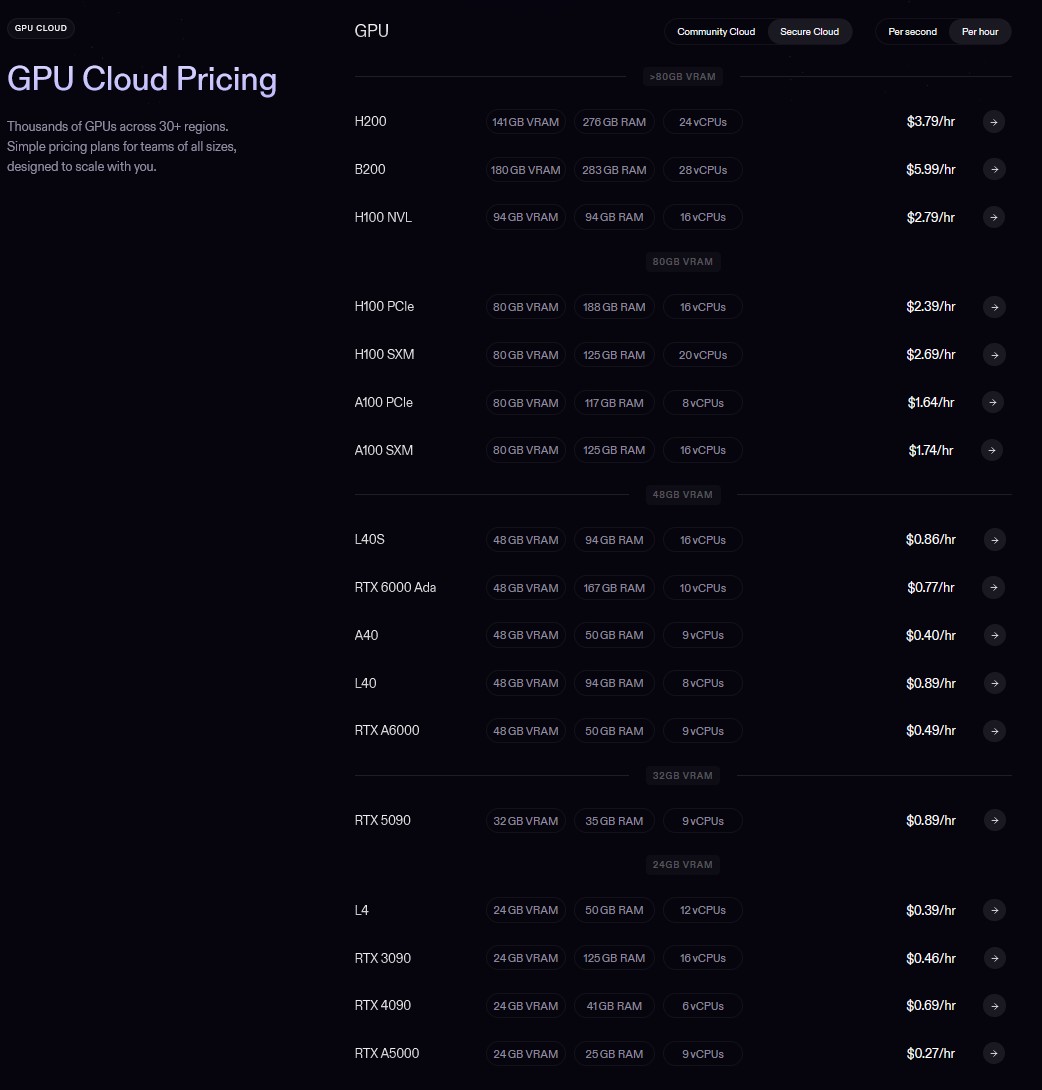
BREAKING NEWS
LATEST POSTS
-
AI and the Law – 𝗬𝗼𝘂𝗿 (𝗽𝗿𝗶𝘃𝗮𝘁𝗲𝗹𝘆) 𝘀𝗵𝗮𝗿𝗲𝗱 𝗖𝗵𝗮𝘁𝗚𝗣𝗧 𝗰𝗵𝗮𝘁𝘀 𝗺𝗶𝗴𝗵𝘁 𝗯𝗲 𝘀𝗵𝗼𝘄𝗶𝗻𝗴 𝘂𝗽 𝗼𝗻 𝗚𝗼𝗼𝗴𝗹𝗲
Many users assume shared conversations are only seen by friends or colleagues — but when you use OpenAI’s share feature, those chats get now indexed by search engines like Google.
Meaning: your “private” AI prompts could end up very public. This is called Google dorking — and it’s shockingly effective.
Over 70,000 chats are now publicly viewable. Some are harmless.
Others? They might expose sensitive strategies, internal docs, product plans, even company secrets.
OpenAI currently does not block indexing. So if you’ve ever shared something thinking it’s “just a link” — it might now be searchable by anyone. You can even build a bot to crawl and analyze these.
Welcome to the new visibility layer of AI. I can’t say I am surprised…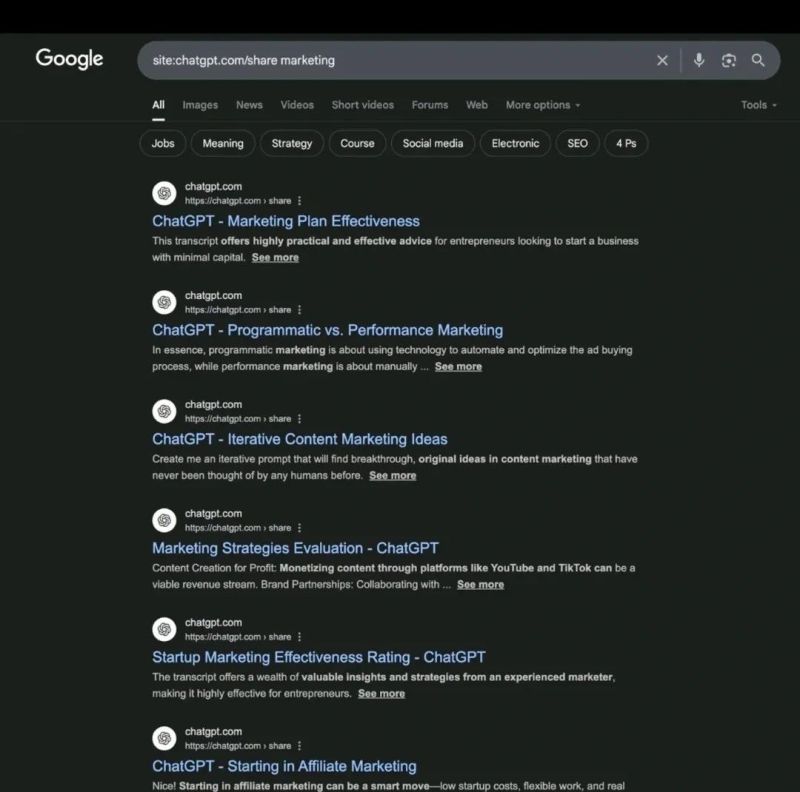
-
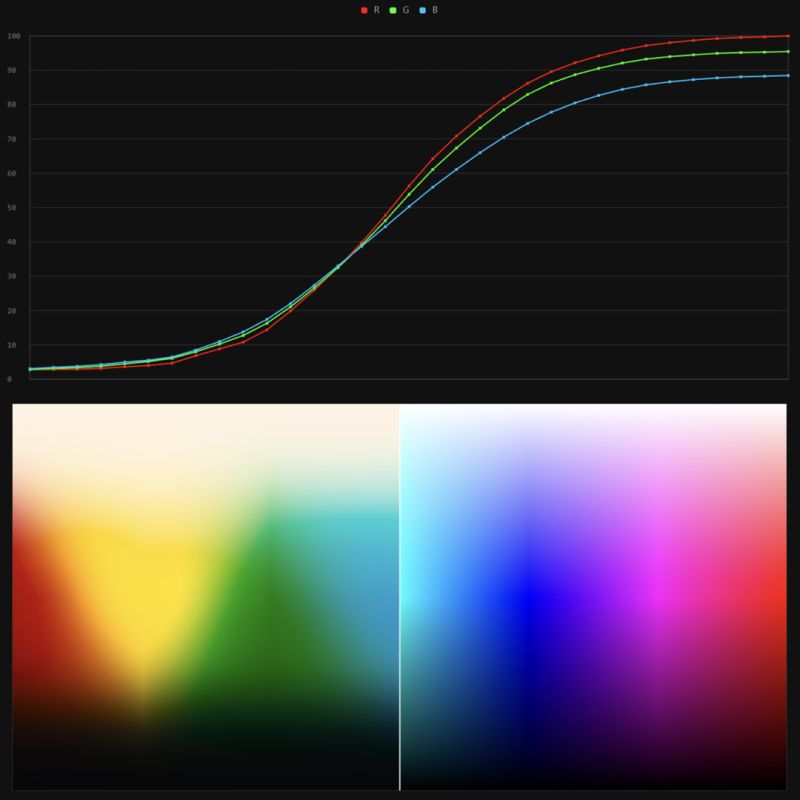
Stefan Ringelschwandtner – LUT Inspector tool
It lets you load any .cube LUT right in your browser, see the RGB curves, and use a split view on the Granger Test Image to compare the original vs. LUT-applied version in real time — perfect for spotting hue shifts, saturation changes, and contrast tweaks.
https://mononodes.com/lut-inspector/
-
Python Automation – Beginner to Advance Guid
WhatApp Message Automation
Automating Instagram
Telegrame Bot Creation
Email Automation with Python
PDF and Document Automation
FEATURED POSTS
-
AI and the Law – The AI-Copyright Trap document by Carys Craig
https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=4905118
“There are many good reasons to be concerned about the rise of generative AI(…). Unfortunately, there are also many good reasons to be concerned about copyright’s growing prevalence in the policy discourse around AI’s regulation. Insisting that copyright protects an exclusive right to use materials for text and data mining practices (whether for informational analysis or machine learning to train generative AI models) is likely to do more harm than good. As many others have explained, imposing copyright constraints will certainly limit competition in the AI industry, creating cost-prohibitive barriers to quality data and ensuring that only the most powerful players have the means to build the best AI tools (provoking all of the usual monopoly concerns that accompany this kind of market reality but arguably on a greater scale than ever before). It will not, however, prevent the continued development and widespread use of generative AI.”
…
“(…) As Michal Shur-Ofry has explained, the technical traits of generative AI already mean that its outputs will tend towards the dominant, likely reflecting ‘a relatively narrow, mainstream view, prioritizing the popular and conventional over diverse contents and narratives.’ Perhaps, then, if the political goal is to push for equality, participation, and representation in the AI age, critics’ demands should focus not on exclusivity but inclusivity. If we want to encourage the development of ethical and responsible AI, maybe we should be asking what kind of material and training data must be included in the inputs and outputs of AI to advance that goal. Certainly, relying on copyright and the market to dictate what is in and what is out is unlikely to advance a public interest or equality-oriented agenda.”
…
“If copyright is not the solution, however, it might reasonably be asked: what is? The first step to answering that question—to producing a purposively sound prescription and evidence-based prognosis, is to correctly diagnose the problem. If, as I have argued, the problem is not that AI models are being trained on copyright works without their owners’ consent, then requiring copyright owners’ consent and/or compensation for the use of their work in AI-training datasets is not the appropriate solution. (…)If the only real copyright problem is that the outputs of generative AI may be substantially similar to specific human-authored and copyright-protected works, then copyright law as we know it already provides the solution.”
-
GretagMacbeth Color Checker Numeric Values and Middle Gray
The human eye perceives half scene brightness not as the linear 50% of the present energy (linear nature values) but as 18% of the overall brightness. We are biased to perceive more information in the dark and contrast areas. A Macbeth chart helps with calibrating back into a photographic capture into this “human perspective” of the world.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Middle_gray
In photography, painting, and other visual arts, middle gray or middle grey is a tone that is perceptually about halfway between black and white on a lightness scale in photography and printing, it is typically defined as 18% reflectance in visible light
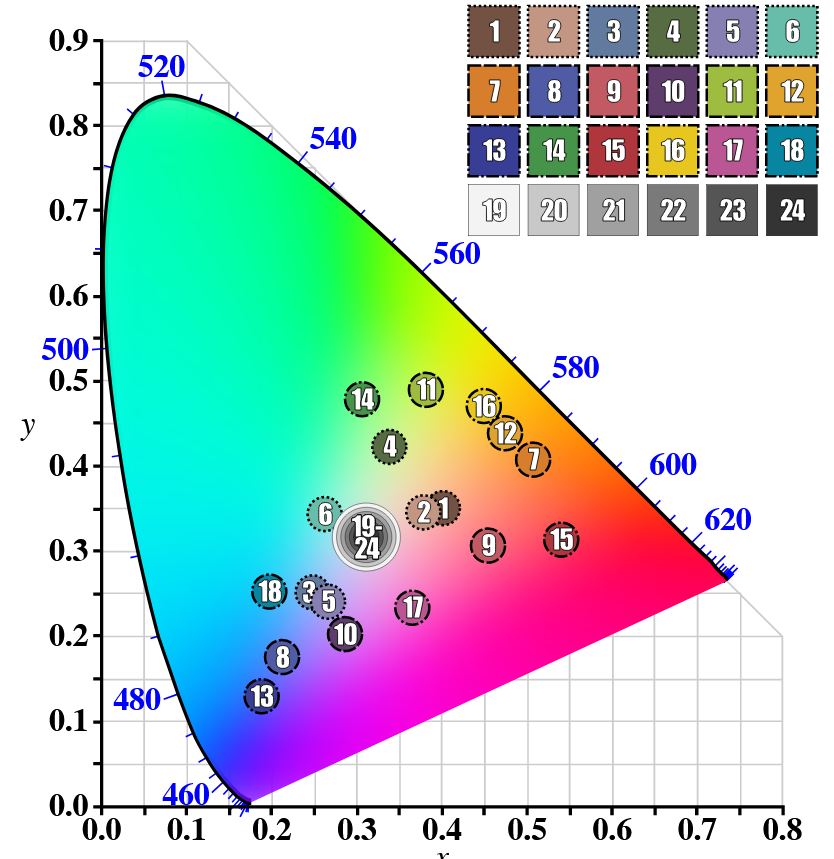
Light meters, cameras, and pictures are often calibrated using an 18% gray card[4][5][6] or a color reference card such as a ColorChecker. On the assumption that 18% is similar to the average reflectance of a scene, a grey card can be used to estimate the required exposure of the film.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ColorChecker
(more…)
-
Willem Zwarthoed – Aces gamut in VFX production pdf
https://www.provideocoalition.com/color-management-part-12-introducing-aces/
Local copy:
https://www.slideshare.net/hpduiker/acescg-a-common-color-encoding-for-visual-effects-applications