COMPOSITION
-
SlowMoVideo – How to make a slow motion shot with the open source program
Read more: SlowMoVideo – How to make a slow motion shot with the open source programhttp://slowmovideo.granjow.net/
slowmoVideo is an OpenSource program that creates slow-motion videos from your footage.
Slow motion cinematography is the result of playing back frames for a longer duration than they were exposed. For example, if you expose 240 frames of film in one second, then play them back at 24 fps, the resulting movie is 10 times longer (slower) than the original filmed event….
Film cameras are relatively simple mechanical devices that allow you to crank up the speed to whatever rate the shutter and pull-down mechanism allow. Some film cameras can operate at 2,500 fps or higher (although film shot in these cameras often needs some readjustment in postproduction). Video, on the other hand, is always captured, recorded, and played back at a fixed rate, with a current limit around 60fps. This makes extreme slow motion effects harder to achieve (and less elegant) on video, because slowing down the video results in each frame held still on the screen for a long time, whereas with high-frame-rate film there are plenty of frames to fill the longer durations of time. On video, the slow motion effect is more like a slide show than smooth, continuous motion.
One obvious solution is to shoot film at high speed, then transfer it to video (a case where film still has a clear advantage, sorry George). Another possibility is to cross dissolve or blur from one frame to the next. This adds a smooth transition from one still frame to the next. The blur reduces the sharpness of the image, and compared to slowing down images shot at a high frame rate, this is somewhat of a cheat. However, there isn’t much you can do about it until video can be recorded at much higher rates. Of course, many film cameras can’t shoot at high frame rates either, so the whole super-slow-motion endeavor is somewhat specialized no matter what medium you are using. (There are some high speed digital cameras available now that allow you to capture lots of digital frames directly to your computer, so technology is starting to catch up with film. However, this feature isn’t going to appear in consumer camcorders any time soon.)
DESIGN
COLOR
-
Photography basics: Why Use a (MacBeth) Color Chart?
Read more: Photography basics: Why Use a (MacBeth) Color Chart?Start here: https://www.pixelsham.com/2013/05/09/gretagmacbeth-color-checker-numeric-values/
https://www.studiobinder.com/blog/what-is-a-color-checker-tool/
In LightRoom
in Final Cut
in Nuke
Note: In Foundry’s Nuke, the software will map 18% gray to whatever your center f/stop is set to in the viewer settings (f/8 by default… change that to EV by following the instructions below).
You can experiment with this by attaching an Exposure node to a Constant set to 0.18, setting your viewer read-out to Spotmeter, and adjusting the stops in the node up and down. You will see that a full stop up or down will give you the respective next value on the aperture scale (f8, f11, f16 etc.).One stop doubles or halves the amount or light that hits the filmback/ccd, so everything works in powers of 2.
So starting with 0.18 in your constant, you will see that raising it by a stop will give you .36 as a floating point number (in linear space), while your f/stop will be f/11 and so on.If you set your center stop to 0 (see below) you will get a relative readout in EVs, where EV 0 again equals 18% constant gray.
In other words. Setting the center f-stop to 0 means that in a neutral plate, the middle gray in the macbeth chart will equal to exposure value 0. EV 0 corresponds to an exposure time of 1 sec and an aperture of f/1.0.
This will set the sun usually around EV12-17 and the sky EV1-4 , depending on cloud coverage.
To switch Foundry’s Nuke’s SpotMeter to return the EV of an image, click on the main viewport, and then press s, this opens the viewer’s properties. Now set the center f-stop to 0 in there. And the SpotMeter in the viewport will change from aperture and fstops to EV.
-
Black Body color aka the Planckian Locus curve for white point eye perception
Read more: Black Body color aka the Planckian Locus curve for white point eye perceptionhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Black-body_radiation
Black-body radiation is the type of electromagnetic radiation within or surrounding a body in thermodynamic equilibrium with its environment, or emitted by a black body (an opaque and non-reflective body) held at constant, uniform temperature. The radiation has a specific spectrum and intensity that depends only on the temperature of the body.
A black-body at room temperature appears black, as most of the energy it radiates is infra-red and cannot be perceived by the human eye. At higher temperatures, black bodies glow with increasing intensity and colors that range from dull red to blindingly brilliant blue-white as the temperature increases.
The Black Body Ultraviolet Catastrophe Experiment
In photography, color temperature describes the spectrum of light which is radiated from a “blackbody” with that surface temperature. A blackbody is an object which absorbs all incident light — neither reflecting it nor allowing it to pass through.
The Sun closely approximates a black-body radiator. Another rough analogue of blackbody radiation in our day to day experience might be in heating a metal or stone: these are said to become “red hot” when they attain one temperature, and then “white hot” for even higher temperatures. Similarly, black bodies at different temperatures also have varying color temperatures of “white light.”
Despite its name, light which may appear white does not necessarily contain an even distribution of colors across the visible spectrum.
Although planets and stars are neither in thermal equilibrium with their surroundings nor perfect black bodies, black-body radiation is used as a first approximation for the energy they emit. Black holes are near-perfect black bodies, and it is believed that they emit black-body radiation (called Hawking radiation), with a temperature that depends on the mass of the hole.
-
colorhunt.co
Read more: colorhunt.coColor Hunt is a free and open platform for color inspiration with thousands of trendy hand-picked color palettes.
-
Scene Referred vs Display Referred color workflows
Read more: Scene Referred vs Display Referred color workflowsDisplay Referred it is tied to the target hardware, as such it bakes color requirements into every type of media output request.
Scene Referred uses a common unified wide gamut and targeting audience through CDL and DI libraries instead.
So that color information stays untouched and only “transformed” as/when needed.Sources:
– Victor Perez – Color Management Fundamentals & ACES Workflows in Nuke
– https://z-fx.nl/ColorspACES.pdf
– Wicus
LIGHTING
-
Gamma correction
Read more: Gamma correction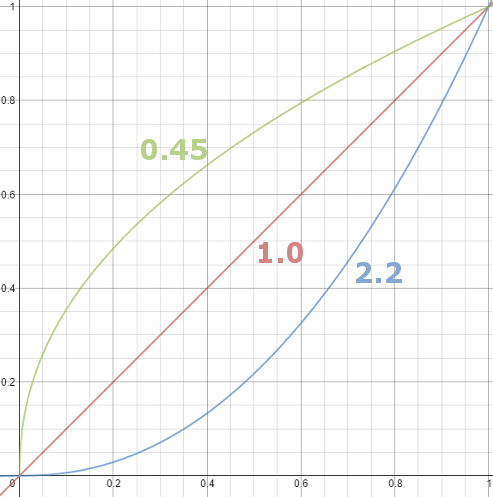
http://www.normankoren.com/makingfineprints1A.html#Gammabox
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gamma_correction
http://www.photoscientia.co.uk/Gamma.htm
https://www.w3.org/Graphics/Color/sRGB.html
http://www.eizoglobal.com/library/basics/lcd_display_gamma/index.html
https://forum.reallusion.com/PrintTopic308094.aspx
Basically, gamma is the relationship between the brightness of a pixel as it appears on the screen, and the numerical value of that pixel. Generally Gamma is just about defining relationships.
Three main types:
– Image Gamma encoded in images
– Display Gammas encoded in hardware and/or viewing time
– System or Viewing Gamma which is the net effect of all gammas when you look back at a final image. In theory this should flatten back to 1.0 gamma.
(more…) -
Sun cone angle (angular diameter) as perceived by earth viewers
Read more: Sun cone angle (angular diameter) as perceived by earth viewersAlso see:
https://www.pixelsham.com/2020/08/01/solid-angle-measures/
The cone angle of the sun refers to the angular diameter of the sun as observed from Earth, which is related to the apparent size of the sun in the sky.
The angular diameter of the sun, or the cone angle of the sunlight as perceived from Earth, is approximately 0.53 degrees on average. This value can vary slightly due to the elliptical nature of Earth’s orbit around the sun, but it generally stays within a narrow range.
Here’s a more precise breakdown:
-
- Average Angular Diameter: About 0.53 degrees (31 arcminutes)
- Minimum Angular Diameter: Approximately 0.52 degrees (when Earth is at aphelion, the farthest point from the sun)
- Maximum Angular Diameter: Approximately 0.54 degrees (when Earth is at perihelion, the closest point to the sun)
This angular diameter remains relatively constant throughout the day because the sun’s distance from Earth does not change significantly over a single day.
To summarize, the cone angle of the sun’s light, or its angular diameter, is typically around 0.53 degrees, regardless of the time of day.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Angular_diameter
-
-
HDRI shooting and editing by Xuan Prada and Greg Zaal
Read more: HDRI shooting and editing by Xuan Prada and Greg Zaalwww.xuanprada.com/blog/2014/11/3/hdri-shooting
http://blog.gregzaal.com/2016/03/16/make-your-own-hdri/
http://blog.hdrihaven.com/how-to-create-high-quality-hdri/
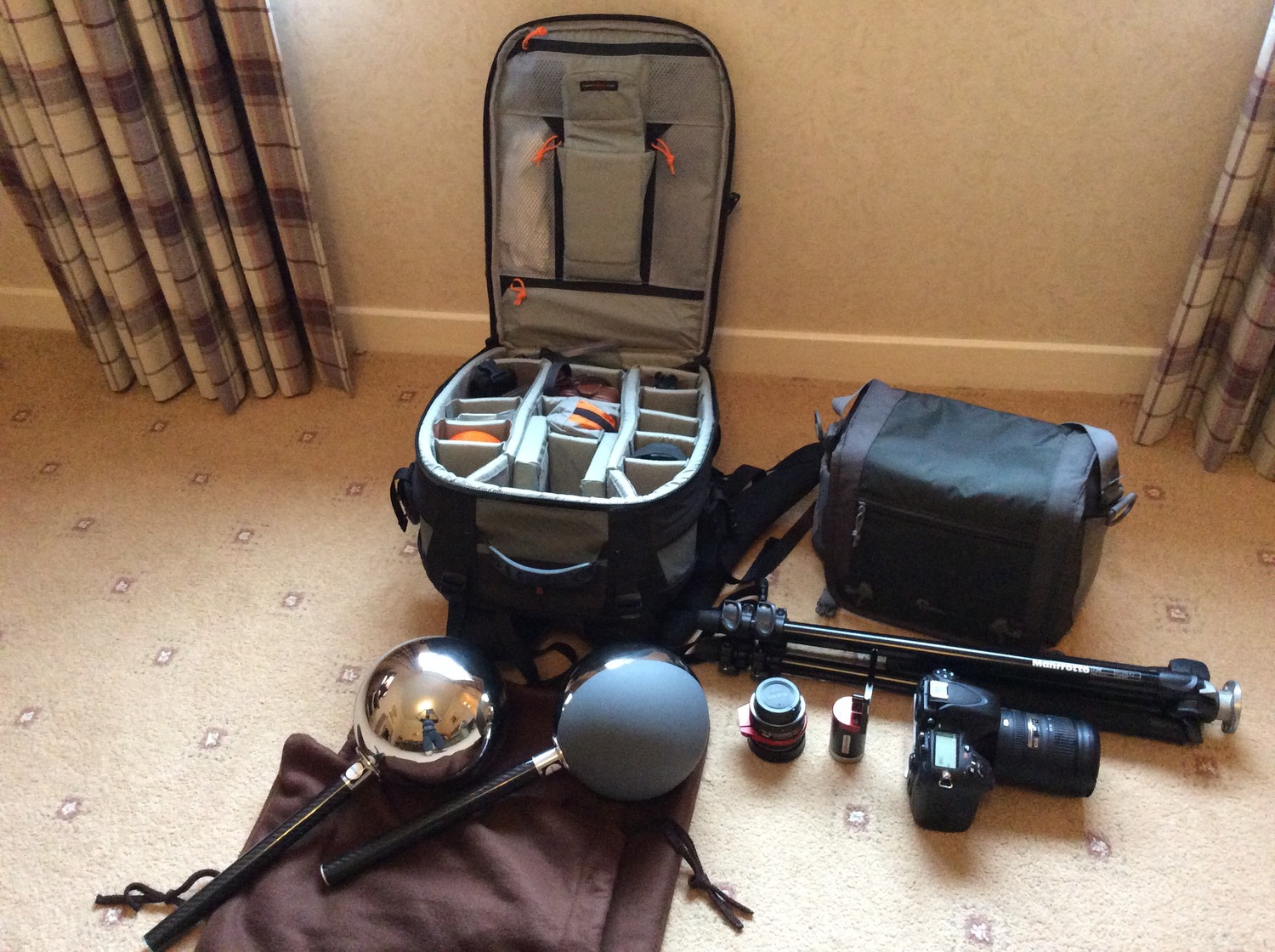

Shooting checklist
- Full coverage of the scene (fish-eye shots)
- Backplates for look-development (including ground or floor)
- Macbeth chart for white balance
- Grey ball for lighting calibration
- Chrome ball for lighting orientation
- Basic scene measurements
- Material samples
- Individual HDR artificial lighting sources if required
Methodology
(more…) -
3D Lighting Tutorial by Amaan Kram
Read more: 3D Lighting Tutorial by Amaan Kramhttp://www.amaanakram.com/lightingT/part1.htm
The goals of lighting in 3D computer graphics are more or less the same as those of real world lighting.
Lighting serves a basic function of bringing out, or pushing back the shapes of objects visible from the camera’s view.
It gives a two-dimensional image on the monitor an illusion of the third dimension-depth.But it does not just stop there. It gives an image its personality, its character. A scene lit in different ways can give a feeling of happiness, of sorrow, of fear etc., and it can do so in dramatic or subtle ways. Along with personality and character, lighting fills a scene with emotion that is directly transmitted to the viewer.
Trying to simulate a real environment in an artificial one can be a daunting task. But even if you make your 3D rendering look absolutely photo-realistic, it doesn’t guarantee that the image carries enough emotion to elicit a “wow” from the people viewing it.
Making 3D renderings photo-realistic can be hard. Putting deep emotions in them can be even harder. However, if you plan out your lighting strategy for the mood and emotion that you want your rendering to express, you make the process easier for yourself.
Each light source can be broken down in to 4 distinct components and analyzed accordingly.
· Intensity
· Direction
· Color
· SizeThe overall thrust of this writing is to produce photo-realistic images by applying good lighting techniques.
COLLECTIONS
| Featured AI
| Design And Composition
| Explore posts
POPULAR SEARCHES
unreal | pipeline | virtual production | free | learn | photoshop | 360 | macro | google | nvidia | resolution | open source | hdri | real-time | photography basics | nuke
FEATURED POSTS
-
Ethan Roffler interviews CG Supervisor Daniele Tosti
-
3D Gaussian Splatting step by step beginner course
-
Web vs Printing or digital RGB vs CMYK
-
Tencent Hunyuan3D 2.1 goes Open Source and adds MV (Multi-view) and MV Mini
-
Glossary of Lighting Terms – cheat sheet
-
AI and the Law – studiobinder.com – What is Fair Use: Definition, Policies, Examples and More
-
WhatDreamsCost Spline-Path-Control – Create motion controls for ComfyUI
-
Gamma correction
Social Links
DISCLAIMER – Links and images on this website may be protected by the respective owners’ copyright. All data submitted by users through this site shall be treated as freely available to share.







