COMPOSITION
-
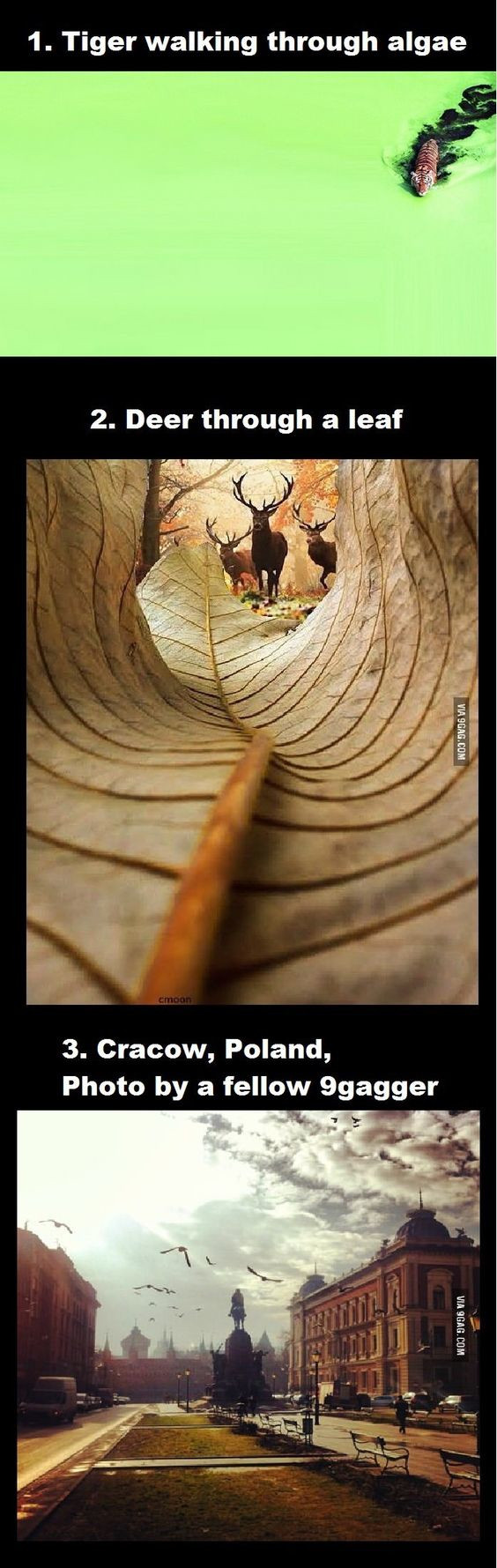
Composition – cinematography Cheat Sheet
Read more: Composition – cinematography Cheat Sheet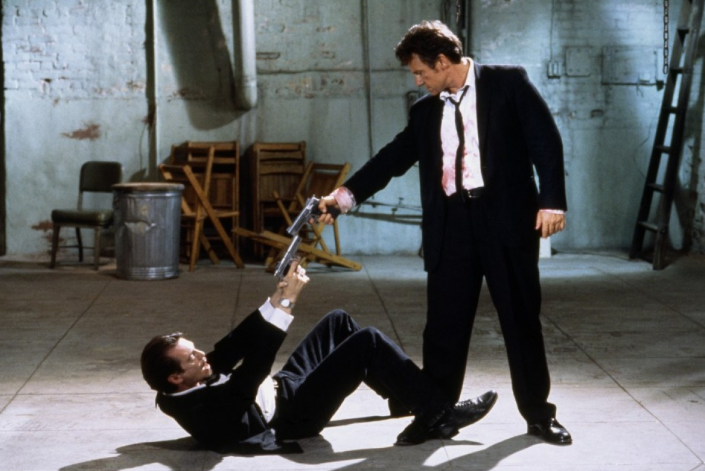
Where is our eye attracted first? Why?
Size. Focus. Lighting. Color.
Size. Mr. White (Harvey Keitel) on the right.
Focus. He’s one of the two objects in focus.
Lighting. Mr. White is large and in focus and Mr. Pink (Steve Buscemi) is highlighted by
a shaft of light.
Color. Both are black and white but the read on Mr. White’s shirt now really stands out.
(more…)
What type of lighting? -
HuggingFace ai-comic-factory – a FREE AI Comic Book Creator
Read more: HuggingFace ai-comic-factory – a FREE AI Comic Book Creatorhttps://huggingface.co/spaces/jbilcke-hf/ai-comic-factory
this is the epic story of a group of talented digital artists trying to overcame daily technical challenges to achieve incredibly photorealistic projects of monsters and aliens
DESIGN
-
Goga Tandashvili – bas-relief master
Read more: Goga Tandashvili – bas-relief master@moltenimmersiveart Goga Tandashvili is a master of the art of Bas-Relief. Using this technique, he creates stunning figures that are slightly raised from a flat surface, bringing scenes inspired by the natural world to life. #Art #Artists #GogaTandashvili #BasReliefSculpture #ArtInspiredByNature #ImpressionistArt #BasRelief #Sculptures #Sculptor #Molten #MoltenArt #MoltenImmersiveArt #MoltenAffect #Curation #Curator #ArtCuration #ArtCurator #DorothyDiStefano ♬ original sound – Molten Immersive Art -
Disco Diffusion V4.1 Google Colab, Dall-E, Starryai – creating images with AI
Read more: Disco Diffusion V4.1 Google Colab, Dall-E, Starryai – creating images with AIDisco Diffusion (DD) is a Google Colab Notebook which leverages an AI Image generating technique called CLIP-Guided Diffusion to allow you to create compelling and beautiful images from just text inputs. Created by Somnai, augmented by Gandamu, and building on the work of RiversHaveWings, nshepperd, and many others.
Phone app: https://www.starryai.com/
docs.google.com/document/d/1l8s7uS2dGqjztYSjPpzlmXLjl5PM3IGkRWI3IiCuK7g
colab.research.google.com/drive/1sHfRn5Y0YKYKi1k-ifUSBFRNJ8_1sa39
Colab, or “Colaboratory”, allows you to write and execute Python in your browser, with
– Zero configuration required
– Access to GPUs free of charge
– Easy sharinghttps://80.lv/articles/a-beautiful-roman-villa-made-with-disco-diffusion-5-2/
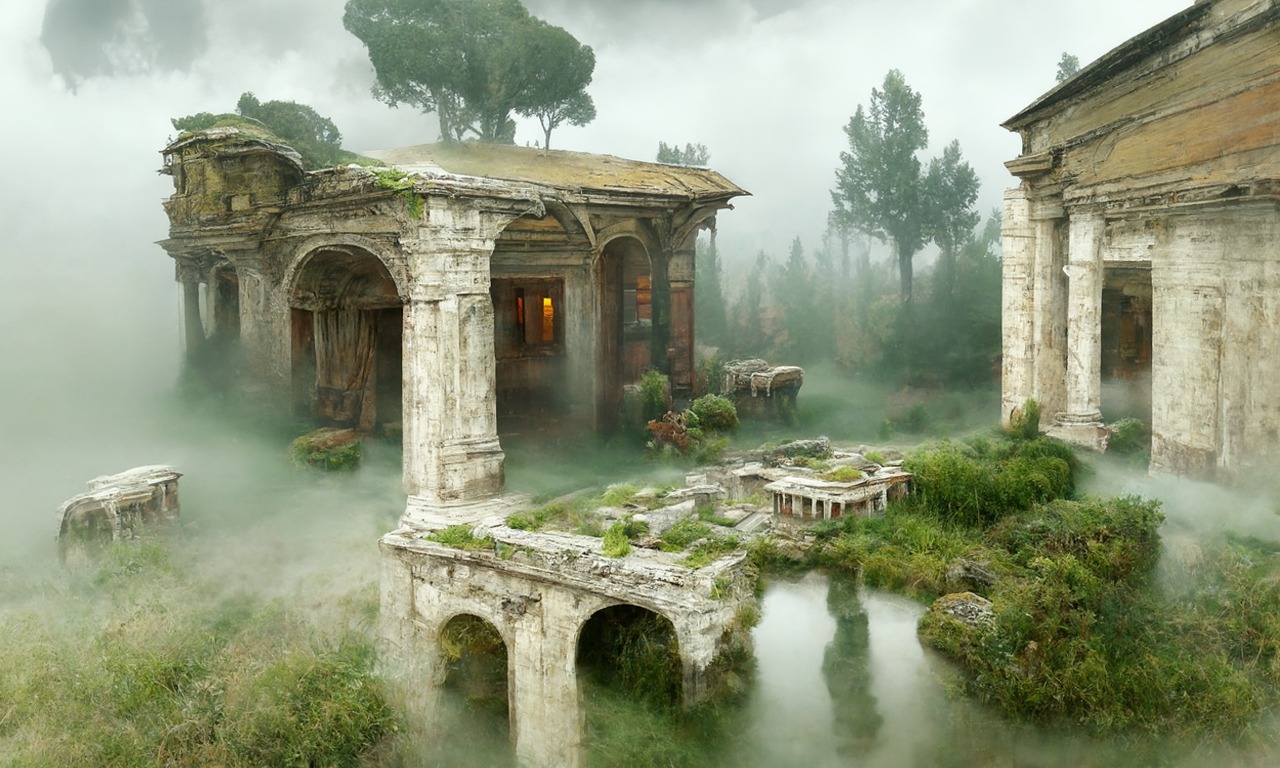
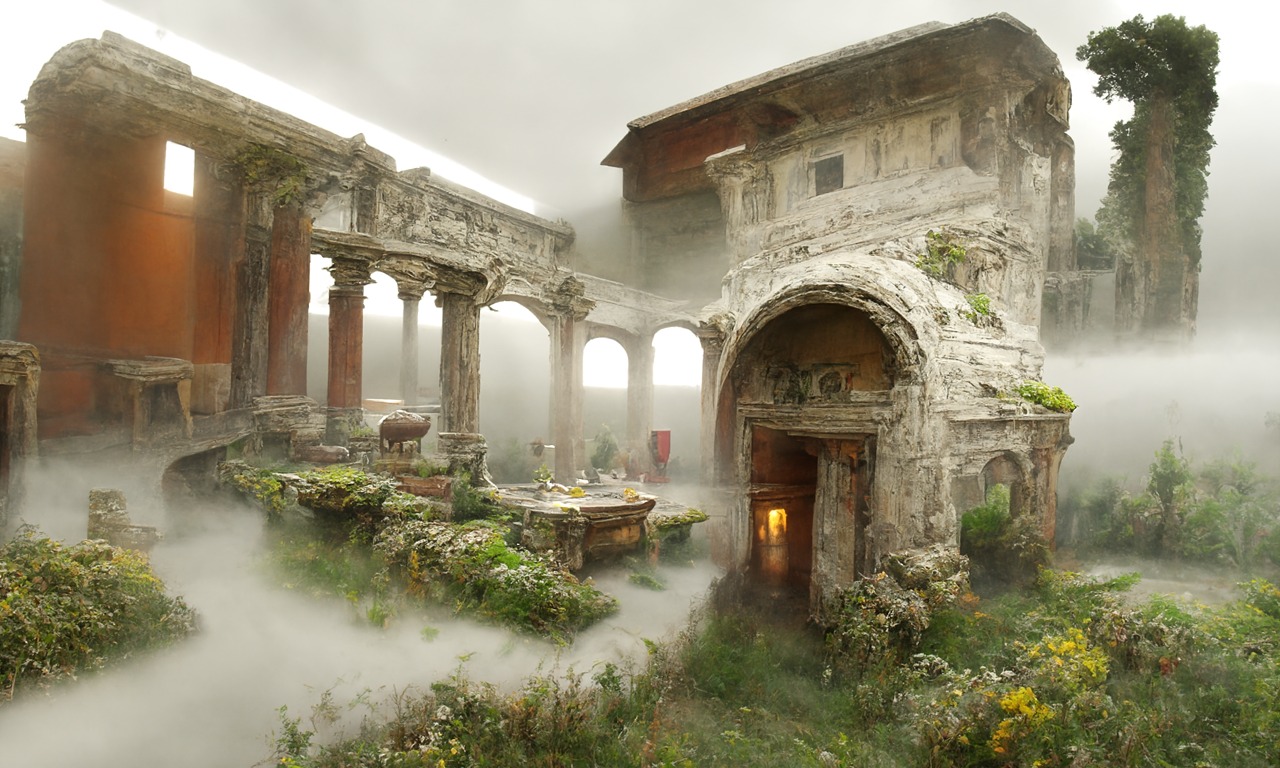
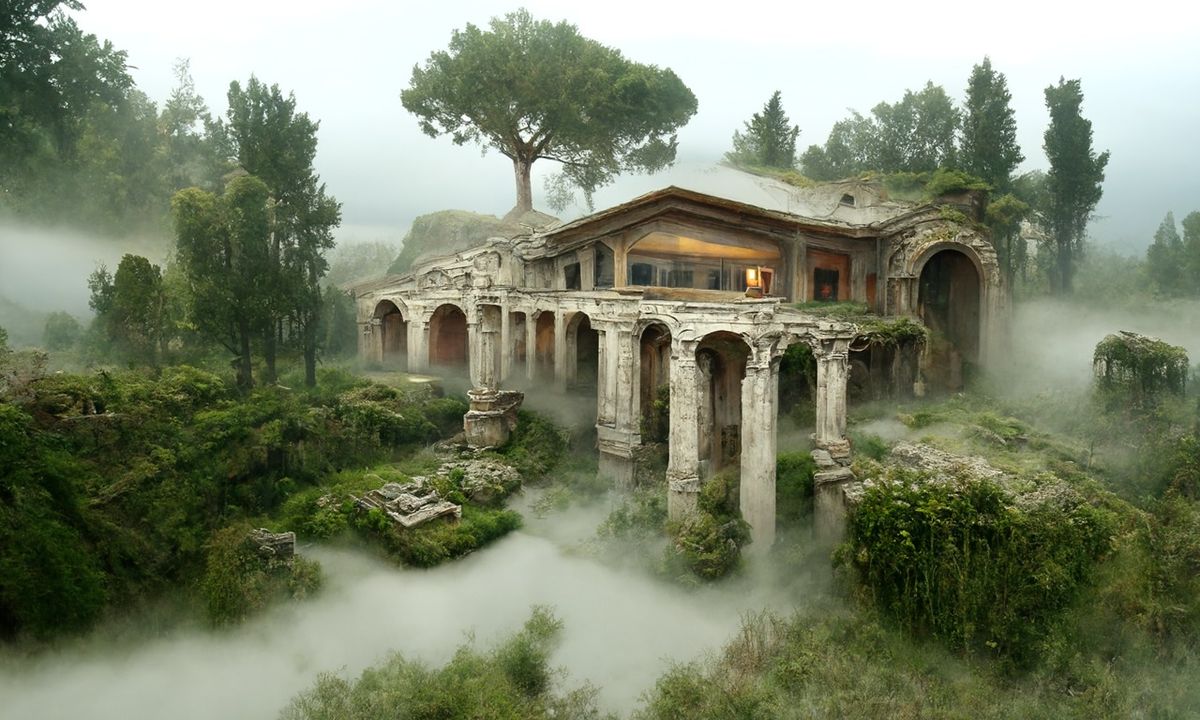



-
Pantheon of the War – The colossal war painting
Read more: Pantheon of the War – The colossal war paintingFour years in the making with the help of 150 artists, in commemoration of WW1.
edition.cnn.com/style/article/pantheon-de-la-guerre-wwi-painting/index.html
A panoramic canvas measuring 402 feet (122 meters) around and 45 feet (13.7 meters) high. It contained over 5,000 life-size portraits of war heroes, royalty and government officials from the Allies of World War I.
Partial section upload:
COLOR
-
A Brief History of Color in Art
Read more: A Brief History of Color in Artwww.artsy.net/article/the-art-genome-project-a-brief-history-of-color-in-art
Of all the pigments that have been banned over the centuries, the color most missed by painters is likely Lead White.
This hue could capture and reflect a gleam of light like no other, though its production was anything but glamorous. The 17th-century Dutch method for manufacturing the pigment involved layering cow and horse manure over lead and vinegar. After three months in a sealed room, these materials would combine to create flakes of pure white. While scientists in the late 19th century identified lead as poisonous, it wasn’t until 1978 that the United States banned the production of lead white paint.
More reading:
www.canva.com/learn/color-meanings/https://www.infogrades.com/history-events-infographics/bizarre-history-of-colors/
-
Polarised vs unpolarized filtering
Read more: Polarised vs unpolarized filteringA light wave that is vibrating in more than one plane is referred to as unpolarized light. …
Polarized light waves are light waves in which the vibrations occur in a single plane. The process of transforming unpolarized light into polarized light is known as polarization.
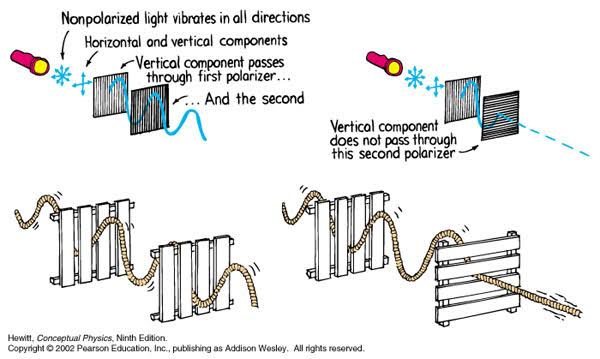
en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Polarizing_filter_(photography)
The most common use of polarized technology is to reduce lighting complexity on the subject.
(more…)
Details such as glare and hard edges are not removed, but greatly reduced. -
Capturing textures albedo
Read more: Capturing textures albedoBuilding a Portable PBR Texture Scanner by Stephane Lb
http://rtgfx.com/pbr-texture-scanner/How To Split Specular And Diffuse In Real Images, by John Hable
http://filmicworlds.com/blog/how-to-split-specular-and-diffuse-in-real-images/Capturing albedo using a Spectralon
https://www.activision.com/cdn/research/Real_World_Measurements_for_Call_of_Duty_Advanced_Warfare.pdfReal_World_Measurements_for_Call_of_Duty_Advanced_Warfare.pdf
Spectralon is a teflon-based pressed powderthat comes closest to being a pure Lambertian diffuse material that reflects 100% of all light. If we take an HDR photograph of the Spectralon alongside the material to be measured, we can derive thediffuse albedo of that material.
The process to capture diffuse reflectance is very similar to the one outlined by Hable.
1. We put a linear polarizing filter in front of the camera lens and a second linear polarizing filterin front of a modeling light or a flash such that the two filters are oriented perpendicular to eachother, i.e. cross polarized.
2. We place Spectralon close to and parallel with the material we are capturing and take brack-eted shots of the setup7. Typically, we’ll take nine photographs, from -4EV to +4EV in 1EVincrements.
3. We convert the bracketed shots to a linear HDR image. We found that many HDR packagesdo not produce an HDR image in which the pixel values are linear. PTGui is an example of apackage which does generate a linear HDR image. At this point, because of the cross polarization,the image is one of surface diffuse response.
4. We open the file in Photoshop and normalize the image by color picking the Spectralon, filling anew layer with that color and setting that layer to “Divide”. This sets the Spectralon to 1 in theimage. All other color values are relative to this so we can consider them as diffuse albedo.
-
If a blind person gained sight, could they recognize objects previously touched?
Read more: If a blind person gained sight, could they recognize objects previously touched?Blind people who regain their sight may find themselves in a world they don’t immediately comprehend. “It would be more like a sighted person trying to rely on tactile information,” Moore says.
Learning to see is a developmental process, just like learning language, Prof Cathleen Moore continues. “As far as vision goes, a three-and-a-half year old child is already a well-calibrated system.”
LIGHTING
-
Lighting Every Darkness with 3DGS: Fast Training and Real-Time Rendering and Denoising for HDR View Synthesis
Read more: Lighting Every Darkness with 3DGS: Fast Training and Real-Time Rendering and Denoising for HDR View Synthesishttps://srameo.github.io/projects/le3d/
LE3D is a method for real-time HDR view synthesis from RAW images. It is particularly effective for nighttime scenes.
https://github.com/Srameo/LE3D
-
Free HDRI libraries
Read more: Free HDRI librariesnoahwitchell.com
http://www.noahwitchell.com/freebieslocationtextures.com
https://locationtextures.com/panoramas/maxroz.com
https://www.maxroz.com/hdri/listHDRI Haven
https://hdrihaven.com/Poly Haven
https://polyhaven.com/hdrisDomeble
https://www.domeble.com/IHDRI
https://www.ihdri.com/HDRMaps
https://hdrmaps.com/NoEmotionHdrs.net
http://noemotionhdrs.net/hdrday.htmlOpenFootage.net
https://www.openfootage.net/hdri-panorama/HDRI-hub
https://www.hdri-hub.com/hdrishop/hdri.zwischendrin
https://www.zwischendrin.com/en/browse/hdriLonger list here:
https://cgtricks.com/list-sites-free-hdri/
-
Rendering – BRDF – Bidirectional reflectance distribution function
Read more: Rendering – BRDF – Bidirectional reflectance distribution functionhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bidirectional_reflectance_distribution_function
The bidirectional reflectance distribution function is a four-dimensional function that defines how light is reflected at an opaque surface
http://www.cs.ucla.edu/~zhu/tutorial/An_Introduction_to_BRDF-Based_Lighting.pdf
In general, when light interacts with matter, a complicated light-matter dynamic occurs. This interaction depends on the physical characteristics of the light as well as the physical composition and characteristics of the matter.
That is, some of the incident light is reflected, some of the light is transmitted, and another portion of the light is absorbed by the medium itself.
A BRDF describes how much light is reflected when light makes contact with a certain material. Similarly, a BTDF (Bi-directional Transmission Distribution Function) describes how much light is transmitted when light makes contact with a certain material
http://www.cs.princeton.edu/~smr/cs348c-97/surveypaper.html
It is difficult to establish exactly how far one should go in elaborating the surface model. A truly complete representation of the reflective behavior of a surface might take into account such phenomena as polarization, scattering, fluorescence, and phosphorescence, all of which might vary with position on the surface. Therefore, the variables in this complete function would be:
incoming and outgoing angle incoming and outgoing wavelength incoming and outgoing polarization (both linear and circular) incoming and outgoing position (which might differ due to subsurface scattering) time delay between the incoming and outgoing light ray
-
About green screens
Read more: About green screenshackaday.com/2015/02/07/how-green-screen-worked-before-computers/
www.newtek.com/blog/tips/best-green-screen-materials/
www.chromawall.com/blog//chroma-key-green
Chroma Key Green, the color of green screens is also known as Chroma Green and is valued at approximately 354C in the Pantone color matching system (PMS).
Chroma Green can be broken down in many different ways. Here is green screen green as other values useful for both physical and digital production:
Green Screen as RGB Color Value: 0, 177, 64
Green Screen as CMYK Color Value: 81, 0, 92, 0
Green Screen as Hex Color Value: #00b140
Green Screen as Websafe Color Value: #009933Chroma Key Green is reasonably close to an 18% gray reflectance.
Illuminate your green screen with an uniform source with less than 2/3 EV variation.
The level of brightness at any given f-stop should be equivalent to a 90% white card under the same lighting.
COLLECTIONS
| Featured AI
| Design And Composition
| Explore posts
POPULAR SEARCHES
unreal | pipeline | virtual production | free | learn | photoshop | 360 | macro | google | nvidia | resolution | open source | hdri | real-time | photography basics | nuke
FEATURED POSTS
-
VFX pipeline – Render Wall Farm management topics
-
PixelSham – Introduction to Python 2022
-
N8N.io – From Zero to Your First AI Agent in 25 Minutes
-
FFmpeg – examples and convenience lines
-
Blender VideoDepthAI – Turn any video into 3D Animated Scenes
-
Animation/VFX/Game Industry JOB POSTINGS by Chris Mayne
-
Want to build a start up company that lasts? Think three-layer cake
-
Godot Cheat Sheets
Social Links
DISCLAIMER – Links and images on this website may be protected by the respective owners’ copyright. All data submitted by users through this site shall be treated as freely available to share.