COMPOSITION
-
Composition and The Expressive Nature Of Light
Read more: Composition and The Expressive Nature Of Lighthttp://www.huffingtonpost.com/bill-danskin/post_12457_b_10777222.html
George Sand once said “ The artist vocation is to send light into the human heart.”
-
HuggingFace ai-comic-factory – a FREE AI Comic Book Creator
Read more: HuggingFace ai-comic-factory – a FREE AI Comic Book Creatorhttps://huggingface.co/spaces/jbilcke-hf/ai-comic-factory
this is the epic story of a group of talented digital artists trying to overcame daily technical challenges to achieve incredibly photorealistic projects of monsters and aliens
DESIGN
-
Create striked-out text
Read more: Create striked-out texthttp://fsymbols.com/generators/strikethrough/
s̶t̶r̶i̶k̶e̶ ̶i̶t̶ ̶l̶i̶k̶̶e̶ ̶i̶t̶s̶ ̶h̶o̶t
COLOR
-
Tobia Montanari – Memory Colors: an essential tool for Colorists
Read more: Tobia Montanari – Memory Colors: an essential tool for Coloristshttps://www.tobiamontanari.com/memory-colors-an-essential-tool-for-colorists/
“Memory colors are colors that are universally associated with specific objects, elements or scenes in our environment. They are the colors that we expect to see in specific situations: these colors are based on our expectation of how certain objects should look based on our past experiences and memories.
For instance, we associate specific hues, saturation and brightness values with human skintones and a slight variation can significantly affect the way we perceive a scene.
Similarly, we expect blue skies to have a particular hue, green trees to be a specific shade and so on.
Memory colors live inside of our brains and we often impose them onto what we see. By considering them during the grading process, the resulting image will be more visually appealing and won’t distract the viewer from the intended message of the story. Even a slight deviation from memory colors in a movie can create a sense of discordance, ultimately detracting from the viewer’s experience.”
-
No one could see the colour blue until modern times
Read more: No one could see the colour blue until modern timeshttps://www.businessinsider.com/what-is-blue-and-how-do-we-see-color-2015-2

The way humans see the world… until we have a way to describe something, even something so fundamental as a colour, we may not even notice that something it’s there.
Ancient languages didn’t have a word for blue — not Greek, not Chinese, not Japanese, not Hebrew, not Icelandic cultures. And without a word for the colour, there’s evidence that they may not have seen it at all.
https://www.wnycstudios.org/story/211119-colorsEvery language first had a word for black and for white, or dark and light. The next word for a colour to come into existence — in every language studied around the world — was red, the colour of blood and wine.
After red, historically, yellow appears, and later, green (though in a couple of languages, yellow and green switch places). The last of these colours to appear in every language is blue.The only ancient culture to develop a word for blue was the Egyptians — and as it happens, they were also the only culture that had a way to produce a blue dye.
https://mymodernmet.com/shades-of-blue-color-history/True blue hues are rare in the natural world because synthesizing pigments that absorb longer-wavelength light (reds and yellows) while reflecting shorter-wavelength blue light requires exceptionally elaborate molecular structures—biochemical feats that most plants and animals simply don’t undertake.
When you gaze at a blueberry’s deep blue surface, you’re actually seeing structural coloration rather than a true blue pigment. A fine, waxy bloom on the berry’s skin contains nanostructures that preferentially scatter blue and violet light, giving the fruit its signature blue sheen even though its inherent pigment is reddish.
Similarly, many of nature’s most striking blues—like those of blue jays and morpho butterflies—arise not from blue pigments but from microscopic architectures in feathers or wing scales. These tiny ridges and air pockets manipulate incoming light so that blue wavelengths emerge most prominently, creating vivid, angle-dependent colors through scattering rather than pigment alone.
(more…) -
The 7 key elements of brand identity design + 10 corporate identity examples
Read more: The 7 key elements of brand identity design + 10 corporate identity exampleswww.lucidpress.com/blog/the-7-key-elements-of-brand-identity-design
1. Clear brand purpose and positioning
2. Thorough market research
3. Likable brand personality
4. Memorable logo
5. Attractive color palette
6. Professional typography
7. On-brand supporting graphics
LIGHTING
-
Disney’s Moana Island Scene – Free data set
Read more: Disney’s Moana Island Scene – Free data sethttps://www.disneyanimation.com/resources/moana-island-scene/
This data set contains everything necessary to render a version of the Motunui island featured in the 2016 film Moana.
-
What’s the Difference Between Ray Casting, Ray Tracing, Path Tracing and Rasterization? Physical light tracing…
Read more: What’s the Difference Between Ray Casting, Ray Tracing, Path Tracing and Rasterization? Physical light tracing…RASTERIZATION
Rasterisation (or rasterization) is the task of taking the information described in a vector graphics format OR the vertices of triangles making 3D shapes and converting them into a raster image (a series of pixels, dots or lines, which, when displayed together, create the image which was represented via shapes), or in other words “rasterizing” vectors or 3D models onto a 2D plane for display on a computer screen.For each triangle of a 3D shape, you project the corners of the triangle on the virtual screen with some math (projective geometry). Then you have the position of the 3 corners of the triangle on the pixel screen. Those 3 points have texture coordinates, so you know where in the texture are the 3 corners. The cost is proportional to the number of triangles, and is only a little bit affected by the screen resolution.
In computer graphics, a raster graphics or bitmap image is a dot matrix data structure that represents a generally rectangular grid of pixels (points of color), viewable via a monitor, paper, or other display medium.
With rasterization, objects on the screen are created from a mesh of virtual triangles, or polygons, that create 3D models of objects. A lot of information is associated with each vertex, including its position in space, as well as information about color, texture and its “normal,” which is used to determine the way the surface of an object is facing.
Computers then convert the triangles of the 3D models into pixels, or dots, on a 2D screen. Each pixel can be assigned an initial color value from the data stored in the triangle vertices.
Further pixel processing or “shading,” including changing pixel color based on how lights in the scene hit the pixel, and applying one or more textures to the pixel, combine to generate the final color applied to a pixel.
The main advantage of rasterization is its speed. However, rasterization is simply the process of computing the mapping from scene geometry to pixels and does not prescribe a particular way to compute the color of those pixels. So it cannot take shading, especially the physical light, into account and it cannot promise to get a photorealistic output. That’s a big limitation of rasterization.
There are also multiple problems:
If you have two triangles one is behind the other, you will draw twice all the pixels. you only keep the pixel from the triangle that is closer to you (Z-buffer), but you still do the work twice.
The borders of your triangles are jagged as it is hard to know if a pixel is in the triangle or out. You can do some smoothing on those, that is anti-aliasing.
You have to handle every triangles (including the ones behind you) and then see that they do not touch the screen at all. (we have techniques to mitigate this where we only look at triangles that are in the field of view)
Transparency is hard to handle (you can’t just do an average of the color of overlapping transparent triangles, you have to do it in the right order)
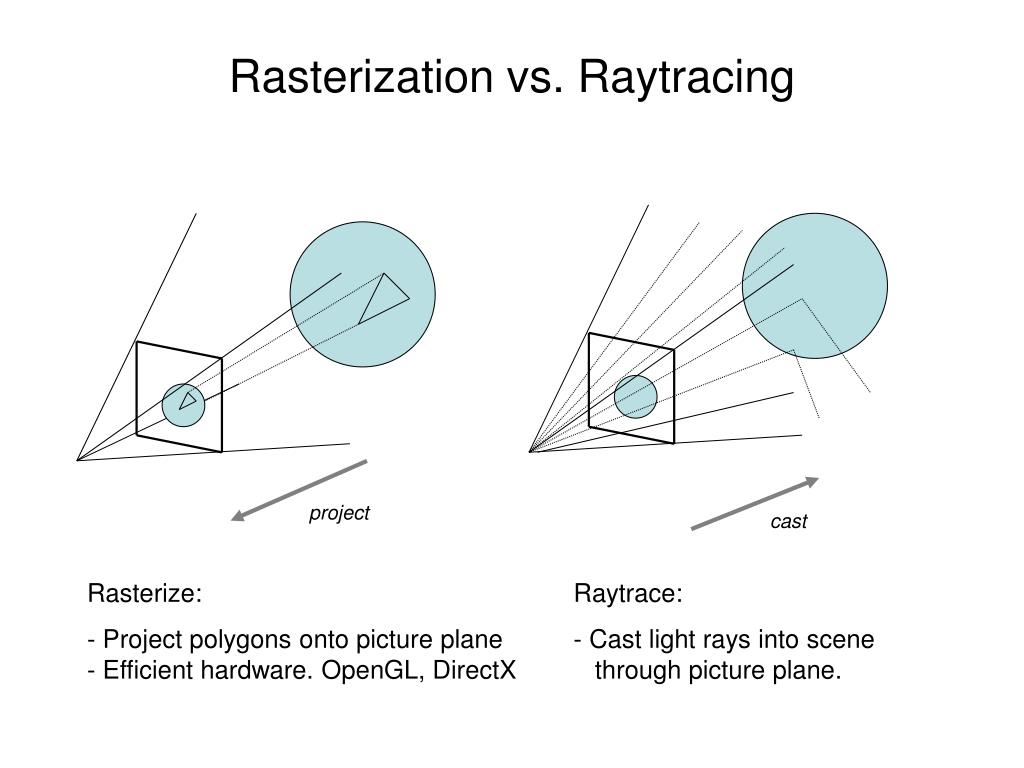
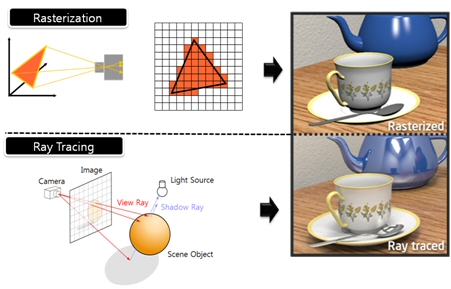
RAY CASTING
It is almost the exact reverse of rasterization: you start from the virtual screen instead of the vector or 3D shapes, and you project a ray, starting from each pixel of the screen, until it intersect with a triangle.The cost is directly correlated to the number of pixels in the screen and you need a really cheap way of finding the first triangle that intersect a ray. In the end, it is more expensive than rasterization but it will, by design, ignore the triangles that are out of the field of view.
You can use it to continue after the first triangle it hit, to take a little bit of the color of the next one, etc… This is useful to handle the border of the triangle cleanly (less jagged) and to handle transparency correctly.
RAYTRACING
Same idea as ray casting except once you hit a triangle you reflect on it and go into a different direction. The number of reflection you allow is the “depth” of your ray tracing. The color of the pixel can be calculated, based off the light source and all the polygons it had to reflect off of to get to that screen pixel.The easiest way to think of ray tracing is to look around you, right now. The objects you’re seeing are illuminated by beams of light. Now turn that around and follow the path of those beams backwards from your eye to the objects that light interacts with. That’s ray tracing.
Ray tracing is eye-oriented process that needs walking through each pixel looking for what object should be shown there, which is also can be described as a technique that follows a beam of light (in pixels) from a set point and simulates how it reacts when it encounters objects.
Compared with rasterization, ray tracing is hard to be implemented in real time, since even one ray can be traced and processed without much trouble, but after one ray bounces off an object, it can turn into 10 rays, and those 10 can turn into 100, 1000…The increase is exponential, and the the calculation for all these rays will be time consuming.
Historically, computer hardware hasn’t been fast enough to use these techniques in real time, such as in video games. Moviemakers can take as long as they like to render a single frame, so they do it offline in render farms. Video games have only a fraction of a second. As a result, most real-time graphics rely on the another technique called rasterization.
PATH TRACING
Path tracing can be used to solve more complex lighting situations.
Path tracing is a type of ray tracing. When using path tracing for rendering, the rays only produce a single ray per bounce. The rays do not follow a defined line per bounce (to a light, for example), but rather shoot off in a random direction. The path tracing algorithm then takes a random sampling of all of the rays to create the final image. This results in sampling a variety of different types of lighting.When a ray hits a surface it doesn’t trace a path to every light source, instead it bounces the ray off the surface and keeps bouncing it until it hits a light source or exhausts some bounce limit.
It then calculates the amount of light transferred all the way to the pixel, including any color information gathered from surfaces along the way.
It then averages out the values calculated from all the paths that were traced into the scene to get the final pixel color value.It requires a ton of computing power and if you don’t send out enough rays per pixel or don’t trace the paths far enough into the scene then you end up with a very spotty image as many pixels fail to find any light sources from their rays. So when you increase the the samples per pixel, you can see the image quality becomes better and better.
Ray tracing tends to be more efficient than path tracing. Basically, the render time of a ray tracer depends on the number of polygons in the scene. The more polygons you have, the longer it will take.
Meanwhile, the rendering time of a path tracer can be indifferent to the number of polygons, but it is related to light situation: If you add a light, transparency, translucence, or other shader effects, the path tracer will slow down considerably.blogs.nvidia.com/blog/2018/03/19/whats-difference-between-ray-tracing-rasterization/
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Rasterisation
https://www.quora.com/Whats-the-difference-between-ray-tracing-and-path-tracing
-
Photography basics: Lumens vs Candelas (candle) vs Lux vs FootCandle vs Watts vs Irradiance vs Illuminance
Read more: Photography basics: Lumens vs Candelas (candle) vs Lux vs FootCandle vs Watts vs Irradiance vs Illuminancehttps://www.translatorscafe.com/unit-converter/en-US/illumination/1-11/
The power output of a light source is measured using the unit of watts W. This is a direct measure to calculate how much power the light is going to drain from your socket and it is not relatable to the light brightness itself.
The amount of energy emitted from it per second. That energy comes out in a form of photons which we can crudely represent with rays of light coming out of the source. The higher the power the more rays emitted from the source in a unit of time.
Not all energy emitted is visible to the human eye, so we often rely on photometric measurements, which takes in account the sensitivity of human eye to different wavelenghts
Details in the post
(more…) -
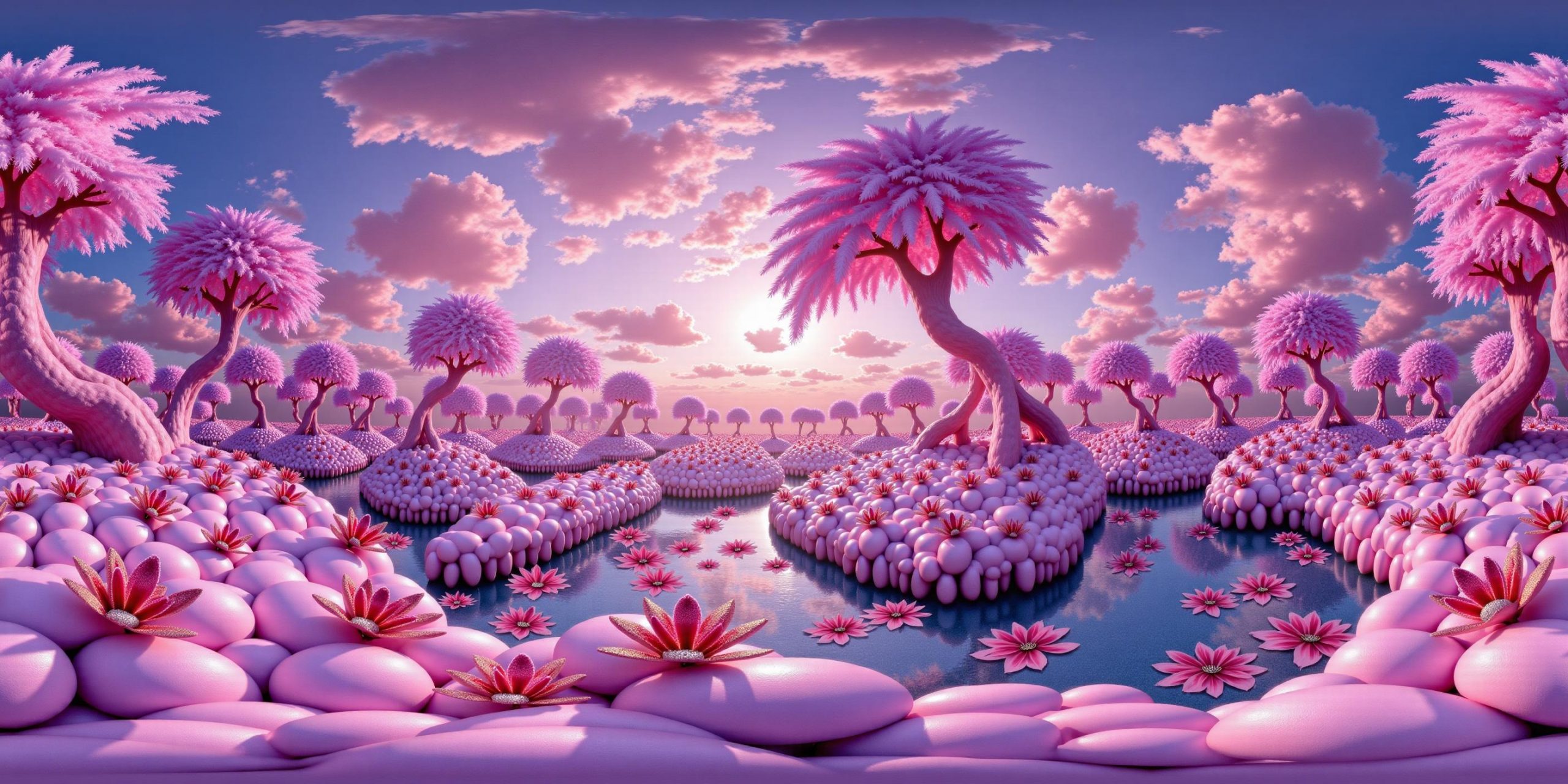
Arto T. – A workflow for creating photorealistic, equirectangular 360° panoramas in ComfyUI using Flux
Read more: Arto T. – A workflow for creating photorealistic, equirectangular 360° panoramas in ComfyUI using Fluxhttps://civitai.com/models/735980/flux-equirectangular-360-panorama
https://civitai.com/models/745010?modelVersionId=833115
The trigger phrase is “equirectangular 360 degree panorama”. I would avoid saying “spherical projection” since that tends to result in non-equirectangular spherical images.
Image resolution should always be a 2:1 aspect ratio. 1024 x 512 or 1408 x 704 work quite well and were used in the training data. 2048 x 1024 also works.
I suggest using a weight of 0.5 – 1.5. If you are having issues with the image generating too flat instead of having the necessary spherical distortion, try increasing the weight above 1, though this could negatively impact small details of the image. For Flux guidance, I recommend a value of about 2.5 for realistic scenes.
8-bit output at the moment

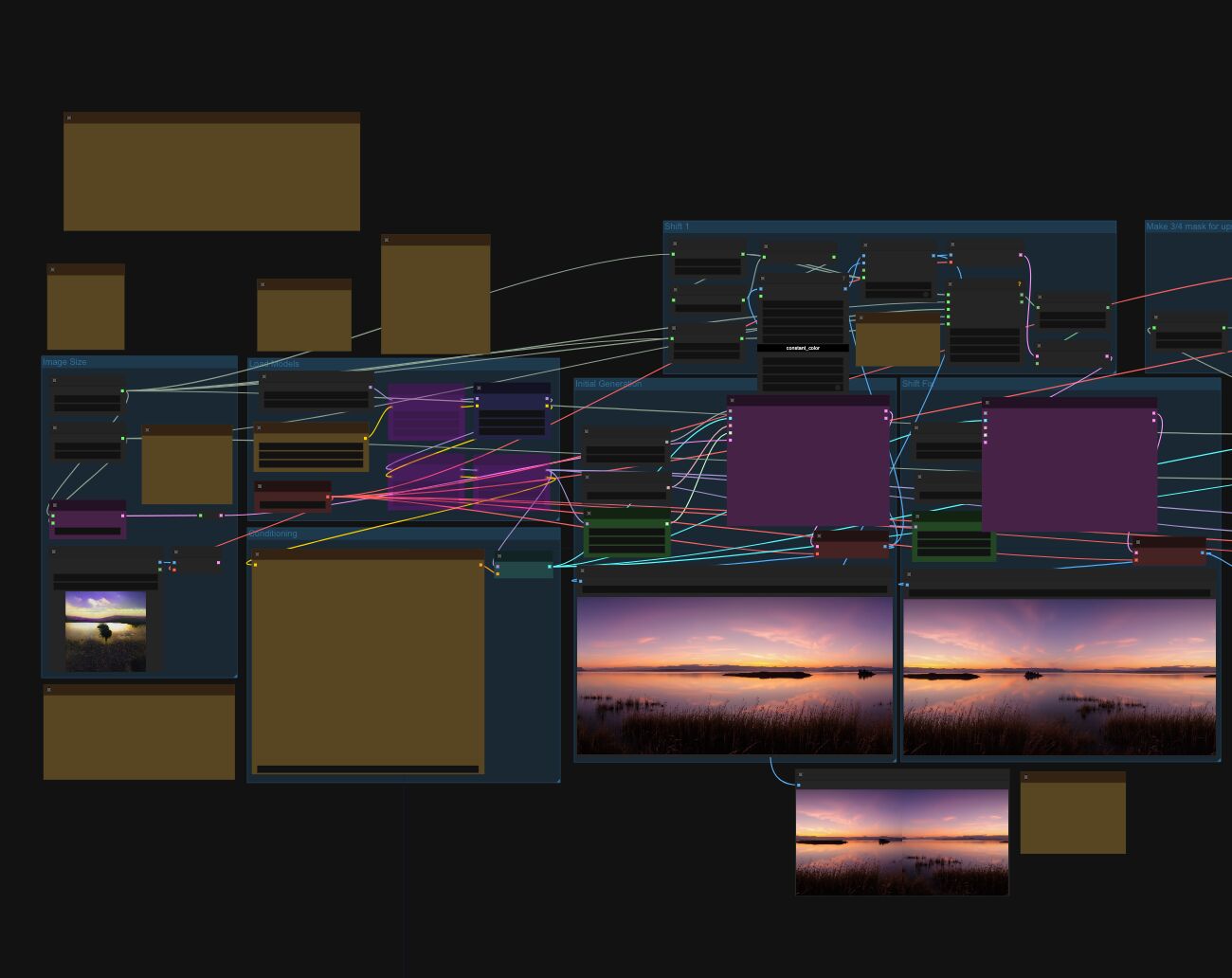
-
Unity 3D resources
Read more: Unity 3D resources
http://answers.unity3d.com/questions/12321/how-can-i-start-learning-unity-fast-list-of-tutori.html
If you have no previous experience with Unity, start with these six video tutorials which give a quick overview of the Unity interface and some important features http://unity3d.com/support/documentation/video/
-
Cinematographers Blueprint 300dpi poster
Read more: Cinematographers Blueprint 300dpi posterThe 300dpi digital poster is now available to all PixelSham.com subscribers.
If you have already subscribed and wish a copy, please send me a note through the contact page.
-
Convert between light exposure and intensity
Read more: Convert between light exposure and intensityimport math,sys def Exposure2Intensity(exposure): exp = float(exposure) result = math.pow(2,exp) print(result) Exposure2Intensity(0) def Intensity2Exposure(intensity): inarg = float(intensity) if inarg == 0: print("Exposure of zero intensity is undefined.") return if inarg < 1e-323: inarg = max(inarg, 1e-323) print("Exposure of negative intensities is undefined. Clamping to a very small value instead (1e-323)") result = math.log(inarg, 2) print(result) Intensity2Exposure(0.1)Why Exposure?
Exposure is a stop value that multiplies the intensity by 2 to the power of the stop. Increasing exposure by 1 results in double the amount of light.
Artists think in “stops.” Doubling or halving brightness is easy math and common in grading and look-dev.
Exposure counts doublings in whole stops:- +1 stop = ×2 brightness
- −1 stop = ×0.5 brightness
This gives perceptually even controls across both bright and dark values.
Why Intensity?
Intensity is linear.
It’s what render engines and compositors expect when:- Summing values
- Averaging pixels
- Multiplying or filtering pixel data
Use intensity when you need the actual math on pixel/light data.
Formulas (from your Python)
- Intensity from exposure: intensity = 2**exposure
- Exposure from intensity: exposure = log₂(intensity)
Guardrails:
- Intensity must be > 0 to compute exposure.
- If intensity = 0 → exposure is undefined.
- Clamp tiny values (e.g.
1e−323) before using log₂.
Use Exposure (stops) when…
- You want artist-friendly sliders (−5…+5 stops)
- Adjusting look-dev or grading in even stops
- Matching plates with quick ±1 stop tweaks
- Tweening brightness changes smoothly across ranges
Use Intensity (linear) when…
- Storing raw pixel/light values
- Multiplying textures or lights by a gain
- Performing sums, averages, and filters
- Feeding values to render engines expecting linear data
Examples
- +2 stops → 2**2 = 4.0 (×4)
- +1 stop → 2**1 = 2.0 (×2)
- 0 stop → 2**0 = 1.0 (×1)
- −1 stop → 2**(−1) = 0.5 (×0.5)
- −2 stops → 2**(−2) = 0.25 (×0.25)
- Intensity 0.1 → exposure = log₂(0.1) ≈ −3.32
Rule of thumb
Think in stops (exposure) for controls and matching.
Compute in linear (intensity) for rendering and math. -
Types of Film Lights and their efficiency – CRI, Color Temperature and Luminous Efficacy
Read more: Types of Film Lights and their efficiency – CRI, Color Temperature and Luminous Efficacynofilmschool.com/types-of-film-lights
“Not every light performs the same way. Lights and lighting are tricky to handle. You have to plan for every circumstance. But the good news is, lighting can be adjusted. Let’s look at different factors that affect lighting in every scene you shoot. “
Use CRI, Luminous Efficacy and color temperature controls to match your needs.Color Temperature
Color temperature describes the “color” of white light by a light source radiated by a perfect black body at a given temperature measured in degrees Kelvinhttps://www.pixelsham.com/2019/10/18/color-temperature/
CRI
“The Color Rendering Index is a measurement of how faithfully a light source reveals the colors of whatever it illuminates, it describes the ability of a light source to reveal the color of an object, as compared to the color a natural light source would provide. The highest possible CRI is 100. A CRI of 100 generally refers to a perfect black body, like a tungsten light source or the sun. “https://www.studiobinder.com/blog/what-is-color-rendering-index
(more…)
COLLECTIONS
| Featured AI
| Design And Composition
| Explore posts
POPULAR SEARCHES
unreal | pipeline | virtual production | free | learn | photoshop | 360 | macro | google | nvidia | resolution | open source | hdri | real-time | photography basics | nuke
FEATURED POSTS
-
MiniTunes V1 – Free MP3 library app
-
Survivorship Bias: The error resulting from systematically focusing on successes and ignoring failures. How a young statistician saved his planes during WW2.
-
Advanced Computer Vision with Python OpenCV and Mediapipe
-
Matt Hallett – WAN 2.1 VACE Total Video Control in ComfyUI
-
Scene Referred vs Display Referred color workflows
-
MiniMax-Remover – Taming Bad Noise Helps Video Object Removal Rotoscoping
-
Google – Artificial Intelligence free courses
-
Matt Gray – How to generate a profitable business
Social Links
DISCLAIMER – Links and images on this website may be protected by the respective owners’ copyright. All data submitted by users through this site shall be treated as freely available to share.