COMPOSITION
-
Cinematographers Blueprint 300dpi poster
Read more: Cinematographers Blueprint 300dpi posterThe 300dpi digital poster is now available to all PixelSham.com subscribers.
If you have already subscribed and wish a copy, please send me a note through the contact page.
DESIGN
COLOR
-
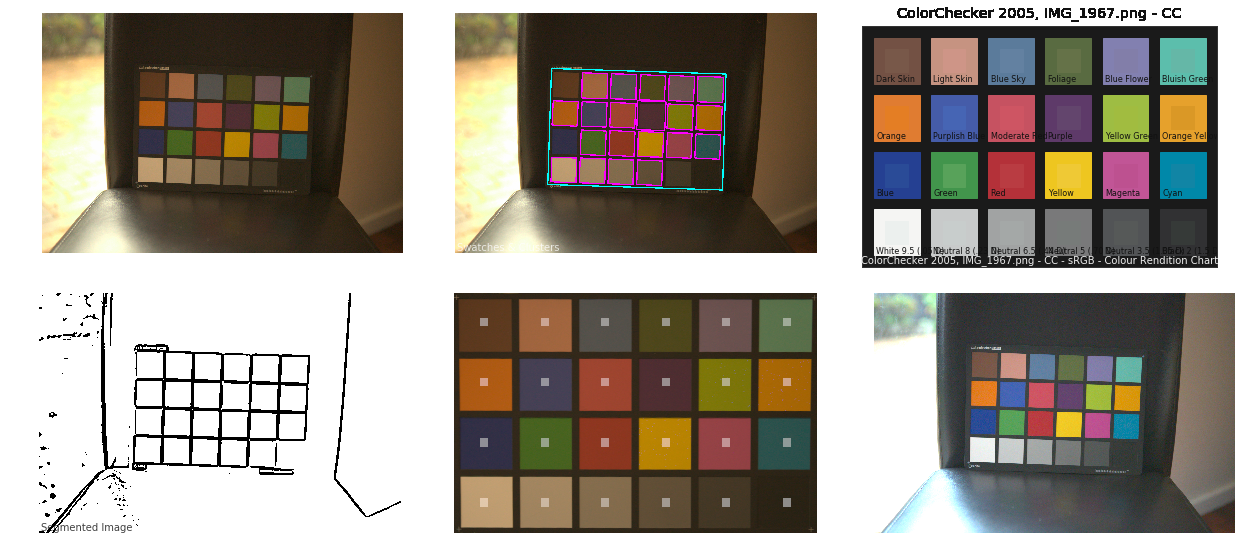
Colour – MacBeth Chart Checker Detection
Read more: Colour – MacBeth Chart Checker Detectiongithub.com/colour-science/colour-checker-detection
A Python package implementing various colour checker detection algorithms and related utilities.
-
Mysterious animation wins best illusion of 2011 – Motion silencing illusion
Read more: Mysterious animation wins best illusion of 2011 – Motion silencing illusionThe 2011 Best Illusion of the Year uses motion to render color changes invisible, and so reveals a quirk in our visual systems that is new to scientists.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Motion_silencing_illusion
“It is a really beautiful effect, revealing something about how our visual system works that we didn’t know before,” said Daniel Simons, a professor at the University of Illinois, Champaign-Urbana. Simons studies visual cognition, and did not work on this illusion. Before its creation, scientists didn’t know that motion had this effect on perception, Simons said.
A viewer stares at a speck at the center of a ring of colored dots, which continuously change color. When the ring begins to rotate around the speck, the color changes appear to stop. But this is an illusion. For some reason, the motion causes our visual system to ignore the color changes. (You can, however, see the color changes if you follow the rotating circles with your eyes.)
-
Willem Zwarthoed – Aces gamut in VFX production pdf
Read more: Willem Zwarthoed – Aces gamut in VFX production pdfhttps://www.provideocoalition.com/color-management-part-12-introducing-aces/
Local copy:
https://www.slideshare.net/hpduiker/acescg-a-common-color-encoding-for-visual-effects-applications
-
Weta Digital – Manuka Raytracer and Gazebo GPU renderers – pipeline
Read more: Weta Digital – Manuka Raytracer and Gazebo GPU renderers – pipelinehttps://jo.dreggn.org/home/2018_manuka.pdf
http://www.fxguide.com/featured/manuka-weta-digitals-new-renderer/

The Manuka rendering architecture has been designed in the spirit of the classic reyes rendering architecture. In its core, reyes is based on stochastic rasterisation of micropolygons, facilitating depth of field, motion blur, high geometric complexity,and programmable shading.
This is commonly achieved with Monte Carlo path tracing, using a paradigm often called shade-on-hit, in which the renderer alternates tracing rays with running shaders on the various ray hits. The shaders take the role of generating the inputs of the local material structure which is then used bypath sampling logic to evaluate contributions and to inform what further rays to cast through the scene.
Over the years, however, the expectations have risen substantially when it comes to image quality. Computing pictures which are indistinguishable from real footage requires accurate simulation of light transport, which is most often performed using some variant of Monte Carlo path tracing. Unfortunately this paradigm requires random memory accesses to the whole scene and does not lend itself well to a rasterisation approach at all.
Manuka is both a uni-directional and bidirectional path tracer and encompasses multiple importance sampling (MIS). Interestingly, and importantly for production character skin work, it is the first major production renderer to incorporate spectral MIS in the form of a new ‘Hero Spectral Sampling’ technique, which was recently published at Eurographics Symposium on Rendering 2014.
Manuka propose a shade-before-hit paradigm in-stead and minimise I/O strain (and some memory costs) on the system, leveraging locality of reference by running pattern generation shaders before we execute light transport simulation by path sampling, “compressing” any bvh structure as needed, and as such also limiting duplication of source data.
The difference with reyes is that instead of baking colors into the geometry like in Reyes, manuka bakes surface closures. This means that light transport is still calculated with path tracing, but all texture lookups etc. are done up-front and baked into the geometry.The main drawback with this method is that geometry has to be tessellated to its highest, stable topology before shading can be evaluated properly. As such, the high cost to first pixel. Even a basic 4 vertices square becomes a much more complex model with this approach.
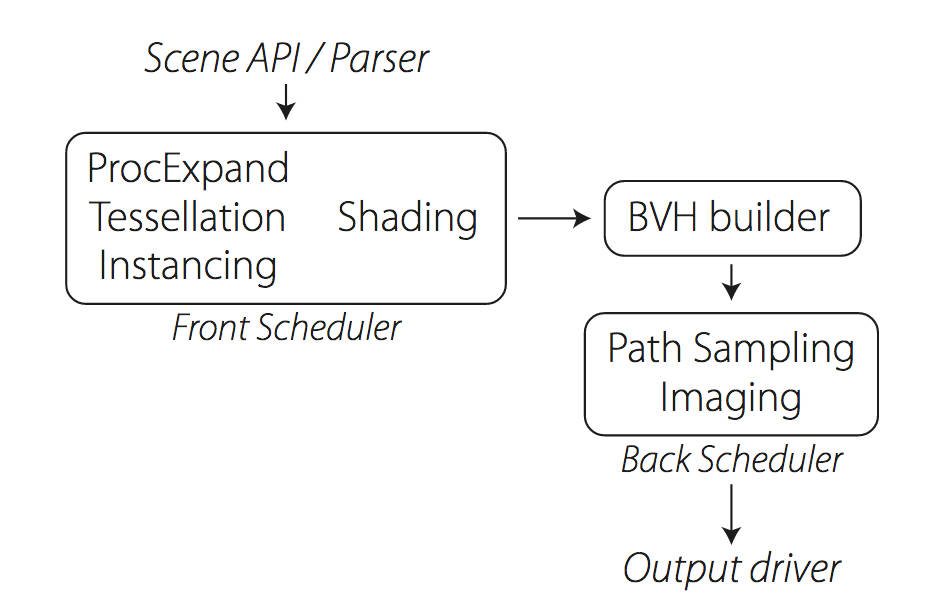
Manuka use the RenderMan Shading Language (rsl) for programmable shading [Pixar Animation Studios 2015], but we do not invoke rsl shaders when intersecting a ray with a surface (often called shade-on-hit). Instead, we pre-tessellate and pre-shade all the input geometry in the front end of the renderer.
This way, we can efficiently order shading computations to sup-port near-optimal texture locality, vectorisation, and parallelism. This system avoids repeated evaluation of shaders at the same surface point, and presents a minimal amount of memory to be accessed during light transport time. An added benefit is that the acceleration structure for ray tracing (abounding volume hierarchy, bvh) is built once on the final tessellated geometry, which allows us to ray trace more efficiently than multi-level bvhs and avoids costly caching of on-demand tessellated micropolygons and the associated scheduling issues.For the shading reasons above, in terms of AOVs, the studio approach is to succeed at combining complex shading with ray paths in the render rather than pass a multi-pass render to compositing.
For the Spectral Rendering component. The light transport stage is fully spectral, using a continuously sampled wavelength which is traced with each path and used to apply the spectral camera sensitivity of the sensor. This allows for faithfully support any degree of observer metamerism as the camera footage they are intended to match as well as complex materials which require wavelength dependent phenomena such as diffraction, dispersion, interference, iridescence, or chromatic extinction and Rayleigh scattering in participating media.
As opposed to the original reyes paper, we use bilinear interpolation of these bsdf inputs later when evaluating bsdfs per pathv ertex during light transport4. This improves temporal stability of geometry which moves very slowly with respect to the pixel raster
In terms of the pipeline, everything rendered at Weta was already completely interwoven with their deep data pipeline. Manuka very much was written with deep data in mind. Here, Manuka not so much extends the deep capabilities, rather it fully matches the already extremely complex and powerful setup Weta Digital already enjoy with RenderMan. For example, an ape in a scene can be selected, its ID is available and a NUKE artist can then paint in 3D say a hand and part of the way up the neutral posed ape.
We called our system Manuka, as a respectful nod to reyes: we had heard a story froma former ILM employee about how reyes got its name from how fond the early Pixar people were of their lunches at Point Reyes, and decided to name our system after our surrounding natural environment, too. Manuka is a kind of tea tree very common in New Zealand which has very many very small leaves, in analogy to micropolygons ina tree structure for ray tracing. It also happens to be the case that Weta Digital’s main site is on Manuka Street.

-
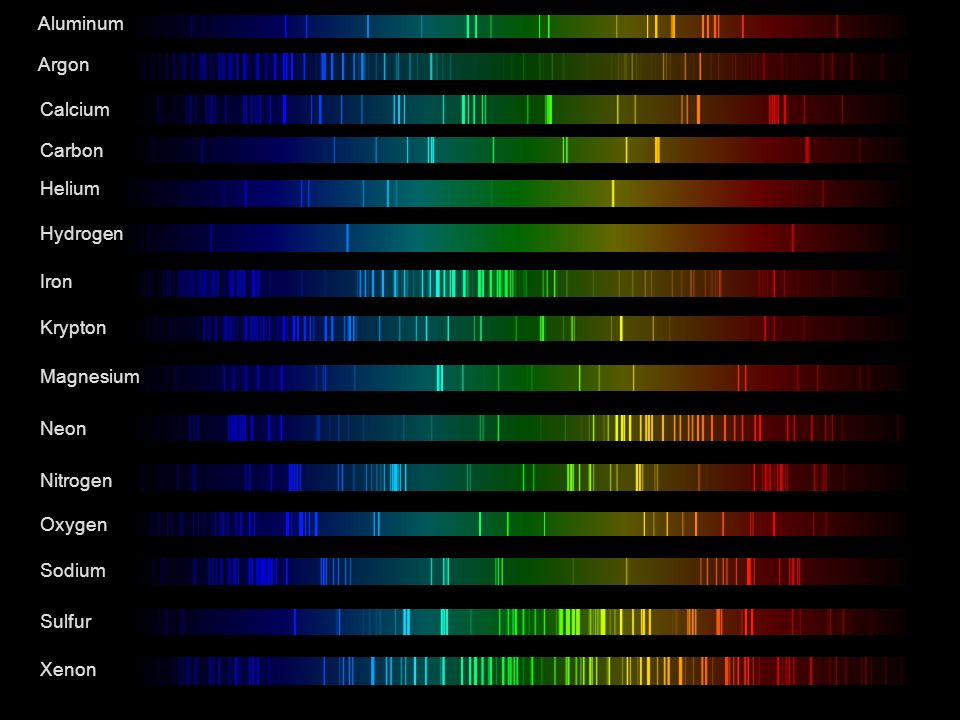
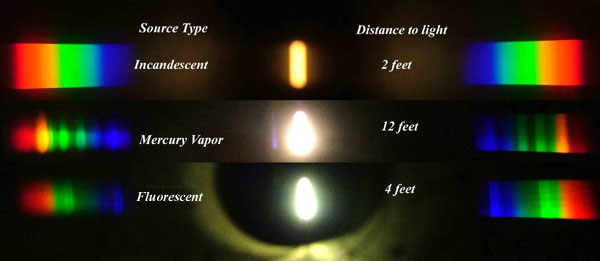
Space bodies’ components and light spectroscopy
Read more: Space bodies’ components and light spectroscopywww.plutorules.com/page-111-space-rocks.html
This help’s us understand the composition of components in/on solar system bodies.
Dips in the observed light spectrum, also known as, lines of absorption occur as gasses absorb energy from light at specific points along the light spectrum.
These dips or darkened zones (lines of absorption) leave a finger print which identify elements and compounds.
In this image the dark absorption bands appear as lines of emission which occur as the result of emitted not reflected (absorbed) light.
Lines of absorption
 Lines of emission
Lines of emission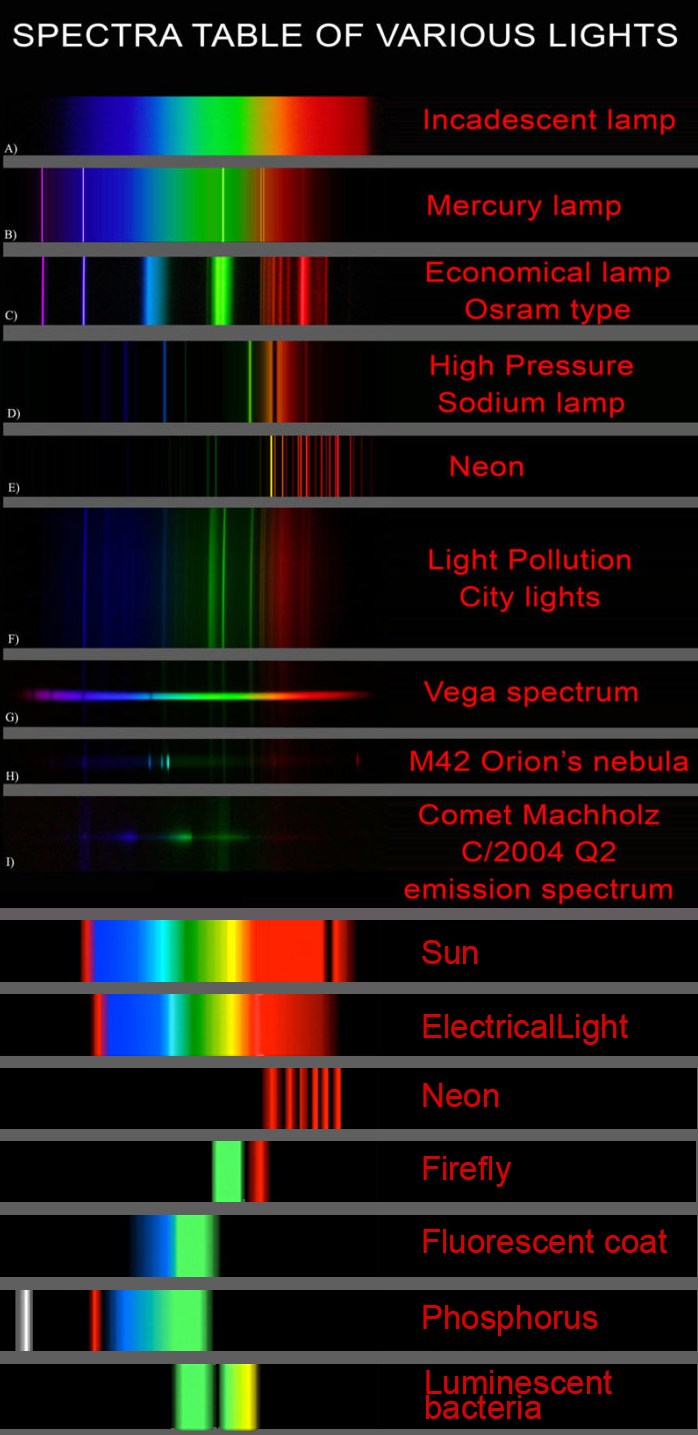

-
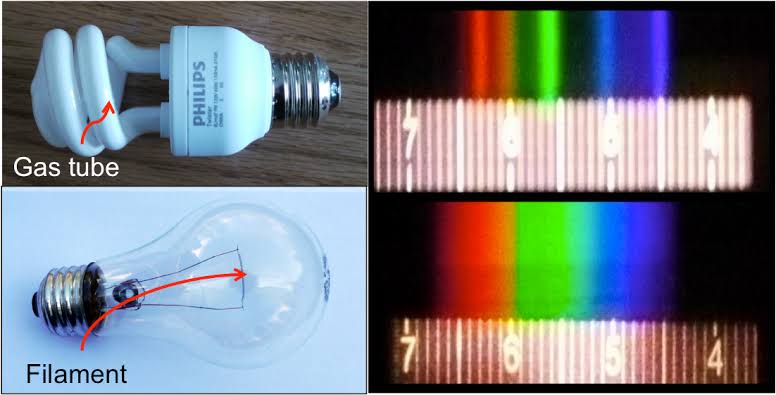
Photography Basics : Spectral Sensitivity Estimation Without a Camera
Read more: Photography Basics : Spectral Sensitivity Estimation Without a Camerahttps://color-lab-eilat.github.io/Spectral-sensitivity-estimation-web/
A number of problems in computer vision and related fields would be mitigated if camera spectral sensitivities were known. As consumer cameras are not designed for high-precision visual tasks, manufacturers do not disclose spectral sensitivities. Their estimation requires a costly optical setup, which triggered researchers to come up with numerous indirect methods that aim to lower cost and complexity by using color targets. However, the use of color targets gives rise to new complications that make the estimation more difficult, and consequently, there currently exists no simple, low-cost, robust go-to method for spectral sensitivity estimation that non-specialized research labs can adopt. Furthermore, even if not limited by hardware or cost, researchers frequently work with imagery from multiple cameras that they do not have in their possession.
To provide a practical solution to this problem, we propose a framework for spectral sensitivity estimation that not only does not require any hardware (including a color target), but also does not require physical access to the camera itself. Similar to other work, we formulate an optimization problem that minimizes a two-term objective function: a camera-specific term from a system of equations, and a universal term that bounds the solution space.
Different than other work, we utilize publicly available high-quality calibration data to construct both terms. We use the colorimetric mapping matrices provided by the Adobe DNG Converter to formulate the camera-specific system of equations, and constrain the solutions using an autoencoder trained on a database of ground-truth curves. On average, we achieve reconstruction errors as low as those that can arise due to manufacturing imperfections between two copies of the same camera. We provide predicted sensitivities for more than 1,000 cameras that the Adobe DNG Converter currently supports, and discuss which tasks can become trivial when camera responses are available.
LIGHTING
-
Unity 3D resources
Read more: Unity 3D resources
http://answers.unity3d.com/questions/12321/how-can-i-start-learning-unity-fast-list-of-tutori.html
If you have no previous experience with Unity, start with these six video tutorials which give a quick overview of the Unity interface and some important features http://unity3d.com/support/documentation/video/
-
Photography basics: Lumens vs Candelas (candle) vs Lux vs FootCandle vs Watts vs Irradiance vs Illuminance
Read more: Photography basics: Lumens vs Candelas (candle) vs Lux vs FootCandle vs Watts vs Irradiance vs Illuminancehttps://www.translatorscafe.com/unit-converter/en-US/illumination/1-11/
The power output of a light source is measured using the unit of watts W. This is a direct measure to calculate how much power the light is going to drain from your socket and it is not relatable to the light brightness itself.
The amount of energy emitted from it per second. That energy comes out in a form of photons which we can crudely represent with rays of light coming out of the source. The higher the power the more rays emitted from the source in a unit of time.
Not all energy emitted is visible to the human eye, so we often rely on photometric measurements, which takes in account the sensitivity of human eye to different wavelenghts
Details in the post
(more…) -
domeble – Hi-Resolution CGI Backplates and 360° HDRI
Read more: domeble – Hi-Resolution CGI Backplates and 360° HDRIWhen collecting hdri make sure the data supports basic metadata, such as:
- Iso
- Aperture
- Exposure time or shutter time
- Color temperature
- Color space Exposure value (what the sensor receives of the sun intensity in lux)
- 7+ brackets (with 5 or 6 being the perceived balanced exposure)
In image processing, computer graphics, and photography, high dynamic range imaging (HDRI or just HDR) is a set of techniques that allow a greater dynamic range of luminances (a Photometry measure of the luminous intensity per unit area of light travelling in a given direction. It describes the amount of light that passes through or is emitted from a particular area, and falls within a given solid angle) between the lightest and darkest areas of an image than standard digital imaging techniques or photographic methods. This wider dynamic range allows HDR images to represent more accurately the wide range of intensity levels found in real scenes ranging from direct sunlight to faint starlight and to the deepest shadows.
The two main sources of HDR imagery are computer renderings and merging of multiple photographs, which in turn are known as low dynamic range (LDR) or standard dynamic range (SDR) images. Tone Mapping (Look-up) techniques, which reduce overall contrast to facilitate display of HDR images on devices with lower dynamic range, can be applied to produce images with preserved or exaggerated local contrast for artistic effect. Photography
In photography, dynamic range is measured in Exposure Values (in photography, exposure value denotes all combinations of camera shutter speed and relative aperture that give the same exposure. The concept was developed in Germany in the 1950s) differences or stops, between the brightest and darkest parts of the image that show detail. An increase of one EV or one stop is a doubling of the amount of light.
The human response to brightness is well approximated by a Steven’s power law, which over a reasonable range is close to logarithmic, as described by the Weber�Fechner law, which is one reason that logarithmic measures of light intensity are often used as well.
HDR is short for High Dynamic Range. It’s a term used to describe an image which contains a greater exposure range than the “black” to “white” that 8 or 16-bit integer formats (JPEG, TIFF, PNG) can describe. Whereas these Low Dynamic Range images (LDR) can hold perhaps 8 to 10 f-stops of image information, HDR images can describe beyond 30 stops and stored in 32 bit images.

-
What is the Light Field?
Read more: What is the Light Field?http://lightfield-forum.com/what-is-the-lightfield/
The light field consists of the total of all light rays in 3D space, flowing through every point and in every direction.
How to Record a Light Field
- a single, robotically controlled camera
- a rotating arc of cameras
- an array of cameras or camera modules
- a single camera or camera lens fitted with a microlens array
-
Black Body color aka the Planckian Locus curve for white point eye perception
Read more: Black Body color aka the Planckian Locus curve for white point eye perceptionhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Black-body_radiation
Black-body radiation is the type of electromagnetic radiation within or surrounding a body in thermodynamic equilibrium with its environment, or emitted by a black body (an opaque and non-reflective body) held at constant, uniform temperature. The radiation has a specific spectrum and intensity that depends only on the temperature of the body.
A black-body at room temperature appears black, as most of the energy it radiates is infra-red and cannot be perceived by the human eye. At higher temperatures, black bodies glow with increasing intensity and colors that range from dull red to blindingly brilliant blue-white as the temperature increases.
The Black Body Ultraviolet Catastrophe Experiment
In photography, color temperature describes the spectrum of light which is radiated from a “blackbody” with that surface temperature. A blackbody is an object which absorbs all incident light — neither reflecting it nor allowing it to pass through.
The Sun closely approximates a black-body radiator. Another rough analogue of blackbody radiation in our day to day experience might be in heating a metal or stone: these are said to become “red hot” when they attain one temperature, and then “white hot” for even higher temperatures. Similarly, black bodies at different temperatures also have varying color temperatures of “white light.”
Despite its name, light which may appear white does not necessarily contain an even distribution of colors across the visible spectrum.
Although planets and stars are neither in thermal equilibrium with their surroundings nor perfect black bodies, black-body radiation is used as a first approximation for the energy they emit. Black holes are near-perfect black bodies, and it is believed that they emit black-body radiation (called Hawking radiation), with a temperature that depends on the mass of the hole.
-
DiffusionLight: HDRI Light Probes for Free by Painting a Chrome Ball
Read more: DiffusionLight: HDRI Light Probes for Free by Painting a Chrome Ballhttps://diffusionlight.github.io/
https://github.com/DiffusionLight/DiffusionLight
https://github.com/DiffusionLight/DiffusionLight?tab=MIT-1-ov-file#readme
https://colab.research.google.com/drive/15pC4qb9mEtRYsW3utXkk-jnaeVxUy-0S
“a simple yet effective technique to estimate lighting in a single input image. Current techniques rely heavily on HDR panorama datasets to train neural networks to regress an input with limited field-of-view to a full environment map. However, these approaches often struggle with real-world, uncontrolled settings due to the limited diversity and size of their datasets. To address this problem, we leverage diffusion models trained on billions of standard images to render a chrome ball into the input image. Despite its simplicity, this task remains challenging: the diffusion models often insert incorrect or inconsistent objects and cannot readily generate images in HDR format. Our research uncovers a surprising relationship between the appearance of chrome balls and the initial diffusion noise map, which we utilize to consistently generate high-quality chrome balls. We further fine-tune an LDR difusion model (Stable Diffusion XL) with LoRA, enabling it to perform exposure bracketing for HDR light estimation. Our method produces convincing light estimates across diverse settings and demonstrates superior generalization to in-the-wild scenarios.”

-
Photography basics: Solid Angle measures
Read more: Photography basics: Solid Angle measureshttp://www.calculator.org/property.aspx?name=solid+angle
A measure of how large the object appears to an observer looking from that point. Thus. A measure for objects in the sky. Useful to retuen the size of the sun and moon… and in perspective, how much of their contribution to lighting. Solid angle can be represented in ‘angular diameter’ as well.
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Solid_angle
http://www.mathsisfun.com/geometry/steradian.html
A solid angle is expressed in a dimensionless unit called a steradian (symbol: sr). By default in terms of the total celestial sphere and before atmospheric’s scattering, the Sun and the Moon subtend fractional areas of 0.000546% (Sun) and 0.000531% (Moon).
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Solid_angle#Sun_and_Moon
On earth the sun is likely closer to 0.00011 solid angle after athmospheric scattering. The sun as perceived from earth has a diameter of 0.53 degrees. This is about 0.000064 solid angle.
http://www.numericana.com/answer/angles.htm
The mean angular diameter of the full moon is 2q = 0.52° (it varies with time around that average, by about 0.009°). This translates into a solid angle of 0.0000647 sr, which means that the whole night sky covers a solid angle roughly one hundred thousand times greater than the full moon.
More info
http://lcogt.net/spacebook/using-angles-describe-positions-and-apparent-sizes-objects
http://amazing-space.stsci.edu/glossary/def.php.s=topic_astronomy
Angular Size
The apparent size of an object as seen by an observer; expressed in units of degrees (of arc), arc minutes, or arc seconds. The moon, as viewed from the Earth, has an angular diameter of one-half a degree.
The angle covered by the diameter of the full moon is about 31 arcmin or 1/2°, so astronomers would say the Moon’s angular diameter is 31 arcmin, or the Moon subtends an angle of 31 arcmin.
COLLECTIONS
| Featured AI
| Design And Composition
| Explore posts
POPULAR SEARCHES
unreal | pipeline | virtual production | free | learn | photoshop | 360 | macro | google | nvidia | resolution | open source | hdri | real-time | photography basics | nuke
FEATURED POSTS
-
sRGB vs REC709 – An introduction and FFmpeg implementations
-
Alejandro Villabón and Rafał Kaniewski – Recover Highlights With 8-Bit to High Dynamic Range Half Float Copycat – Nuke
-
Advanced Computer Vision with Python OpenCV and Mediapipe
-
NVidia – High-Fidelity 3D Mesh Generation at Scale with Meshtron
-
AI Search – Find The Best AI Tools & Apps
-
AI and the Law – Netflix : Using Generative AI in Content Production
-
copypastecharacter.com – alphabets, special characters, alt codes and symbols library
-
3D Gaussian Splatting step by step beginner course
Social Links
DISCLAIMER – Links and images on this website may be protected by the respective owners’ copyright. All data submitted by users through this site shall be treated as freely available to share.







