COMPOSITION
-
Types of Film Lights and their efficiency – CRI, Color Temperature and Luminous Efficacy
Read more: Types of Film Lights and their efficiency – CRI, Color Temperature and Luminous Efficacynofilmschool.com/types-of-film-lights
“Not every light performs the same way. Lights and lighting are tricky to handle. You have to plan for every circumstance. But the good news is, lighting can be adjusted. Let’s look at different factors that affect lighting in every scene you shoot. “
Use CRI, Luminous Efficacy and color temperature controls to match your needs.Color Temperature
Color temperature describes the “color” of white light by a light source radiated by a perfect black body at a given temperature measured in degrees Kelvinhttps://www.pixelsham.com/2019/10/18/color-temperature/
CRI
“The Color Rendering Index is a measurement of how faithfully a light source reveals the colors of whatever it illuminates, it describes the ability of a light source to reveal the color of an object, as compared to the color a natural light source would provide. The highest possible CRI is 100. A CRI of 100 generally refers to a perfect black body, like a tungsten light source or the sun. “https://www.studiobinder.com/blog/what-is-color-rendering-index
(more…) -
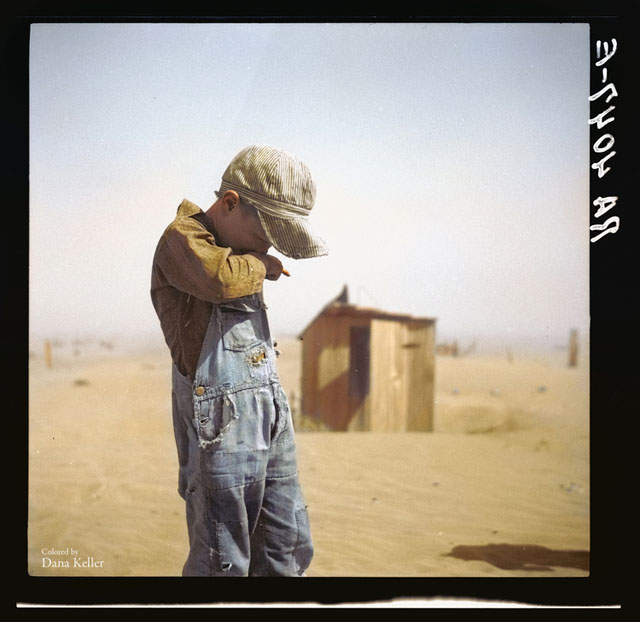
Composition – cinematography Cheat Sheet
Read more: Composition – cinematography Cheat Sheet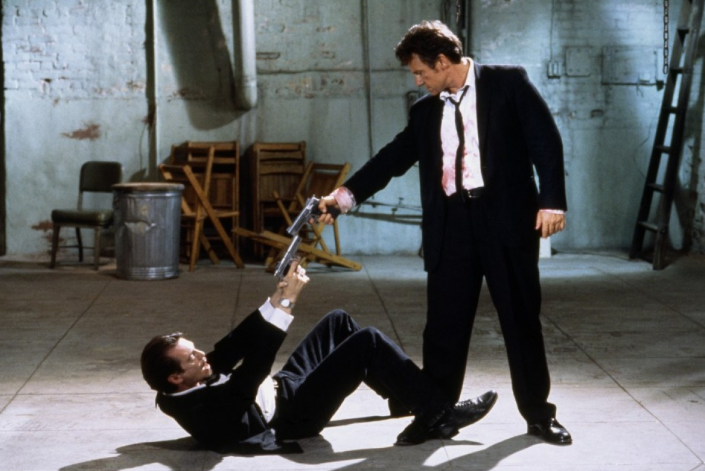
Where is our eye attracted first? Why?
Size. Focus. Lighting. Color.
Size. Mr. White (Harvey Keitel) on the right.
Focus. He’s one of the two objects in focus.
Lighting. Mr. White is large and in focus and Mr. Pink (Steve Buscemi) is highlighted by
a shaft of light.
Color. Both are black and white but the read on Mr. White’s shirt now really stands out.
(more…)
What type of lighting? -
Photography basics: Depth of Field and composition
Read more: Photography basics: Depth of Field and compositionDepth of field is the range within which focusing is resolved in a photo.
Aperture has a huge affect on to the depth of field.Changing the f-stops (f/#) of a lens will change aperture and as such the DOF.
f-stops are a just certain number which is telling you the size of the aperture. That’s how f-stop is related to aperture (and DOF).
If you increase f-stops, it will increase DOF, the area in focus (and decrease the aperture). On the other hand, decreasing the f-stop it will decrease DOF (and increase the aperture).
The red cone in the figure is an angular representation of the resolution of the system. Versus the dotted lines, which indicate the aperture coverage. Where the lines of the two cones intersect defines the total range of the depth of field.
This image explains why the longer the depth of field, the greater the range of clarity.
-
Composition – 5 tips for creating perfect cinematic lighting and making your work look stunning
Read more: Composition – 5 tips for creating perfect cinematic lighting and making your work look stunninghttp://www.diyphotography.net/5-tips-creating-perfect-cinematic-lighting-making-work-look-stunning/
1. Learn the rules of lighting
2. Learn when to break the rules
3. Make your key light larger
4. Reverse keying
5. Always be backlighting
-
9 Best Hacks to Make a Cinematic Video with Any Camera
Read more: 9 Best Hacks to Make a Cinematic Video with Any Camerahttps://www.flexclip.com/learn/cinematic-video.html
- Frame Your Shots to Create Depth
- Create Shallow Depth of Field
- Avoid Shaky Footage and Use Flexible Camera Movements
- Properly Use Slow Motion
- Use Cinematic Lighting Techniques
- Apply Color Grading
- Use Cinematic Music and SFX
- Add Cinematic Fonts and Text Effects
- Create the Cinematic Bar at the Top and the Bottom

DESIGN
-
Pasquale Scionti – Production Walkthrough with Virtual Camera and iPad pro 11.5 on Unreal Engine 4.25
Read more: Pasquale Scionti – Production Walkthrough with Virtual Camera and iPad pro 11.5 on Unreal Engine 4.2580.lv/articles/creating-an-old-abandoned-mansion-with-quixel-tools/
www.artstation.com/artwork/Poexyo

COLOR
-
Paul Debevec, Chloe LeGendre, Lukas Lepicovsky – Jointly Optimizing Color Rendition and In-Camera Backgrounds in an RGB Virtual Production Stage
Read more: Paul Debevec, Chloe LeGendre, Lukas Lepicovsky – Jointly Optimizing Color Rendition and In-Camera Backgrounds in an RGB Virtual Production Stagehttps://arxiv.org/pdf/2205.12403.pdf
RGB LEDs vs RGBWP (RGB + lime + phospor converted amber) LEDs
Local copy:
-
FXGuide – ACES 2.0 with ILM’s Alex Fry
Read more: FXGuide – ACES 2.0 with ILM’s Alex Fryhttps://draftdocs.acescentral.com/background/whats-new/
ACES 2.0 is the second major release of the components that make up the ACES system. The most significant change is a new suite of rendering transforms whose design was informed by collected feedback and requests from users of ACES 1. The changes aim to improve the appearance of perceived artifacts and to complete previously unfinished components of the system, resulting in a more complete, robust, and consistent product.
Highlights of the key changes in ACES 2.0 are as follows:
- New output transforms, including:
- A less aggressive tone scale
- More intuitive controls to create custom outputs to non-standard displays
- Robust gamut mapping to improve perceptual uniformity
- Improved performance of the inverse transforms
- Enhanced AMF specification
- An updated specification for ACES Transform IDs
- OpenEXR compression recommendations
- Enhanced tools for generating Input Transforms and recommended procedures for characterizing prosumer cameras
- Look Transform Library
- Expanded documentation
Rendering Transform
The most substantial change in ACES 2.0 is a complete redesign of the rendering transform.
ACES 2.0 was built as a unified system, rather than through piecemeal additions. Different deliverable outputs “match” better and making outputs to display setups other than the provided presets is intended to be user-driven. The rendering transforms are less likely to produce undesirable artifacts “out of the box”, which means less time can be spent fixing problematic images and more time making pictures look the way you want.
Key design goals
- Improve consistency of tone scale and provide an easy to use parameter to allow for outputs between preset dynamic ranges
- Minimize hue skews across exposure range in a region of same hue
- Unify for structural consistency across transform type
- Easy to use parameters to create outputs other than the presets
- Robust gamut mapping to improve harsh clipping artifacts
- Fill extents of output code value cube (where appropriate and expected)
- Invertible – not necessarily reversible, but Output > ACES > Output round-trip should be possible
- Accomplish all of the above while maintaining an acceptable “out-of-the box” rendering
- New output transforms, including:
-
What is OLED and what can it do for your TV
Read more: What is OLED and what can it do for your TVhttps://www.cnet.com/news/what-is-oled-and-what-can-it-do-for-your-tv/
OLED stands for Organic Light Emitting Diode. Each pixel in an OLED display is made of a material that glows when you jab it with electricity. Kind of like the heating elements in a toaster, but with less heat and better resolution. This effect is called electroluminescence, which is one of those delightful words that is big, but actually makes sense: “electro” for electricity, “lumin” for light and “escence” for, well, basically “essence.”
OLED TV marketing often claims “infinite” contrast ratios, and while that might sound like typical hyperbole, it’s one of the extremely rare instances where such claims are actually true. Since OLED can produce a perfect black, emitting no light whatsoever, its contrast ratio (expressed as the brightest white divided by the darkest black) is technically infinite.
OLED is the only technology capable of absolute blacks and extremely bright whites on a per-pixel basis. LCD definitely can’t do that, and even the vaunted, beloved, dearly departed plasma couldn’t do absolute blacks.
LIGHTING
-
StudioBinder.com – CRI color rendering index
Read more: StudioBinder.com – CRI color rendering indexwww.studiobinder.com/blog/what-is-color-rendering-index
“The Color Rendering Index is a measurement of how faithfully a light source reveals the colors of whatever it illuminates, it describes the ability of a light source to reveal the color of an object, as compared to the color a natural light source would provide. The highest possible CRI is 100. A CRI of 100 generally refers to a perfect black body, like a tungsten light source or the sun. ”
www.pixelsham.com/2021/04/28/types-of-film-lights-and-their-efficiency
-
DiffusionLight: HDRI Light Probes for Free by Painting a Chrome Ball
Read more: DiffusionLight: HDRI Light Probes for Free by Painting a Chrome Ballhttps://diffusionlight.github.io/
https://github.com/DiffusionLight/DiffusionLight
https://github.com/DiffusionLight/DiffusionLight?tab=MIT-1-ov-file#readme
https://colab.research.google.com/drive/15pC4qb9mEtRYsW3utXkk-jnaeVxUy-0S
“a simple yet effective technique to estimate lighting in a single input image. Current techniques rely heavily on HDR panorama datasets to train neural networks to regress an input with limited field-of-view to a full environment map. However, these approaches often struggle with real-world, uncontrolled settings due to the limited diversity and size of their datasets. To address this problem, we leverage diffusion models trained on billions of standard images to render a chrome ball into the input image. Despite its simplicity, this task remains challenging: the diffusion models often insert incorrect or inconsistent objects and cannot readily generate images in HDR format. Our research uncovers a surprising relationship between the appearance of chrome balls and the initial diffusion noise map, which we utilize to consistently generate high-quality chrome balls. We further fine-tune an LDR difusion model (Stable Diffusion XL) with LoRA, enabling it to perform exposure bracketing for HDR light estimation. Our method produces convincing light estimates across diverse settings and demonstrates superior generalization to in-the-wild scenarios.”

-
Black Body color aka the Planckian Locus curve for white point eye perception
Read more: Black Body color aka the Planckian Locus curve for white point eye perceptionhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Black-body_radiation
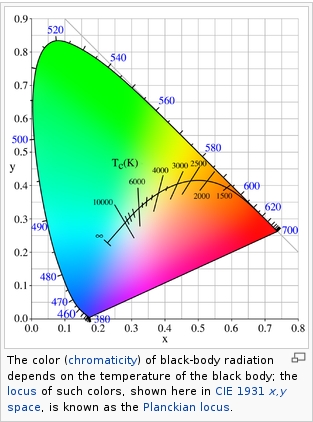
Black-body radiation is the type of electromagnetic radiation within or surrounding a body in thermodynamic equilibrium with its environment, or emitted by a black body (an opaque and non-reflective body) held at constant, uniform temperature. The radiation has a specific spectrum and intensity that depends only on the temperature of the body.
A black-body at room temperature appears black, as most of the energy it radiates is infra-red and cannot be perceived by the human eye. At higher temperatures, black bodies glow with increasing intensity and colors that range from dull red to blindingly brilliant blue-white as the temperature increases.
(more…) -
Free HDRI libraries
Read more: Free HDRI librariesnoahwitchell.com
http://www.noahwitchell.com/freebieslocationtextures.com
https://locationtextures.com/panoramas/maxroz.com
https://www.maxroz.com/hdri/listHDRI Haven
https://hdrihaven.com/Poly Haven
https://polyhaven.com/hdrisDomeble
https://www.domeble.com/IHDRI
https://www.ihdri.com/HDRMaps
https://hdrmaps.com/NoEmotionHdrs.net
http://noemotionhdrs.net/hdrday.htmlOpenFootage.net
https://www.openfootage.net/hdri-panorama/HDRI-hub
https://www.hdri-hub.com/hdrishop/hdri.zwischendrin
https://www.zwischendrin.com/en/browse/hdriLonger list here:
https://cgtricks.com/list-sites-free-hdri/
-
HDRI Resources
Read more: HDRI ResourcesText2Light
- https://www.cgtrader.com/free-3d-models/exterior/other/10-free-hdr-panoramas-created-with-text2light-zero-shot
- https://frozenburning.github.io/projects/text2light/
- https://github.com/FrozenBurning/Text2Light
Royalty free links
- https://locationtextures.com/panoramas/
- http://www.noahwitchell.com/freebies
- https://polyhaven.com/hdris
- https://hdrmaps.com/
- https://www.ihdri.com/
- https://hdrihaven.com/
- https://www.domeble.com/
- http://www.hdrlabs.com/sibl/archive.html
- https://www.hdri-hub.com/hdrishop/hdri
- http://noemotionhdrs.net/hdrevening.html
- https://www.openfootage.net/hdri-panorama/
- https://www.zwischendrin.com/en/browse/hdri
Nvidia GauGAN360
COLLECTIONS
| Featured AI
| Design And Composition
| Explore posts
POPULAR SEARCHES
unreal | pipeline | virtual production | free | learn | photoshop | 360 | macro | google | nvidia | resolution | open source | hdri | real-time | photography basics | nuke
FEATURED POSTS
-
UV maps
-
4dv.ai – Remote Interactive 3D Holographic Presentation Technology and System running on the PlayCanvas engine
-
59 AI Filmmaking Tools For Your Workflow
-
Ross Pettit on The Agile Manager – How tech firms went for prioritizing cash flow instead of talent (and artists)
-
Photography basics: Exposure Value vs Photographic Exposure vs Il/Luminance vs Pixel luminance measurements
-
What the Boeing 737 MAX’s crashes can teach us about production business – the effects of commoditisation
-
What’s the Difference Between Ray Casting, Ray Tracing, Path Tracing and Rasterization? Physical light tracing…
-
AI and the Law – Netflix : Using Generative AI in Content Production
Social Links
DISCLAIMER – Links and images on this website may be protected by the respective owners’ copyright. All data submitted by users through this site shall be treated as freely available to share.