COMPOSITION
-
Types of Film Lights and their efficiency – CRI, Color Temperature and Luminous Efficacy
Read more: Types of Film Lights and their efficiency – CRI, Color Temperature and Luminous Efficacynofilmschool.com/types-of-film-lights
“Not every light performs the same way. Lights and lighting are tricky to handle. You have to plan for every circumstance. But the good news is, lighting can be adjusted. Let’s look at different factors that affect lighting in every scene you shoot. “
Use CRI, Luminous Efficacy and color temperature controls to match your needs.Color Temperature
Color temperature describes the “color” of white light by a light source radiated by a perfect black body at a given temperature measured in degrees Kelvinhttps://www.pixelsham.com/2019/10/18/color-temperature/
CRI
“The Color Rendering Index is a measurement of how faithfully a light source reveals the colors of whatever it illuminates, it describes the ability of a light source to reveal the color of an object, as compared to the color a natural light source would provide. The highest possible CRI is 100. A CRI of 100 generally refers to a perfect black body, like a tungsten light source or the sun. “https://www.studiobinder.com/blog/what-is-color-rendering-index
(more…) -
Christopher Butler – Understanding the Eye-Mind Connection – Vision is a mental process
Read more: Christopher Butler – Understanding the Eye-Mind Connection – Vision is a mental processhttps://www.chrbutler.com/understanding-the-eye-mind-connection
The intricate relationship between the eyes and the brain, often termed the eye-mind connection, reveals that vision is predominantly a cognitive process. This understanding has profound implications for fields such as design, where capturing and maintaining attention is paramount. This essay delves into the nuances of visual perception, the brain’s role in interpreting visual data, and how this knowledge can be applied to effective design strategies.
This cognitive aspect of vision is evident in phenomena such as optical illusions, where the brain interprets visual information in a way that contradicts physical reality. These illusions underscore that what we “see” is not merely a direct recording of the external world but a constructed experience shaped by cognitive processes.
Understanding the cognitive nature of vision is crucial for effective design. Designers must consider how the brain processes visual information to create compelling and engaging visuals. This involves several key principles:
- Attention and Engagement
- Visual Hierarchy
- Cognitive Load Management
- Context and Meaning

DESIGN
-
Myriam Catrin – amazing design
Read more: Myriam Catrin – amazing designhttps://www.artstation.com/myriamcatrin
Creator of the comic book ” Passages. Book I” released with @therealarttitude
https://arttitudebootleg.bigcartel.com/product/passages-myriam-catrin
instagram/ FB page: @myriamcatrin / @MyriamCatrinComics
COLOR
-
The Maya civilization and the color blue
Read more: The Maya civilization and the color blueMaya blue is a highly unusual pigment because it is a mix of organic indigo and an inorganic clay mineral called palygorskite.
Echoing the color of an azure sky, the indelible pigment was used to accentuate everything from ceramics to human sacrifices in the Late Preclassic period (300 B.C. to A.D. 300).
A team of researchers led by Dean Arnold, an adjunct curator of anthropology at the Field Museum in Chicago, determined that the key to Maya blue was actually a sacred incense called copal.
By heating the mixture of indigo, copal and palygorskite over a fire, the Maya produced the unique pigment, he reported at the time.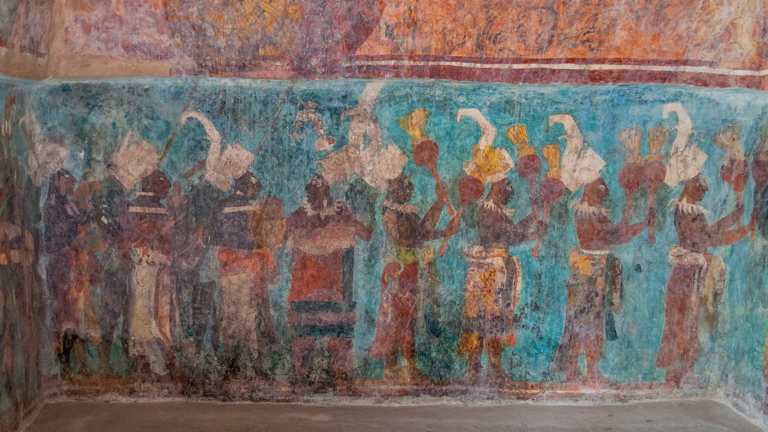
-
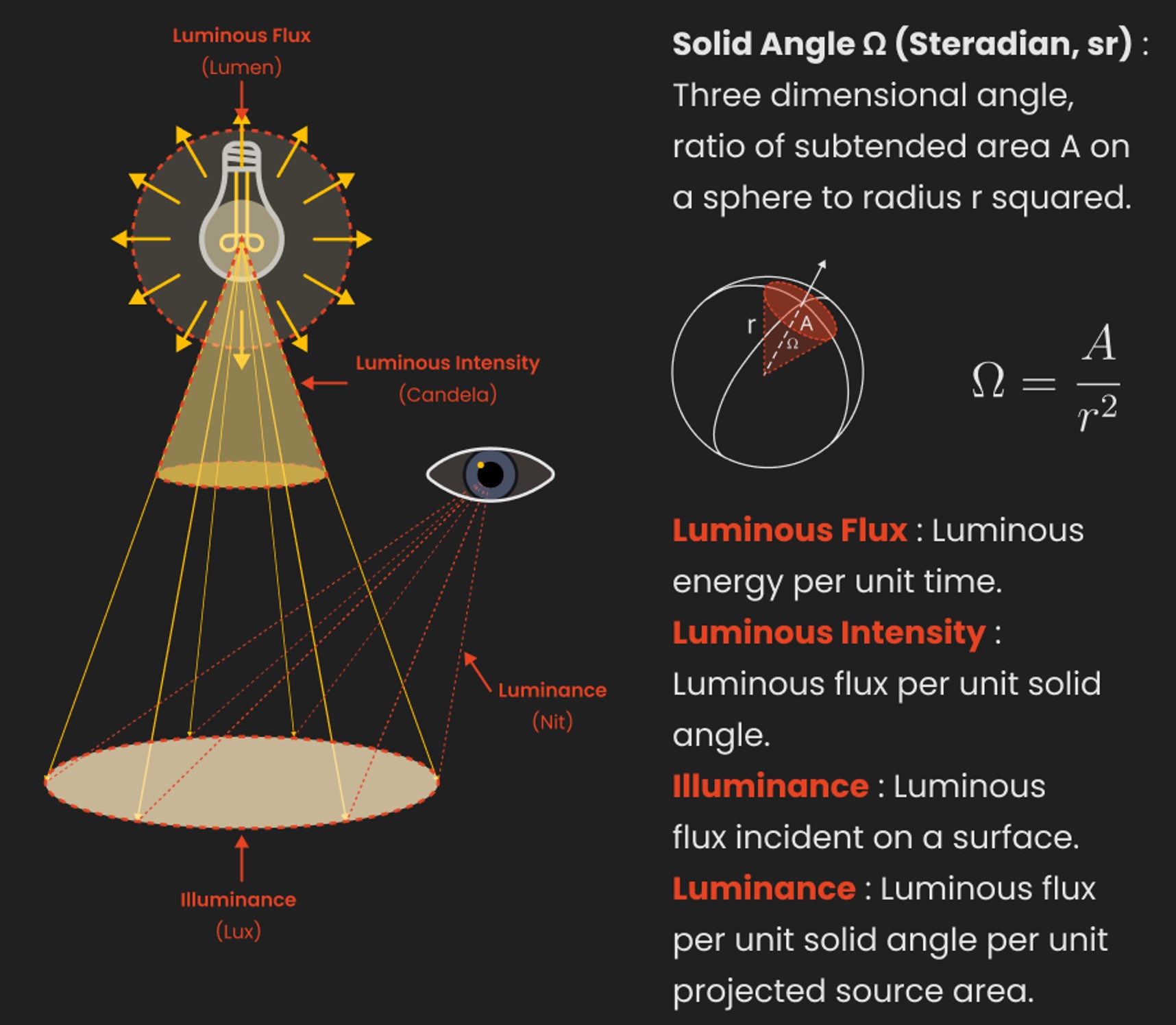
Photography basics: Lumens vs Candelas (candle) vs Lux vs FootCandle vs Watts vs Irradiance vs Illuminance
Read more: Photography basics: Lumens vs Candelas (candle) vs Lux vs FootCandle vs Watts vs Irradiance vs Illuminancehttps://www.translatorscafe.com/unit-converter/en-US/illumination/1-11/
The power output of a light source is measured using the unit of watts W. This is a direct measure to calculate how much power the light is going to drain from your socket and it is not relatable to the light brightness itself.
The amount of energy emitted from it per second. That energy comes out in a form of photons which we can crudely represent with rays of light coming out of the source. The higher the power the more rays emitted from the source in a unit of time.
Not all energy emitted is visible to the human eye, so we often rely on photometric measurements, which takes in account the sensitivity of human eye to different wavelenghts
Details in the post
(more…) -
Practical Aspects of Spectral Data and LEDs in Digital Content Production and Virtual Production – SIGGRAPH 2022
Read more: Practical Aspects of Spectral Data and LEDs in Digital Content Production and Virtual Production – SIGGRAPH 2022Comparison to the commercial side

https://www.ecolorled.com/blog/detail/what-is-rgb-rgbw-rgbic-strip-lights
RGBW (RGB + White) LED strip uses a 4-in-1 LED chip made up of red, green, blue, and white.
RGBWW (RGB + White + Warm White) LED strip uses either a 5-in-1 LED chip with red, green, blue, white, and warm white for color mixing. The only difference between RGBW and RGBWW is the intensity of the white color. The term RGBCCT consists of RGB and CCT. CCT (Correlated Color Temperature) means that the color temperature of the led strip light can be adjusted to change between warm white and white. Thus, RGBWW strip light is another name of RGBCCT strip.
RGBCW is the acronym for Red, Green, Blue, Cold, and Warm. These 5-in-1 chips are used in supper bright smart LED lighting products
-
Mysterious animation wins best illusion of 2011 – Motion silencing illusion
Read more: Mysterious animation wins best illusion of 2011 – Motion silencing illusionThe 2011 Best Illusion of the Year uses motion to render color changes invisible, and so reveals a quirk in our visual systems that is new to scientists.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Motion_silencing_illusion
“It is a really beautiful effect, revealing something about how our visual system works that we didn’t know before,” said Daniel Simons, a professor at the University of Illinois, Champaign-Urbana. Simons studies visual cognition, and did not work on this illusion. Before its creation, scientists didn’t know that motion had this effect on perception, Simons said.
A viewer stares at a speck at the center of a ring of colored dots, which continuously change color. When the ring begins to rotate around the speck, the color changes appear to stop. But this is an illusion. For some reason, the motion causes our visual system to ignore the color changes. (You can, however, see the color changes if you follow the rotating circles with your eyes.)
LIGHTING
-
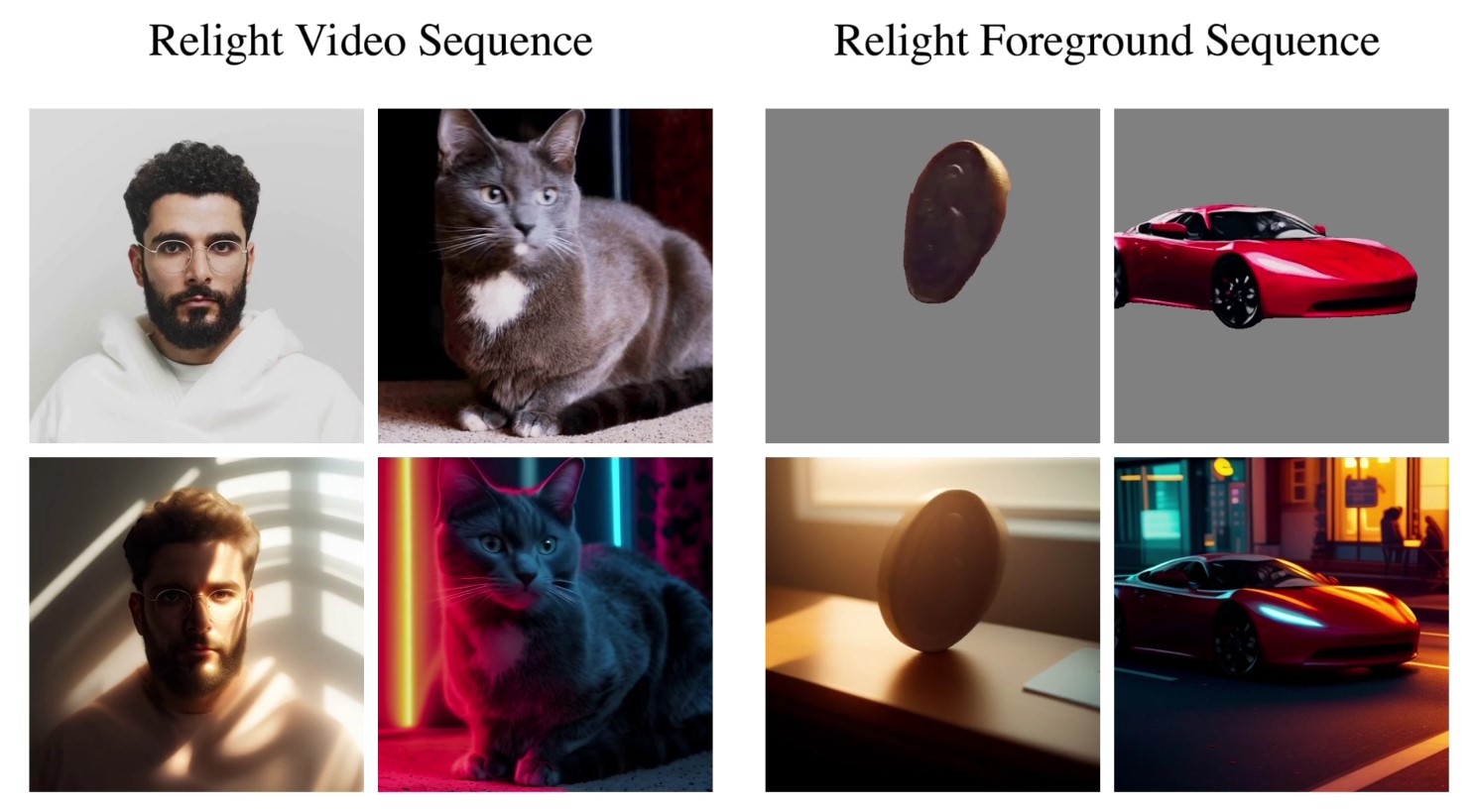
ICLight – Krea and ComfyUI light editing
Read more: ICLight – Krea and ComfyUI light editinghttps://drive.google.com/drive/folders/16Aq1mqZKP-h8vApaN4FX5at3acidqPUv
https://github.com/lllyasviel/IC-Light
https://generativematte.blogspot.com/2025/03/comfyui-ic-light-relighting-exploration.html

Workflow Local copy

-
7 Easy Portrait Lighting Setups
Read more: 7 Easy Portrait Lighting SetupsButterfly
Loop
Rembrandt
Split
Rim
Broad
Short
-
Fast, optimized ‘for’ pixel loops with OpenCV and Python to create tone mapped HDR images
Read more: Fast, optimized ‘for’ pixel loops with OpenCV and Python to create tone mapped HDR imageshttps://pyimagesearch.com/2017/08/28/fast-optimized-for-pixel-loops-with-opencv-and-python/
https://learnopencv.com/exposure-fusion-using-opencv-cpp-python/
Exposure Fusion is a method for combining images taken with different exposure settings into one image that looks like a tone mapped High Dynamic Range (HDR) image.
-
Insta360-Research-Team DiT360 – High-Fidelity Panoramic Image Generation via Hybrid Training
Read more: Insta360-Research-Team DiT360 – High-Fidelity Panoramic Image Generation via Hybrid Traininghttps://github.com/Insta360-Research-Team/DiT360
DiT360 is a framework for high-quality panoramic image generation, leveraging both perspective and panoramic data in a hybrid training scheme. It adopts a two-level strategy—image-level cross-domain guidance and token-level hybrid supervision—to enhance perceptual realism and geometric fidelity.

COLLECTIONS
| Featured AI
| Design And Composition
| Explore posts
POPULAR SEARCHES
unreal | pipeline | virtual production | free | learn | photoshop | 360 | macro | google | nvidia | resolution | open source | hdri | real-time | photography basics | nuke
FEATURED POSTS
-
AI and the Law – Netflix : Using Generative AI in Content Production
-
Scene Referred vs Display Referred color workflows
-
Photography basics: Color Temperature and White Balance
-
Principles of Animation with Alan Becker, Dermot OConnor and Shaun Keenan
-
Ethan Roffler interviews CG Supervisor Daniele Tosti
-
How to paint a boardgame miniatures
-
Types of Film Lights and their efficiency – CRI, Color Temperature and Luminous Efficacy
-
MiniTunes V1 – Free MP3 library app
Social Links
DISCLAIMER – Links and images on this website may be protected by the respective owners’ copyright. All data submitted by users through this site shall be treated as freely available to share.








![sRGB gamma correction test [gamma correction test]](http://www.madore.org/~david/misc/color/gammatest.png)