COMPOSITION
-
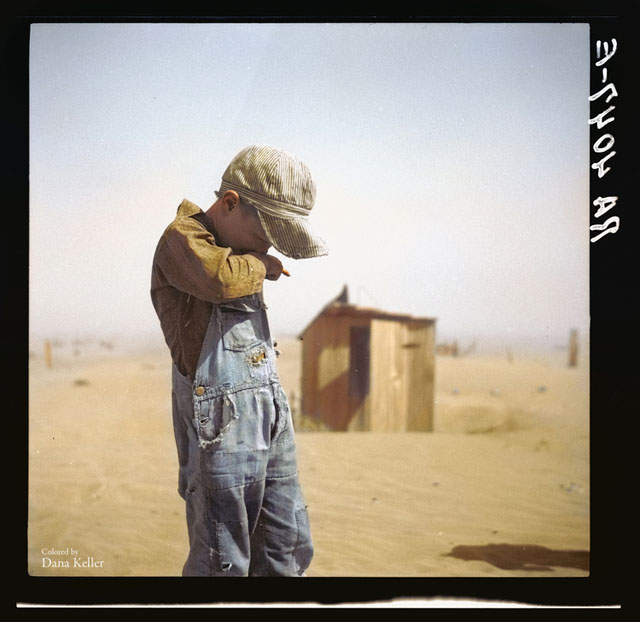
Mastering Camera Shots and Angles: A Guide for Filmmakers
Read more: Mastering Camera Shots and Angles: A Guide for Filmmakershttps://website.ltx.studio/blog/mastering-camera-shots-and-angles
1. Extreme Wide Shot
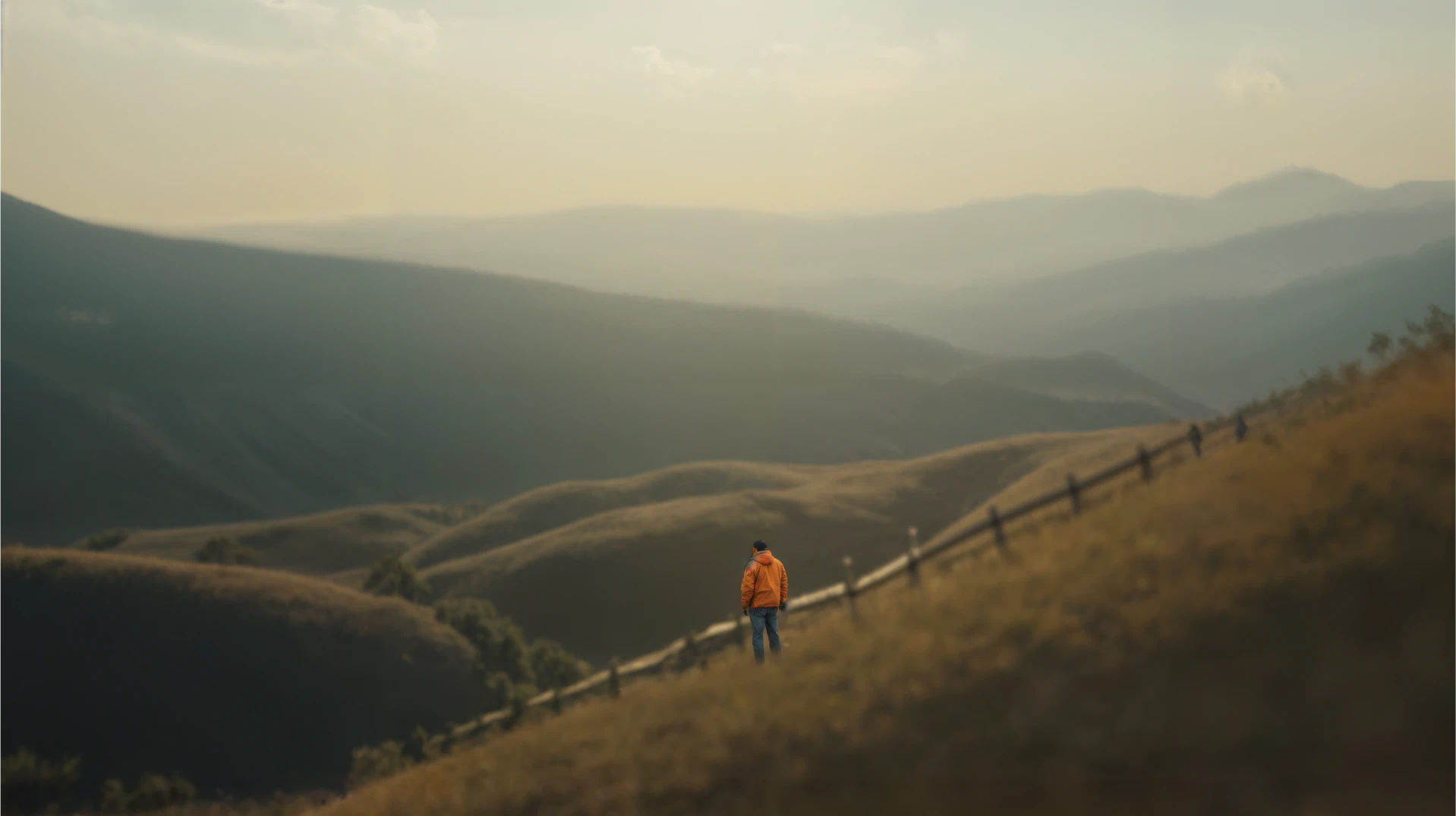

2. Wide Shot
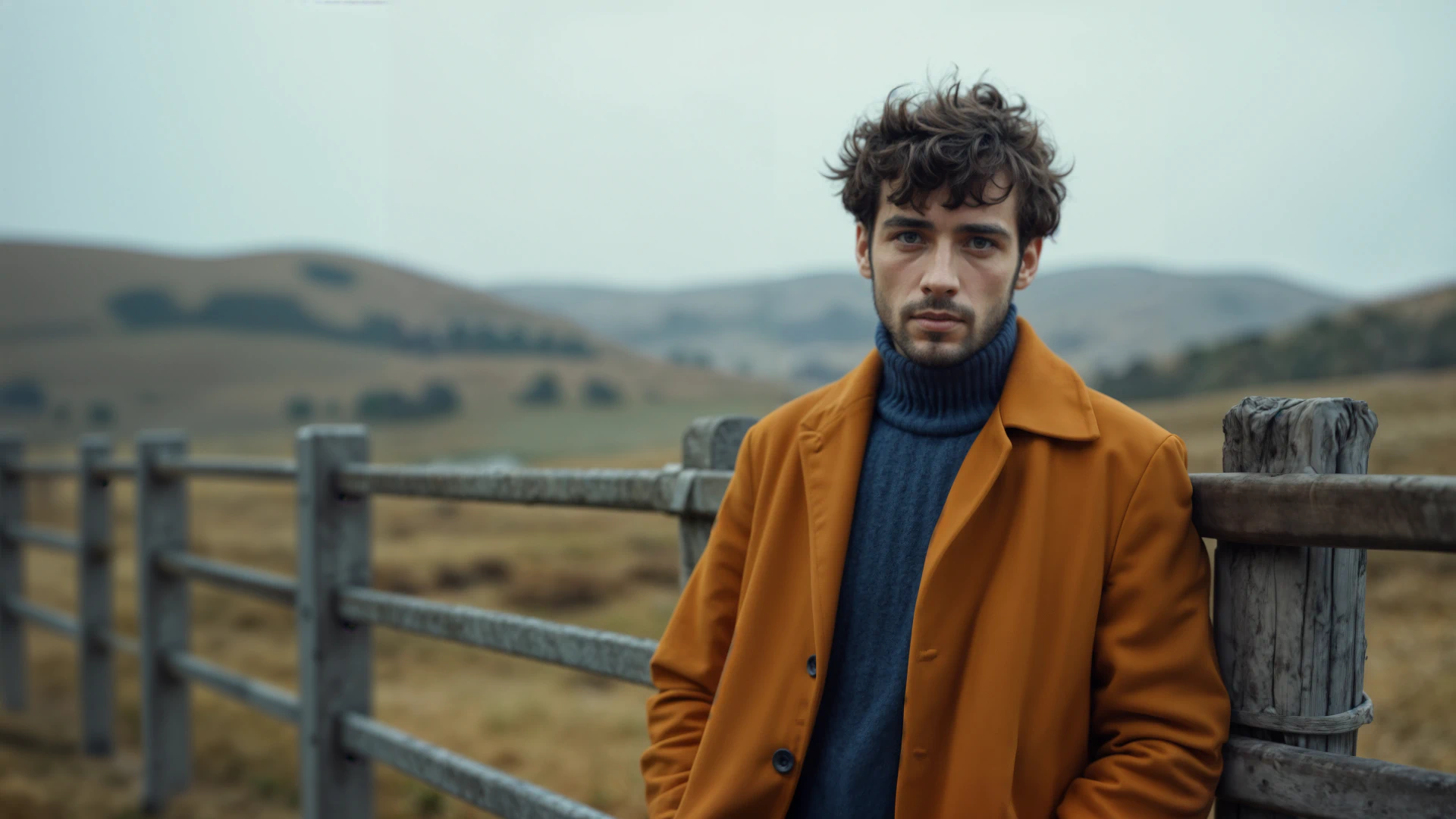

3. Medium Shot
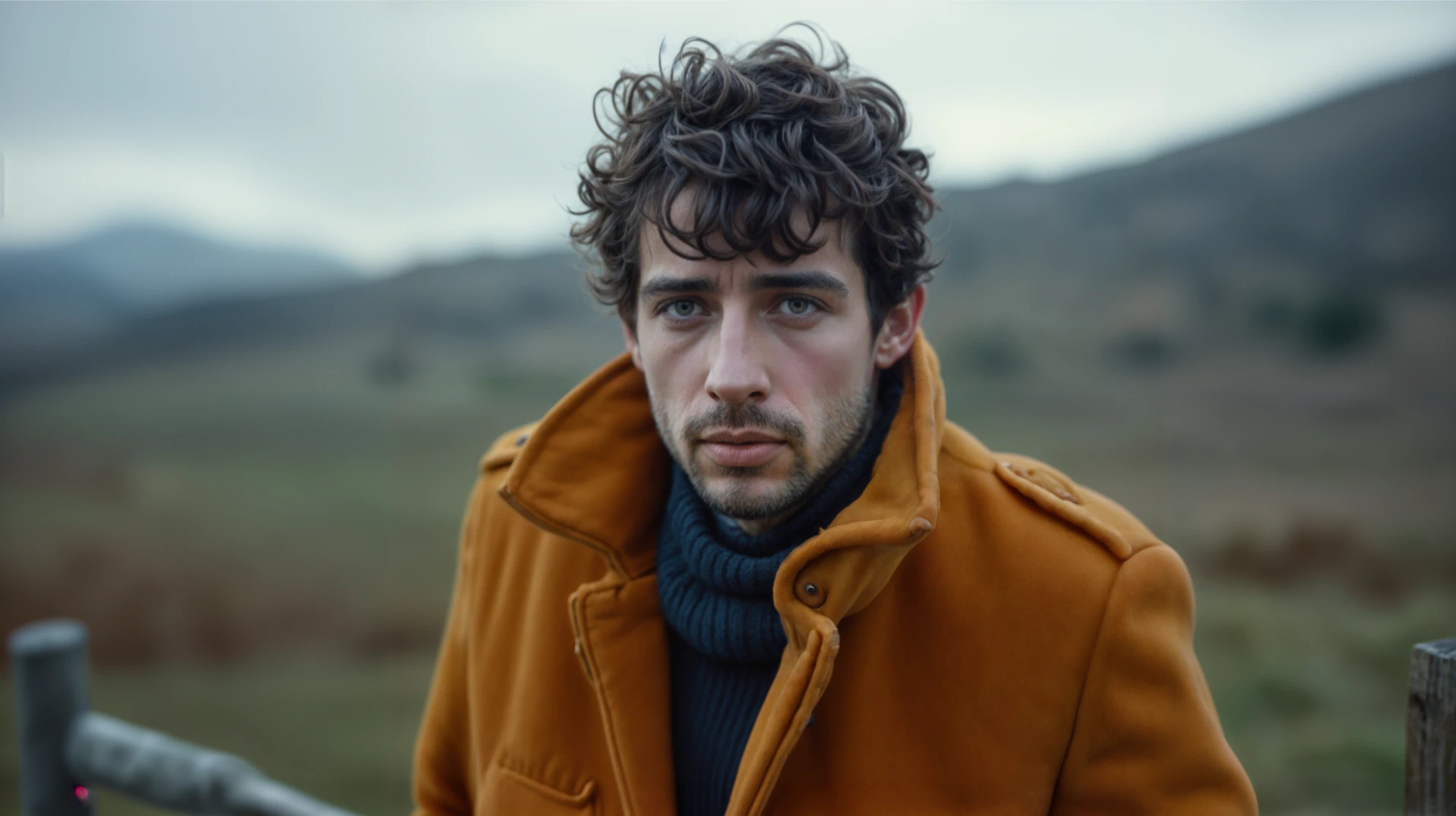

4. Close Up
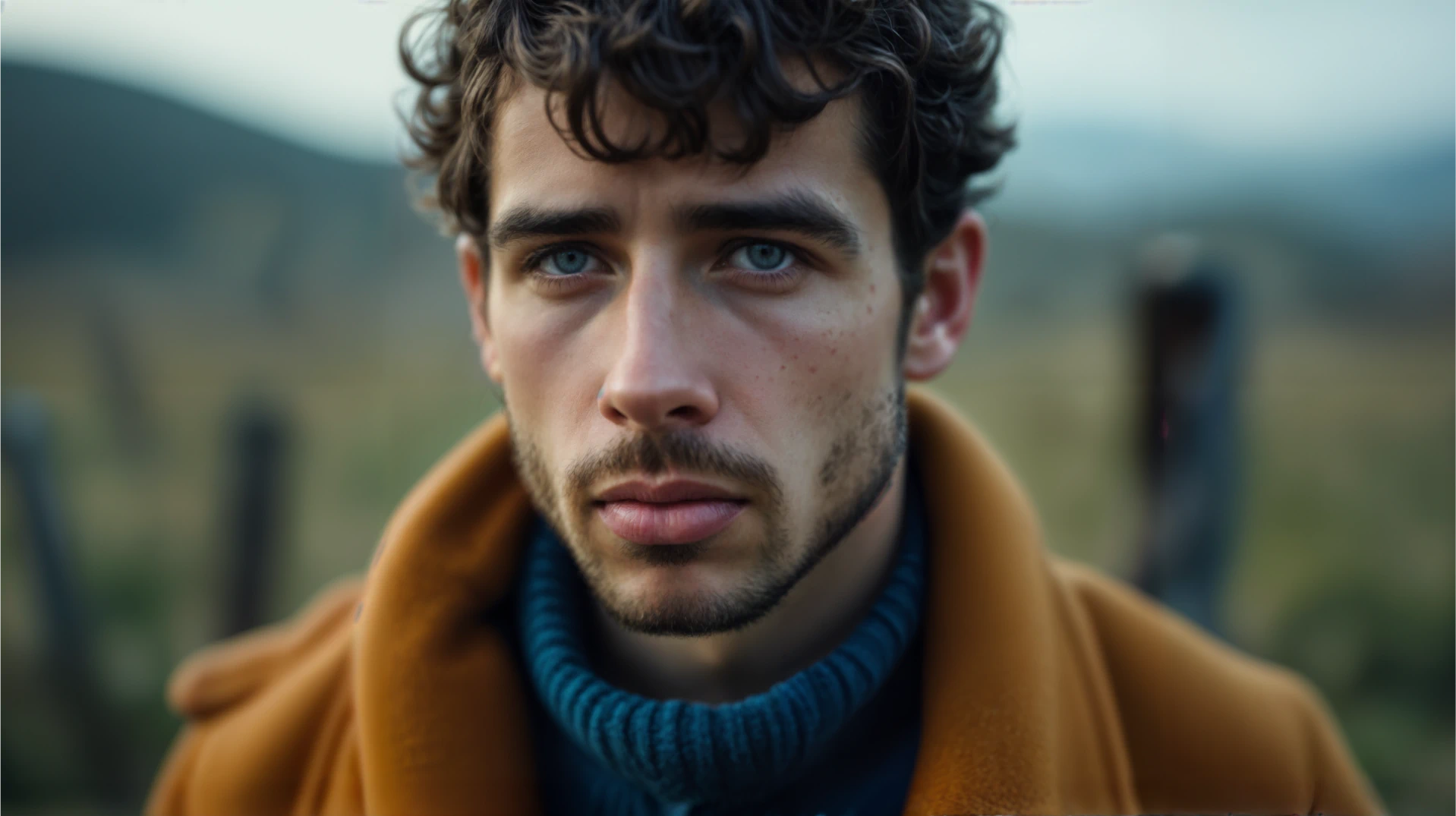

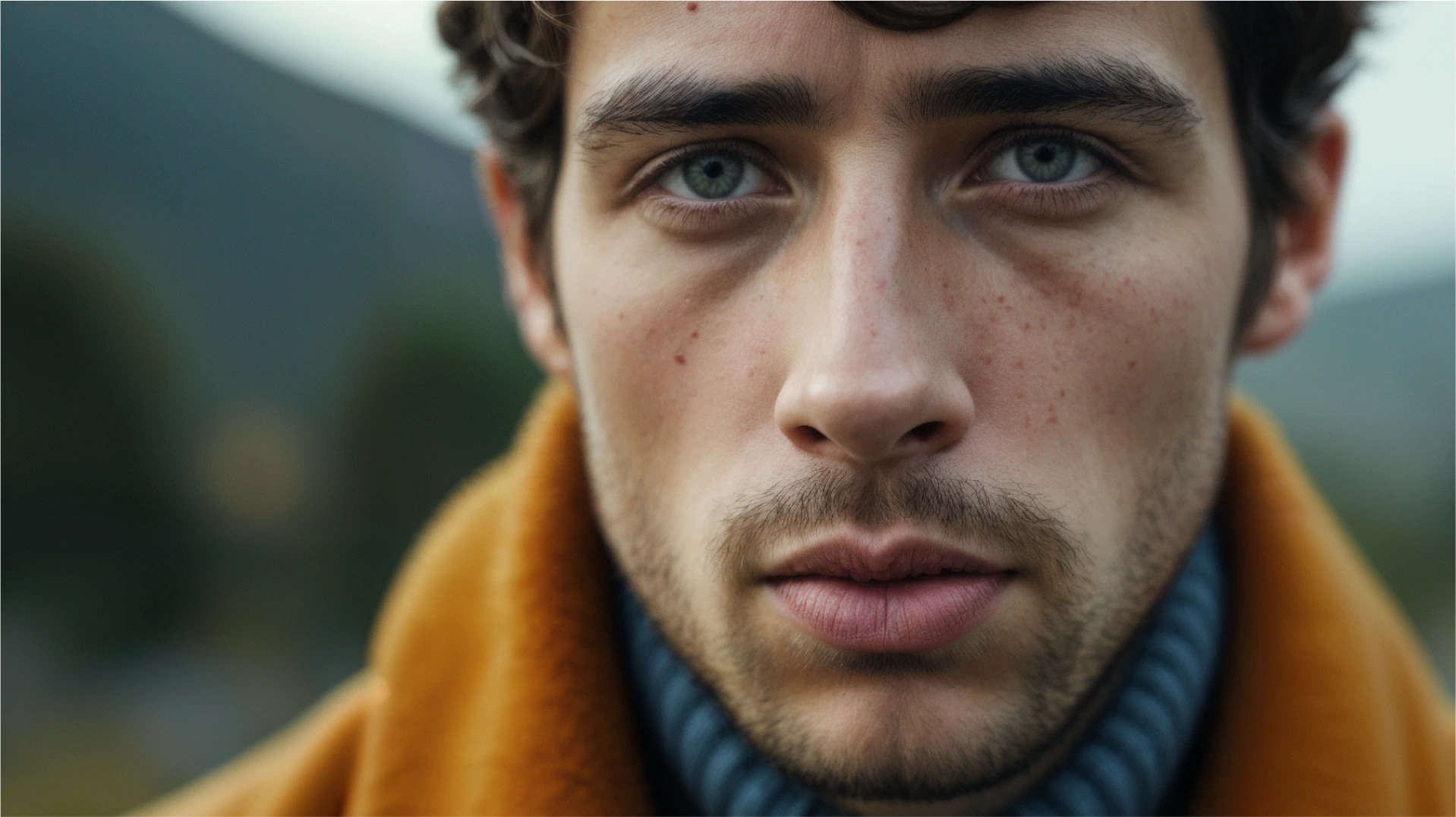
5. Extreme Close Up

DESIGN
COLOR
-
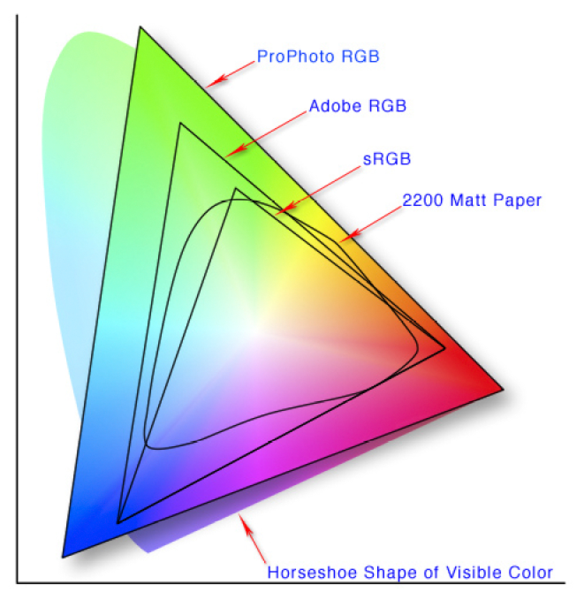
What is a Gamut or Color Space and why do I need to know about CIE
Read more: What is a Gamut or Color Space and why do I need to know about CIE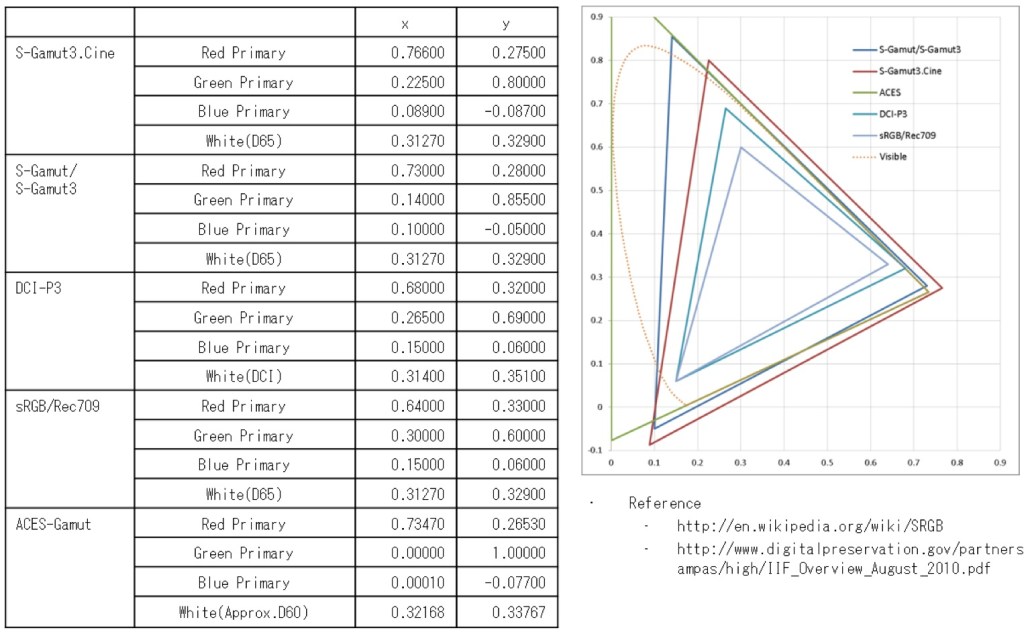
http://www.xdcam-user.com/2014/05/what-is-a-gamut-or-color-space-and-why-do-i-need-to-know-about-it/
In video terms gamut is normally related to as the full range of colours and brightness that can be either captured or displayed.
(more…) -
Paul Debevec, Chloe LeGendre, Lukas Lepicovsky – Jointly Optimizing Color Rendition and In-Camera Backgrounds in an RGB Virtual Production Stage
Read more: Paul Debevec, Chloe LeGendre, Lukas Lepicovsky – Jointly Optimizing Color Rendition and In-Camera Backgrounds in an RGB Virtual Production Stagehttps://arxiv.org/pdf/2205.12403.pdf
RGB LEDs vs RGBWP (RGB + lime + phospor converted amber) LEDs
Local copy:
-
PBR Color Reference List for Materials – by Grzegorz Baran
Read more: PBR Color Reference List for Materials – by Grzegorz Baran“The list should be helpful for every material artist who work on PBR materials as it contains over 200 color values measured with PCE-RGB2 1002 Color Spectrometer device and presented in linear and sRGB (2.2) gamma space.
All color values, HUE and Saturation in this list come from measurements taken with PCE-RGB2 1002 Color Spectrometer device and are presented in linear and sRGB (2.2) gamma space (more info at the end of this video) I calculated Relative Luminance and Luminance values based on captured color using my own equation which takes color based luminance perception into consideration. Bare in mind that there is no ‘one’ color per substance as nothing in nature is even 100% uniform and any value in +/-10% range from these should be considered as correct one. Therefore this list should be always considered as a color reference for material’s albedos, not ulitimate and absolute truth.“
-
Gamma correction
Read more: Gamma correction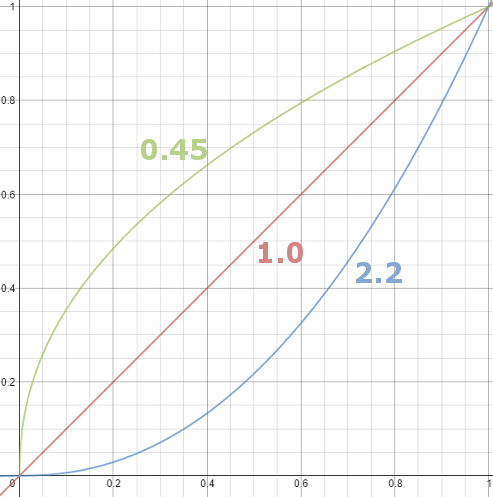
http://www.normankoren.com/makingfineprints1A.html#Gammabox
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gamma_correction
http://www.photoscientia.co.uk/Gamma.htm
https://www.w3.org/Graphics/Color/sRGB.html
http://www.eizoglobal.com/library/basics/lcd_display_gamma/index.html
https://forum.reallusion.com/PrintTopic308094.aspx
Basically, gamma is the relationship between the brightness of a pixel as it appears on the screen, and the numerical value of that pixel. Generally Gamma is just about defining relationships.
Three main types:
– Image Gamma encoded in images
– Display Gammas encoded in hardware and/or viewing time
– System or Viewing Gamma which is the net effect of all gammas when you look back at a final image. In theory this should flatten back to 1.0 gamma.
(more…) -
HDR and Color
Read more: HDR and Colorhttps://www.soundandvision.com/content/nits-and-bits-hdr-and-color
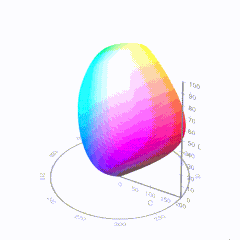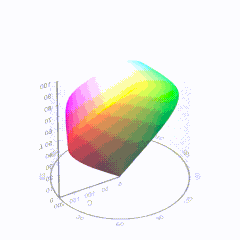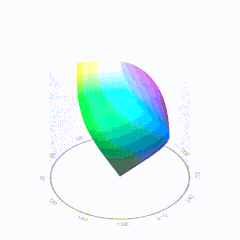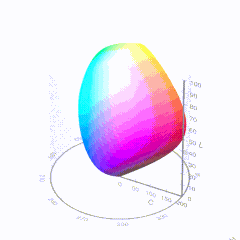
In HD we often refer to the range of available colors as a color gamut. Such a color gamut is typically plotted on a two-dimensional diagram, called a CIE chart, as shown in at the top of this blog. Each color is characterized by its x/y coordinates.
Good enough for government work, perhaps. But for HDR, with its higher luminance levels and wider color, the gamut becomes three-dimensional.
For HDR the color gamut therefore becomes a characteristic we now call the color volume. It isn’t easy to show color volume on a two-dimensional medium like the printed page or a computer screen, but one method is shown below. As the luminance becomes higher, the picture eventually turns to white. As it becomes darker, it fades to black. The traditional color gamut shown on the CIE chart is simply a slice through this color volume at a selected luminance level, such as 50%.
Three different color volumes—we still refer to them as color gamuts though their third dimension is important—are currently the most significant. The first is BT.709 (sometimes referred to as Rec.709), the color gamut used for pre-UHD/HDR formats, including standard HD.
The largest is known as BT.2020; it encompasses (roughly) the range of colors visible to the human eye (though ET might find it insufficient!).
Between these two is the color gamut used in digital cinema, known as DCI-P3.
sRGB
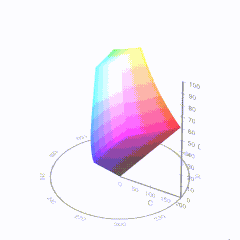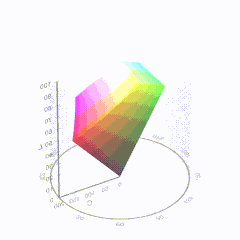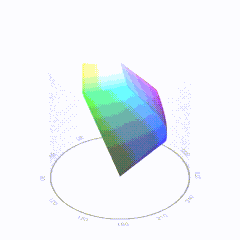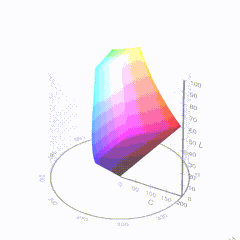
D65
LIGHTING
-
Lighting Every Darkness with 3DGS: Fast Training and Real-Time Rendering and Denoising for HDR View Synthesis
Read more: Lighting Every Darkness with 3DGS: Fast Training and Real-Time Rendering and Denoising for HDR View Synthesishttps://srameo.github.io/projects/le3d/
LE3D is a method for real-time HDR view synthesis from RAW images. It is particularly effective for nighttime scenes.
https://github.com/Srameo/LE3D
-
Black Body color aka the Planckian Locus curve for white point eye perception
Read more: Black Body color aka the Planckian Locus curve for white point eye perceptionhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Black-body_radiation
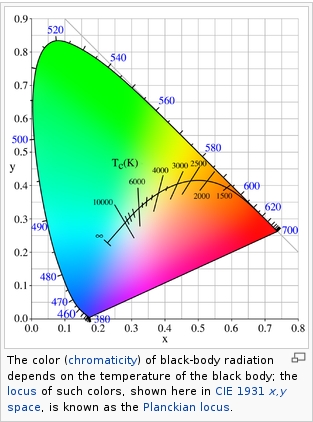
Black-body radiation is the type of electromagnetic radiation within or surrounding a body in thermodynamic equilibrium with its environment, or emitted by a black body (an opaque and non-reflective body) held at constant, uniform temperature. The radiation has a specific spectrum and intensity that depends only on the temperature of the body.
A black-body at room temperature appears black, as most of the energy it radiates is infra-red and cannot be perceived by the human eye. At higher temperatures, black bodies glow with increasing intensity and colors that range from dull red to blindingly brilliant blue-white as the temperature increases.
(more…) -
9 Best Hacks to Make a Cinematic Video with Any Camera
Read more: 9 Best Hacks to Make a Cinematic Video with Any Camerahttps://www.flexclip.com/learn/cinematic-video.html
- Frame Your Shots to Create Depth
- Create Shallow Depth of Field
- Avoid Shaky Footage and Use Flexible Camera Movements
- Properly Use Slow Motion
- Use Cinematic Lighting Techniques
- Apply Color Grading
- Use Cinematic Music and SFX
- Add Cinematic Fonts and Text Effects
- Create the Cinematic Bar at the Top and the Bottom

-
Free HDRI libraries
Read more: Free HDRI librariesnoahwitchell.com
http://www.noahwitchell.com/freebieslocationtextures.com
https://locationtextures.com/panoramas/maxroz.com
https://www.maxroz.com/hdri/listHDRI Haven
https://hdrihaven.com/Poly Haven
https://polyhaven.com/hdrisDomeble
https://www.domeble.com/IHDRI
https://www.ihdri.com/HDRMaps
https://hdrmaps.com/NoEmotionHdrs.net
http://noemotionhdrs.net/hdrday.htmlOpenFootage.net
https://www.openfootage.net/hdri-panorama/HDRI-hub
https://www.hdri-hub.com/hdrishop/hdri.zwischendrin
https://www.zwischendrin.com/en/browse/hdriLonger list here:
https://cgtricks.com/list-sites-free-hdri/
-
Narcis Calin’s Galaxy Engine – A free, open source simulation software
Read more: Narcis Calin’s Galaxy Engine – A free, open source simulation softwareThis 2025 I decided to start learning how to code, so I installed Visual Studio and I started looking into C++. After days of watching tutorials and guides about the basics of C++ and programming, I decided to make something physics-related. I started with a dot that fell to the ground and then I wanted to simulate gravitational attraction, so I made 2 circles attracting each other. I thought it was really cool to see something I made with code actually work, so I kept building on top of that small, basic program. And here we are after roughly 8 months of learning programming. This is Galaxy Engine, and it is a simulation software I have been making ever since I started my learning journey. It currently can simulate gravity, dark matter, galaxies, the Big Bang, temperature, fluid dynamics, breakable solids, planetary interactions, etc. The program can run many tens of thousands of particles in real time on the CPU thanks to the Barnes-Hut algorithm, mixed with Morton curves. It also includes its own PBR 2D path tracer with BVH optimizations. The path tracer can simulate a bunch of stuff like diffuse lighting, specular reflections, refraction, internal reflection, fresnel, emission, dispersion, roughness, IOR, nested IOR and more! I tried to make the path tracer closer to traditional 3D render engines like V-Ray. I honestly never imagined I would go this far with programming, and it has been an amazing learning experience so far. I think that mixing this knowledge with my 3D knowledge can unlock countless new possibilities. In case you are curious about Galaxy Engine, I made it completely free and Open-Source so that anyone can build and compile it locally! You can find the source code in GitHub
https://github.com/NarcisCalin/Galaxy-Engine
COLLECTIONS
| Featured AI
| Design And Composition
| Explore posts
POPULAR SEARCHES
unreal | pipeline | virtual production | free | learn | photoshop | 360 | macro | google | nvidia | resolution | open source | hdri | real-time | photography basics | nuke
FEATURED POSTS
-
Most common ways to smooth 3D prints
-
Matt Hallett – WAN 2.1 VACE Total Video Control in ComfyUI
-
Decart AI Mirage – The first ever World Transformation Model – turning any video, game, or camera feed into a new digital world, in real time
-
Yann Lecun: Meta AI, Open Source, Limits of LLMs, AGI & the Future of AI | Lex Fridman Podcast #416
-
Key/Fill ratios and scene composition using false colors and Nuke node
-
QR code logos
-
SourceTree vs Github Desktop – Which one to use
-
MiniTunes V1 – Free MP3 library app
Social Links
DISCLAIMER – Links and images on this website may be protected by the respective owners’ copyright. All data submitted by users through this site shall be treated as freely available to share.