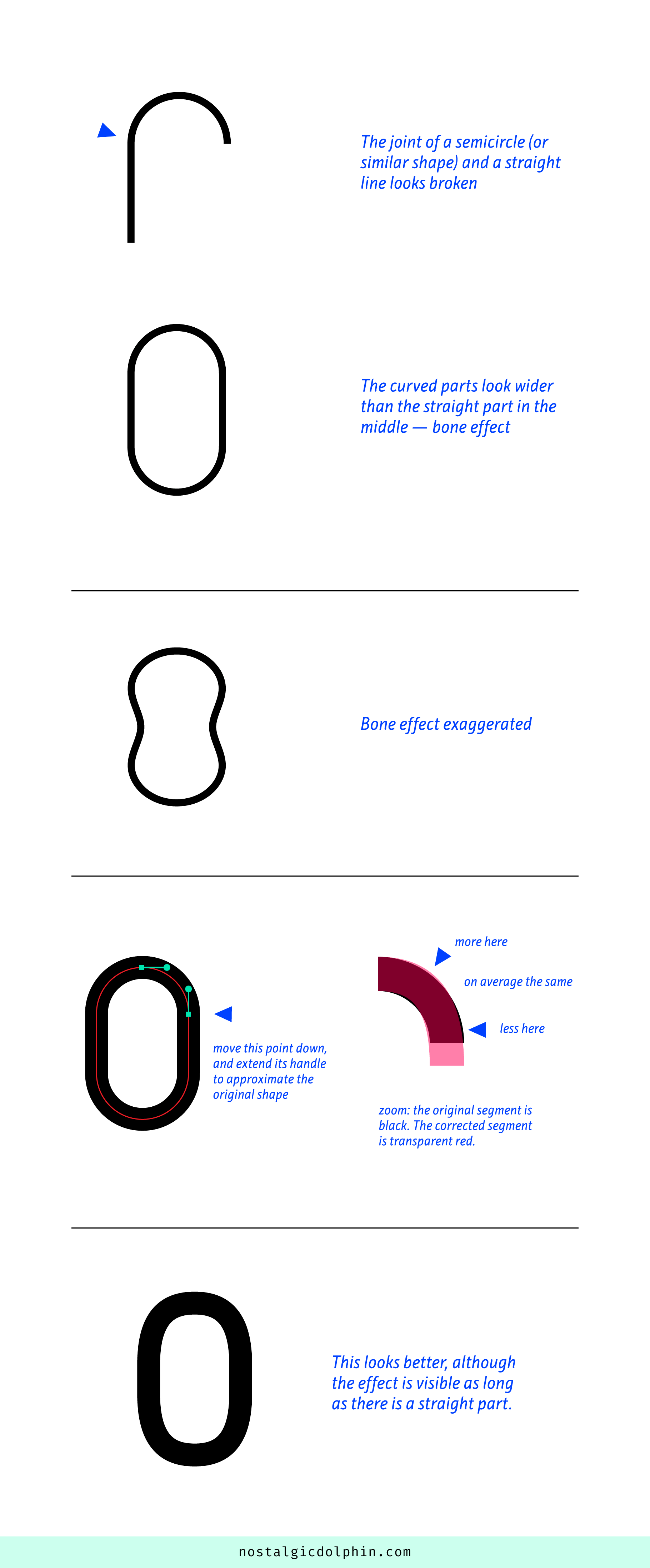
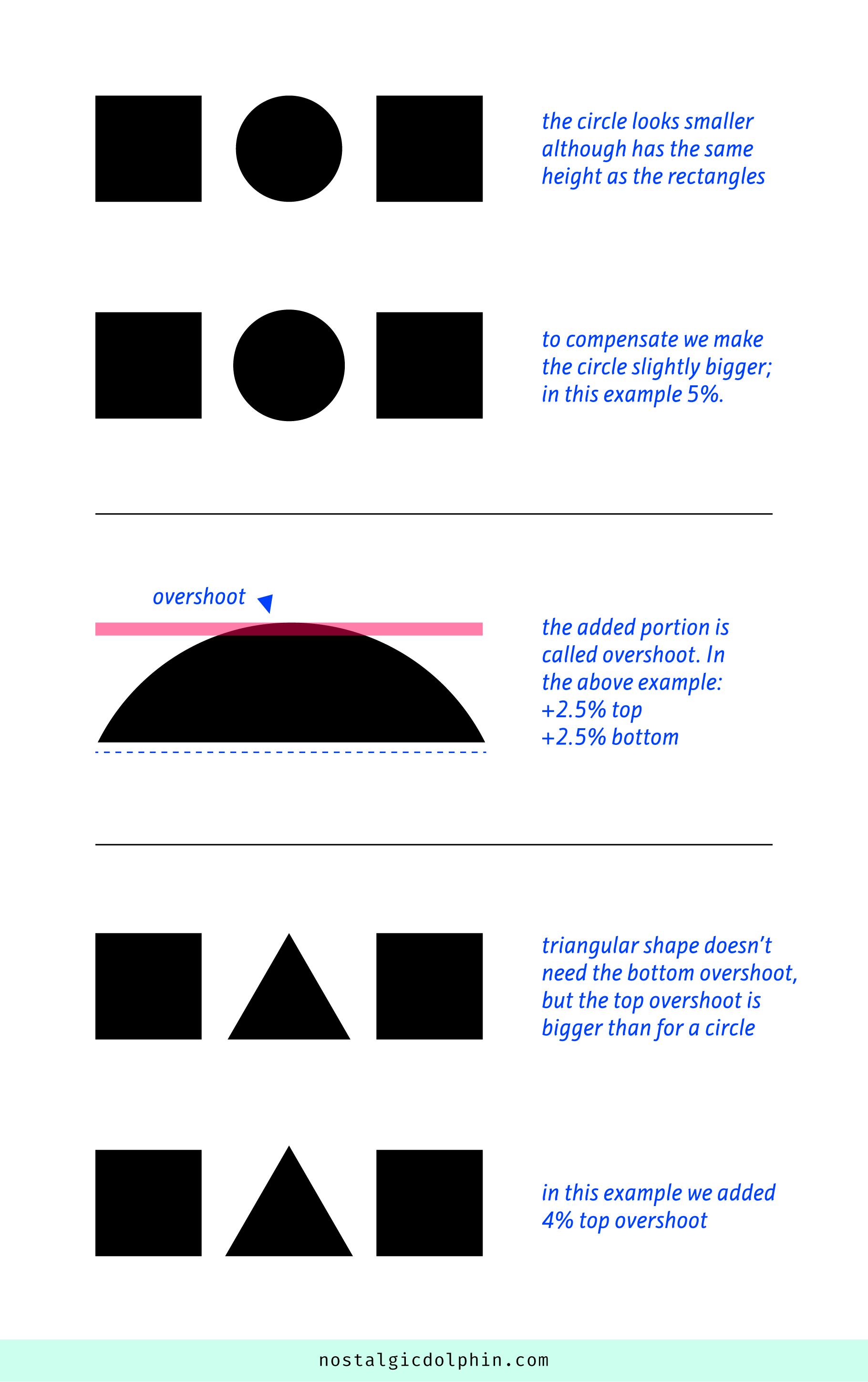
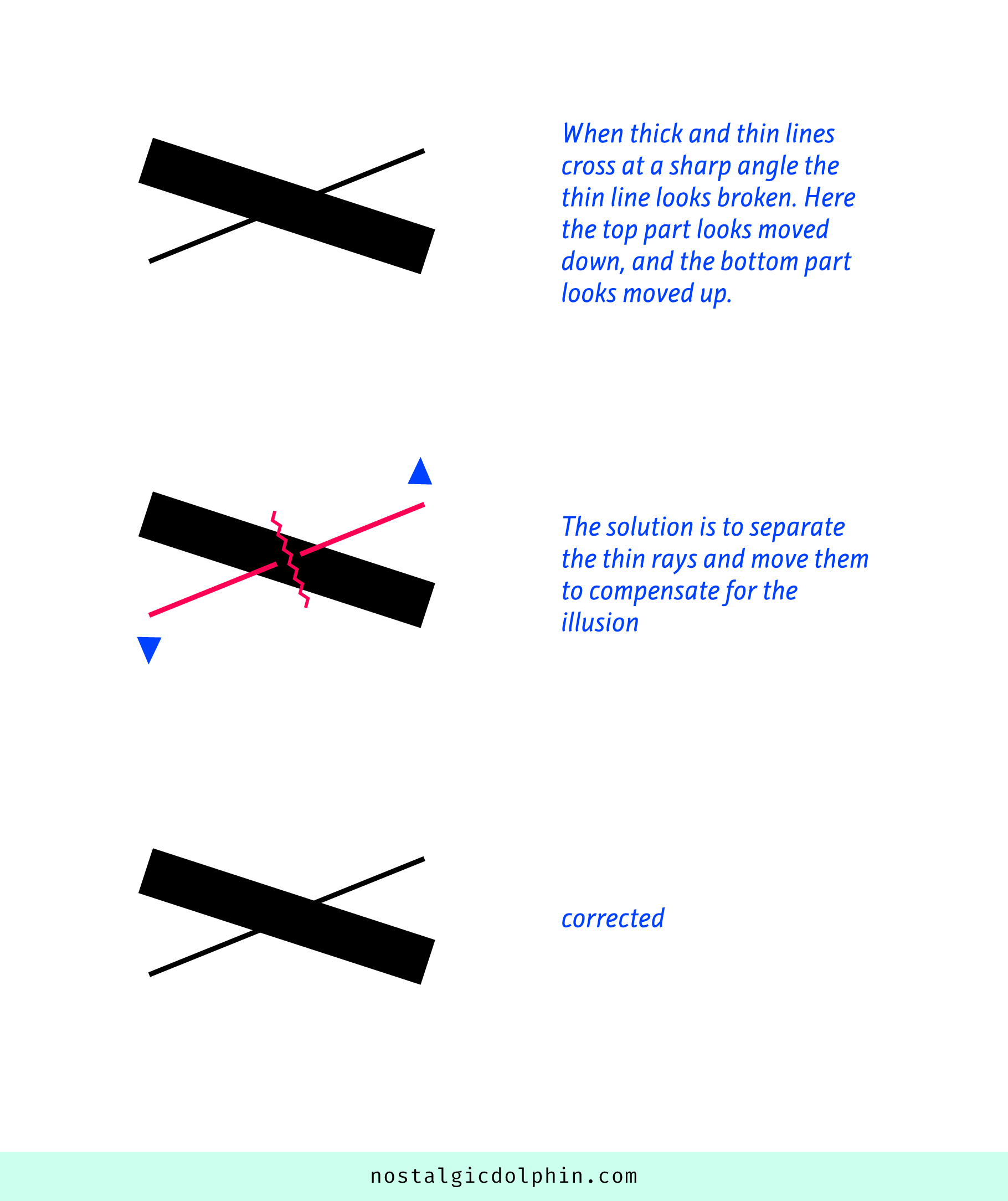
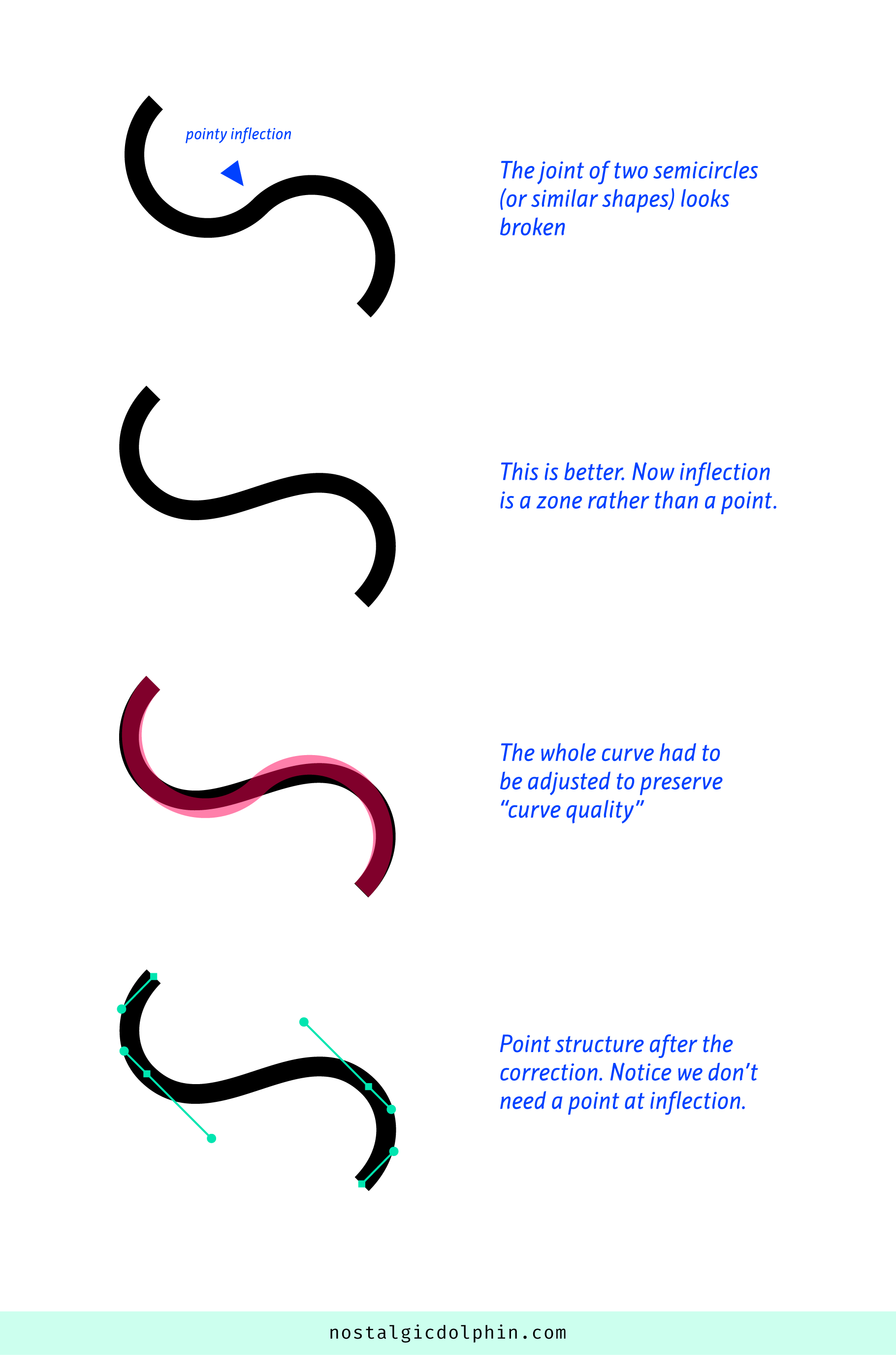COMPOSITION
DESIGN
COLOR
-
FXGuide – ACES 2.0 with ILM’s Alex Fry
Read more: FXGuide – ACES 2.0 with ILM’s Alex Fryhttps://draftdocs.acescentral.com/background/whats-new/
ACES 2.0 is the second major release of the components that make up the ACES system. The most significant change is a new suite of rendering transforms whose design was informed by collected feedback and requests from users of ACES 1. The changes aim to improve the appearance of perceived artifacts and to complete previously unfinished components of the system, resulting in a more complete, robust, and consistent product.
Highlights of the key changes in ACES 2.0 are as follows:
- New output transforms, including:
- A less aggressive tone scale
- More intuitive controls to create custom outputs to non-standard displays
- Robust gamut mapping to improve perceptual uniformity
- Improved performance of the inverse transforms
- Enhanced AMF specification
- An updated specification for ACES Transform IDs
- OpenEXR compression recommendations
- Enhanced tools for generating Input Transforms and recommended procedures for characterizing prosumer cameras
- Look Transform Library
- Expanded documentation
Rendering Transform
The most substantial change in ACES 2.0 is a complete redesign of the rendering transform.
ACES 2.0 was built as a unified system, rather than through piecemeal additions. Different deliverable outputs “match” better and making outputs to display setups other than the provided presets is intended to be user-driven. The rendering transforms are less likely to produce undesirable artifacts “out of the box”, which means less time can be spent fixing problematic images and more time making pictures look the way you want.
Key design goals
- Improve consistency of tone scale and provide an easy to use parameter to allow for outputs between preset dynamic ranges
- Minimize hue skews across exposure range in a region of same hue
- Unify for structural consistency across transform type
- Easy to use parameters to create outputs other than the presets
- Robust gamut mapping to improve harsh clipping artifacts
- Fill extents of output code value cube (where appropriate and expected)
- Invertible – not necessarily reversible, but Output > ACES > Output round-trip should be possible
- Accomplish all of the above while maintaining an acceptable “out-of-the box” rendering
- New output transforms, including:
-
Photography Basics : Spectral Sensitivity Estimation Without a Camera
Read more: Photography Basics : Spectral Sensitivity Estimation Without a Camerahttps://color-lab-eilat.github.io/Spectral-sensitivity-estimation-web/
A number of problems in computer vision and related fields would be mitigated if camera spectral sensitivities were known. As consumer cameras are not designed for high-precision visual tasks, manufacturers do not disclose spectral sensitivities. Their estimation requires a costly optical setup, which triggered researchers to come up with numerous indirect methods that aim to lower cost and complexity by using color targets. However, the use of color targets gives rise to new complications that make the estimation more difficult, and consequently, there currently exists no simple, low-cost, robust go-to method for spectral sensitivity estimation that non-specialized research labs can adopt. Furthermore, even if not limited by hardware or cost, researchers frequently work with imagery from multiple cameras that they do not have in their possession.
To provide a practical solution to this problem, we propose a framework for spectral sensitivity estimation that not only does not require any hardware (including a color target), but also does not require physical access to the camera itself. Similar to other work, we formulate an optimization problem that minimizes a two-term objective function: a camera-specific term from a system of equations, and a universal term that bounds the solution space.
Different than other work, we utilize publicly available high-quality calibration data to construct both terms. We use the colorimetric mapping matrices provided by the Adobe DNG Converter to formulate the camera-specific system of equations, and constrain the solutions using an autoencoder trained on a database of ground-truth curves. On average, we achieve reconstruction errors as low as those that can arise due to manufacturing imperfections between two copies of the same camera. We provide predicted sensitivities for more than 1,000 cameras that the Adobe DNG Converter currently supports, and discuss which tasks can become trivial when camera responses are available.
-
Victor Perez – The Color Management Handbook for Visual Effects Artists
Read more: Victor Perez – The Color Management Handbook for Visual Effects ArtistsDigital Color Principles, Color Management Fundamentals & ACES Workflows
-
The Maya civilization and the color blue
Read more: The Maya civilization and the color blueMaya blue is a highly unusual pigment because it is a mix of organic indigo and an inorganic clay mineral called palygorskite.
Echoing the color of an azure sky, the indelible pigment was used to accentuate everything from ceramics to human sacrifices in the Late Preclassic period (300 B.C. to A.D. 300).
A team of researchers led by Dean Arnold, an adjunct curator of anthropology at the Field Museum in Chicago, determined that the key to Maya blue was actually a sacred incense called copal.
By heating the mixture of indigo, copal and palygorskite over a fire, the Maya produced the unique pigment, he reported at the time.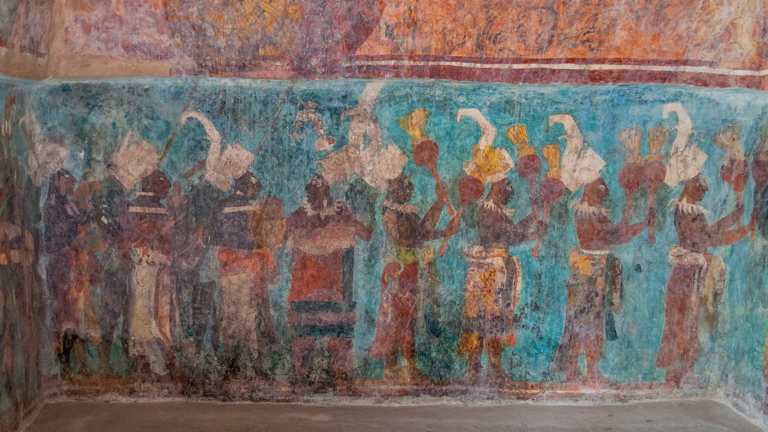
LIGHTING
-
GretagMacbeth Color Checker Numeric Values and Middle Gray
Read more: GretagMacbeth Color Checker Numeric Values and Middle GrayThe human eye perceives half scene brightness not as the linear 50% of the present energy (linear nature values) but as 18% of the overall brightness. We are biased to perceive more information in the dark and contrast areas. A Macbeth chart helps with calibrating back into a photographic capture into this “human perspective” of the world.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Middle_gray
In photography, painting, and other visual arts, middle gray or middle grey is a tone that is perceptually about halfway between black and white on a lightness scale in photography and printing, it is typically defined as 18% reflectance in visible light
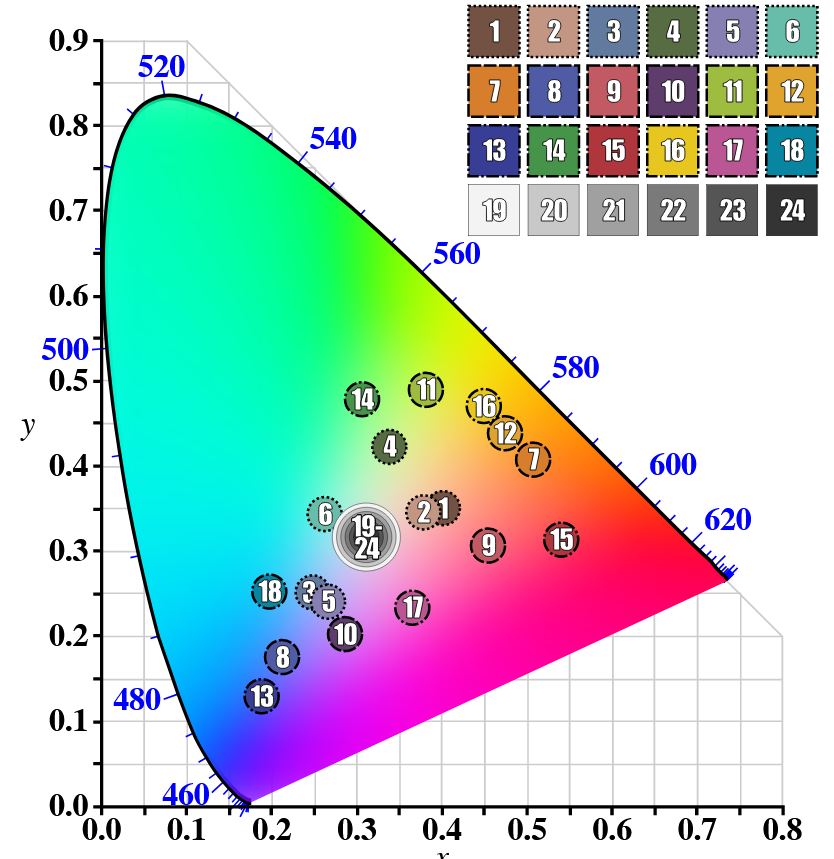
Light meters, cameras, and pictures are often calibrated using an 18% gray card[4][5][6] or a color reference card such as a ColorChecker. On the assumption that 18% is similar to the average reflectance of a scene, a grey card can be used to estimate the required exposure of the film.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ColorChecker
(more…) -
Composition – cinematography Cheat Sheet
Read more: Composition – cinematography Cheat Sheet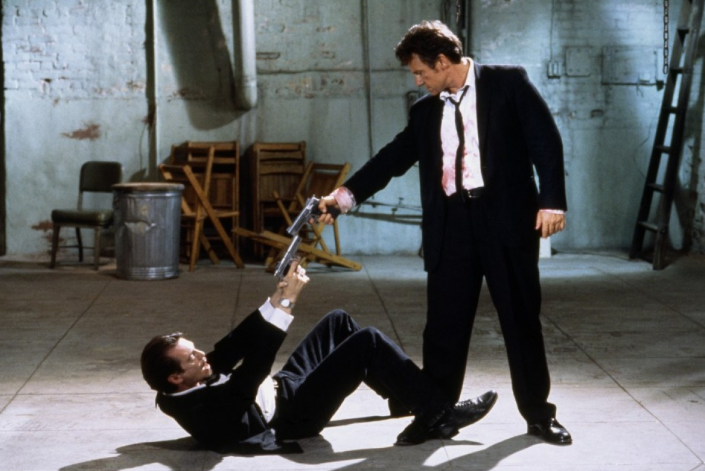
Where is our eye attracted first? Why?
Size. Focus. Lighting. Color.
Size. Mr. White (Harvey Keitel) on the right.
Focus. He’s one of the two objects in focus.
Lighting. Mr. White is large and in focus and Mr. Pink (Steve Buscemi) is highlighted by
a shaft of light.
Color. Both are black and white but the read on Mr. White’s shirt now really stands out.
(more…)
What type of lighting? -
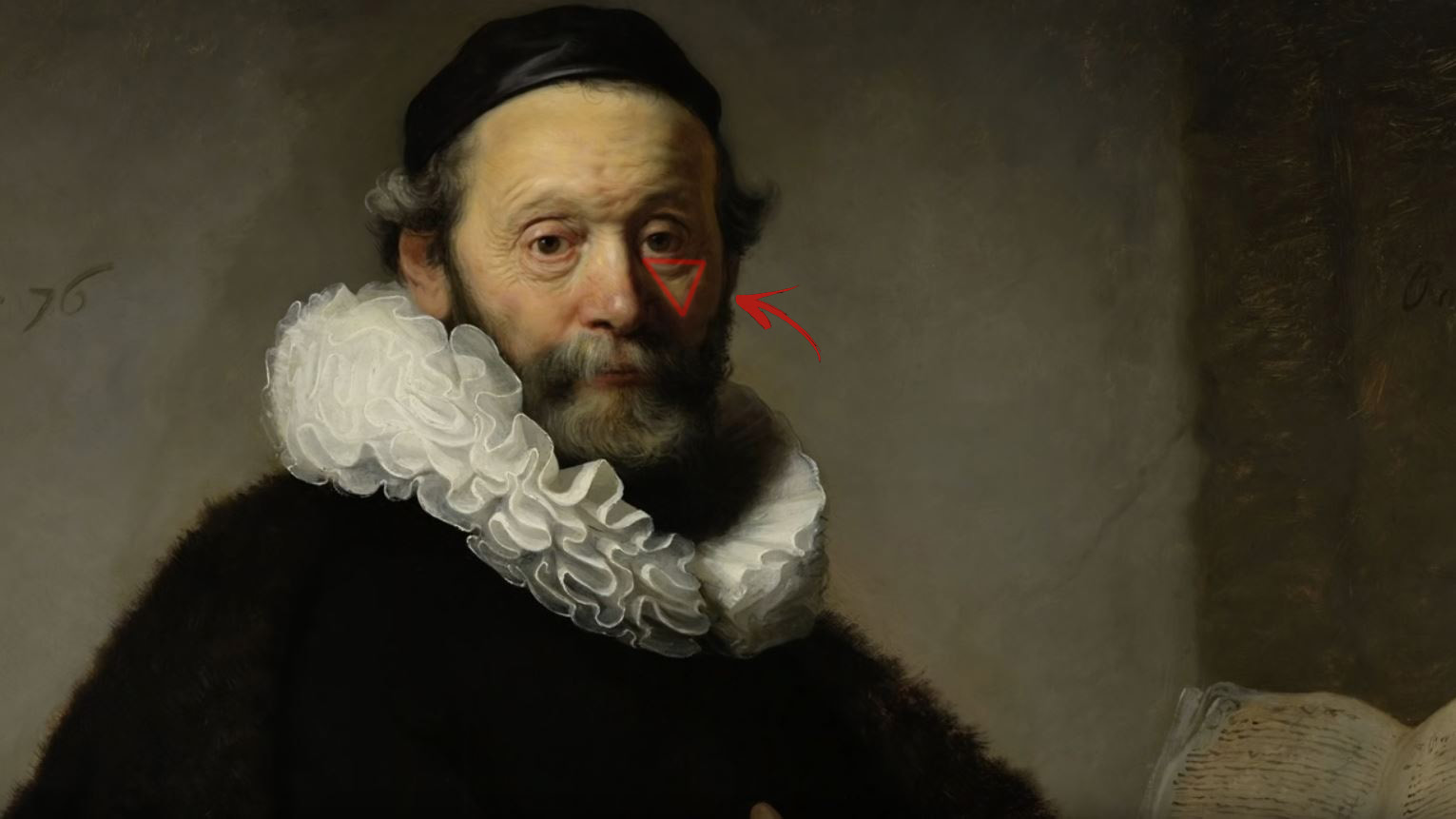
7 Easy Portrait Lighting Setups
Read more: 7 Easy Portrait Lighting SetupsButterfly
Loop
Rembrandt
Split
Rim
Broad
Short
COLLECTIONS
| Featured AI
| Design And Composition
| Explore posts
POPULAR SEARCHES
unreal | pipeline | virtual production | free | learn | photoshop | 360 | macro | google | nvidia | resolution | open source | hdri | real-time | photography basics | nuke
FEATURED POSTS
-
Python and TCL: Tips and Tricks for Foundry Nuke
-
Kling 1.6 and competitors – advanced tests and comparisons
-
Top 3D Printing Website Resources
-
Steven Stahlberg – Perception and Composition
-
JavaScript how-to free resources
-
Ross Pettit on The Agile Manager – How tech firms went for prioritizing cash flow instead of talent (and artists)
-
How does Stable Diffusion work?
-
What’s the Difference Between Ray Casting, Ray Tracing, Path Tracing and Rasterization? Physical light tracing…
Social Links
DISCLAIMER – Links and images on this website may be protected by the respective owners’ copyright. All data submitted by users through this site shall be treated as freely available to share.