COMPOSITION
DESIGN
-
Glenn Marshall – The Crow
Read more: Glenn Marshall – The CrowCreated with AI ‘Style Transfer’ processes to transform video footage into AI video art.
COLOR
-
RawTherapee – a free, open source, cross-platform raw image and HDRi processing program
Read more: RawTherapee – a free, open source, cross-platform raw image and HDRi processing program5.10 of this tool includes excellent tools to clean up cr2 and cr3 used on set to support HDRI processing.
Converting raw to AcesCG 32 bit tiffs with metadata. -
Photography basics: Color Temperature and White Balance
Read more: Photography basics: Color Temperature and White BalanceColor Temperature of a light source describes the spectrum of light which is radiated from a theoretical “blackbody” (an ideal physical body that absorbs all radiation and incident light – neither reflecting it nor allowing it to pass through) with a given surface temperature.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Color_temperature
Or. Most simply it is a method of describing the color characteristics of light through a numerical value that corresponds to the color emitted by a light source, measured in degrees of Kelvin (K) on a scale from 1,000 to 10,000.
More accurately. The color temperature of a light source is the temperature of an ideal backbody that radiates light of comparable hue to that of the light source.
(more…)
LIGHTING
-
Convert between light exposure and intensity
Read more: Convert between light exposure and intensityimport math,sys def Exposure2Intensity(exposure): exp = float(exposure) result = math.pow(2,exp) print(result) Exposure2Intensity(0) def Intensity2Exposure(intensity): inarg = float(intensity) if inarg == 0: print("Exposure of zero intensity is undefined.") return if inarg < 1e-323: inarg = max(inarg, 1e-323) print("Exposure of negative intensities is undefined. Clamping to a very small value instead (1e-323)") result = math.log(inarg, 2) print(result) Intensity2Exposure(0.1)Why Exposure?
Exposure is a stop value that multiplies the intensity by 2 to the power of the stop. Increasing exposure by 1 results in double the amount of light.
Artists think in “stops.” Doubling or halving brightness is easy math and common in grading and look-dev.
Exposure counts doublings in whole stops:- +1 stop = ×2 brightness
- −1 stop = ×0.5 brightness
This gives perceptually even controls across both bright and dark values.
Why Intensity?
Intensity is linear.
It’s what render engines and compositors expect when:- Summing values
- Averaging pixels
- Multiplying or filtering pixel data
Use intensity when you need the actual math on pixel/light data.
Formulas (from your Python)
- Intensity from exposure: intensity = 2**exposure
- Exposure from intensity: exposure = log₂(intensity)
Guardrails:
- Intensity must be > 0 to compute exposure.
- If intensity = 0 → exposure is undefined.
- Clamp tiny values (e.g.
1e−323) before using log₂.
Use Exposure (stops) when…
- You want artist-friendly sliders (−5…+5 stops)
- Adjusting look-dev or grading in even stops
- Matching plates with quick ±1 stop tweaks
- Tweening brightness changes smoothly across ranges
Use Intensity (linear) when…
- Storing raw pixel/light values
- Multiplying textures or lights by a gain
- Performing sums, averages, and filters
- Feeding values to render engines expecting linear data
Examples
- +2 stops → 2**2 = 4.0 (×4)
- +1 stop → 2**1 = 2.0 (×2)
- 0 stop → 2**0 = 1.0 (×1)
- −1 stop → 2**(−1) = 0.5 (×0.5)
- −2 stops → 2**(−2) = 0.25 (×0.25)
- Intensity 0.1 → exposure = log₂(0.1) ≈ −3.32
Rule of thumb
Think in stops (exposure) for controls and matching.
Compute in linear (intensity) for rendering and math. -
Photography basics: Lumens vs Candelas (candle) vs Lux vs FootCandle vs Watts vs Irradiance vs Illuminance
Read more: Photography basics: Lumens vs Candelas (candle) vs Lux vs FootCandle vs Watts vs Irradiance vs Illuminancehttps://www.translatorscafe.com/unit-converter/en-US/illumination/1-11/
The power output of a light source is measured using the unit of watts W. This is a direct measure to calculate how much power the light is going to drain from your socket and it is not relatable to the light brightness itself.
The amount of energy emitted from it per second. That energy comes out in a form of photons which we can crudely represent with rays of light coming out of the source. The higher the power the more rays emitted from the source in a unit of time.
Not all energy emitted is visible to the human eye, so we often rely on photometric measurements, which takes in account the sensitivity of human eye to different wavelenghts
Details in the post
(more…) -
GretagMacbeth Color Checker Numeric Values and Middle Gray
Read more: GretagMacbeth Color Checker Numeric Values and Middle GrayThe human eye perceives half scene brightness not as the linear 50% of the present energy (linear nature values) but as 18% of the overall brightness. We are biased to perceive more information in the dark and contrast areas. A Macbeth chart helps with calibrating back into a photographic capture into this “human perspective” of the world.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Middle_gray
In photography, painting, and other visual arts, middle gray or middle grey is a tone that is perceptually about halfway between black and white on a lightness scale in photography and printing, it is typically defined as 18% reflectance in visible light
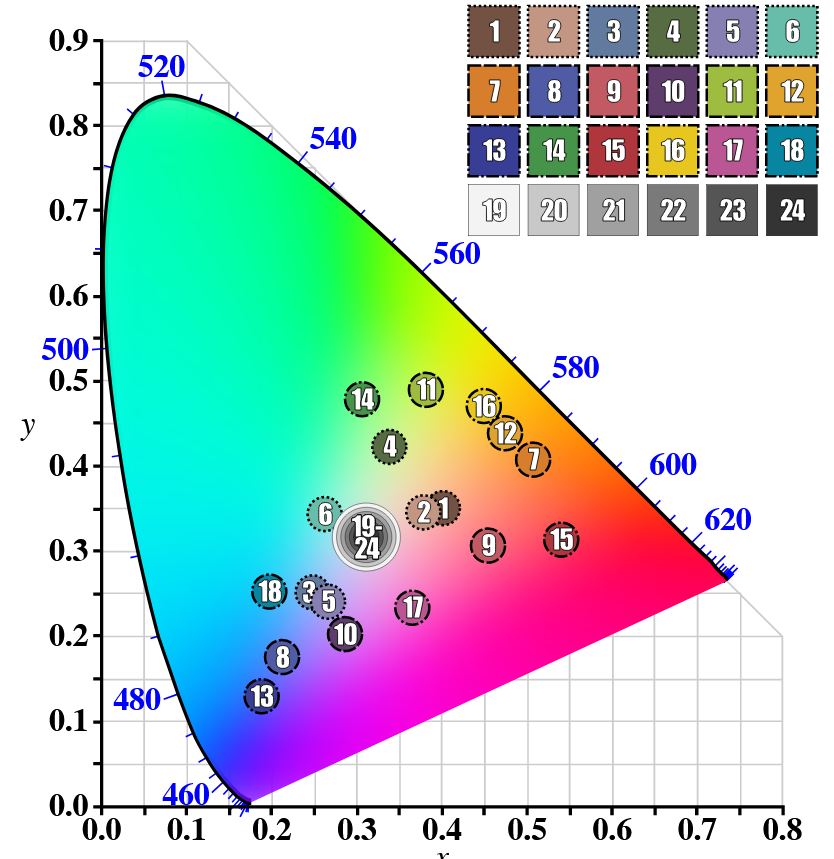
Light meters, cameras, and pictures are often calibrated using an 18% gray card[4][5][6] or a color reference card such as a ColorChecker. On the assumption that 18% is similar to the average reflectance of a scene, a grey card can be used to estimate the required exposure of the film.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ColorChecker
(more…) -
RawTherapee – a free, open source, cross-platform raw image and HDRi processing program
Read more: RawTherapee – a free, open source, cross-platform raw image and HDRi processing program5.10 of this tool includes excellent tools to clean up cr2 and cr3 used on set to support HDRI processing.
Converting raw to AcesCG 32 bit tiffs with metadata.
COLLECTIONS
| Featured AI
| Design And Composition
| Explore posts
POPULAR SEARCHES
unreal | pipeline | virtual production | free | learn | photoshop | 360 | macro | google | nvidia | resolution | open source | hdri | real-time | photography basics | nuke
FEATURED POSTS
-
Image rendering bit depth
-
ComfyDock – The Easiest (Free) Way to Safely Run ComfyUI Sessions in a Boxed Container
-
AI Search – Find The Best AI Tools & Apps
-
QR code logos
-
Matt Gray – How to generate a profitable business
-
Photography basics: Lumens vs Candelas (candle) vs Lux vs FootCandle vs Watts vs Irradiance vs Illuminance
-
How do LLMs like ChatGPT (Generative Pre-Trained Transformer) work? Explained by Deep-Fake Ryan Gosling
-
Ross Pettit on The Agile Manager – How tech firms went for prioritizing cash flow instead of talent (and artists)
Social Links
DISCLAIMER – Links and images on this website may be protected by the respective owners’ copyright. All data submitted by users through this site shall be treated as freely available to share.