COMPOSITION
-
Composition – cinematography Cheat Sheet
Read more: Composition – cinematography Cheat Sheet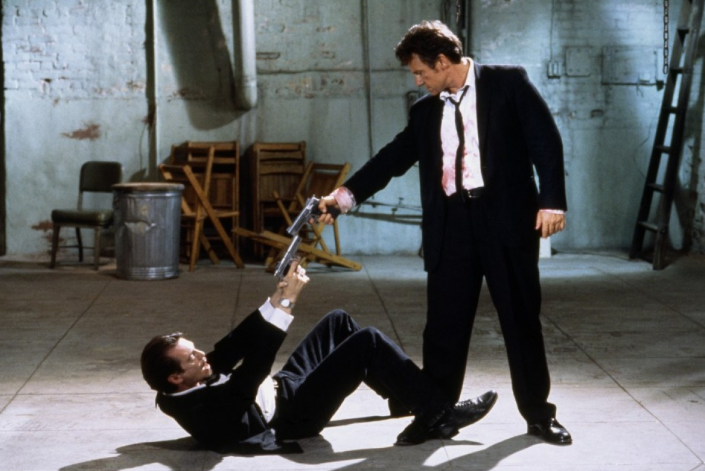
Where is our eye attracted first? Why?
Size. Focus. Lighting. Color.
Size. Mr. White (Harvey Keitel) on the right.
Focus. He’s one of the two objects in focus.
Lighting. Mr. White is large and in focus and Mr. Pink (Steve Buscemi) is highlighted by
a shaft of light.
Color. Both are black and white but the read on Mr. White’s shirt now really stands out.
(more…)
What type of lighting? -
Mastering Camera Shots and Angles: A Guide for Filmmakers
Read more: Mastering Camera Shots and Angles: A Guide for Filmmakershttps://website.ltx.studio/blog/mastering-camera-shots-and-angles
1. Extreme Wide Shot

2. Wide Shot

3. Medium Shot
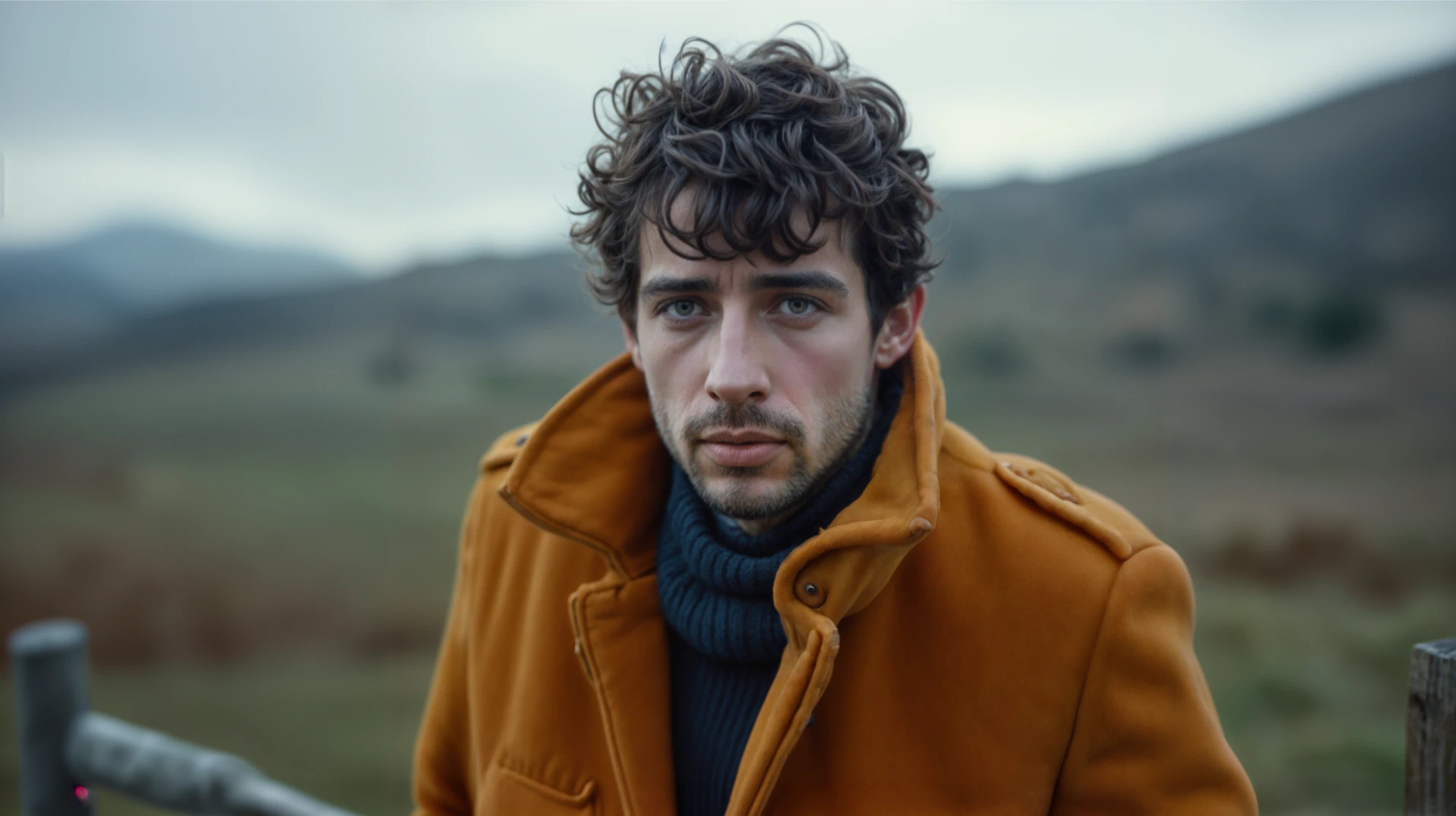

4. Close Up
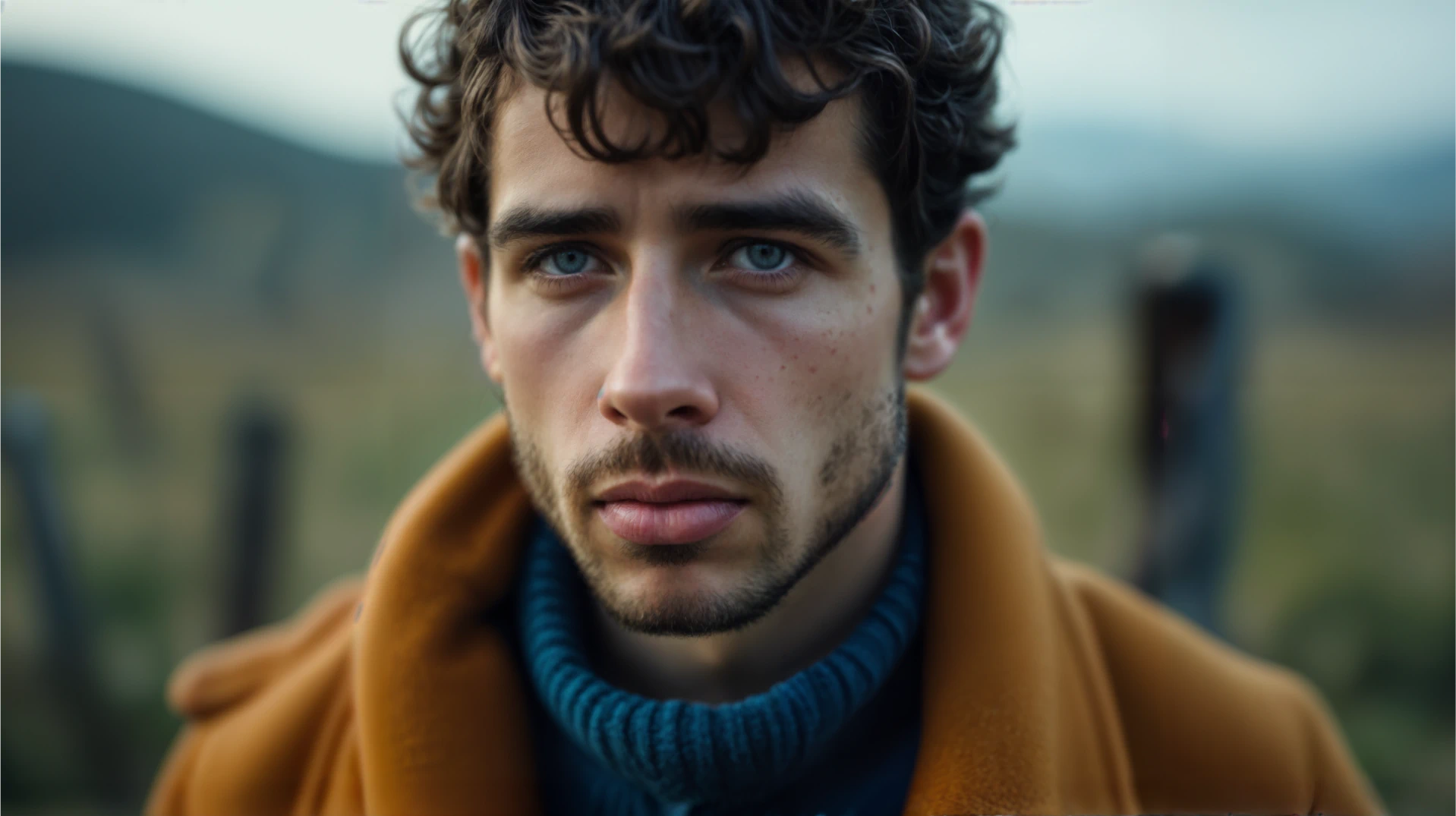

5. Extreme Close Up
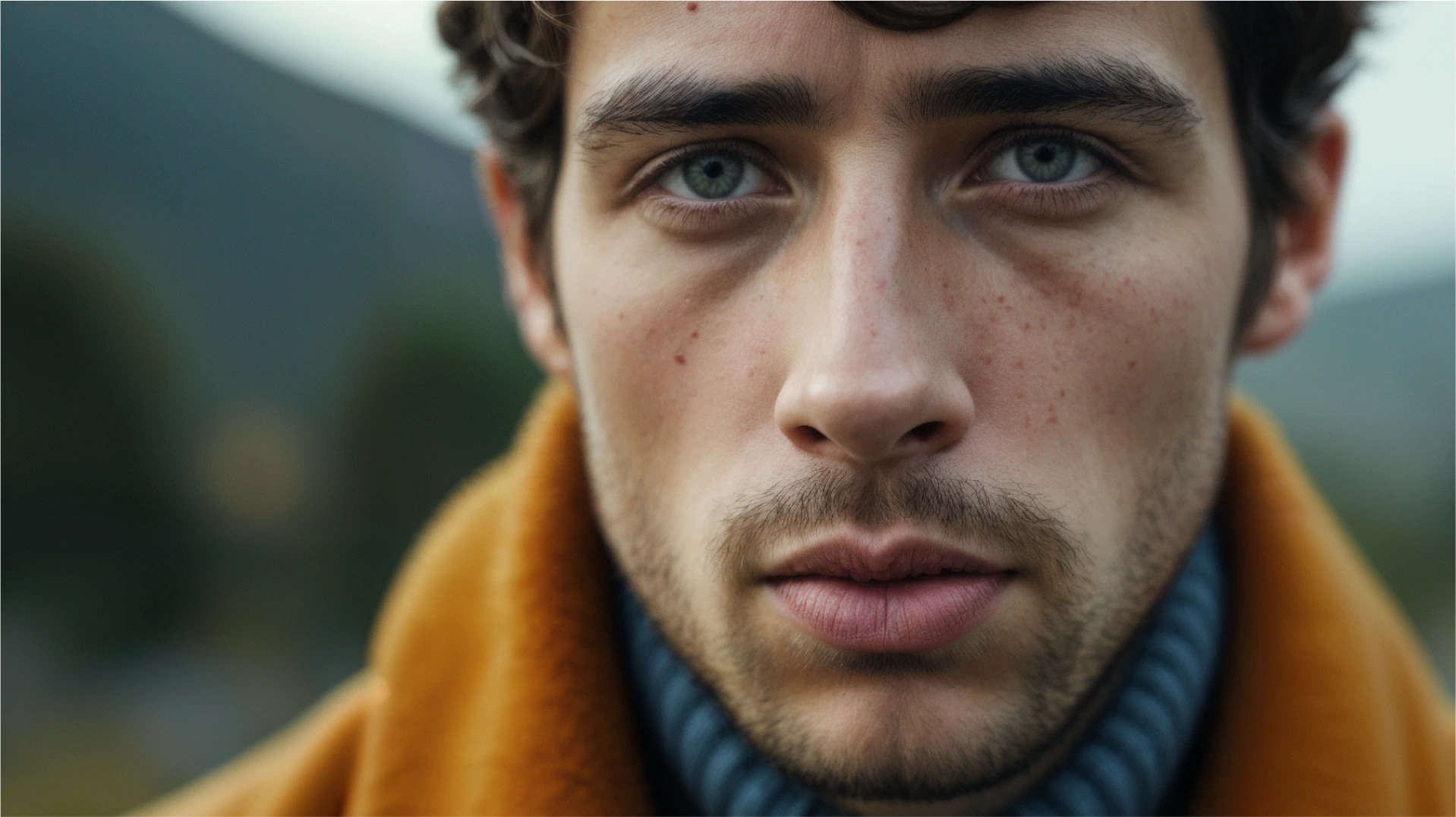

-
Photography basics: Camera Aspect Ratio, Sensor Size and Depth of Field – resolutions
Read more: Photography basics: Camera Aspect Ratio, Sensor Size and Depth of Field – resolutionshttp://www.shutterangle.com/2012/cinematic-look-aspect-ratio-sensor-size-depth-of-field/
http://www.shutterangle.com/2012/film-video-aspect-ratio-artistic-choice/
DESIGN
COLOR
-
The Forbidden colors – Red-Green & Blue-Yellow: The Stunning Colors You Can’t See
Read more: The Forbidden colors – Red-Green & Blue-Yellow: The Stunning Colors You Can’t Seewww.livescience.com/17948-red-green-blue-yellow-stunning-colors.html
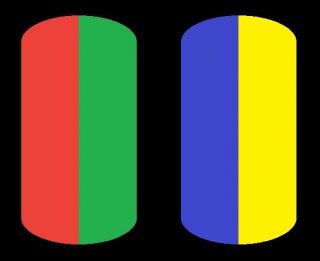
While the human eye has red, green, and blue-sensing cones, those cones are cross-wired in the retina to produce a luminance channel plus a red-green and a blue-yellow channel, and it’s data in that color space (known technically as “LAB”) that goes to the brain. That’s why we can’t perceive a reddish-green or a yellowish-blue, whereas such colors can be represented in the RGB color space used by digital cameras.
https://en.rockcontent.com/blog/the-use-of-yellow-in-data-design
The back of the retina is covered in light-sensitive neurons known as cone cells and rod cells. There are three types of cone cells, each sensitive to different ranges of light. These ranges overlap, but for convenience the cones are referred to as blue (short-wavelength), green (medium-wavelength), and red (long-wavelength). The rod cells are primarily used in low-light situations, so we’ll ignore those for now.
When light enters the eye and hits the cone cells, the cones get excited and send signals to the brain through the visual cortex. Different wavelengths of light excite different combinations of cones to varying levels, which generates our perception of color. You can see that the red cones are most sensitive to light, and the blue cones are least sensitive. The sensitivity of green and red cones overlaps for most of the visible spectrum.
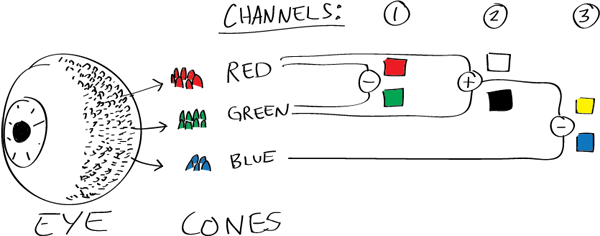
Here’s how your brain takes the signals of light intensity from the cones and turns it into color information. To see red or green, your brain finds the difference between the levels of excitement in your red and green cones. This is the red-green channel.
To get “brightness,” your brain combines the excitement of your red and green cones. This creates the luminance, or black-white, channel. To see yellow or blue, your brain then finds the difference between this luminance signal and the excitement of your blue cones. This is the yellow-blue channel.
From the calculations made in the brain along those three channels, we get four basic colors: blue, green, yellow, and red. Seeing blue is what you experience when low-wavelength light excites the blue cones more than the green and red.
Seeing green happens when light excites the green cones more than the red cones. Seeing red happens when only the red cones are excited by high-wavelength light.
Here’s where it gets interesting. Seeing yellow is what happens when BOTH the green AND red cones are highly excited near their peak sensitivity. This is the biggest collective excitement that your cones ever have, aside from seeing pure white.
Notice that yellow occurs at peak intensity in the graph to the right. Further, the lens and cornea of the eye happen to block shorter wavelengths, reducing sensitivity to blue and violet light.
-
Victor Perez – The Color Management Handbook for Visual Effects Artists
Read more: Victor Perez – The Color Management Handbook for Visual Effects ArtistsDigital Color Principles, Color Management Fundamentals & ACES Workflows
-
Brett Jones / Phil Reyneri (Lightform) / Philipp7pc: The study of Projection Mapping through Projectors
Read more: Brett Jones / Phil Reyneri (Lightform) / Philipp7pc: The study of Projection Mapping through ProjectorsVideo Projection Tool Software
https://hcgilje.wordpress.com/vpt/https://www.projectorpoint.co.uk/news/how-bright-should-my-projector-be/
http://www.adwindowscreens.com/the_calculator/
heavym
https://heavym.net/en/MadMapper
https://madmapper.com/ -
The Maya civilization and the color blue
Read more: The Maya civilization and the color blueMaya blue is a highly unusual pigment because it is a mix of organic indigo and an inorganic clay mineral called palygorskite.
Echoing the color of an azure sky, the indelible pigment was used to accentuate everything from ceramics to human sacrifices in the Late Preclassic period (300 B.C. to A.D. 300).
A team of researchers led by Dean Arnold, an adjunct curator of anthropology at the Field Museum in Chicago, determined that the key to Maya blue was actually a sacred incense called copal.
By heating the mixture of indigo, copal and palygorskite over a fire, the Maya produced the unique pigment, he reported at the time.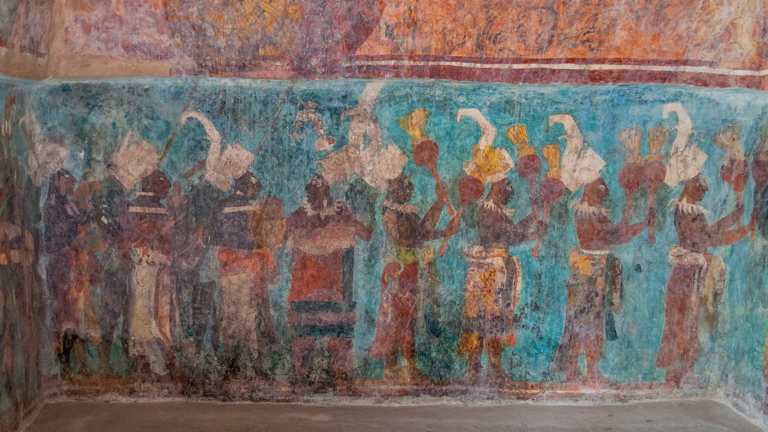
-
Rec-2020 – TVs new color gamut standard used by Dolby Vision?
Read more: Rec-2020 – TVs new color gamut standard used by Dolby Vision?https://www.hdrsoft.com/resources/dri.html#bit-depth
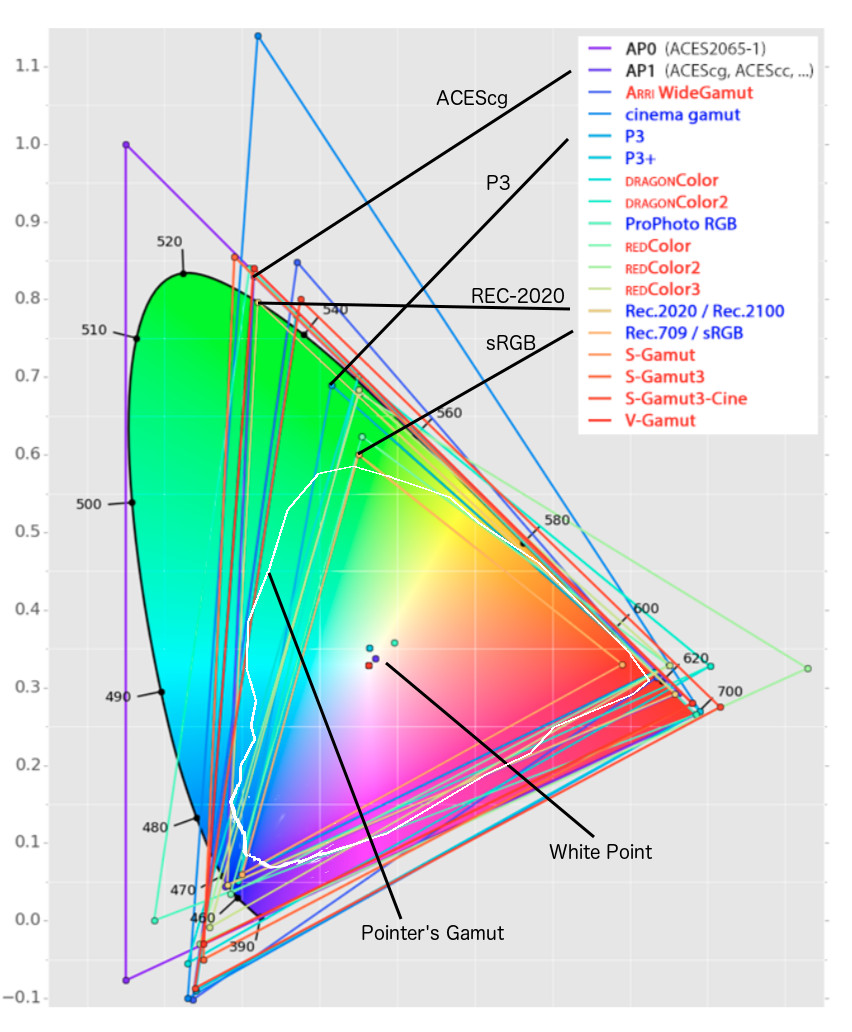
The dynamic range is a ratio between the maximum and minimum values of a physical measurement. Its definition depends on what the dynamic range refers to.
For a scene: Dynamic range is the ratio between the brightest and darkest parts of the scene.
For a camera: Dynamic range is the ratio of saturation to noise. More specifically, the ratio of the intensity that just saturates the camera to the intensity that just lifts the camera response one standard deviation above camera noise.
For a display: Dynamic range is the ratio between the maximum and minimum intensities emitted from the screen.
The Dynamic Range of real-world scenes can be quite high — ratios of 100,000:1 are common in the natural world. An HDR (High Dynamic Range) image stores pixel values that span the whole tonal range of real-world scenes. Therefore, an HDR image is encoded in a format that allows the largest range of values, e.g. floating-point values stored with 32 bits per color channel. Another characteristics of an HDR image is that it stores linear values. This means that the value of a pixel from an HDR image is proportional to the amount of light measured by the camera.
For TVs HDR is great, but it’s not the only new TV feature worth discussing.
(more…) -
Polarised vs unpolarized filtering
Read more: Polarised vs unpolarized filteringA light wave that is vibrating in more than one plane is referred to as unpolarized light. …
Polarized light waves are light waves in which the vibrations occur in a single plane. The process of transforming unpolarized light into polarized light is known as polarization.
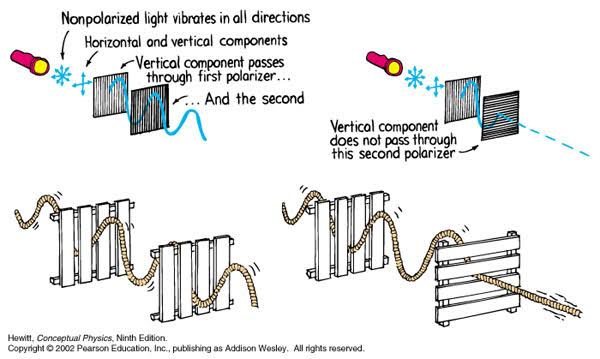
en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Polarizing_filter_(photography)
The most common use of polarized technology is to reduce lighting complexity on the subject.
(more…)
Details such as glare and hard edges are not removed, but greatly reduced. -
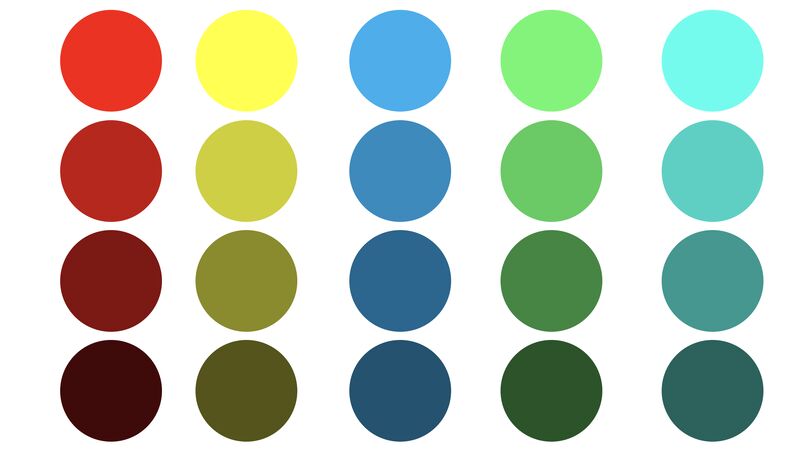
Is it possible to get a dark yellow
Read more: Is it possible to get a dark yellowhttps://www.patreon.com/posts/102660674
https://www.linkedin.com/posts/stephenwestland_here-is-a-post-about-the-dark-yellow-problem-activity-7187131643764092929-7uCL
LIGHTING
-
Unity 3D resources
Read more: Unity 3D resources
http://answers.unity3d.com/questions/12321/how-can-i-start-learning-unity-fast-list-of-tutori.html
If you have no previous experience with Unity, start with these six video tutorials which give a quick overview of the Unity interface and some important features http://unity3d.com/support/documentation/video/
-
Lighting Every Darkness with 3DGS: Fast Training and Real-Time Rendering and Denoising for HDR View Synthesis
Read more: Lighting Every Darkness with 3DGS: Fast Training and Real-Time Rendering and Denoising for HDR View Synthesishttps://srameo.github.io/projects/le3d/
LE3D is a method for real-time HDR view synthesis from RAW images. It is particularly effective for nighttime scenes.
https://github.com/Srameo/LE3D
-
Narcis Calin’s Galaxy Engine – A free, open source simulation software
Read more: Narcis Calin’s Galaxy Engine – A free, open source simulation softwareThis 2025 I decided to start learning how to code, so I installed Visual Studio and I started looking into C++. After days of watching tutorials and guides about the basics of C++ and programming, I decided to make something physics-related. I started with a dot that fell to the ground and then I wanted to simulate gravitational attraction, so I made 2 circles attracting each other. I thought it was really cool to see something I made with code actually work, so I kept building on top of that small, basic program. And here we are after roughly 8 months of learning programming. This is Galaxy Engine, and it is a simulation software I have been making ever since I started my learning journey. It currently can simulate gravity, dark matter, galaxies, the Big Bang, temperature, fluid dynamics, breakable solids, planetary interactions, etc. The program can run many tens of thousands of particles in real time on the CPU thanks to the Barnes-Hut algorithm, mixed with Morton curves. It also includes its own PBR 2D path tracer with BVH optimizations. The path tracer can simulate a bunch of stuff like diffuse lighting, specular reflections, refraction, internal reflection, fresnel, emission, dispersion, roughness, IOR, nested IOR and more! I tried to make the path tracer closer to traditional 3D render engines like V-Ray. I honestly never imagined I would go this far with programming, and it has been an amazing learning experience so far. I think that mixing this knowledge with my 3D knowledge can unlock countless new possibilities. In case you are curious about Galaxy Engine, I made it completely free and Open-Source so that anyone can build and compile it locally! You can find the source code in GitHub
https://github.com/NarcisCalin/Galaxy-Engine
COLLECTIONS
| Featured AI
| Design And Composition
| Explore posts
POPULAR SEARCHES
unreal | pipeline | virtual production | free | learn | photoshop | 360 | macro | google | nvidia | resolution | open source | hdri | real-time | photography basics | nuke
FEATURED POSTS
-
NVidia – High-Fidelity 3D Mesh Generation at Scale with Meshtron
-
AI and the Law – studiobinder.com – What is Fair Use: Definition, Policies, Examples and More
-
What’s the Difference Between Ray Casting, Ray Tracing, Path Tracing and Rasterization? Physical light tracing…
-
Emmanuel Tsekleves – Writing Research Papers
-
PixelSham – Introduction to Python 2022
-
The Public Domain Is Working Again — No Thanks To Disney
-
Zibra.AI – Real-Time Volumetric Effects in Virtual Production. Now free for Indies!
-
Advanced Computer Vision with Python OpenCV and Mediapipe
Social Links
DISCLAIMER – Links and images on this website may be protected by the respective owners’ copyright. All data submitted by users through this site shall be treated as freely available to share.







