COMPOSITION
DESIGN
COLOR
-
HDR and Color
Read more: HDR and Colorhttps://www.soundandvision.com/content/nits-and-bits-hdr-and-color
In HD we often refer to the range of available colors as a color gamut. Such a color gamut is typically plotted on a two-dimensional diagram, called a CIE chart, as shown in at the top of this blog. Each color is characterized by its x/y coordinates.
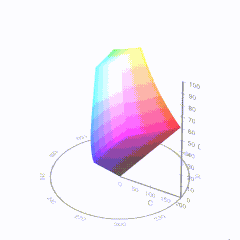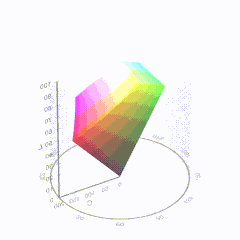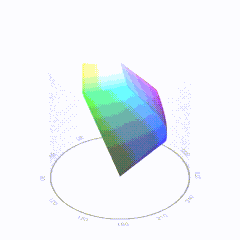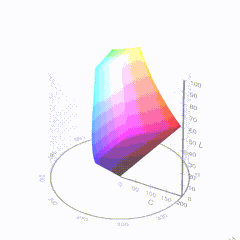
Good enough for government work, perhaps. But for HDR, with its higher luminance levels and wider color, the gamut becomes three-dimensional.
For HDR the color gamut therefore becomes a characteristic we now call the color volume. It isn’t easy to show color volume on a two-dimensional medium like the printed page or a computer screen, but one method is shown below. As the luminance becomes higher, the picture eventually turns to white. As it becomes darker, it fades to black. The traditional color gamut shown on the CIE chart is simply a slice through this color volume at a selected luminance level, such as 50%.
Three different color volumes—we still refer to them as color gamuts though their third dimension is important—are currently the most significant. The first is BT.709 (sometimes referred to as Rec.709), the color gamut used for pre-UHD/HDR formats, including standard HD.
The largest is known as BT.2020; it encompasses (roughly) the range of colors visible to the human eye (though ET might find it insufficient!).
Between these two is the color gamut used in digital cinema, known as DCI-P3.
sRGB
D65
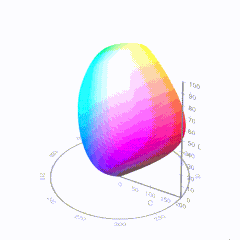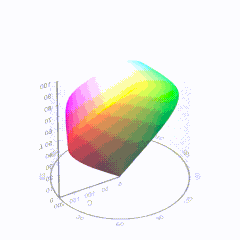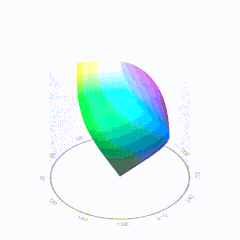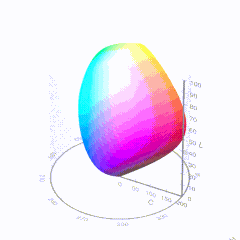
-
Gamma correction
Read more: Gamma correction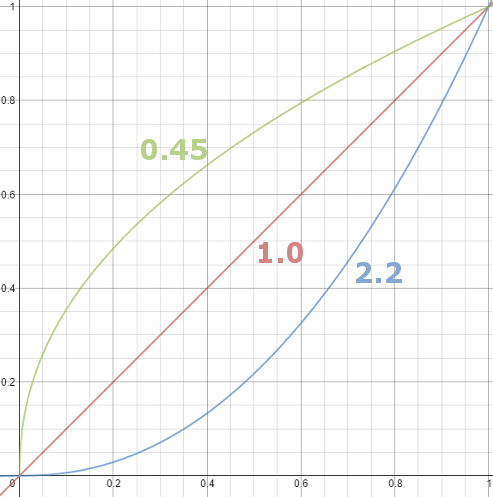
http://www.normankoren.com/makingfineprints1A.html#Gammabox
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gamma_correction
http://www.photoscientia.co.uk/Gamma.htm
https://www.w3.org/Graphics/Color/sRGB.html
http://www.eizoglobal.com/library/basics/lcd_display_gamma/index.html
https://forum.reallusion.com/PrintTopic308094.aspx
Basically, gamma is the relationship between the brightness of a pixel as it appears on the screen, and the numerical value of that pixel. Generally Gamma is just about defining relationships.
Three main types:
– Image Gamma encoded in images
– Display Gammas encoded in hardware and/or viewing time
– System or Viewing Gamma which is the net effect of all gammas when you look back at a final image. In theory this should flatten back to 1.0 gamma.
(more…) -
What Is The Resolution and view coverage Of The human Eye. And what distance is TV at best?
Read more: What Is The Resolution and view coverage Of The human Eye. And what distance is TV at best?https://www.discovery.com/science/mexapixels-in-human-eye
About 576 megapixels for the entire field of view.
Consider a view in front of you that is 90 degrees by 90 degrees, like looking through an open window at a scene. The number of pixels would be:
90 degrees * 60 arc-minutes/degree * 1/0.3 * 90 * 60 * 1/0.3 = 324,000,000 pixels (324 megapixels).At any one moment, you actually do not perceive that many pixels, but your eye moves around the scene to see all the detail you want. But the human eye really sees a larger field of view, close to 180 degrees. Let’s be conservative and use 120 degrees for the field of view. Then we would see:
120 * 120 * 60 * 60 / (0.3 * 0.3) = 576 megapixels.
Or.
7 megapixels for the 2 degree focus arc… + 1 megapixel for the rest.
https://clarkvision.com/articles/eye-resolution.html
Details in the post
-
No one could see the colour blue until modern times
Read more: No one could see the colour blue until modern timeshttps://www.businessinsider.com/what-is-blue-and-how-do-we-see-color-2015-2

The way humans see the world… until we have a way to describe something, even something so fundamental as a colour, we may not even notice that something it’s there.
Ancient languages didn’t have a word for blue — not Greek, not Chinese, not Japanese, not Hebrew, not Icelandic cultures. And without a word for the colour, there’s evidence that they may not have seen it at all.
https://www.wnycstudios.org/story/211119-colorsEvery language first had a word for black and for white, or dark and light. The next word for a colour to come into existence — in every language studied around the world — was red, the colour of blood and wine.
After red, historically, yellow appears, and later, green (though in a couple of languages, yellow and green switch places). The last of these colours to appear in every language is blue.The only ancient culture to develop a word for blue was the Egyptians — and as it happens, they were also the only culture that had a way to produce a blue dye.
https://mymodernmet.com/shades-of-blue-color-history/True blue hues are rare in the natural world because synthesizing pigments that absorb longer-wavelength light (reds and yellows) while reflecting shorter-wavelength blue light requires exceptionally elaborate molecular structures—biochemical feats that most plants and animals simply don’t undertake.
When you gaze at a blueberry’s deep blue surface, you’re actually seeing structural coloration rather than a true blue pigment. A fine, waxy bloom on the berry’s skin contains nanostructures that preferentially scatter blue and violet light, giving the fruit its signature blue sheen even though its inherent pigment is reddish.
Similarly, many of nature’s most striking blues—like those of blue jays and morpho butterflies—arise not from blue pigments but from microscopic architectures in feathers or wing scales. These tiny ridges and air pockets manipulate incoming light so that blue wavelengths emerge most prominently, creating vivid, angle-dependent colors through scattering rather than pigment alone.
(more…) -
StudioBinder.com – CRI color rendering index
Read more: StudioBinder.com – CRI color rendering indexwww.studiobinder.com/blog/what-is-color-rendering-index
“The Color Rendering Index is a measurement of how faithfully a light source reveals the colors of whatever it illuminates, it describes the ability of a light source to reveal the color of an object, as compared to the color a natural light source would provide. The highest possible CRI is 100. A CRI of 100 generally refers to a perfect black body, like a tungsten light source or the sun. ”
www.pixelsham.com/2021/04/28/types-of-film-lights-and-their-efficiency
-
SecretWeapons MixBox – a practical library for paint-like digital color mixing
Read more: SecretWeapons MixBox – a practical library for paint-like digital color mixingInternally, Mixbox treats colors as real-life pigments using the Kubelka & Munk theory to predict realistic color behavior.
https://scrtwpns.com/mixbox/painter/
https://scrtwpns.com/mixbox.pdf
https://github.com/scrtwpns/mixbox
https://scrtwpns.com/mixbox/docs/
LIGHTING
-
Magnific.ai Relight – change the entire lighting of a scene
Read more: Magnific.ai Relight – change the entire lighting of a sceneIt’s a new Magnific spell that allows you to change the entire lighting of a scene and, optionally, the background with just:
1/ A prompt OR
2/ A reference image OR
3/ A light map (drawing your own lights)https://x.com/javilopen/status/1805274155065176489
-
Is a MacBeth Colour Rendition Chart the Safest Way to Calibrate a Camera?
Read more: Is a MacBeth Colour Rendition Chart the Safest Way to Calibrate a Camera?www.colour-science.org/posts/the-colorchecker-considered-mostly-harmless/
“Unless you have all the relevant spectral measurements, a colour rendition chart should not be used to perform colour-correction of camera imagery but only for white balancing and relative exposure adjustments.”
“Using a colour rendition chart for colour-correction might dramatically increase error if the scene light source spectrum is different from the illuminant used to compute the colour rendition chart’s reference values.”
“other factors make using a colour rendition chart unsuitable for camera calibration:
– Uncontrolled geometry of the colour rendition chart with the incident illumination and the camera.
– Unknown sample reflectances and ageing as the colour of the samples vary with time.
– Low samples count.
– Camera noise and flare.
– Etc…“Those issues are well understood in the VFX industry, and when receiving plates, we almost exclusively use colour rendition charts to white balance and perform relative exposure adjustments, i.e. plate neutralisation.”
-
ICLight – Krea and ComfyUI light editing
Read more: ICLight – Krea and ComfyUI light editinghttps://drive.google.com/drive/folders/16Aq1mqZKP-h8vApaN4FX5at3acidqPUv
https://github.com/lllyasviel/IC-Light
https://generativematte.blogspot.com/2025/03/comfyui-ic-light-relighting-exploration.html

Workflow Local copy

-
What’s the Difference Between Ray Casting, Ray Tracing, Path Tracing and Rasterization? Physical light tracing…
Read more: What’s the Difference Between Ray Casting, Ray Tracing, Path Tracing and Rasterization? Physical light tracing…RASTERIZATION
Rasterisation (or rasterization) is the task of taking the information described in a vector graphics format OR the vertices of triangles making 3D shapes and converting them into a raster image (a series of pixels, dots or lines, which, when displayed together, create the image which was represented via shapes), or in other words “rasterizing” vectors or 3D models onto a 2D plane for display on a computer screen.For each triangle of a 3D shape, you project the corners of the triangle on the virtual screen with some math (projective geometry). Then you have the position of the 3 corners of the triangle on the pixel screen. Those 3 points have texture coordinates, so you know where in the texture are the 3 corners. The cost is proportional to the number of triangles, and is only a little bit affected by the screen resolution.
In computer graphics, a raster graphics or bitmap image is a dot matrix data structure that represents a generally rectangular grid of pixels (points of color), viewable via a monitor, paper, or other display medium.
With rasterization, objects on the screen are created from a mesh of virtual triangles, or polygons, that create 3D models of objects. A lot of information is associated with each vertex, including its position in space, as well as information about color, texture and its “normal,” which is used to determine the way the surface of an object is facing.
Computers then convert the triangles of the 3D models into pixels, or dots, on a 2D screen. Each pixel can be assigned an initial color value from the data stored in the triangle vertices.
Further pixel processing or “shading,” including changing pixel color based on how lights in the scene hit the pixel, and applying one or more textures to the pixel, combine to generate the final color applied to a pixel.
The main advantage of rasterization is its speed. However, rasterization is simply the process of computing the mapping from scene geometry to pixels and does not prescribe a particular way to compute the color of those pixels. So it cannot take shading, especially the physical light, into account and it cannot promise to get a photorealistic output. That’s a big limitation of rasterization.
There are also multiple problems:
If you have two triangles one is behind the other, you will draw twice all the pixels. you only keep the pixel from the triangle that is closer to you (Z-buffer), but you still do the work twice.
The borders of your triangles are jagged as it is hard to know if a pixel is in the triangle or out. You can do some smoothing on those, that is anti-aliasing.
You have to handle every triangles (including the ones behind you) and then see that they do not touch the screen at all. (we have techniques to mitigate this where we only look at triangles that are in the field of view)
Transparency is hard to handle (you can’t just do an average of the color of overlapping transparent triangles, you have to do it in the right order)
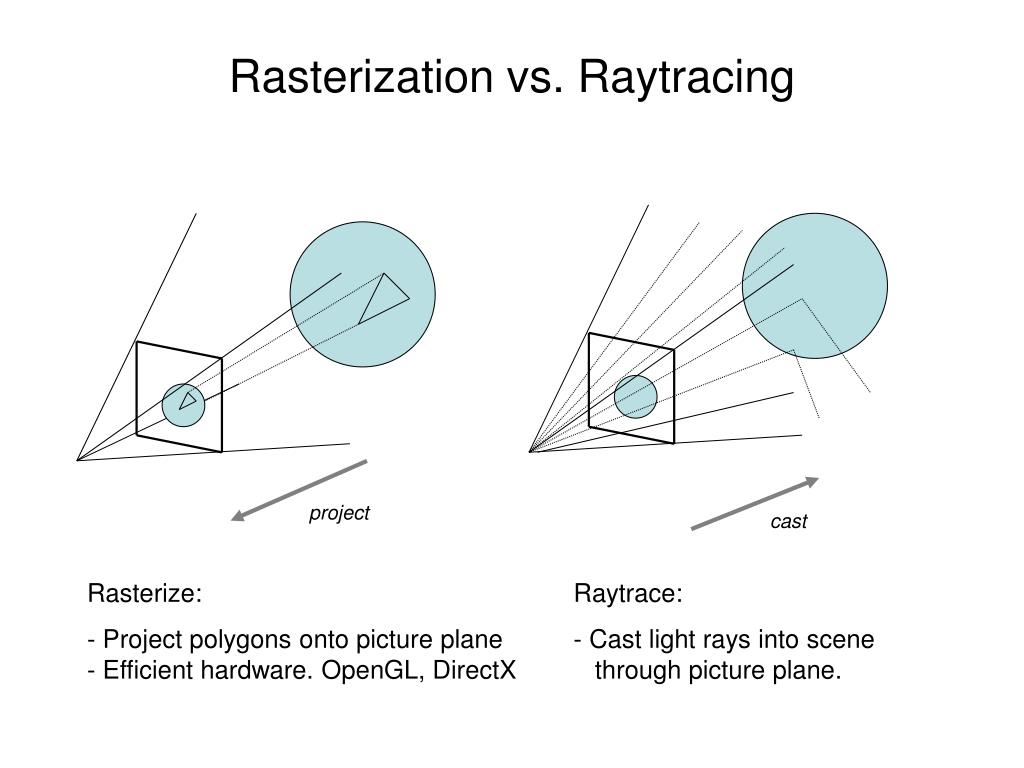
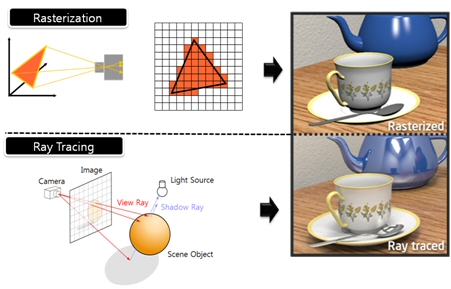
RAY CASTING
It is almost the exact reverse of rasterization: you start from the virtual screen instead of the vector or 3D shapes, and you project a ray, starting from each pixel of the screen, until it intersect with a triangle.The cost is directly correlated to the number of pixels in the screen and you need a really cheap way of finding the first triangle that intersect a ray. In the end, it is more expensive than rasterization but it will, by design, ignore the triangles that are out of the field of view.
You can use it to continue after the first triangle it hit, to take a little bit of the color of the next one, etc… This is useful to handle the border of the triangle cleanly (less jagged) and to handle transparency correctly.
RAYTRACING
Same idea as ray casting except once you hit a triangle you reflect on it and go into a different direction. The number of reflection you allow is the “depth” of your ray tracing. The color of the pixel can be calculated, based off the light source and all the polygons it had to reflect off of to get to that screen pixel.The easiest way to think of ray tracing is to look around you, right now. The objects you’re seeing are illuminated by beams of light. Now turn that around and follow the path of those beams backwards from your eye to the objects that light interacts with. That’s ray tracing.
Ray tracing is eye-oriented process that needs walking through each pixel looking for what object should be shown there, which is also can be described as a technique that follows a beam of light (in pixels) from a set point and simulates how it reacts when it encounters objects.
Compared with rasterization, ray tracing is hard to be implemented in real time, since even one ray can be traced and processed without much trouble, but after one ray bounces off an object, it can turn into 10 rays, and those 10 can turn into 100, 1000…The increase is exponential, and the the calculation for all these rays will be time consuming.
Historically, computer hardware hasn’t been fast enough to use these techniques in real time, such as in video games. Moviemakers can take as long as they like to render a single frame, so they do it offline in render farms. Video games have only a fraction of a second. As a result, most real-time graphics rely on the another technique called rasterization.
PATH TRACING
Path tracing can be used to solve more complex lighting situations.
Path tracing is a type of ray tracing. When using path tracing for rendering, the rays only produce a single ray per bounce. The rays do not follow a defined line per bounce (to a light, for example), but rather shoot off in a random direction. The path tracing algorithm then takes a random sampling of all of the rays to create the final image. This results in sampling a variety of different types of lighting.When a ray hits a surface it doesn’t trace a path to every light source, instead it bounces the ray off the surface and keeps bouncing it until it hits a light source or exhausts some bounce limit.
It then calculates the amount of light transferred all the way to the pixel, including any color information gathered from surfaces along the way.
It then averages out the values calculated from all the paths that were traced into the scene to get the final pixel color value.It requires a ton of computing power and if you don’t send out enough rays per pixel or don’t trace the paths far enough into the scene then you end up with a very spotty image as many pixels fail to find any light sources from their rays. So when you increase the the samples per pixel, you can see the image quality becomes better and better.
Ray tracing tends to be more efficient than path tracing. Basically, the render time of a ray tracer depends on the number of polygons in the scene. The more polygons you have, the longer it will take.
Meanwhile, the rendering time of a path tracer can be indifferent to the number of polygons, but it is related to light situation: If you add a light, transparency, translucence, or other shader effects, the path tracer will slow down considerably.blogs.nvidia.com/blog/2018/03/19/whats-difference-between-ray-tracing-rasterization/
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Rasterisation
https://www.quora.com/Whats-the-difference-between-ray-tracing-and-path-tracing
-
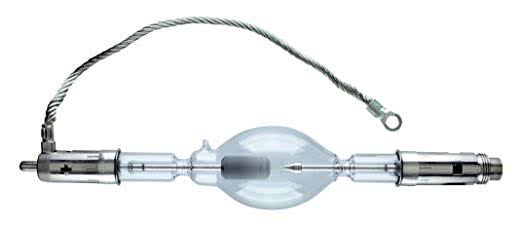
What light is best to illuminate gems for resale
Read more: What light is best to illuminate gems for resalewww.palagems.com/gem-lighting2
Artificial light sources, not unlike the diverse phases of natural light, vary considerably in their properties. As a result, some lamps render an object’s color better than others do.
The most important criterion for assessing the color-rendering ability of any lamp is its spectral power distribution curve.
Natural daylight varies too much in strength and spectral composition to be taken seriously as a lighting standard for grading and dealing colored stones. For anything to be a standard, it must be constant in its properties, which natural light is not.
For dealers in particular to make the transition from natural light to an artificial light source, that source must offer:
1- A degree of illuminance at least as strong as the common phases of natural daylight.
2- Spectral properties identical or comparable to a phase of natural daylight.A source combining these two things makes gems appear much the same as when viewed under a given phase of natural light. From the viewpoint of many dealers, this corresponds to a naturalappearance.
The 6000° Kelvin xenon short-arc lamp appears closest to meeting the criteria for a standard light source. Besides the strong illuminance this lamp affords, its spectrum is very similar to CIE standard illuminants of similar color temperature.

COLLECTIONS
| Featured AI
| Design And Composition
| Explore posts
POPULAR SEARCHES
unreal | pipeline | virtual production | free | learn | photoshop | 360 | macro | google | nvidia | resolution | open source | hdri | real-time | photography basics | nuke
FEATURED POSTS
Social Links
DISCLAIMER – Links and images on this website may be protected by the respective owners’ copyright. All data submitted by users through this site shall be treated as freely available to share.