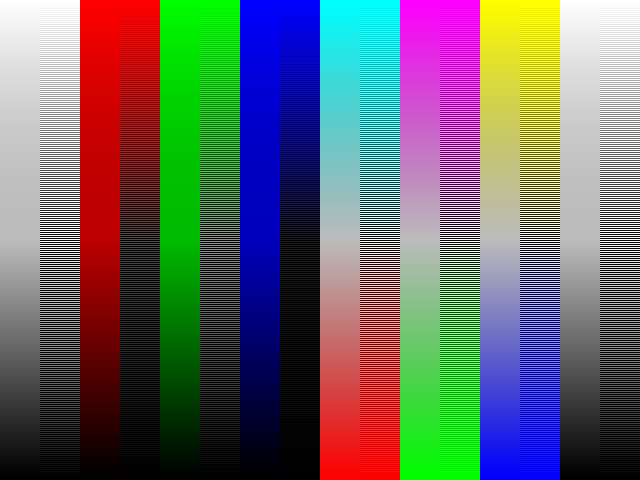
Gamma correction
Read more: Gamma correction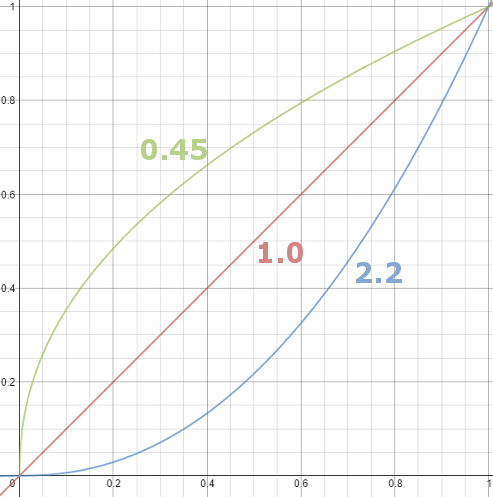
http://www.normankoren.com/makingfineprints1A.html#Gammabox
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gamma_correction
http://www.photoscientia.co.uk/Gamma.htm
https://www.w3.org/Graphics/Color/sRGB.html
http://www.eizoglobal.com/library/basics/lcd_display_gamma/index.html
https://forum.reallusion.com/PrintTopic308094.aspx
Basically, gamma is the relationship between the brightness of a pixel as it appears on the screen, and the numerical value of that pixel. Generally Gamma is just about defining relationships.
Three main types:
– Image Gamma encoded in images
– Display Gammas encoded in hardware and/or viewing time
– System or Viewing Gamma which is the net effect of all gammas when you look back at a final image. In theory this should flatten back to 1.0 gamma.
(more…) -
Colour – MacBeth Chart Checker Detection
Read more: Colour – MacBeth Chart Checker Detectiongithub.com/colour-science/colour-checker-detection
A Python package implementing various colour checker detection algorithms and related utilities.
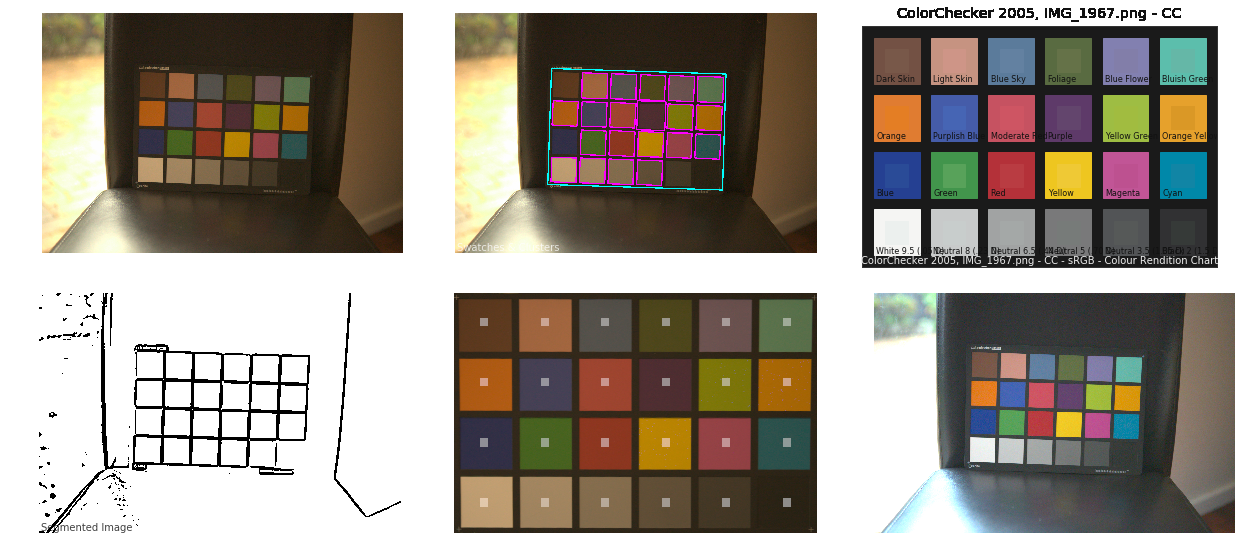
-
Photography basics: Color Temperature and White Balance
Read more: Photography basics: Color Temperature and White BalanceColor Temperature of a light source describes the spectrum of light which is radiated from a theoretical “blackbody” (an ideal physical body that absorbs all radiation and incident light – neither reflecting it nor allowing it to pass through) with a given surface temperature.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Color_temperature
Or. Most simply it is a method of describing the color characteristics of light through a numerical value that corresponds to the color emitted by a light source, measured in degrees of Kelvin (K) on a scale from 1,000 to 10,000.
More accurately. The color temperature of a light source is the temperature of an ideal backbody that radiates light of comparable hue to that of the light source.
(more…) -
Scientists claim to have discovered ‘new colour’ no one has seen before: Olo
Read more: Scientists claim to have discovered ‘new colour’ no one has seen before: Olohttps://www.bbc.com/news/articles/clyq0n3em41o
By stimulating specific cells in the retina, the participants claim to have witnessed a blue-green colour that scientists have called “olo”, but some experts have said the existence of a new colour is “open to argument”.
The findings, published in the journal Science Advances on Friday, have been described by the study’s co-author, Prof Ren Ng from the University of California, as “remarkable”.
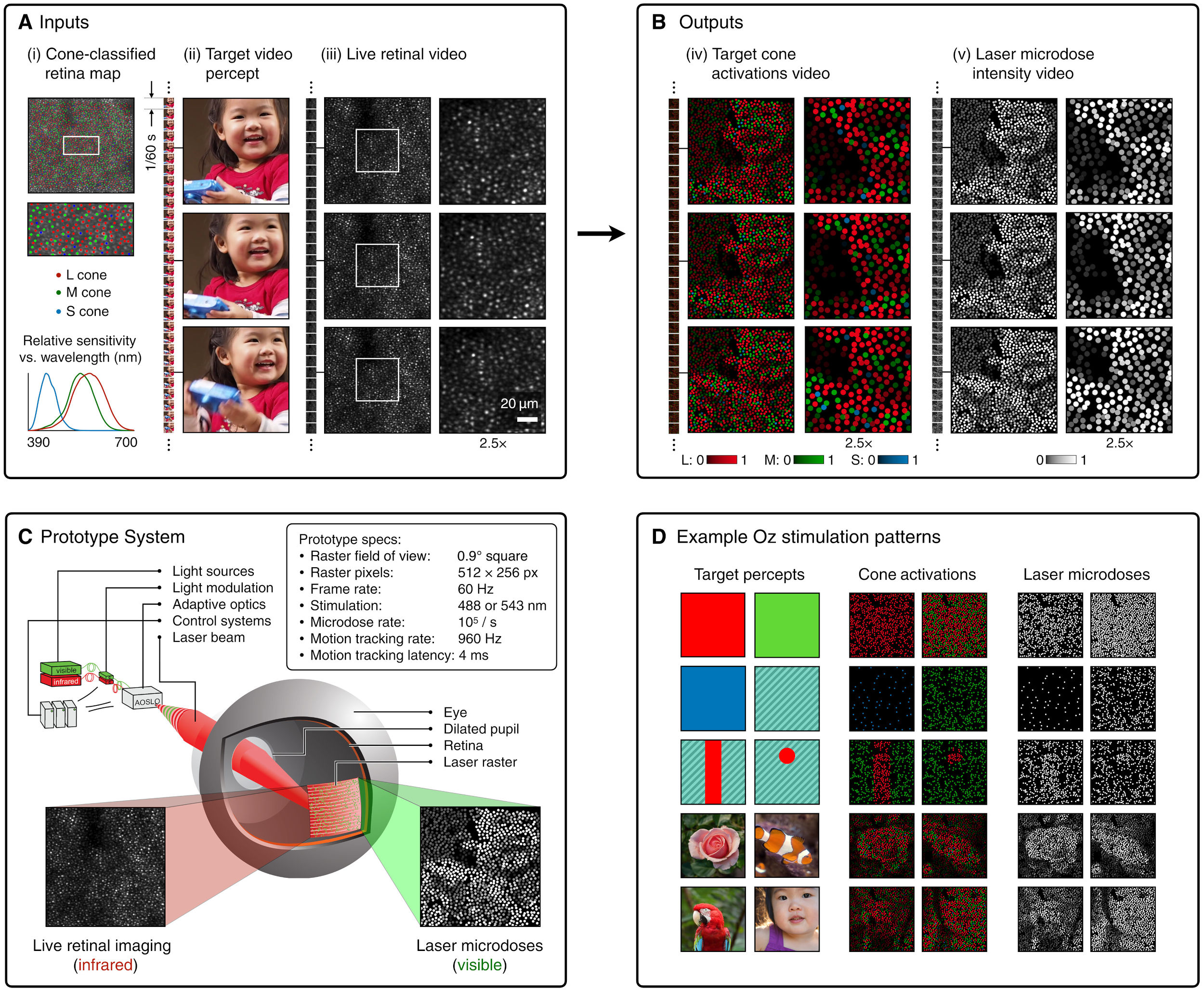
(A) System inputs. (i) Retina map of 103 cone cells preclassified by spectral type (7). (ii) Target visual percept (here, a video of a child, see movie S1 at 1:04). (iii) Infrared cellular-scale imaging of the retina with 60-frames-per-second rolling shutter. Fixational eye movement is visible over the three frames shown.
(B) System outputs. (iv) Real-time per-cone target activation levels to reproduce the target percept, computed by: extracting eye motion from the input video relative to the retina map; identifying the spectral type of every cone in the field of view; computing the per-cone activation the target percept would have produced. (v) Intensities of visible-wavelength 488-nm laser microdoses at each cone required to achieve its target activation level.
(C) Infrared imaging and visible-wavelength stimulation are physically accomplished in a raster scan across the retinal region using AOSLO. By modulating the visible-wavelength beam’s intensity, the laser microdoses shown in (v) are delivered. Drawing adapted with permission [Harmening and Sincich (54)].
(D) Examples of target percepts with corresponding cone activations and laser microdoses, ranging from colored squares to complex imagery. Teal-striped regions represent the color “olo” of stimulating only M cones.
-
Light and Matter : The 2018 theory of Physically-Based Rendering and Shading by Allegorithmic
Read more: Light and Matter : The 2018 theory of Physically-Based Rendering and Shading by Allegorithmicacademy.substance3d.com/courses/the-pbr-guide-part-1
academy.substance3d.com/courses/the-pbr-guide-part-2
Local copy:
-
Polarised vs unpolarized filtering
Read more: Polarised vs unpolarized filteringA light wave that is vibrating in more than one plane is referred to as unpolarized light. …
Polarized light waves are light waves in which the vibrations occur in a single plane. The process of transforming unpolarized light into polarized light is known as polarization.
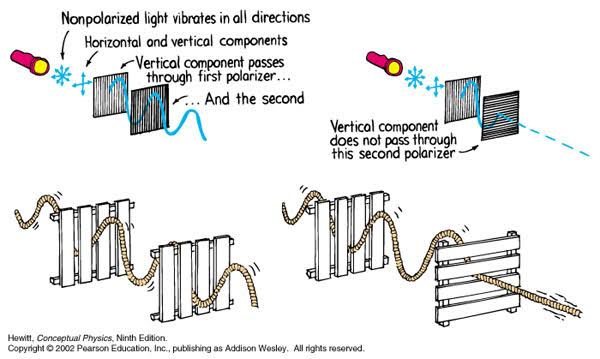
en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Polarizing_filter_(photography)
The most common use of polarized technology is to reduce lighting complexity on the subject.
(more…)
Details such as glare and hard edges are not removed, but greatly reduced.
LIGHTING
-
Free HDRI libraries
Read more: Free HDRI librariesnoahwitchell.com
http://www.noahwitchell.com/freebieslocationtextures.com
https://locationtextures.com/panoramas/maxroz.com
https://www.maxroz.com/hdri/listHDRI Haven
https://hdrihaven.com/Poly Haven
https://polyhaven.com/hdrisDomeble
https://www.domeble.com/IHDRI
https://www.ihdri.com/HDRMaps
https://hdrmaps.com/NoEmotionHdrs.net
http://noemotionhdrs.net/hdrday.htmlOpenFootage.net
https://www.openfootage.net/hdri-panorama/HDRI-hub
https://www.hdri-hub.com/hdrishop/hdri.zwischendrin
https://www.zwischendrin.com/en/browse/hdriLonger list here:
https://cgtricks.com/list-sites-free-hdri/
-
Rendering – BRDF – Bidirectional reflectance distribution function
Read more: Rendering – BRDF – Bidirectional reflectance distribution functionhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bidirectional_reflectance_distribution_function
The bidirectional reflectance distribution function is a four-dimensional function that defines how light is reflected at an opaque surface
http://www.cs.ucla.edu/~zhu/tutorial/An_Introduction_to_BRDF-Based_Lighting.pdf
In general, when light interacts with matter, a complicated light-matter dynamic occurs. This interaction depends on the physical characteristics of the light as well as the physical composition and characteristics of the matter.
That is, some of the incident light is reflected, some of the light is transmitted, and another portion of the light is absorbed by the medium itself.
A BRDF describes how much light is reflected when light makes contact with a certain material. Similarly, a BTDF (Bi-directional Transmission Distribution Function) describes how much light is transmitted when light makes contact with a certain material
http://www.cs.princeton.edu/~smr/cs348c-97/surveypaper.html
It is difficult to establish exactly how far one should go in elaborating the surface model. A truly complete representation of the reflective behavior of a surface might take into account such phenomena as polarization, scattering, fluorescence, and phosphorescence, all of which might vary with position on the surface. Therefore, the variables in this complete function would be:
incoming and outgoing angle incoming and outgoing wavelength incoming and outgoing polarization (both linear and circular) incoming and outgoing position (which might differ due to subsurface scattering) time delay between the incoming and outgoing light ray
COLLECTIONS
| Featured AI
| Design And Composition
| Explore posts
POPULAR SEARCHES
unreal | pipeline | virtual production | free | learn | photoshop | 360 | macro | google | nvidia | resolution | open source | hdri | real-time | photography basics | nuke
FEATURED POSTS
-
How to paint a boardgame miniatures
-
The Public Domain Is Working Again — No Thanks To Disney
-
SourceTree vs Github Desktop – Which one to use
-
Black Forest Labs released FLUX.1 Kontext
-
Photography basics: Production Rendering Resolution Charts
-
Key/Fill ratios and scene composition using false colors and Nuke node
-
Canva bought Affinity – Now Affinity Photo and Affinity Designer are… GONE?!
-
What’s the Difference Between Ray Casting, Ray Tracing, Path Tracing and Rasterization? Physical light tracing…
Social Links
DISCLAIMER – Links and images on this website may be protected by the respective owners’ copyright. All data submitted by users through this site shall be treated as freely available to share.








![sRGB gamma correction test [gamma correction test]](http://www.madore.org/~david/misc/color/gammatest.png)