BREAKING NEWS
LATEST POSTS
-
CUDA Programming for Python Developers
https://www.pyspur.dev/blog/introduction_cuda_programming
Check your Cuda version, it will be the release version here:
>>> nvcc --version nvcc: NVIDIA (R) Cuda compiler driver Copyright (c) 2005-2024 NVIDIA Corporation Built on Wed_Apr_17_19:36:51_Pacific_Daylight_Time_2024 Cuda compilation tools, release 12.5, V12.5.40 Build cuda_12.5.r12.5/compiler.34177558_0or from here:
>>> nvidia-smi Mon Jun 16 12:35:20 2025 +-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+ | NVIDIA-SMI 555.85 Driver Version: 555.85 CUDA Version: 12.5 | |-----------------------------------------+------------------------+----------------------+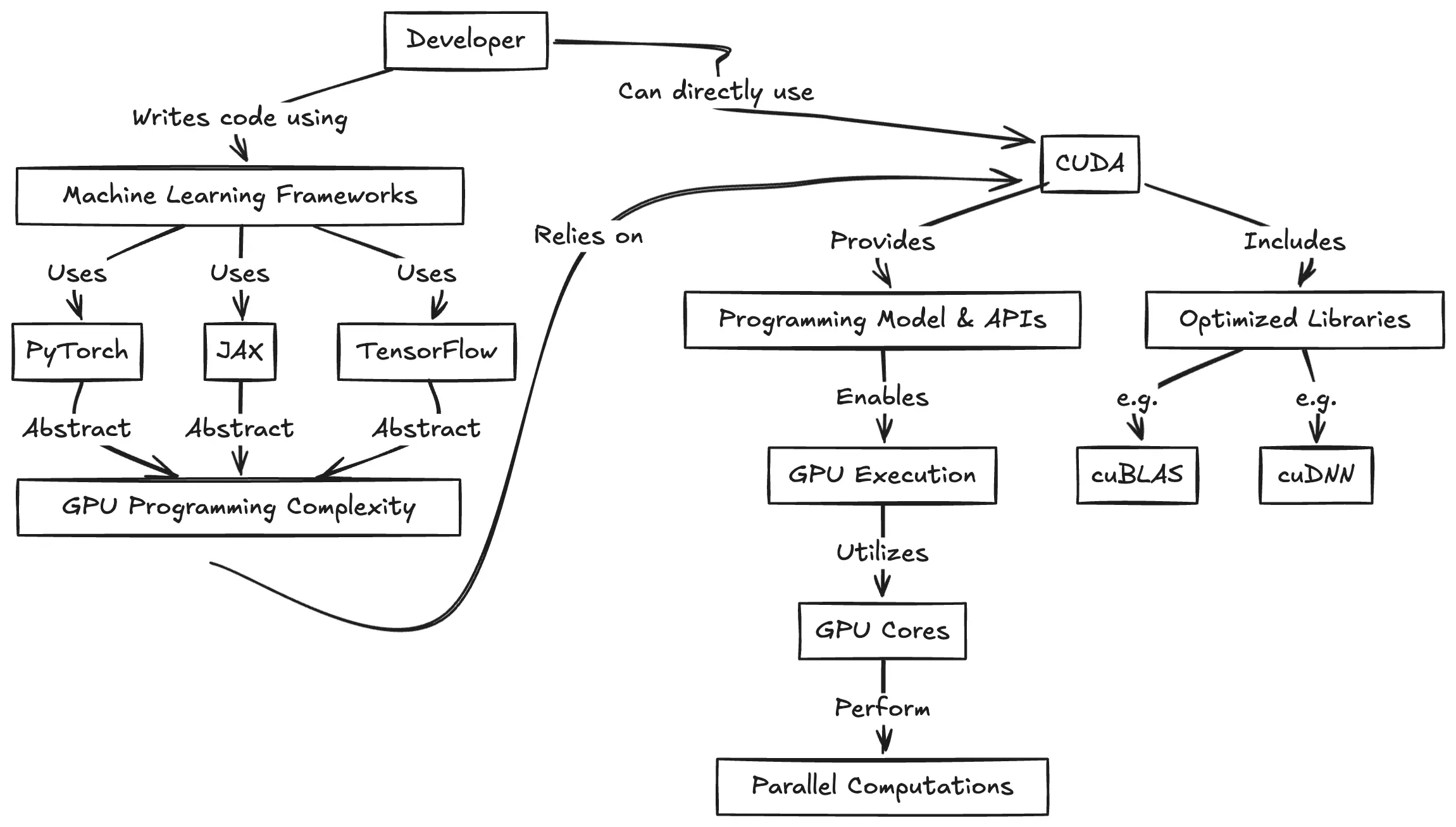
-
PixVerse – Prompt, lypsync and extended video generation
https://app.pixverse.ai/onboard
PixVerse now has 3 main features:
text to video➡️ How To Generate Videos With Text Promptsimage to video➡️ How To Animate Your Images And Bring Them To Lifeupscale➡️ How to Upscale Your Video
Enhanced Capabilities
– Improved Prompt Understanding: Achieve more accurate prompt interpretation and stunning video dynamics.
– Supports Various Video Ratios: Choose from 16:9, 9:16, 3:4, 4:3, and 1:1 ratios.
– Upgraded Styles: Style functionality returns with options like Anime, Realistic, Clay, and 3D. It supports both text-to-video and image-to-video stylization.New Features
– Lipsync: The new Lipsync feature enables users to add text or upload audio, and PixVerse will automatically sync the characters’ lip movements in the generated video based on the text or audio.
– Effect: Offers 8 creative effects, including Zombie Transformation, Wizard Hat, Monster Invasion, and other Halloween-themed effects, enabling one-click creativity.
– Extend: Extend the generated video by an additional 5-8 seconds, with control over the content of the extended segment. -
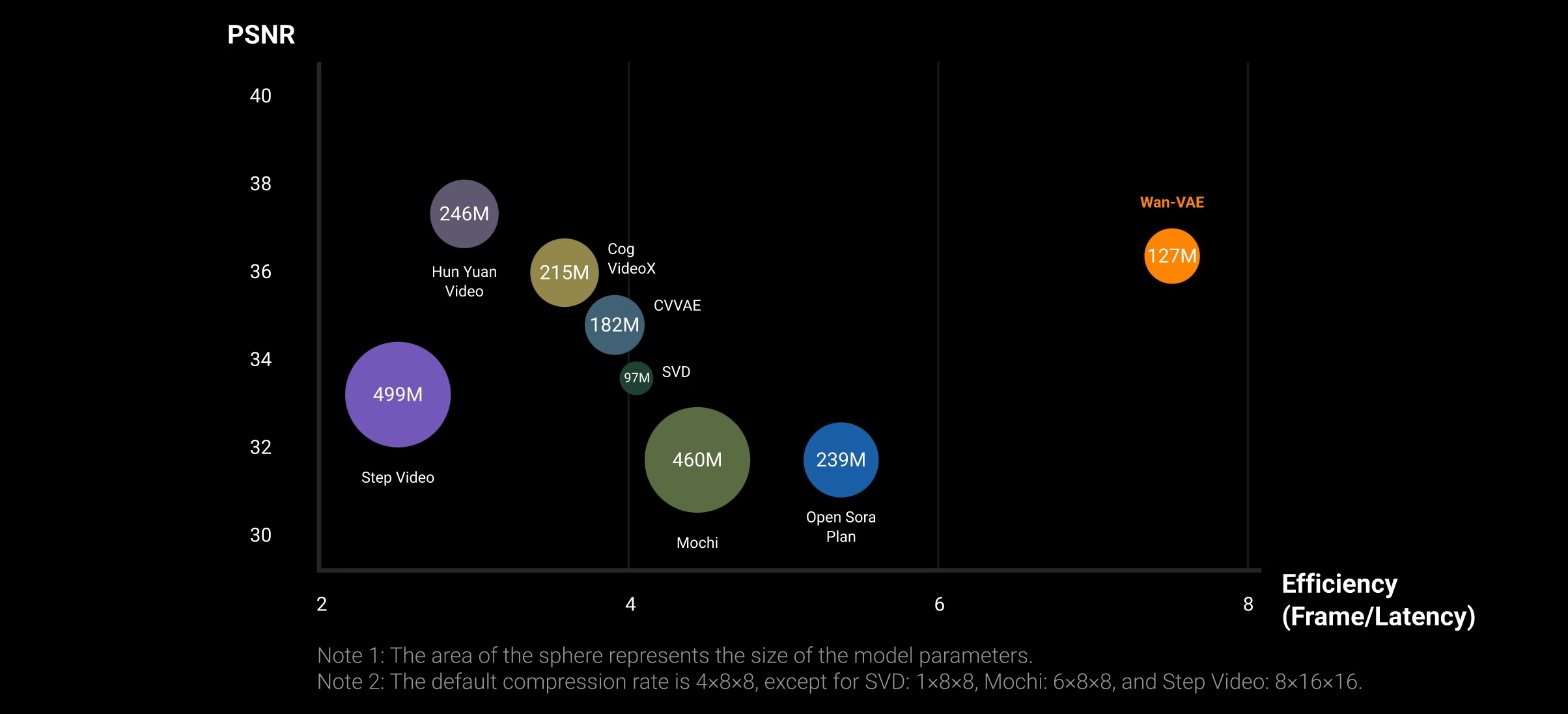
Alibaba Group Tongyi Lab WanxAI Wan2.1 – open source model
👍 SOTA Performance: Wan2.1 consistently outperforms existing open-source models and state-of-the-art commercial solutions across multiple benchmarks.
🚀 Supports Consumer-grade GPUs: The T2V-1.3B model requires only 8.19 GB VRAM, making it compatible with almost all consumer-grade GPUs. It can generate a 5-second 480P video on an RTX 4090 in about 4 minutes (without optimization techniques like quantization). Its performance is even comparable to some closed-source models.
🎉 Multiple tasks: Wan2.1 excels in Text-to-Video, Image-to-Video, Video Editing, Text-to-Image, and Video-to-Audio, advancing the field of video generation.
🔮 Visual Text Generation: Wan2.1 is the first video model capable of generating both Chinese and English text, featuring robust text generation that enhances its practical applications.
💪 Powerful Video VAE: Wan-VAE delivers exceptional efficiency and performance, encoding and decoding 1080P videos of any length while preserving temporal information, making it an ideal foundation for video and image generation.
https://huggingface.co/Comfy-Org/Wan_2.1_ComfyUI_repackaged/tree/main/split_files
https://huggingface.co/Comfy-Org/Wan_2.1_ComfyUI_repackaged/tree/main/example%20workflows_Wan2.1
https://huggingface.co/Wan-AI/Wan2.1-T2V-14B
https://huggingface.co/Kijai/WanVideo_comfy/tree/main
-
VES Cinematic Color – Motion-Picture Color Management
This paper presents an introduction to the color pipelines behind modern feature-film visual-effects and animation.
Authored by Jeremy Selan, and reviewed by the members of the VES Technology Committee including Rob Bredow, Dan Candela, Nick Cannon, Paul Debevec, Ray Feeney, Andy Hendrickson, Gautham Krishnamurti, Sam Richards, Jordan Soles, and Sebastian Sylwan.
-
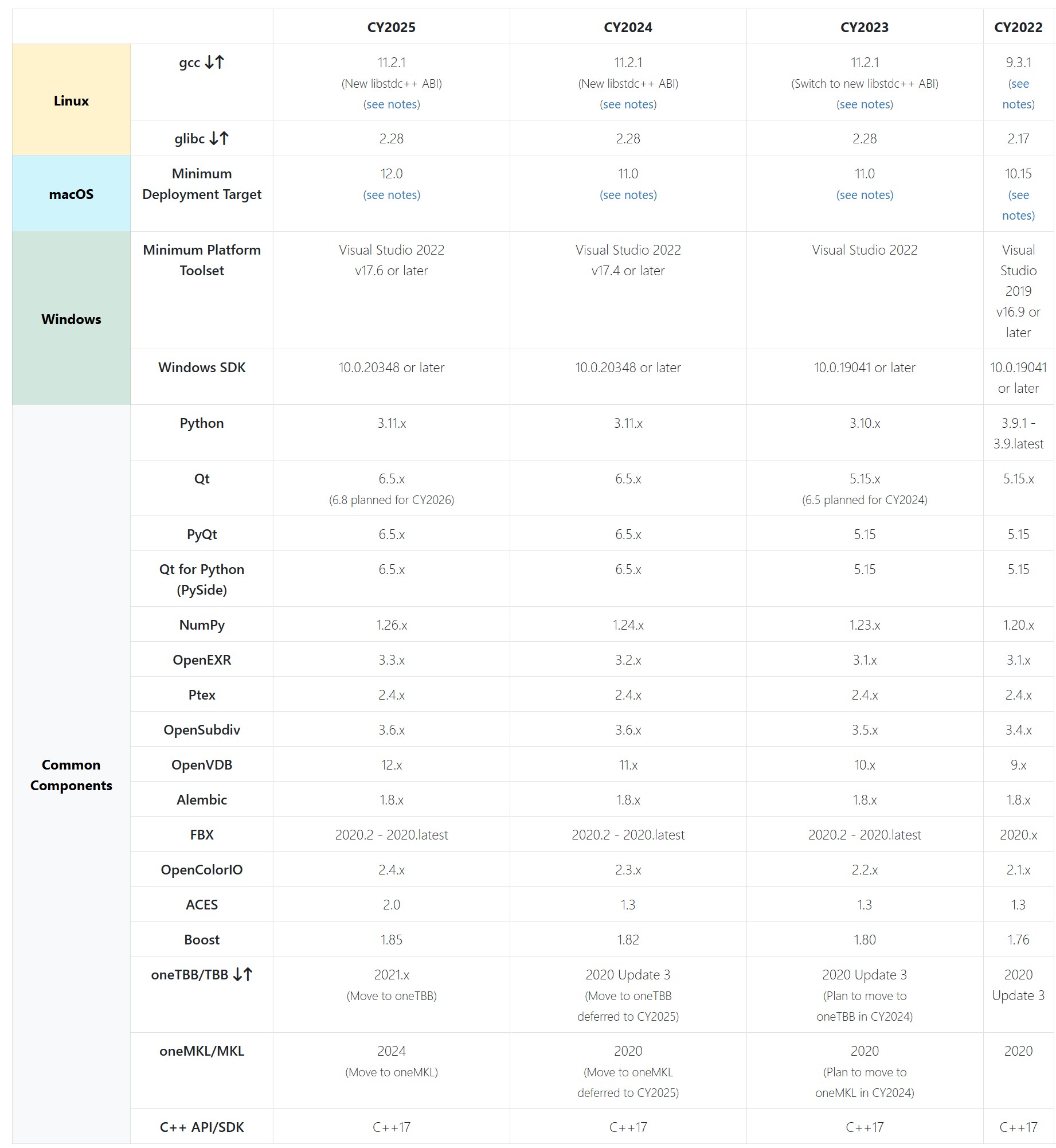
The VFX Reference Platform
The VFX Reference Platform is a set of tool and library versions to be used as a common target platform for building software for the VFX industry. Its purpose is to minimise incompatibilities between different software packages, ease the support burden for integrated pipelines and encourage further adoption of Linux by both studios and software vendors. The Reference Platform is updated annually by a group of software vendors in collaboration with the Visual Effects Society Technology Committee.
Each annual reference platform is designated by the calendar year in which major product releases should be targeting that particular reference.
-
Deep Compositing in Nuke – a walkthrough
Depth Map: A depth map is a representation of the distance or depth information for each pixel in a scene. It is typically a two-dimensional array where each pixel contains a value that represents the distance from the camera to the corresponding point in the scene. The depth values are usually represented in metric units, such as meters. A depth map provides a continuous representation of the scene’s depth information.
For example, in Arnold this is achieved through a Z AOV, this collects depth of the shading points as seen from the camera.
(more…)
https://help.autodesk.com/view/ARNOL/ENU/?guid=arnold_user_guide_ac_output_aovs_ac_aovs_html
https://help.autodesk.com/view/ARNOL/ENU/?guid=arnold_for_3ds_max_ax_aov_tutorials_ax_zdepth_aov_html -
VFX Giant MPC and Parent Company Technicolor Shut Down Amid ‘Severe Financial Challenges
https://variety.com/2025/film/global/technicolor-vfx-mpc-shutter-severe-challenges-1236316354
Shaun Severi, Head of Creative Production at the Mill, claimed in a LinkedIn post that 4,500 had lost their jobs in 24 hours: “The problem wasn’t talent or execution — it was mismanagement at the highest levels…the incompetence at the top was nothing short of disastrous.”
According to Severi, successive company presidents “buried the company under massive debt by acquiring VFX Studios…the second president, after a disastrous merger of the post houses, took us public, artificially inflating the company’s value — only for it to come crashing down when the real numbers were revealed….and the third and final president, who came from a car rental company, had no vision of what she was building, selling or managing.”

-
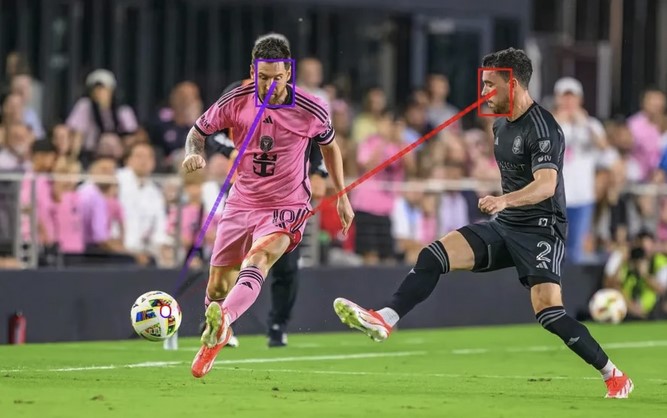
Moondream Gaze Detection – Open source code
This is convenient for captioning videos, understanding social dynamics, and for specific cases such as sports analytics, or detecting when drivers or operators are distracted.
https://huggingface.co/spaces/moondream/gaze-demo
https://moondream.ai/blog/announcing-gaze-detection

-
X-Dyna – Expressive Dynamic Human Image Animation
https://x-dyna.github.io/xdyna.github.io
A novel zero-shot, diffusion-based pipeline for animating a single human image using facial expressions and body movements derived from a driving video, that generates realistic, context-aware dynamics for both the subject and the surrounding environment.

FEATURED POSTS
-
VFX pipeline – Render Wall management topics
1: Introduction Title: Managing a VFX Facility’s Render Wall
- Briefly introduce the importance of managing a VFX facility’s render wall.
- Highlight how efficient management contributes to project timelines and overall productivity.
2: Daily Overview Title: Daily Management Routine
- Monitor Queues: Begin each day by reviewing render queues to assess workload and priorities.
- Resource Allocation: Allocate resources based on project demands and available hardware.
- Job Prioritization: Set rendering priorities according to project deadlines and importance.
- Queue Optimization: Adjust queue settings to maximize rendering efficiency.
3: Resource Allocation Title: Efficient Resource Management
- Hardware Utilization: Distribute rendering tasks across available machines for optimal resource usage.
- Balance Workloads: Avoid overloading specific machines while others remain underutilized.
- Consider Off-Peak Times: Schedule resource-intensive tasks during off-peak hours to enhance overall performance.
4: Job Prioritization Title: Prioritizing Rendering Tasks
- Deadline Sensitivity: Give higher priority to tasks with imminent deadlines to ensure timely delivery.
- Critical Shots: Identify shots crucial to the project’s narrative or visual impact for prioritization.
- Dependent Shots: Sequence shots that depend on others should be prioritized together.
5: Queue Optimization and Reporting Title: Streamlining Render Queues
- Dependency Management: Set up dependencies to ensure shots are rendered in the correct order.
- Error Handling: Implement automated error detection and requeueing mechanisms.
- Progress Tracking: Regularly monitor rendering progress and update stakeholders.
- Data Management: Archive completed renders and remove redundant data to free up storage.
- Reporting: Provide daily reports on rendering status, resource usage, and potential bottlenecks.
6: Conclusion Title: Enhancing VFX Workflow
- Effective management of a VFX facility’s render wall is essential for project success.
- Daily monitoring, resource allocation, job prioritization, queue optimization, and reporting are key components.
- A well-managed render wall ensures efficient production, timely delivery, and overall project success.
-
STOP FCC – SAVE THE FREE NET
Help saving free sites like this one.
The FCC voted to kill net neutrality and let ISPs like Comcast ruin the web with throttling, censorship, and new fees. Congress has 60 legislative days to overrule them and save the Internet using the Congressional Review Act
https://www.battleforthenet.com/http://mashable.com/2012/01/17/sopa-dangerous-opinion/
-
Rendering – BRDF – Bidirectional reflectance distribution function
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bidirectional_reflectance_distribution_function
The bidirectional reflectance distribution function is a four-dimensional function that defines how light is reflected at an opaque surface
http://www.cs.ucla.edu/~zhu/tutorial/An_Introduction_to_BRDF-Based_Lighting.pdf
In general, when light interacts with matter, a complicated light-matter dynamic occurs. This interaction depends on the physical characteristics of the light as well as the physical composition and characteristics of the matter.
That is, some of the incident light is reflected, some of the light is transmitted, and another portion of the light is absorbed by the medium itself.
A BRDF describes how much light is reflected when light makes contact with a certain material. Similarly, a BTDF (Bi-directional Transmission Distribution Function) describes how much light is transmitted when light makes contact with a certain material
http://www.cs.princeton.edu/~smr/cs348c-97/surveypaper.html
It is difficult to establish exactly how far one should go in elaborating the surface model. A truly complete representation of the reflective behavior of a surface might take into account such phenomena as polarization, scattering, fluorescence, and phosphorescence, all of which might vary with position on the surface. Therefore, the variables in this complete function would be:
incoming and outgoing angle incoming and outgoing wavelength incoming and outgoing polarization (both linear and circular) incoming and outgoing position (which might differ due to subsurface scattering) time delay between the incoming and outgoing light ray