COMPOSITION
-
9 Best Hacks to Make a Cinematic Video with Any Camera
Read more: 9 Best Hacks to Make a Cinematic Video with Any Camerahttps://www.flexclip.com/learn/cinematic-video.html
- Frame Your Shots to Create Depth
- Create Shallow Depth of Field
- Avoid Shaky Footage and Use Flexible Camera Movements
- Properly Use Slow Motion
- Use Cinematic Lighting Techniques
- Apply Color Grading
- Use Cinematic Music and SFX
- Add Cinematic Fonts and Text Effects
- Create the Cinematic Bar at the Top and the Bottom

-
Composition – These are the basic lighting techniques you need to know for photography and film
Read more: Composition – These are the basic lighting techniques you need to know for photography and filmhttp://www.diyphotography.net/basic-lighting-techniques-need-know-photography-film/
Amongst the basic techniques, there’s…
1- Side lighting – Literally how it sounds, lighting a subject from the side when they’re faced toward you
2- Rembrandt lighting – Here the light is at around 45 degrees over from the front of the subject, raised and pointing down at 45 degrees
3- Back lighting – Again, how it sounds, lighting a subject from behind. This can help to add drama with silouettes
4- Rim lighting – This produces a light glowing outline around your subject
5- Key light – The main light source, and it’s not necessarily always the brightest light source
6- Fill light – This is used to fill in the shadows and provide detail that would otherwise be blackness
7- Cross lighting – Using two lights placed opposite from each other to light two subjects
DESIGN
COLOR
-
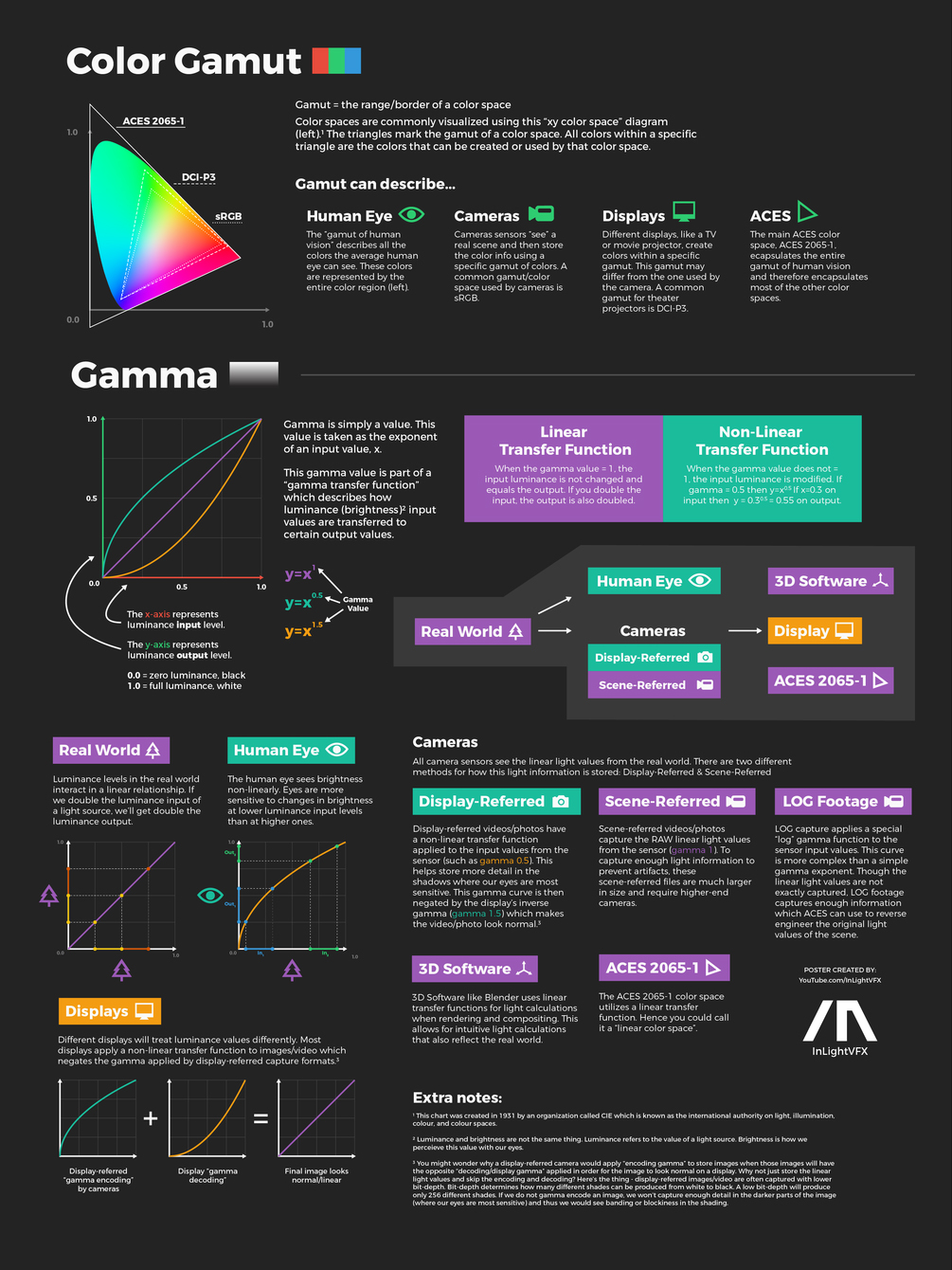
Light and Matter : The 2018 theory of Physically-Based Rendering and Shading by Allegorithmic
Read more: Light and Matter : The 2018 theory of Physically-Based Rendering and Shading by Allegorithmicacademy.substance3d.com/courses/the-pbr-guide-part-1
academy.substance3d.com/courses/the-pbr-guide-part-2
Local copy:
-
PTGui 13 beta adds control through a Patch Editor
Read more: PTGui 13 beta adds control through a Patch EditorAdditions:
- Patch Editor (PTGui Pro)
- DNG output
- Improved RAW / DNG handling
- JPEG 2000 support
- Performance improvements
-
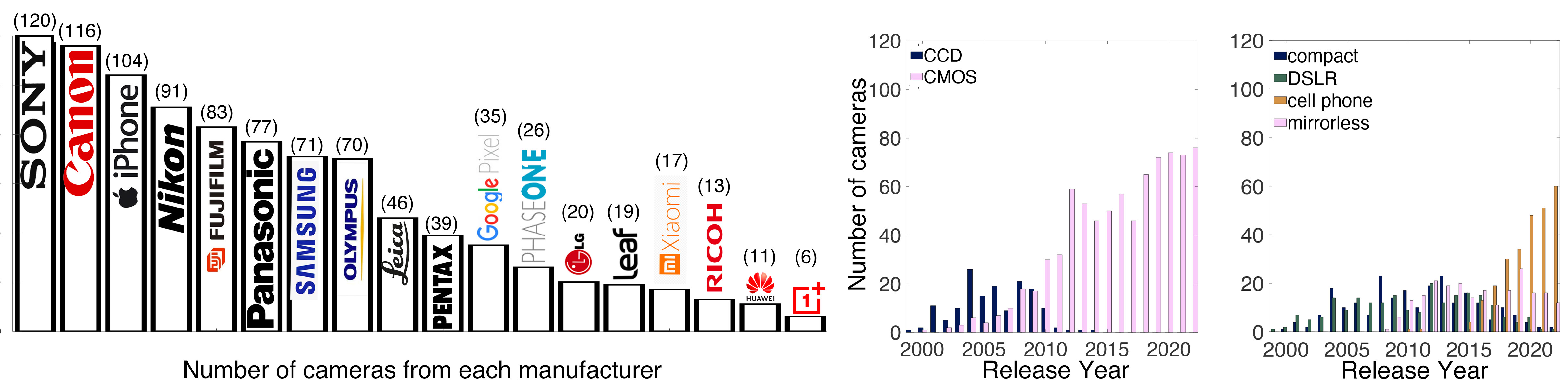
Photography Basics : Spectral Sensitivity Estimation Without a Camera
Read more: Photography Basics : Spectral Sensitivity Estimation Without a Camerahttps://color-lab-eilat.github.io/Spectral-sensitivity-estimation-web/
A number of problems in computer vision and related fields would be mitigated if camera spectral sensitivities were known. As consumer cameras are not designed for high-precision visual tasks, manufacturers do not disclose spectral sensitivities. Their estimation requires a costly optical setup, which triggered researchers to come up with numerous indirect methods that aim to lower cost and complexity by using color targets. However, the use of color targets gives rise to new complications that make the estimation more difficult, and consequently, there currently exists no simple, low-cost, robust go-to method for spectral sensitivity estimation that non-specialized research labs can adopt. Furthermore, even if not limited by hardware or cost, researchers frequently work with imagery from multiple cameras that they do not have in their possession.
To provide a practical solution to this problem, we propose a framework for spectral sensitivity estimation that not only does not require any hardware (including a color target), but also does not require physical access to the camera itself. Similar to other work, we formulate an optimization problem that minimizes a two-term objective function: a camera-specific term from a system of equations, and a universal term that bounds the solution space.
Different than other work, we utilize publicly available high-quality calibration data to construct both terms. We use the colorimetric mapping matrices provided by the Adobe DNG Converter to formulate the camera-specific system of equations, and constrain the solutions using an autoencoder trained on a database of ground-truth curves. On average, we achieve reconstruction errors as low as those that can arise due to manufacturing imperfections between two copies of the same camera. We provide predicted sensitivities for more than 1,000 cameras that the Adobe DNG Converter currently supports, and discuss which tasks can become trivial when camera responses are available.
-
VES Cinematic Color – Motion-Picture Color Management
Read more: VES Cinematic Color – Motion-Picture Color ManagementThis paper presents an introduction to the color pipelines behind modern feature-film visual-effects and animation.
Authored by Jeremy Selan, and reviewed by the members of the VES Technology Committee including Rob Bredow, Dan Candela, Nick Cannon, Paul Debevec, Ray Feeney, Andy Hendrickson, Gautham Krishnamurti, Sam Richards, Jordan Soles, and Sebastian Sylwan.
-
The 7 key elements of brand identity design + 10 corporate identity examples
Read more: The 7 key elements of brand identity design + 10 corporate identity exampleswww.lucidpress.com/blog/the-7-key-elements-of-brand-identity-design
1. Clear brand purpose and positioning
2. Thorough market research
3. Likable brand personality
4. Memorable logo
5. Attractive color palette
6. Professional typography
7. On-brand supporting graphics
LIGHTING
-
Lighting Every Darkness with 3DGS: Fast Training and Real-Time Rendering and Denoising for HDR View Synthesis
Read more: Lighting Every Darkness with 3DGS: Fast Training and Real-Time Rendering and Denoising for HDR View Synthesishttps://srameo.github.io/projects/le3d/
LE3D is a method for real-time HDR view synthesis from RAW images. It is particularly effective for nighttime scenes.
https://github.com/Srameo/LE3D
-
3D Lighting Tutorial by Amaan Kram
Read more: 3D Lighting Tutorial by Amaan Kramhttp://www.amaanakram.com/lightingT/part1.htm
The goals of lighting in 3D computer graphics are more or less the same as those of real world lighting.
Lighting serves a basic function of bringing out, or pushing back the shapes of objects visible from the camera’s view.
It gives a two-dimensional image on the monitor an illusion of the third dimension-depth.But it does not just stop there. It gives an image its personality, its character. A scene lit in different ways can give a feeling of happiness, of sorrow, of fear etc., and it can do so in dramatic or subtle ways. Along with personality and character, lighting fills a scene with emotion that is directly transmitted to the viewer.
Trying to simulate a real environment in an artificial one can be a daunting task. But even if you make your 3D rendering look absolutely photo-realistic, it doesn’t guarantee that the image carries enough emotion to elicit a “wow” from the people viewing it.
Making 3D renderings photo-realistic can be hard. Putting deep emotions in them can be even harder. However, if you plan out your lighting strategy for the mood and emotion that you want your rendering to express, you make the process easier for yourself.
Each light source can be broken down in to 4 distinct components and analyzed accordingly.
· Intensity
· Direction
· Color
· SizeThe overall thrust of this writing is to produce photo-realistic images by applying good lighting techniques.
-
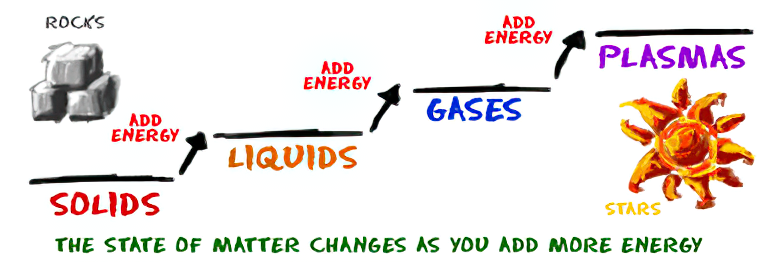
How are Energy and Matter the Same?
Read more: How are Energy and Matter the Same?www.turnerpublishing.com/blog/detail/everything-is-energy-everything-is-one-everything-is-possible/
www.universetoday.com/116615/how-are-energy-and-matter-the-same/
As Einstein showed us, light and matter and just aspects of the same thing. Matter is just frozen light. And light is matter on the move. Albert Einstein’s most famous equation says that energy and matter are two sides of the same coin. How does one become the other?
Relativity requires that the faster an object moves, the more mass it appears to have. This means that somehow part of the energy of the car’s motion appears to transform into mass. Hence the origin of Einstein’s equation. How does that happen? We don’t really know. We only know that it does.
Matter is 99.999999999999 percent empty space. Not only do the atom and solid matter consist mainly of empty space, it is the same in outer space
The quantum theory researchers discovered the answer: Not only do particles consist of energy, but so does the space between. This is the so-called zero-point energy. Therefore it is true: Everything consists of energy.
Energy is the basis of material reality. Every type of particle is conceived of as a quantum vibration in a field: Electrons are vibrations in electron fields, protons vibrate in a proton field, and so on. Everything is energy, and everything is connected to everything else through fields.
-
Light and Matter : The 2018 theory of Physically-Based Rendering and Shading by Allegorithmic
Read more: Light and Matter : The 2018 theory of Physically-Based Rendering and Shading by Allegorithmicacademy.substance3d.com/courses/the-pbr-guide-part-1
academy.substance3d.com/courses/the-pbr-guide-part-2
Local copy:
-
What is physically correct lighting all about?
Read more: What is physically correct lighting all about?http://gamedev.stackexchange.com/questions/60638/what-is-physically-correct-lighting-all-about
2012-08 Nathan Reed wrote:
Physically-based shading means leaving behind phenomenological models, like the Phong shading model, which are simply built to “look good” subjectively without being based on physics in any real way, and moving to lighting and shading models that are derived from the laws of physics and/or from actual measurements of the real world, and rigorously obey physical constraints such as energy conservation.
For example, in many older rendering systems, shading models included separate controls for specular highlights from point lights and reflection of the environment via a cubemap. You could create a shader with the specular and the reflection set to wildly different values, even though those are both instances of the same physical process. In addition, you could set the specular to any arbitrary brightness, even if it would cause the surface to reflect more energy than it actually received.
In a physically-based system, both the point light specular and the environment reflection would be controlled by the same parameter, and the system would be set up to automatically adjust the brightness of both the specular and diffuse components to maintain overall energy conservation. Moreover you would want to set the specular brightness to a realistic value for the material you’re trying to simulate, based on measurements.
Physically-based lighting or shading includes physically-based BRDFs, which are usually based on microfacet theory, and physically correct light transport, which is based on the rendering equation (although heavily approximated in the case of real-time games).
It also includes the necessary changes in the art process to make use of these features. Switching to a physically-based system can cause some upsets for artists. First of all it requires full HDR lighting with a realistic level of brightness for light sources, the sky, etc. and this can take some getting used to for the lighting artists. It also requires texture/material artists to do some things differently (particularly for specular), and they can be frustrated by the apparent loss of control (e.g. locking together the specular highlight and environment reflection as mentioned above; artists will complain about this). They will need some time and guidance to adapt to the physically-based system.
On the plus side, once artists have adapted and gained trust in the physically-based system, they usually end up liking it better, because there are fewer parameters overall (less work for them to tweak). Also, materials created in one lighting environment generally look fine in other lighting environments too. This is unlike more ad-hoc models, where a set of material parameters might look good during daytime, but it comes out ridiculously glowy at night, or something like that.
Here are some resources to look at for physically-based lighting in games:
SIGGRAPH 2013 Physically Based Shading Course, particularly the background talk by Naty Hoffman at the beginning. You can also check out the previous incarnations of this course for more resources.
Sébastien Lagarde, Adopting a physically-based shading model and Feeding a physically-based shading model
And of course, I would be remiss if I didn’t mention Physically-Based Rendering by Pharr and Humphreys, an amazing reference on this whole subject and well worth your time, although it focuses on offline rather than real-time rendering.
-
Simulon – a Hollywood production studio app in the hands of an independent creator with access to consumer hardware, LDRi to HDRi through ML
Read more: Simulon – a Hollywood production studio app in the hands of an independent creator with access to consumer hardware, LDRi to HDRi through MLDivesh Naidoo: The video below was made with a live in-camera preview and auto-exposure matching, no camera solve, no HDRI capture and no manual compositing setup. Using the new Simulon phone app.
LDR to HDR through ML
https://simulon.typeform.com/betatest
(more…)Process example
COLLECTIONS
| Featured AI
| Design And Composition
| Explore posts
POPULAR SEARCHES
unreal | pipeline | virtual production | free | learn | photoshop | 360 | macro | google | nvidia | resolution | open source | hdri | real-time | photography basics | nuke
FEATURED POSTS
-
N8N.io – From Zero to Your First AI Agent in 25 Minutes
-
Ross Pettit on The Agile Manager – How tech firms went for prioritizing cash flow instead of talent (and artists)
-
AI Data Laundering: How Academic and Nonprofit Researchers Shield Tech Companies from Accountability
-
Convert 2D Images or Text to 3D Models
-
copypastecharacter.com – alphabets, special characters, alt codes and symbols library
-
MiniTunes V1 – Free MP3 library app
-
AnimationXpress.com interviews Daniele Tosti for TheCgCareer.com channel
-
Kling 1.6 and competitors – advanced tests and comparisons
Social Links
DISCLAIMER – Links and images on this website may be protected by the respective owners’ copyright. All data submitted by users through this site shall be treated as freely available to share.